前言:
论文中直接提供了GitHub 的代码下载地址
GitHub - junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix: Image-to-Image Translation in PyTorch
这里面简单的解读一下.
目录:
1. 模型参数配置
2: 生成器模型
3: 鉴别器模型
4: network代码
5: cycleGAN代码
6: 训练和测试代码
一 参数配置模块
文件目录:options\train_options.py
参数配置是通过argparse 实现的,这样通过google colab 调试的时候
可以动态的设置超参数进行训练

动态设置超参数命令
python my_program.py--gender male--height1.75
二 生成器模型
在network.py中实现,后面在代码示例中,我直接提供了一个入口可以Debug一下
Total params: 11,378,179
Trainable params: 11,378,179
Non-trainable params: 0
生成器主要由5个模块组成
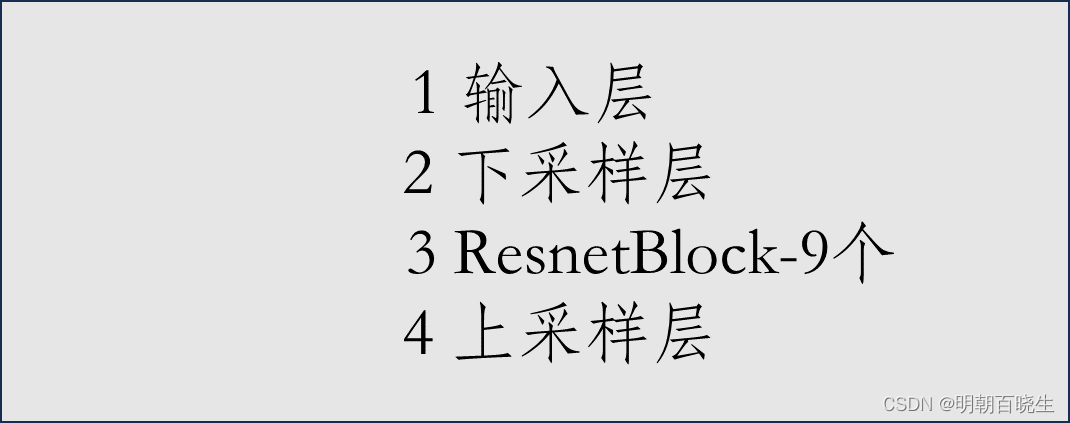
2.1 输入层
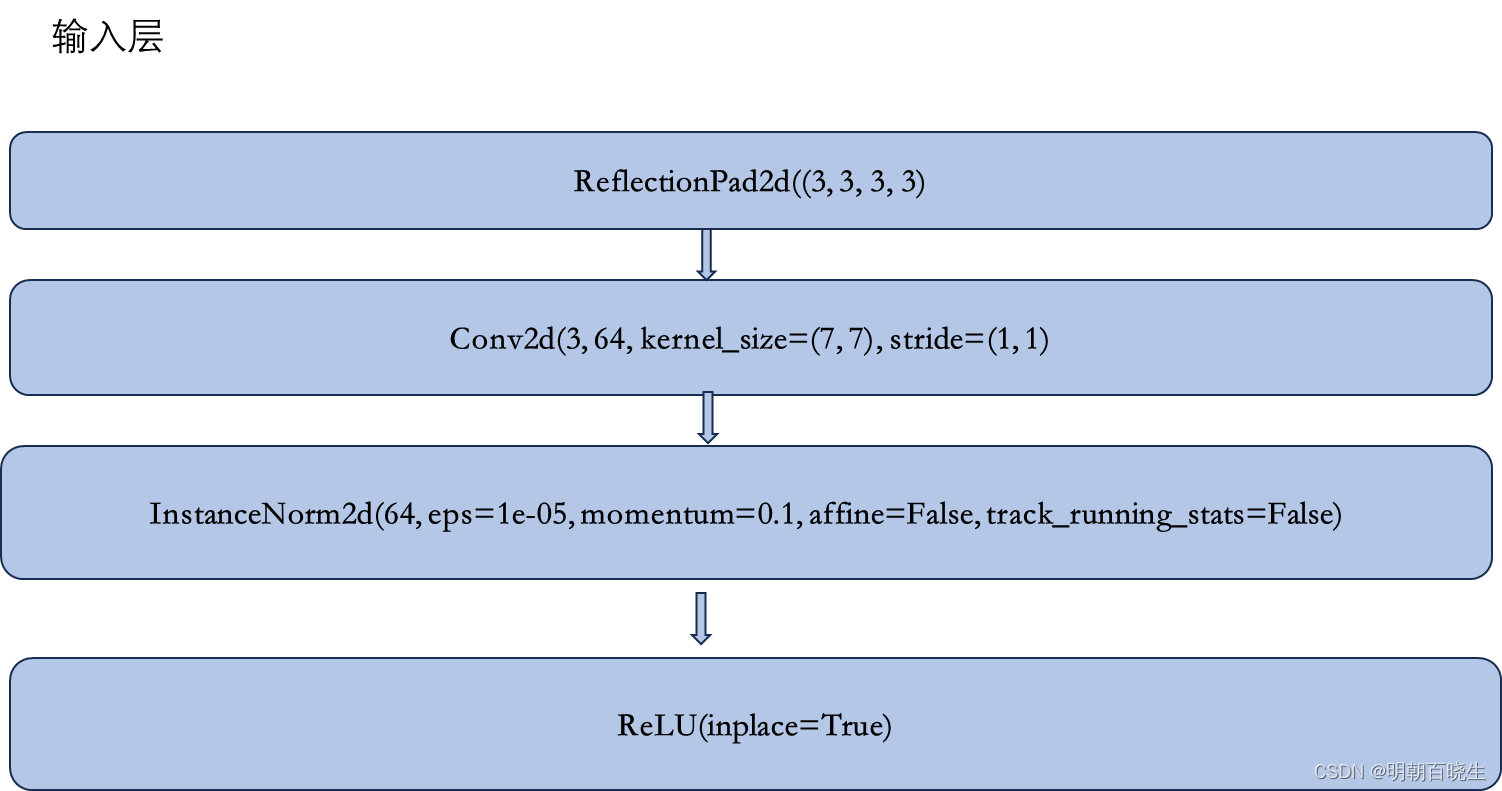
2.2 下采样层
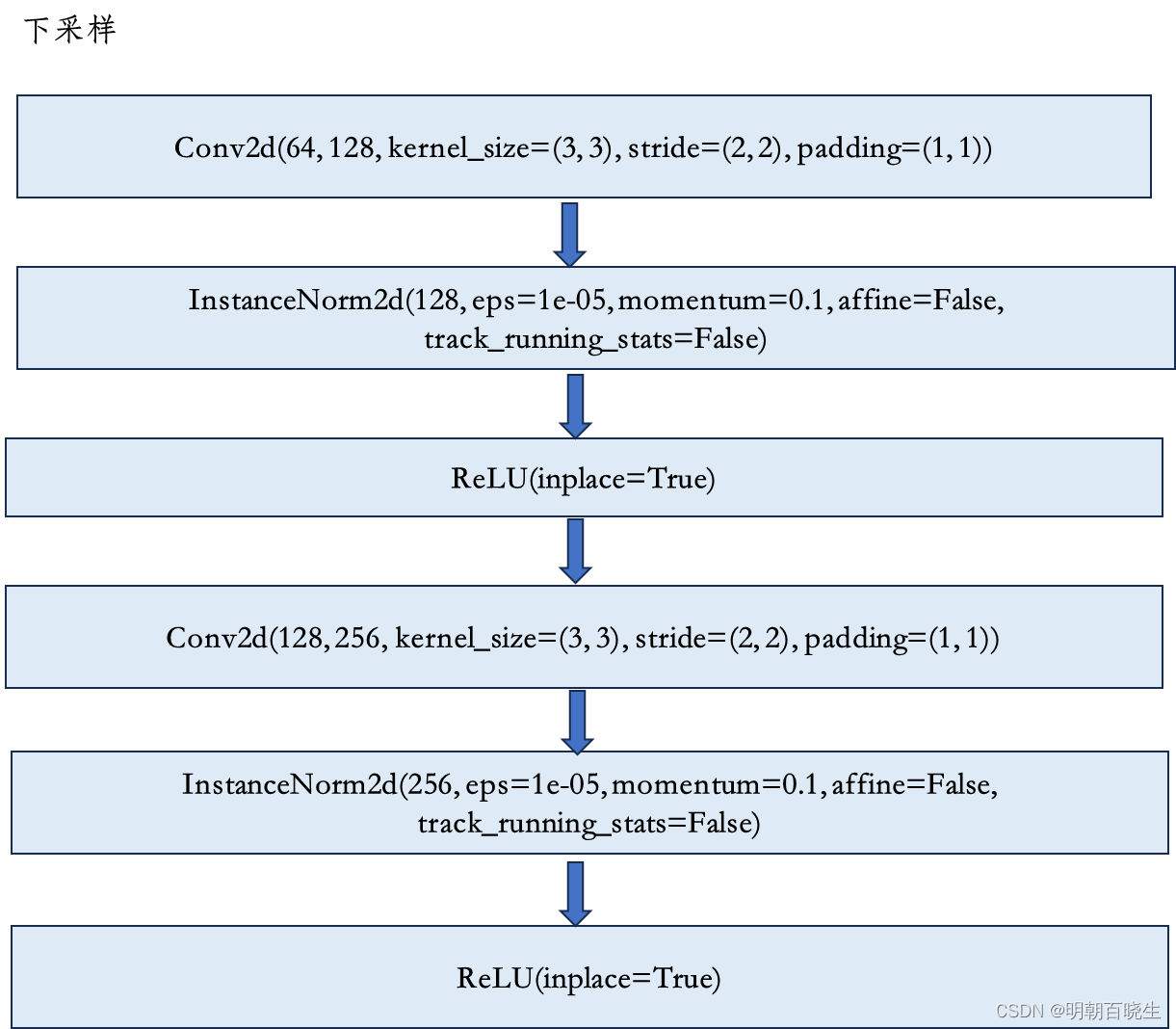
2.3 残差网络层,默认9个
2.4 上采样层
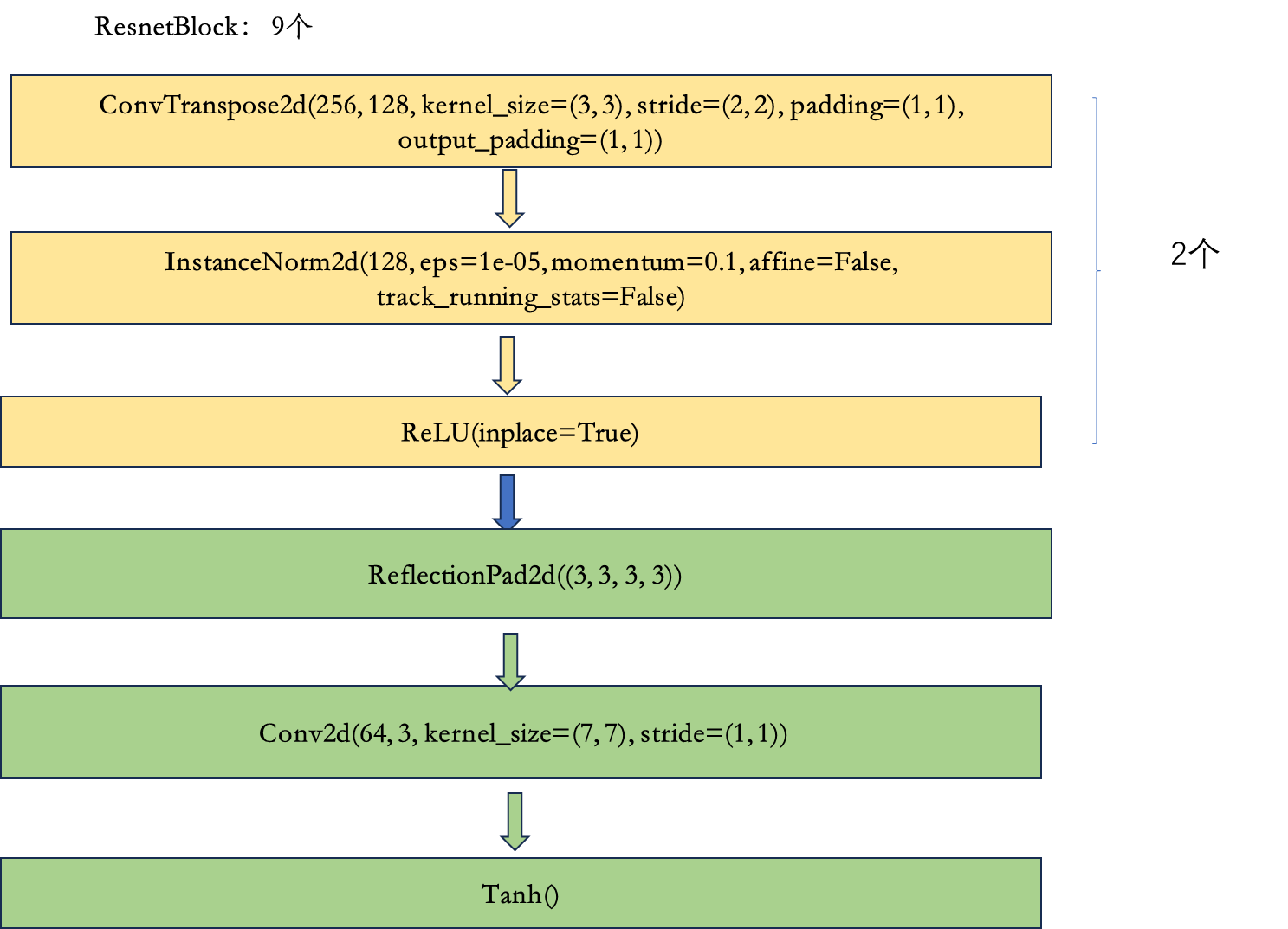
三 鉴别器模型
network.py中实现
Total params: 2,764,737
Trainable params: 2,764,737
Non-trainable params: 0
模型结构

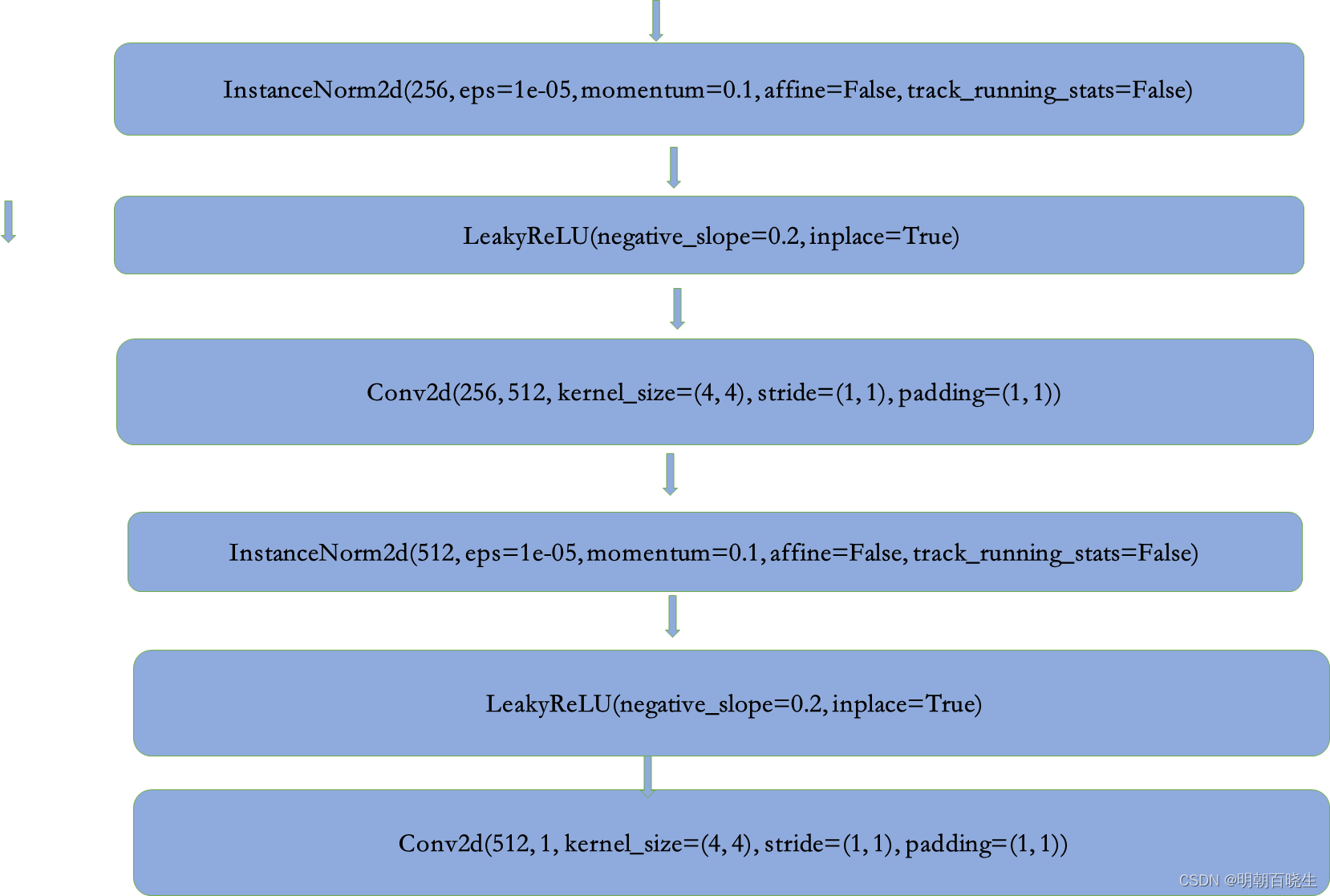
四 networks.py
主要定义了生成器,鉴别器的网络结构
define_G 生成器
define_D 鉴别器
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Apr 1 13:48:33 2024@author: chengxf2
"""import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import init
import functools
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
from torchsummary import summary###############################################################################
# Helper Functions
###############################################################################class Identity(nn.Module):def forward(self, x):return xdef init_weights(net, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02):"""Initialize network weights.Parameters:net (network) -- network to be initializedinit_type (str) -- the name of an initialization method: normal | xavier | kaiming | orthogonalinit_gain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.We use 'normal' in the original pix2pix and CycleGAN paper. But xavier and kaiming mightwork better for some applications. Feel free to try yourself."""def init_func(m): # define the initialization functionclassname = m.__class__.__name__if hasattr(m, 'weight') and (classname.find('Conv') != -1 or classname.find('Linear') != -1):if init_type == 'normal':init.normal_(m.weight.data, 0.0, init_gain)elif init_type == 'xavier':init.xavier_normal_(m.weight.data, gain=init_gain)elif init_type == 'kaiming':init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight.data, a=0, mode='fan_in')elif init_type == 'orthogonal':init.orthogonal_(m.weight.data, gain=init_gain)else:raise NotImplementedError('initialization method [%s] is not implemented' % init_type)if hasattr(m, 'bias') and m.bias is not None:init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)elif classname.find('BatchNorm2d') != -1: # BatchNorm Layer's weight is not a matrix; only normal distribution applies.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, init_gain)init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)print('initialize network with %s' % init_type)net.apply(init_func) # apply the initialization function <init_func>def get_norm_layer(norm_type='instance'):"""Return a normalization layerParameters:affine:代表gamma,beta是否可学。如果设为True,代表两个参数是通过学习得到的;如果设为False,代表两个参数是固定值,默认情况下,gamma是1,beta是0。track_running_stats:BatchNorm2d中存储的的均值和方差是否需要更新,若为True,表示需要更新;反之不需要更新。更新公式参考momentum参数介绍 。"""if norm_type == 'batch':norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.BatchNorm2d, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)elif norm_type == 'instance':norm_layer = functools.partial(nn.InstanceNorm2d, affine=False, track_running_stats=False)elif norm_type == 'none':def norm_layer(x):return Identity()else:raise NotImplementedError('normalization layer [%s] is not found' % norm_type)return norm_layerdef init_net(net, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):"""Initialize a network: 1. register CPU/GPU device (with multi-GPU support); 2. initialize the network weightsParameters:net (network) -- the network to be initializedinit_type (str) -- the name of an initialization method: normal | xavier | kaiming | orthogonalgain (float) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2Return an initialized network."""if len(gpu_ids) > 