1、View生命周期以及View层级
1.1、View生命周期
View的主要生命周期如下所示, 包括创建、测量(onMeasure)、布局(onLayout)、绘制(onDraw)以及销毁等流程。

自定义View主要涉及到onMeasure、onLayout和onDraw这三个过程,其中
(1)自定义View(继承自View类):主要实现onMeasure和onDraw,
(2)自定义ViewGroup(继承自ViewGroup类):主要实现onMeasure和onLayout。
1.2、View层级
View层级是一个树形结构。
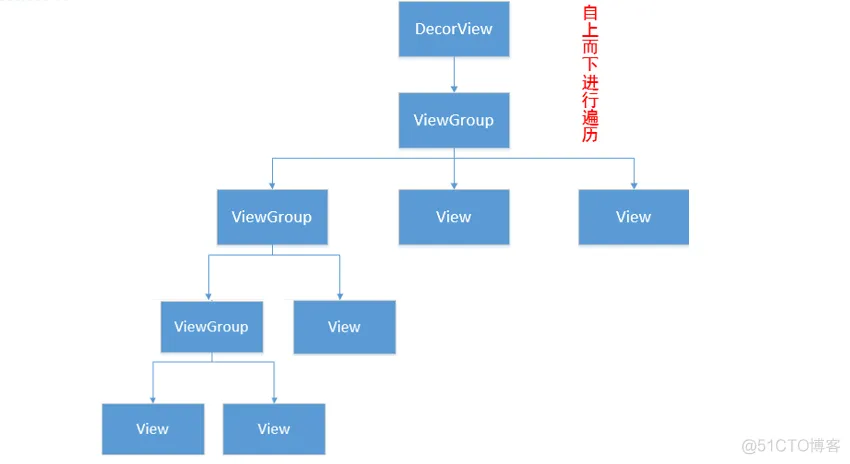
onMeasure、onLayout和onDraw这三个过程都是按照View层级从上到下进行的:(1)ViewGroup主要负责onMeasure和onLayout,确定自身及其子View的大小和放置方式,例如LinearLayout通过onMeasure确定尺寸,通过onLayout对子View进行横向或者纵向布局;(2)View主要负责onMeasure和onDraw,例如TextView通过onMeasure确定自身尺寸,通过onDraw绘制文字。
2、View测量与MeasureSpec类
View测量中最难的一点就是如何根据View的LayoutParams参数确定其实际的宽高,如:
android:layout_width="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"这三种情况,View的宽度究竟应该是多少?这就要从View的测量过程分析了,
2.1、MeasureSpec类
View类的内部类MeasureSpec用来辅助View的测量,使用一个int型变量measureSpec来表示View测量的模式和具体的尺寸(宽和高各一个measureSpec值)。measureSpec共32位,用高两位表示测量模式mode, 通过MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec)计算获得, 低30位表示尺寸size,通过MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec)计算获得。
mode共有三种情况:
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:不对View大小做限制,系统使用
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:确切的大小,如:10dp
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:大小不可超过某数值,最大不能超过其父类
2.2、父View的限制 :测量约束,限制最大宽度、最大高度等
View的测量过程受到父View的限制,如对一个ViewGroup测量时,其高度测量模式mode为EXACTLY,高度尺寸size为100dp,其子View的高度测量依据对应的android:layout_height参数来确定:
(1)具体尺寸值,如50dp,则该子View高度测量中mode为EXACTLY,尺寸为50dp;
(2)match_parent,则该子View高度和其父View高度相同,也是确定的,高度测量中mode为EXACTLY,尺寸为100dp;
(3)wrap_content, 则该子View最大高度为100dp, 确切高度需要根据内部逻辑确定,像TextView需要根据文字内容、宽度等综合确定,于是高度测量中mode为AT_MOST, 尺寸size为100dp。
其他情况类似,如父View的mode分别为AT_MOST、UNSPECIFIED,具体见下表:
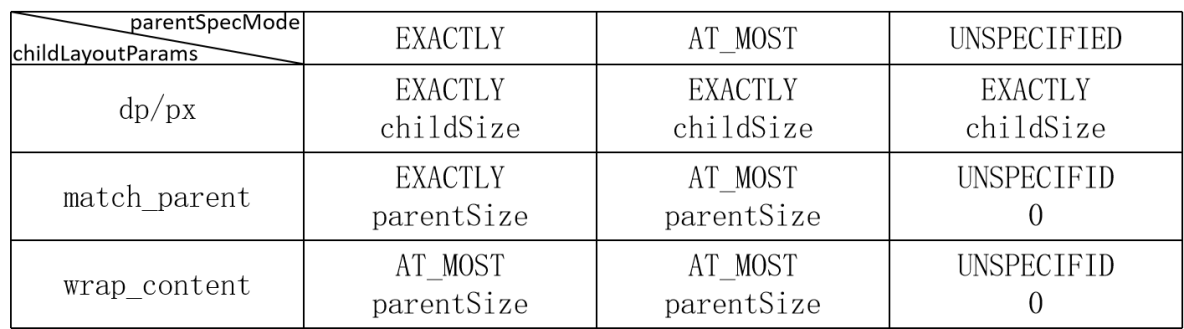
高度测量中mode和size确定后,可通过MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(size, mode)来确定heightMeasureSpec,widthMeasureSpec使用同样的方法确定。该方法的具体实现为ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec()方法。
2.3、子View的影响:实际测量
测量过程以LinearLayout作为例子说明:
(1) LinearLayout根据父View的measureSpec以及自身的LayoutParams确定了自身的widthMeasureSpec、heightMeasureSpec后, 调用measure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec) -----> onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)来进行实际的测量;
(2) 当该LinearLayout方向为vertical时,实际测量中应该计算所有子View的高度之和,作为LinearLayout的测量高度needHeight;
(3) heightMeasureSpec中size为父类给该LinearLayout的限制高度,根据heightMeasureSpec中mode判断是取needHeight, 还是heightMeasureSpec中size, 然后调用setMeasuredDimension将测量的高度和宽度设置进去。
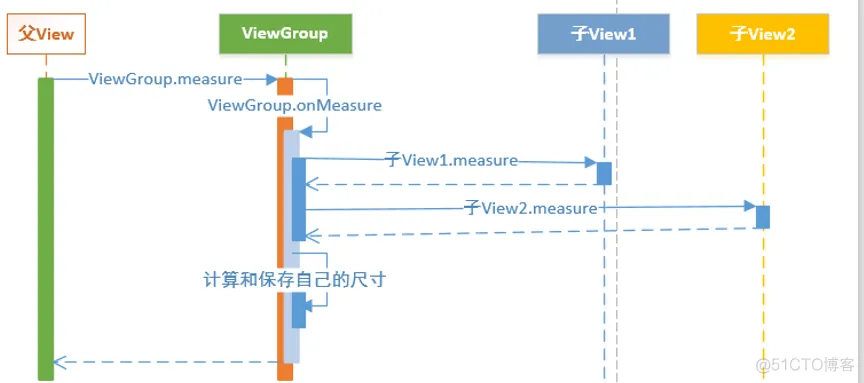
2.4、View的测量过程
Android中View测量是一种递归的过程(见下图),首先View调用measure方法,内部调用了自身的onMeasure方法,这个方法内部调用子View的measure方法(子View同样会调用自身的onMeasure方法),对子View进行测量,保存子View的测量尺寸,测量完所有的子View后再对自身测量,保存测量尺寸,之后便可以通过View.getMeasuredWidth()和View.getMeasuredHeight()来获取View的测量宽高。
3、自定义流式布局FlowLayout
主要思路:
对FlowLayout的所有子View逐个进行测量,获得measuredHeight和measuredWidth,在水平方向上根据这个尺寸依次对View进行放置,放不下则另起一行,每一行的高度取该行所有View的measuredHeight最大值。
3.1、单个子View测量
对其指定子View----child的测量代码如下,其中paddingLeft、paddingRight、paddingTop、paddingBottom分别是FlowLayout四边上的padding,widthMeasureSpec以及heightMeasureSpec是FlowLayout中onMeasure中的两个参数。
int childWidthSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec, paddingLeft + paddingRight, child.getLayoutParams().width);
int childHeightSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec, paddingTop + paddingBottom, child.getLayoutParams().height);
child.measure(childWidthSpec, childHeightSpec);于是子View的测量宽、高分别可以通过child.getMeasuredWidth() 和child.getMeasuredHeight()来进行获得。
3.2、onMeasure:测量与模拟布局View
//子View的横向间隔、纵向间隔private final int horizontalSpace = dp2px(20);private final int verticalSpace = dp2px(10);//保存测量的子View, 每一个元素为一行的子View数组private final List<List<View>> allLines = new ArrayList<>();//记录每一行的最大高度,用于布局private final List<Integer> heights = new ArrayList<>();@Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {allLines.clear();heights.clear();int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();int usedWidth = 0;int height = 0;//父布局对FlowLayout的约束宽高int seftWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) - paddingLeft -paddingRight;int seftHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec) - paddingTop - paddingBottom;//FlowLayout的测量宽高int needHeight = 0;int needWidth = 0;List<View> line = new ArrayList<>();int count = getChildCount();for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {View child = getChildAt(i);int childWidthSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,paddingLeft + paddingRight, child.getLayoutParams().width);int childHeightSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec, paddingTop + paddingBottom, child.getLayoutParams().height);child.measure(childWidthSpec, childHeightSpec);if (usedWidth + horizontalSpace + child.getMeasuredWidth() > seftWidth) {//当前行无法在放下下一个view,则保存当前行的Views集合以及当前行的最大高度,heights.add(height + verticalSpace);allLines.add(line);//所有行的最大宽度needWidth = Math.max(needWidth, usedWidth);//所有行的高度之和needHeight += height + verticalSpace;//重置下一行的使用宽度、高度、View集合usedWidth = 0;height = 0;line = new ArrayList<>();}//获取当前行的最大高度,作为当前行的高度height = Math.max(height, child.getMeasuredHeight());//记录已经使用的宽度(第一个元素不需要加横向间隔usedWidth += child.getMeasuredWidth() + (line.size() == 0 ? 0 : horizontalSpace);//保存已经测量及模拟布局的Viewline.add(child);//记录最后一行的数据if (i == count - 1) {heights.add(height + verticalSpace);allLines.add(line);needWidth = Math.max(needWidth, usedWidth);needHeight += height + verticalSpace;}}int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);//如果mode为MeasureSpec.EXACTLY, 则使用widthMeasureSpec中的size,//不然使用测量得到的size, 宽高同理int realWidth = widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? seftWidth : needWidth;int realHeight = heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? seftHeight : needHeight;//保存测量的宽和高setMeasuredDimension(realWidth + paddingLeft + paddingRight,//如果只有一行,不需要纵向间隔realHeight + paddingTop + paddingBottom - (allLines.size() > 0 ?verticalSpace : 0));}
3.3、布局:onLayout
@Overrideprotected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {int left = getPaddingLeft();int top = getPaddingTop();for (int i = 0; i < allLines.size(); i++) {List<View> line = allLines.get(i);for (int j = 0; j < line.size(); j++) {View child = line.get(j);child.layout(left, top, left + child.getMeasuredWidth(), top + child.getMeasuredHeight());//一行中View布局后每次向后移动child的测量宽 + 横向间隔left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + horizontalSpace;}//每一行布局从paddingLeft开始left = getPaddingLeft();//布局完成一行,向下移动当前行的最大高度top += heights.get(i);}}
3.4、测试
测试代码如下:
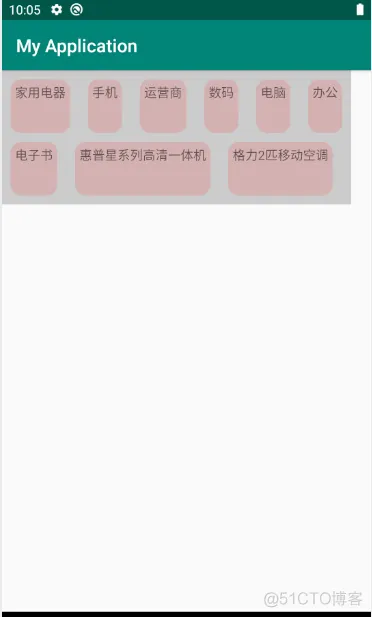
