解释器模式
1)概述
1.定义
定义一个语言的文法,并且建立一个解释器来解释该语言中的句子,这里的“语言”是指使用规定格式和语法的代码。
2.结构图
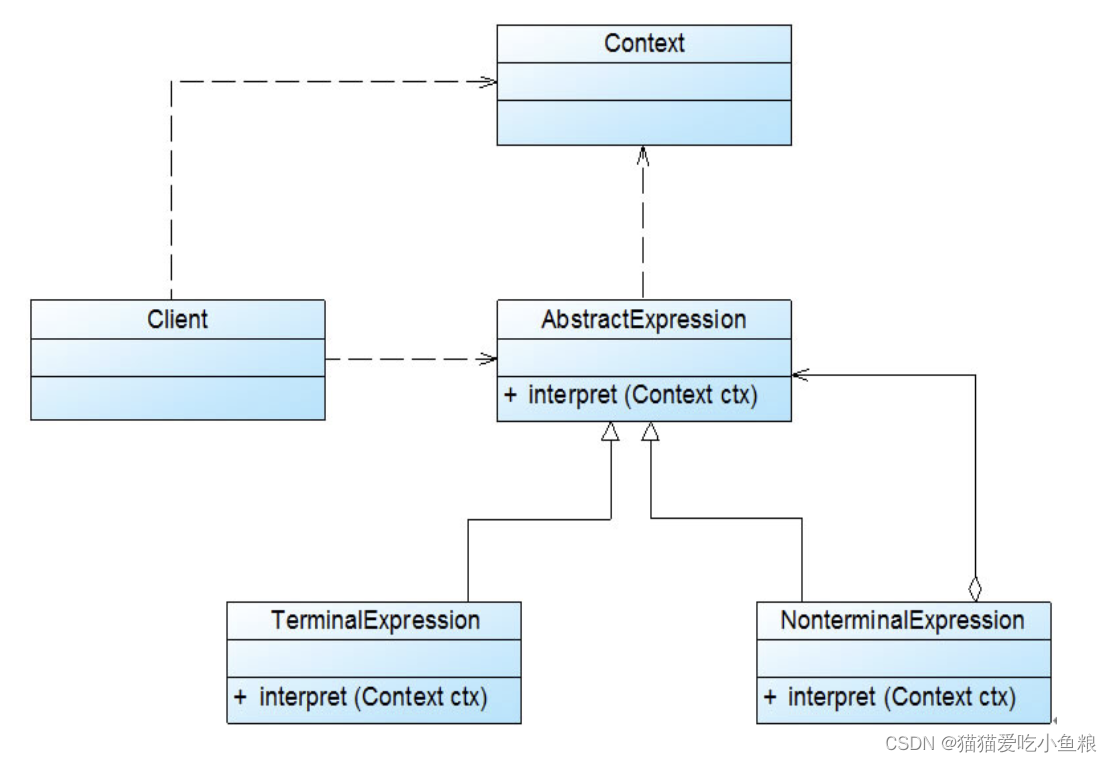
3.角色
AbstractExpression(抽象表达式):在抽象表达式中声明了抽象的解释操作,它是所有终结符表达式和非终结符表达式的公共父类。
TerminalExpression(终结符表达式):它实现了与文法中的终结符相关联的解释操作,在句子中的每一个终结符都是该类的一个实例,通常在一个解释器模式中只有少数几个终结符表达式类,它们的实例可以通过非终结符表达式组成较为复杂的句子。
NonterminalExpression(非终结符表达式):它实现了文法中非终结符的解释操作,由于在非终结符表达式中可以包含终结符表达式,也可以继续包含非终结符表达式,因此其解释操作一般通过递归的方式来完成。
Context(环境类):环境类又称为上下文类,它用于存储解释器之外的一些全局信息,通常它临时存储了需要解释的语句。
注意:
在解释器模式中,每一种终结符和非终结符都有一个具体类与之对应,正因为使用类来表示每一条文法规则,所以系统将具有较好的灵活性和可扩展性。
4.代码实现
抽象表达式类
abstract class AbstractExpression {public abstract void interpret(Context ctx);
}
终结符表达式
public class TerminalExpression extends AbstractExpression {public void interpret(Context ctx) {//终结符表达式的解释操作}
}
非终结符表达式
public class NonterminalExpression extends AbstractExpression {private AbstractExpression left;private AbstractExpression right;public NonterminalExpression(AbstractExpression left,AbstractExpression right) {this.left=left;this.right=right;}public void interpret(Context ctx) {//递归调用每一个组成部分的interpret()方法//在递归调用时指定组成部分的连接方式,即非终结符的功能}
}
环境类