0:assert(torch.cuda.is_available())net.to(gpu_ids[0])net = torch.nn.DataParallel(net, gpu_ids) # multi-GPUsinit_weights(net, init_type, init_gain=init_gain)return netclass NLayerDiscriminator(nn.Module):"""Defines a PatchGAN discriminator"""def __init__(self, input_nc, ndf=64, n_layers=3, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d):"""Construct a PatchGAN discriminatorParameters:input_nc (int) -- the number of channels in input imagesndf (int) -- the number of filters in the last conv layern_layers (int) -- the number of conv layers in the discriminatornorm_layer -- normalization layer"""super(NLayerDiscriminator, self).__init__()if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial: # no need to use bias as BatchNorm2d has affine parametersuse_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2delse:use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2dkw = 4padw = 1sequence = [nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)]nf_mult = 1nf_mult_prev = 1for n in range(1, n_layers): # gradually increase the number of filtersnf_mult_prev = nf_multnf_mult = min(2 ** n, 8)sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult, kernel_size=kw, stride=2, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)]nf_mult_prev = nf_multnf_mult = min(2 ** n_layers, 8)sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult_prev, ndf * nf_mult, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw, bias=use_bias),norm_layer(ndf * nf_mult),nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, True)]sequence += [nn.Conv2d(ndf * nf_mult, 1, kernel_size=kw, stride=1, padding=padw)] # output 1 channel prediction mapself.model = nn.Sequential(*sequence)def forward(self, input):"""Standard forward."""return self.model(input)def define_D(input_nc, ndf, netD, n_layers_D=3, norm='batch', init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):"""鉴别器Parameters:input_nc (3) -- the number of channels in input imagesndf (64) -- the number of filters in the first conv layernetD ('basic') -- the architecture's name: basic | n_layers | pixeln_layers_D (3) -- the number of conv layers in the discriminator; effective when netD=='n_layers'norm ('instance') -- the type of normalization layers used in the network.init_type ('normal') -- the name of the initialization method.init_gain (0.02) -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2Returns a discriminatorOur current implementation provides three types of discriminators:[basic]: 'PatchGAN' classifier described in the original pix2pix paper.It can classify whether 70×70 overlapping patches are real or fake.Such a patch-level discriminator architecture has fewer parametersthan a full-image discriminator and can work on arbitrarily-sized imagesin a fully convolutional fashion.[n_layers]: With this mode, you can specify the number of conv layers in the discriminatorwith the parameter <n_layers_D> (default=3 as used in [basic] (PatchGAN).)[pixel]: 1x1 PixelGAN discriminator can classify whether a pixel is real or not.It encourages greater color diversity but has no effect on spatial statistics.The discriminator has been initialized by <init_net>. It uses Leakly RELU for non-linearity."""net = Nonenorm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm)if netD == 'basic': # default PatchGAN classifiernet = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers=3, norm_layer=norm_layer)elif netD == 'n_layers': # more optionsnet = NLayerDiscriminator(input_nc, ndf, n_layers_D, norm_layer=norm_layer)raise NotImplementedError('Discriminator model name [%s] is not recognized' % netD)return init_net(net, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids)def define_G(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, netG, norm='batch', use_dropout=False, init_type='normal', init_gain=0.02, gpu_ids=[]):"""创建一个生成器Parameters:input_nc=3-- input image channels: 3 for RGB and 1 for grayscaleoutput_nc=3 -- output image channels: 3 for RGB and 1 for grayscale'ngf =64 -- the number of filters in the last conv layernetG='resnet_9blocks' -- the architecture's name: resnet_9blocks | resnet_6blocks | unet_256 | unet_128norm='instance' -- the name of normalization layers used in the network: batch | instance | noneuse_dropout =False -- if use dropout layers.init_type ='normal' -- the name of our initialization method.init_gain =0.02 -- scaling factor for normal, xavier and orthogonal.gpu_ids (int list) -- which GPUs the network runs on: e.g., 0,1,2Returns a generatorOur current implementation provides two types of generators:U-Net: [unet_128] (for 128x128 input images) and [unet_256] (for 256x256 input images)The original U-Net paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597Resnet-based generator: [resnet_6blocks] (with 6 Resnet blocks) and [resnet_9blocks] (with 9 Resnet blocks)Resnet-based generator consists of several Resnet blocks between a few downsampling/upsampling operations.We adapt Torch code from Justin Johnson's neural style transfer project (https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style).The generator has been initialized by <init_net>. It uses RELU for non-linearity."""net = Nonenorm_layer = get_norm_layer(norm_type=norm)if netG == 'resnet_9blocks':net = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=9)elif netG == 'resnet_6blocks':net = ResnetGenerator(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, n_blocks=6)else:raise NotImplementedError('Generator model name [%s] is not recognized' % netG)return init_net(net, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids)class ResnetGenerator(nn.Module):"""Resnet-based generator that consists of Resnet blocks between a few downsampling/upsampling operations.We adapt Torch code and idea from Justin Johnson's neural style transfer project(https://github.com/jcjohnson/fast-neural-style)"""def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, ngf=64, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2d, use_dropout=False, n_blocks=6, padding_type='reflect'):"""Construct a Resnet-based generatorParameters:input_nc (3) -- the number of channels in input imagesoutput_nc (3) -- the number of channels in output imagesngf (64) -- the number of filters in the last conv layernorm_layer -- normalization layeruse_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layersn_blocks (int) -- the number of ResNet blockspadding_type (str) -- the name of padding layer in conv layers: reflect | replicate | zero"""assert(n_blocks >= 0)super(ResnetGenerator, self).__init__()if type(norm_layer) == functools.partial:use_bias = norm_layer.func == nn.InstanceNorm2delse:use_bias = norm_layer == nn.InstanceNorm2d#镜像天聪,卷积model = [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3),nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ngf, kernel_size=7, padding=0, bias=use_bias),norm_layer(ngf),nn.ReLU(True)]n_downsampling = 2 for i in range(n_downsampling): # add downsampling layersmult = 2 ** i[]model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf * mult, ngf * mult * 2, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=use_bias),norm_layer(ngf * mult * 2),nn.ReLU(True)]mult = 2 ** n_downsamplingfor i in range(n_blocks): # add ResNet blocksmodel += [ResnetBlock(ngf * mult, padding_type=padding_type, norm_layer=norm_layer, use_dropout=use_dropout, use_bias=use_bias)]for i in range(n_downsampling): # add upsampling layersmult = 2 ** (n_downsampling - i)model += [nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * mult, int(ngf * mult / 2),kernel_size=3, stride=2,padding=1, output_padding=1,bias=use_bias),norm_layer(int(ngf * mult / 2)),nn.ReLU(True)]model += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(3)]model += [nn.Conv2d(ngf, output_nc, kernel_size=7, padding=0)]model += [nn.Tanh()]self.model = nn.Sequential(*model)def forward(self, input):"""Standard forward"""return self.model(input)class ResnetBlock(nn.Module):"""Define a Resnet block"""def __init__(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias):"""Initialize the Resnet blockA resnet block is a conv block with skip connectionsWe construct a conv block with build_conv_block function,and implement skip connections in <forward> function.Original Resnet paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf"""super(ResnetBlock, self).