private final List<String> words = Arrays.asList("家用电器", "手机", "运营商", "数码","电脑", "办公", "电子书", "惠普星系列高清一体机", "格力2匹移动空调");@Overridepublic void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.layout_flow);FlowLayout layout = findViewById(R.id.flow_layout);for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++) {TextView textView = new TextView(this);textView.setText(words.get(i));textView.setBackground(ContextCompat.getDrawable(this,R.drawable.round_background));textView.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, FlowLayout.dp2px(60)));//textView.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(// ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, // ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));int padding = FlowLayout.dp2px(5);textView.setPadding(padding, padding, padding, padding);layout.addView(textView);}}
效果图:
android中获取view在布局中的高度和宽度
https://www.jianshu.com/p/a4d1093e2e59
这里贴一个比较好用的, AndroidUtilCode收藏的方法。
public static int[] measureView(final View view) {ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = view.getLayoutParams();if (lp == null) {lp = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);}int widthSpec = ViewGroup.getChildMeasureSpec(0, 0, lp.width);int lpHeight = lp.height;int heightSpec;if (lpHeight > 0) {heightSpec = View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(lpHeight, View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);} else {heightSpec = View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(0, View.MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED);}view.measure(widthSpec, heightSpec);return new int[]{view.getMeasuredWidth(), view.getMeasuredHeight()};}核心代码:
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {//存放容器中所有的Viewprivate List<List<View>> mAllViews = newArrayList<List<View>>();//存放每一行最高View的高度private List<Integer> mPerLineMaxHeight = new ArrayList<>();public FlowLayout(Context context) {super(context);}public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);}public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr){super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);}@Overrideprotected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {return new MarginLayoutParams(p);}@Overridepublic LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);}@Overrideprotected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);}//测量控件的宽和高@Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);//获得宽高的测量模式和测量值int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);//获得容器中子View的个数int childCount = getChildCount();//记录每一行View的总宽度int totalLineWidth = 0;//记录每一行最高View的高度int perLineMaxHeight = 0;//记录当前ViewGroup的总高度int totalHeight = 0;for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {View childView = getChildAt(i);//对子View进行测量measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();//获得子View的测量宽度int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin +lp.rightMargin;//获得子View的测量高度int childHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin +lp.bottomMargin;if (totalLineWidth + childWidth > widthSize) {//统计总高度totalHeight +=perLineMaxHeight;//开启新的一行totalLineWidth = childWidth;perLineMaxHeight = childHeight;} else {//记录每一行的总宽度totalLineWidth += childWidth;//比较每一行最高的ViewperLineMaxHeight =Math.max(perLineMaxHeight, childHeight);}//当该View已是最后一个View时,将该行最大高度添加到totalHeight中if (i == childCount - 1) {totalHeight +=perLineMaxHeight;}}//如果高度的测量模式是EXACTLY,则高度用测量值,否则用计算出来的总高度(这时高度的设置为wrap_content)heightSize = heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? heightSize : totalHeight;setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);}//摆放控件//1.