__init__()self.conv_block = self.build_conv_block(dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias)def build_conv_block(self, dim, padding_type, norm_layer, use_dropout, use_bias):"""Construct a convolutional block.Parameters:dim (int) -- the number of channels in the conv layer.padding_type (str) -- the name of padding layer: reflect | replicate | zeronorm_layer -- normalization layeruse_dropout (bool) -- if use dropout layers.use_bias (bool) -- if the conv layer uses bias or notReturns a conv block (with a conv layer, a normalization layer, and a non-linearity layer (ReLU))"""conv_block = []p = 0if padding_type == 'reflect':conv_block += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(1)]elif padding_type == 'replicate':conv_block += [nn.ReplicationPad2d(1)]elif padding_type == 'zero':p = 1else:raise NotImplementedError('padding [%s] is not implemented' % padding_type)conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p, bias=use_bias), norm_layer(dim), nn.ReLU(True)]if use_dropout:conv_block += [nn.Dropout(0.5)]p = 0if padding_type == 'reflect':conv_block += [nn.ReflectionPad2d(1)]elif padding_type == 'replicate':conv_block += [nn.ReplicationPad2d(1)]elif padding_type == 'zero':p = 1else:raise NotImplementedError('padding [%s] is not implemented' % padding_type)conv_block += [nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, kernel_size=3, padding=p, bias=use_bias), norm_layer(dim)]return nn.Sequential(*conv_block)def forward(self, x):"""Forward function (with skip connections)"""out = x + self.conv_block(x) # add skip connectionsreturn outif __name__ == '__main__':input_nc =3output_nc =3ndf = 64ngf= 64 netD ='basic'netG = 'resnet_9blocks'n_layers_D =3norm ='instance'init_type = 'normal'init_gain = 0.02gpu_ids = []use_dropout=FalsenetG_A = define_G(input_nc, output_nc, ngf, netG, norm, use_dropout, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids)#print(netG_A)summary(model=netG_A, input_size=(3,256,256),batch_size=1, device="cpu")netD_A= define_D(input_nc, ndf, netD,n_layers_D,norm, init_type, init_gain, gpu_ids)summary(model=netD_A, input_size=(3,256,256),batch_size=1, device="cpu")五cycleGAN 模型
cycle_gan_model.py
主要定义了 损失函数,训练方法
GAN 模型是先训练鉴别器D, 再训练生成器G
CycleGAN 是先训练生成器G, 再训练鉴别器D
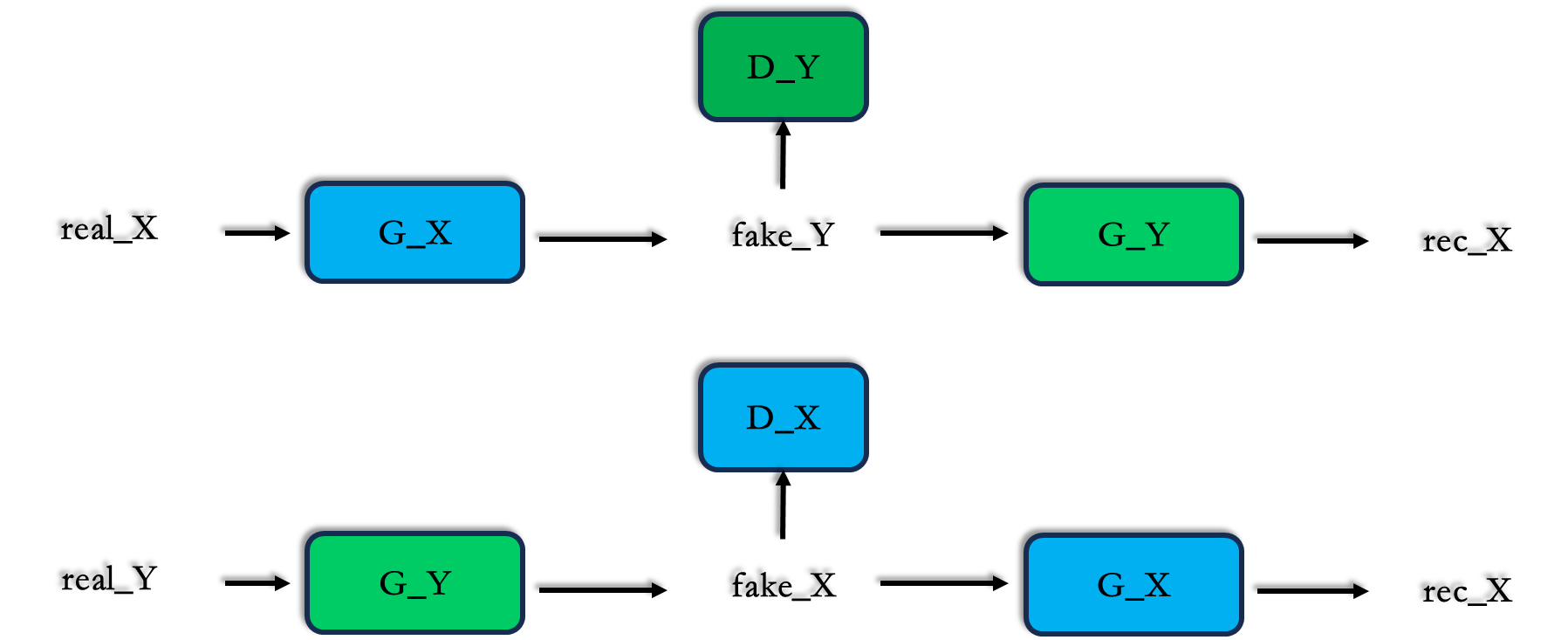
3.1 cycle_gan_model.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Mar 28 14:02:15 2024@author: chengxf2
"""import torch
import itertoolsfrom . import networks
from . import ImagePool
from .base_model import BaseModelclass CycleGANModel():"""netG: 生成器netD: 鉴别器"""def __init__(self,opt):"""初始化CycleGAN 模型"""BaseModel.__init__(self, opt)#论文实例代码 code(vs. paper) G_A(G) G_B(F),D_A(D_Y),D_B(D_X),这里直接更改成论文的命名方式self.netG_X = networks.define_G(opt.input_nc, opt.output_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, opt.norm,not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)self.netG_Y = networks.define_G(opt.output_nc, opt.input_nc, opt.ngf, opt.netG, opt.norm,not opt.no_dropout, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)if self.isTrain: #定义鉴别器self.netD_X = networks.define_D(opt.input_nc, opt.ndf, opt.netD,opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)self.netD_Y = networks.define_D(opt.output_nc, opt.ndf, opt.netD,opt.n_layers_D, opt.norm, opt.init_type, opt.init_gain, self.gpu_ids)if self.isTrain:if opt.lambda_identity > 0.0: # only works when input and output images have the same number of channelsassert(opt.input_nc == opt.output_nc)self.fake_A_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size) # create image buffer to store previously generated imagesself.fake_B_pool = ImagePool(opt.pool_size) # create image buffer to store previously generated images# define loss functionsself.criterionGAN = networks.GANLoss(opt.gan_mode).to(self.device) # define GAN loss.self.criterionCycle = torch.nn.L1Loss()self.criterionIdt = torch.nn.L1Loss()# initialize optimizers; schedulers will be automatically created by function <BaseModel.setup>.self.optimizer_G = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.netG_X.parameters(), self.netG_Y.parameters()), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))self.optimizer_D = torch.optim.Adam(itertools.chain(self.netD_X.parameters(), self.netD_Y.parameters()), lr=opt.lr, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_G)self.optimizers.append(self.optimizer_D)def set_input(self):"""从数据加载器中解压缩输入数据,并执行必要的预处理步骤。参数:input(dict):包括数据本身及其元数据信息选项“direction”可用于交换域X和域Y。"""XtoY = self.opt.direction == 'XtoY'self.real_X = input['X' if XtoY else 'Y'].to(self.device)self.real_Y= input['Y' if XtoY else 'X'].to(self.device)self.image_path = input['X_paths' if XtoY else 'Y_Paths']def forward(self):"""运行前向传播;由函数 <optimize_parameters> 和 <test> 调用"""self.fake_Y = self.netG_X(self.real_X) #G_X(X)self.rec_X = self.netG_Y(self.fake_Y) #G_Y(G_X(X)) 重构self.fake_X = self.netG_Y(self.real_Y) #G_Y(Y)self.rec_Y = self.netG_X(self.fake_Y) #G_X(fake_Y)def optimize_parameters(self):"""计算损失、梯度并更新网络权重;在每次训练迭代中调用"""# forwardself.forward() # compute fake images and reconstruction images.#先训练生成器 G_X and G_Y,这个跟GAN是相反的self.set_requires_grad([self.netD_X, self.netD_Y], False) # Ds require no gradients when optimizing Gsself.optimizer_G.zero_grad() # set G_A and G_B's gradients to zeroself.backward_G() # calculate gradients for G_A and G_Bself.optimizer_G.step() # update G_A and G_B's weights# D_X and D_Yself.set_requires_grad([self.netD_X, self.netD_Y], True)self.optimizer_D.zero_grad() # set D_A and D_B's gradients to zeroself.backward_D_X() # calculate gradients for D_Aself.backward_D_Y() # calculate graidents for D_Bself.optimizer_D.step() # update D_A and D_B's weightsdef backward_G(self):"""Calculate the loss for generators G_X and G_Y"""lambda_idt = self.opt.lambda_identitylambda_X = self.opt.lambda_Xlambda_Y = self.opt.lambda_Y# Identity lossif lambda_idt > 0:# identity if real_Y is fed: self.idt_X = self.netG_X(self.real_Y)self.loss_idt_X = self.criterionIdt(self.idt_X, self.real_Y) * lambda_X * lambda_idt# identity if real_X is fed:self.idt_Y = self.netG_Y(self.real_X)self.loss_idt_Y = self.criterionIdt(self.idt_Y, self.real_X) * lambda_Y * lambda_idtelse:self.loss_idt_X = 0self.loss_idt_Y = 0# GAN loss D_A(G_A(A))self.loss_G_X = self.criterionGAN(self.netD_Y(self.fake_Y), True)# GAN loss D_B(G_B(B))self.loss_G_Y = self.criterionGAN(self.netD_X(self.fake_X), True)# Forward cycle loss || G_B(G_A(A)) - A||self.loss_cycle_X = self.criterionCycle(self.rec_X, self.real_X) * lambda_X# Backward cycle loss || G_A(G_B(B)) - B||self.loss_cycle_Y = self.criterionCycle(self.rec_Y, self.real_Y) * lambda_Y# combined loss and calculate gradientsself.loss_G = self.loss_G_X + self.loss_G_Y + self.loss_cycle_X + self.loss_cycle_Y + self.loss_idt_X + self.loss_idt_Yself.loss_G.backward()def backward_D_Y(self):"""Calculate GAN loss for discriminator D_X"""fake_Y = self.fake_B_pool.query(self.fake_Y)self.loss_D_Y = self.backward_D_basic(self.netD_Y, self.real_Y, fake_Y)def backward_D_X(self):"""Calculate GAN loss for discriminator D_B"""fake_X = self.fake_A_pool.query(self.fake_X)self.loss_D_X = self.backward_D_basic(self.netD_X, self.real_X, fake_X)def backward_D_basic(self, netD, real, fake):"""Calculate GAN loss for the discriminator,patchGANParameters:netD (network) -- the discriminator Dreal (tensor array) -- real imagesfake (tensor array) -- images generated by a generatorReturn the discriminator loss.We also call loss_D.backward() to calculate the gradients."""# Realpred_real = netD(real)loss_D_real = self.criterionGAN(pred_real, True)# Fakepred_fake = netD(fake.detach())loss_D_fake = self.criterionGAN(pred_fake, False)# Combined loss and calculate gradientsloss_D = (loss_D_real + loss_D_fake) * 0.5loss_D.backward()return loss_D3.2 base_model.py
基类
import os
import torch
from collections import OrderedDict