表示该ViewGroup的大小或者位置是否发生变化//2.3.4.5.控件的位置@Overrideprotected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {mAllViews.clear();mPerLineMaxHeight.clear();//存放每一行的子ViewList<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<>();//记录每一行已存放View的总宽度int totalLineWidth = 0;//记录每一行最高View的高度int lineMaxHeight = 0;/*********************************遍历所有View,将View添加到List<List<View>>集合中***************************************///获得子View的总个数int childCount = getChildCount();for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {View childView = getChildAt(i);MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams)childView.getLayoutParams();int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin +lp.rightMargin;int childHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin +lp.bottomMargin;if (totalLineWidth + childWidth > getWidth()) {mAllViews.add(lineViews);mPerLineMaxHeight.add(lineMaxHeight);//开启新的一行totalLineWidth = 0;lineMaxHeight = 0;lineViews = newArrayList<>();}totalLineWidth += childWidth;lineViews.add(childView);lineMaxHeight = Math.max(lineMaxHeight, childHeight);}//单独处理最后一行mAllViews.add(lineViews);mPerLineMaxHeight.add(lineMaxHeight);
/**********************************遍历集合中的所有View并显示出来******************************************///表示一个View和父容器左边的距离int mLeft = 0;//表示View和父容器顶部的距离int mTop = 0;for (int i = 0; i < mAllViews.size(); i++) {//获得每一行的所有ViewlineViews = mAllViews.get(i);lineMaxHeight = mPerLineMaxHeight.get(i);for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {View childView =lineViews.get(j);MarginLayoutParams lp =(MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();int leftChild = mLeft +lp.leftMargin;int topChild = mTop +lp.topMargin;int rightChild = leftChild+ childView.getMeasuredWidth();int bottomChild = topChild +childView.getMeasuredHeight();//四个参数分别表示View的左上角和右下角childView.layout(leftChild,topChild, rightChild, bottomChild);mLeft += lp.leftMargin +childView.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.rightMargin;}mLeft = 0;mTop += lineMaxHeight;}}
}Android中View与ViewGroup获取内容宽高
1. 什么是内容的高度?
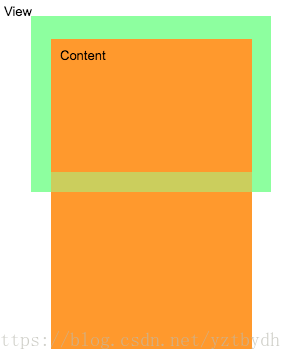
如图中,绿色的为View,Content为内容,如果View是ViewGroup,content可看做所有子节点
2. 为什么获取内容宽高
当我们自定义滑动时,期望滑动到内容最底部时,不能再往下滑动,故需要获取内容的宽高来限定。
3. 如何获取内容高度?
3.1 ViewGroup获取内容高度?(以竖直方向的LinearLayout为例)
不同的ViewGroup会有不同的内部规则,需要根据不同的ViewGroup通过不同的规则获取。
linearLayout.post(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {View last = linearLayout.getChildAt(linearLayout.getChildCount() - 1);int contentHeight = last.getTop() + last.getHeight() + linearLayout.getPaddingBottom();}
});
3.2 View的内容高度获取(以TextView为例)
很多View的内容宽高是和View的宽高一致的,但是有些时候,会不统一,比如长文字,文字总高度高于 TextView的高度时。如果其他View需要获取内容高度与宽度,需要了解内部实现,并依据推算出获取方法。
int contentHeight = textView.getLayout().getHeight() // 文字的高度+ textView.getPaddingTop() + textView.getPaddingBottom();