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from . import networksclass BaseModel(ABC):"""This class is an abstract base class (ABC) for models.To create a subclass, you need to implement the following five functions:-- <__init__>: initialize the class; first call BaseModel.__init__(self, opt).-- <set_input>: unpack data from dataset and apply preprocessing.-- <forward>: produce intermediate results.-- <optimize_parameters>: calculate losses, gradients, and update network weights.-- <modify_commandline_options>: (optionally) add model-specific options and set default options."""def __init__(self, opt):"""Initialize the BaseModel class.Parameters:opt (Option class)-- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptionsWhen creating your custom class, you need to implement your own initialization.In this function, you should first call <BaseModel.__init__(self, opt)>Then, you need to define four lists:-- self.loss_names (str list): specify the training losses that you want to plot and save.-- self.model_names (str list): define networks used in our training.-- self.visual_names (str list): specify the images that you want to display and save.-- self.optimizers (optimizer list): define and initialize optimizers. You can define one optimizer for each network. If two networks are updated at the same time, you can use itertools.chain to group them. See cycle_gan_model.py for an example."""self.opt = optself.gpu_ids = opt.gpu_idsself.isTrain = opt.isTrainself.device = torch.device('cuda:{}'.format(self.gpu_ids[0])) if self.gpu_ids else torch.device('cpu') # get device name: CPU or GPUself.save_dir = os.path.join(opt.checkpoints_dir, opt.name) # save all the checkpoints to save_dirif opt.preprocess != 'scale_width': # with [scale_width], input images might have different sizes, which hurts the performance of cudnn.benchmark.torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = Trueself.loss_names = []self.model_names = []self.visual_names = []self.optimizers = []self.image_paths = []self.metric = 0 # used for learning rate policy 'plateau'@staticmethoddef modify_commandline_options(parser, is_train):"""Add new model-specific options, and rewrite default values for existing options.Parameters:parser -- original option parseris_train (bool) -- whether training phase or test phase. You can use this flag to add training-specific or test-specific options.Returns:the modified parser."""return parser@abstractmethoddef set_input(self, input):"""Unpack input data from the dataloader and perform necessary pre-processing steps.Parameters:input (dict): includes the data itself and its metadata information."""pass@abstractmethoddef forward(self):"""Run forward pass; called by both functions <optimize_parameters> and <test>."""pass@abstractmethoddef optimize_parameters(self):"""Calculate losses, gradients, and update network weights; called in every training iteration"""passdef setup(self, opt):"""Load and print networks; create schedulersParameters:opt (Option class) -- stores all the experiment flags; needs to be a subclass of BaseOptions"""if self.isTrain:self.schedulers = [networks.get_scheduler(optimizer, opt) for optimizer in self.optimizers]if not self.isTrain or opt.continue_train:load_suffix = 'iter_%d' % opt.load_iter if opt.load_iter > 0 else opt.epochself.load_networks(load_suffix)self.print_networks(opt.verbose)def eval(self):"""Make models eval mode during test time"""for name in self.model_names:if isinstance(name, str):net = getattr(self, 'net' + name)net.eval()def test(self):"""Forward function used in test time.This function wraps <forward> function in no_grad() so we don't save intermediate steps for backpropIt also calls <compute_visuals> to produce additional visualization results"""with torch.no_grad():self.forward()self.compute_visuals()def compute_visuals(self):"""Calculate additional output images for visdom and HTML visualization"""passdef get_image_paths(self):""" Return image paths that are used to load current data"""return self.image_pathsdef update_learning_rate(self):"""Update learning rates for all the networks; called at the end of every epoch"""old_lr = self.optimizers[0].param_groups[0]['lr']for scheduler in self.schedulers:if self.opt.lr_policy == 'plateau':scheduler.step(self.metric)else:scheduler.step()lr = self.optimizers[0].param_groups[0]['lr']print('learning rate %.7f -> %.7f' % (old_lr, lr))def get_current_visuals(self):"""Return visualization images. train.py will display these images with visdom, and save the images to a HTML"""visual_ret = OrderedDict()for name in self.visual_names:if isinstance(name, str):visual_ret[name] = getattr(self, name)return visual_retdef get_current_losses(self):"""Return traning losses / errors. train.py will print out these errors on console, and save them to a file"""errors_ret = OrderedDict()for name in self.loss_names:if isinstance(name, str):errors_ret[name] = float(getattr(self, 'loss_' + name)) # float(...) works for both scalar tensor and float numberreturn errors_retdef save_networks(self, epoch):"""Save all the networks to the disk.Parameters:epoch (int) -- current epoch; used in the file name '%s_net_%s.pth' % (epoch, name)"""for name in self.model_names:if isinstance(name, str):save_filename = '%s_net_%s.pth' % (epoch, name)save_path = os.path.join(self.save_dir, save_filename)net = getattr(self, 'net' + name)if len(self.gpu_ids) > 0 and torch.cuda.is_available():torch.save(net.module.cpu().state_dict(), save_path)net.cuda(self.gpu_ids[0])else:torch.save(net.cpu().state_dict(), save_path)def __patch_instance_norm_state_dict(self, state_dict, module, keys, i=0):"""Fix InstanceNorm checkpoints incompatibility (prior to 0.4)"""key = keys[i]if i + 1 == len(keys): # at the end, pointing to a parameter/bufferif module.__class__.__name__.startswith('InstanceNorm') and \(key == 'running_mean' or key == 'running_var'):if getattr(module, key) is None:state_dict.pop('.'.join(keys))if module.__class__.__name__.startswith('InstanceNorm') and \(key == 'num_batches_tracked'):state_dict.pop('.'.join(keys))else:self.__patch_instance_norm_state_dict(state_dict, getattr(module, key), keys, i + 1)def load_networks(self, epoch):"""Load all the networks from the disk.Parameters:epoch (int) -- current epoch; used in the file name '%s_net_%s.pth' % (epoch, name)"""for name in self.model_names:if isinstance(name, str):load_filename = '%s_net_%s.pth' % (epoch, name)load_path = os.path.join(self.save_dir, load_filename)net = getattr(self, 'net' + name)if isinstance(net, torch.nn.DataParallel):net = net.moduleprint('loading the model from %s' % load_path)# if you are using PyTorch newer than 0.4 (e.g., built from# GitHub source), you can remove str() on self.devicestate_dict = torch.load(load_path, map_location=str(self.device))if hasattr(state_dict, '_metadata'):del state_dict._metadata# patch InstanceNorm checkpoints prior to 0.4for key in list(state_dict.keys()): # need to copy keys here because we mutate in loopself.__patch_instance_norm_state_dict(state_dict, net, key.split('.'))net.load_state_dict(state_dict)def print_networks(self, verbose):"""Print the total number of parameters in the network and (if verbose) network architectureParameters:verbose (bool) -- if verbose: print the network architecture"""print('---------- Networks initialized -------------')for name in self.model_names:if isinstance(name, str):net = getattr(self, 'net' + name)num_params = 0for param in net.parameters():num_params += param.numel()if verbose:print(net)print('[Network %s] Total number of parameters : %.3f M' % (name, num_params / 1e6))print('-----------------------------------------------')def set_requires_grad(self, nets, requires_grad=False):"""Set requies_grad=Fasle for all the networks to avoid unnecessary computationsParameters:nets (network list) -- a list of networksrequires_grad (bool) -- whether the networks require gradients or not"""if not isinstance(nets, list):nets = [nets]for net in nets:if net is not None:for param in net.parameters():param.requires_grad = requires_grad
四 训练和测试
4.1 train.py
"""General-purpose training script for image-to-image translation.This script works for various models (with option '--model': e.g., pix2pix, cyclegan, colorization) and
different datasets (with option '--dataset_mode': e.g., aligned, unaligned, single, colorization).
You need to specify the dataset ('--dataroot'), experiment name ('--name'), and model ('--model').It first creates model, dataset, and visualizer given the option.
It then does standard network training. During the training, it also visualize/save the images, print/save the loss plot, and save models.
The script supports continue/resume training. Use '--continue_train' to resume your previous training.Example:Train a CycleGAN model:python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_ganTrain a pix2pix model:python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoASee options/base_options.py and options/train_options.py for more training options.
See training and test tips at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md
See frequently asked questions at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/qa.md
"""
import time
from options.train_options import TrainOptions
from data import create_dataset
from models import create_model
from util.visualizer import Visualizerif __name__ == '__main__':opt = TrainOptions().parse() # get training optionsdataset = create_dataset(opt) # create a dataset given opt.dataset_mode and other optionsdataset_size = len(dataset) # get the number of images in the dataset.print('The number of training images = %d' % dataset_size)model = create_model(opt) # create a model given opt.model and other optionsmodel.setup(opt) # regular setup: load and print networks; create schedulersvisualizer = Visualizer(opt) # create a visualizer that display/save images and plotstotal_iters = 0 # the total number of training iterationsfor epoch in range(opt.epoch_count, opt.n_epochs + opt.n_epochs_decay + 1): # outer loop for different epochs; we save the model by <epoch_count>, <epoch_count>+<save_latest_freq>epoch_start_time = time.time() # timer for entire epochiter_data_time = time.time() # timer for data loading per iterationepoch_iter = 0 # the number of training iterations in current epoch, reset to 0 every epochvisualizer.reset() # reset the visualizer: make sure it saves the results to HTML at least once every epochmodel.update_learning_rate() # update learning rates in the beginning of every epoch.for i, data in enumerate(dataset): # inner loop within one epochiter_start_time = time.time() # timer for computation per iterationif total_iters % opt.print_freq == 0:t_data = iter_start_time - iter_data_timetotal_iters += opt.batch_sizeepoch_iter += opt.batch_sizemodel.set_input(data) # unpack data from dataset and apply preprocessingmodel.optimize_parameters() # calculate loss functions, get gradients, update network weightsif total_iters % opt.display_freq == 0: # display images on visdom and save images to a HTML filesave_result = total_iters % opt.update_html_freq == 0model.compute_visuals()visualizer.display_current_results(model.get_current_visuals(), epoch, save_result)if total_iters % opt.print_freq == 0: # print training losses and save logging information to the disklosses = model.get_current_losses()t_comp = (time.time() - iter_start_time) / opt.batch_sizevisualizer.print_current_losses(epoch, epoch_iter, losses, t_comp, t_data)if opt.display_id > 0:visualizer.plot_current_losses(epoch, float(epoch_iter) / dataset_size, losses)if total_iters % opt.save_latest_freq == 0: # cache our latest model every <save_latest_freq> iterationsprint('saving the latest model (epoch %d, total_iters %d)' % (epoch, total_iters))save_suffix = 'iter_%d' % total_iters if opt.save_by_iter else 'latest'model.save_networks(save_suffix)iter_data_time = time.time()if epoch % opt.save_epoch_freq == 0: # cache our model every <save_epoch_freq> epochsprint('saving the model at the end of epoch %d, iters %d' % (epoch, total_iters))model.save_networks('latest')model.save_networks(epoch)print('End of epoch %d / %d \t Time Taken: %d sec' % (epoch, opt.n_epochs + opt.n_epochs_decay, time.time() - epoch_start_time))
4.2 test.py
测试代码
"""General-purpose test script for image-to-image translation.Once you have trained your model with train.py, you can use this script to test the model.
It will load a saved model from '--checkpoints_dir' and save the results to '--results_dir'.It first creates model and dataset given the option. It will hard-code some parameters.
It then runs inference for '--num_test' images and save results to an HTML file.Example (You need to train models first or download pre-trained models from our website):Test a CycleGAN model (both sides):python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_ganTest a CycleGAN model (one side only):python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --name horse2zebra_pretrained --model test --no_dropoutThe option '--model test' is used for generating CycleGAN results only for one side.This option will automatically set '--dataset_mode single', which only loads the images from one set.On the contrary, using '--model cycle_gan' requires loading and generating results in both directions,which is sometimes unnecessary. The results will be saved at ./results/.Use '--results_dir <directory_path_to_save_result>' to specify the results directory.Test a pix2pix model:python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --direction BtoASee options/base_options.py and options/test_options.py for more test options.
See training and test tips at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/tips.md
See frequently asked questions at: https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix/blob/master/docs/qa.md
"""
import os
from options.test_options import TestOptions
from data import create_dataset
from models import create_model
from util.visualizer import save_images
from util import htmltry:import wandb
except ImportError:print('Warning: wandb package cannot be found. The option "--use_wandb" will result in error.')if __name__ == '__main__':opt = TestOptions().parse() # get test options# hard-code some parameters for testopt.num_threads = 0 # test code only supports num_threads = 0opt.batch_size = 1 # test code only supports batch_size = 1opt.serial_batches = True # disable data shuffling; comment this line if results on randomly chosen images are needed.opt.no_flip = True # no flip; comment this line if results on flipped images are needed.opt.display_id = -1 # no visdom display; the test code saves the results to a HTML file.dataset = create_dataset(opt) # create a dataset given opt.dataset_mode and other optionsmodel = create_model(opt) # create a model given opt.model and other optionsmodel.setup(opt) # regular setup: load and print networks; create schedulers# initialize loggerif opt.use_wandb:wandb_run = wandb.init(project=opt.wandb_project_name, name=opt.name, config=opt) if not wandb.run else wandb.runwandb_run._label(repo='CycleGAN-and-pix2pix')# create a websiteweb_dir = os.path.join(opt.results_dir, opt.name, '{}_{}'.format(opt.phase, opt.epoch)) # define the website directoryif opt.load_iter > 0: # load_iter is 0 by defaultweb_dir = '{:s}_iter{:d}'.format(web_dir, opt.load_iter)print('creating web directory', web_dir)webpage = html.HTML(web_dir, 'Experiment = %s, Phase = %s, Epoch = %s' % (opt.name, opt.phase, opt.epoch))# test with eval mode. This only affects layers like batchnorm and dropout.# For [pix2pix]: we use batchnorm and dropout in the original pix2pix. You can experiment it with and without eval() mode.# For [CycleGAN]: It should not affect CycleGAN as CycleGAN uses instancenorm without dropout.if opt.eval:model.eval()for i, data in enumerate(dataset):if i >= opt.num_test: # only apply our model to opt.num_test images.breakmodel.set_input(data) # unpack data from data loadermodel.test() # run inferencevisuals = model.get_current_visuals() # get image resultsimg_path = model.get_image_paths() # get image pathsif i % 5 == 0: # save images to an HTML fileprint('processing (%04d)-th image... %s' % (i, img_path))save_images(webpage, visuals, img_path, aspect_ratio=opt.aspect_ratio, width=opt.display_winsize, use_wandb=opt.use_wandb)webpage.save() # save the HTML