public class Context {private HashMap map = new HashMap();public void assign(String key, String value) {//往环境类中设值}public String lookup(String key) {//获取存储在环境类中的值}
}
2)完整解决方案
1.解释过程-抽象语法树
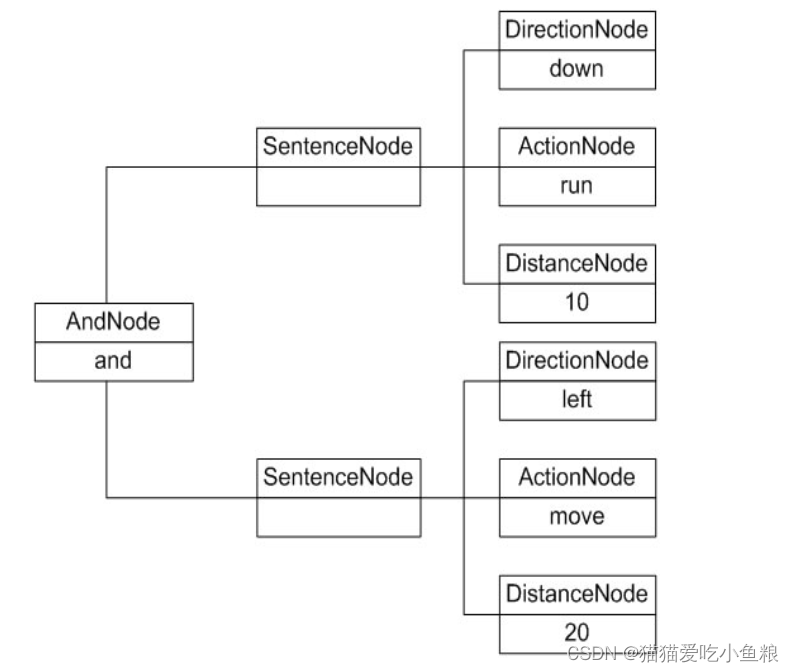
2.结构图
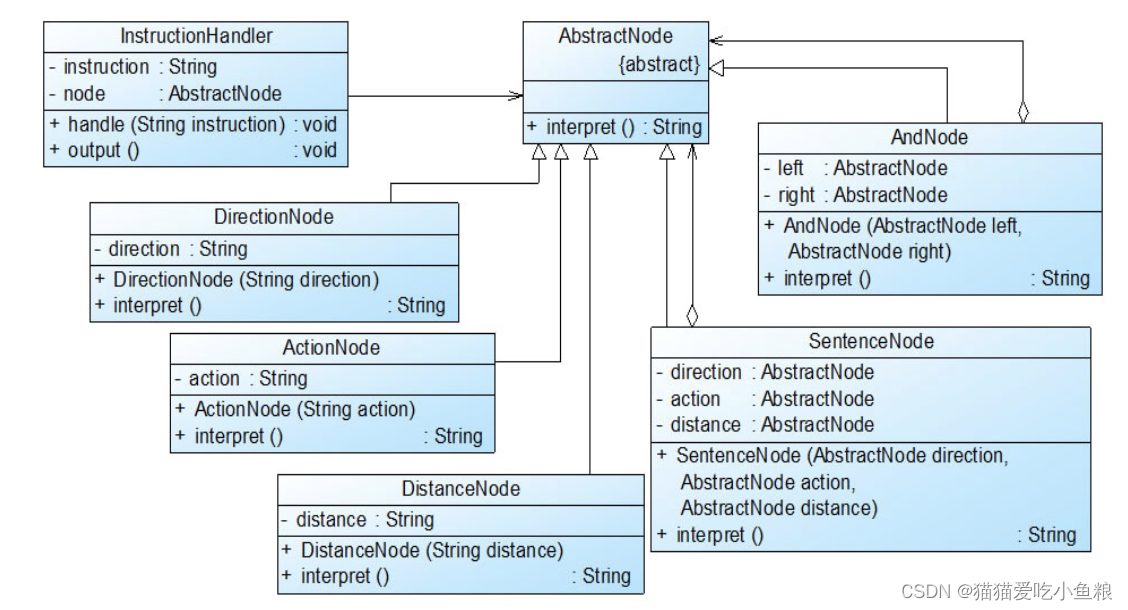
AbstractNode充当抽象表达式角色,DirectionNode、ActionNode和DistanceNode充当终结符表达式角色,AndNode和SentenceNode充当非终结符表达式角色。
3.代码实现
抽象表达式
//抽象表达式
abstract class AbstractNode {public abstract String interpret();
}
非终结符表达式
//And解释:非终结符表达式
public class AndNode extends AbstractNode {private AbstractNode left; //And的左表达式private AbstractNode right; //And的右表达式public AndNode(AbstractNode left, AbstractNode right) {this.left = left;this.right = right;}//And表达式解释操作public String interpret() {return left.interpret() + "再" + right.interpret();}
}//简单句子解释:非终结符表达式
public class SentenceNode extends AbstractNode {private AbstractNode direction;private AbstractNode action;private AbstractNode distance;public SentenceNode(AbstractNode direction, AbstractNode action, AbstractNode distance) {this.direction = direction;this.action = action;this.distance = distance;}//简单句子的解释操作public String interpret() {return direction.interpret() + action.interpret() + distance.interpret();}
}
终结符表达式
//方向解释:终结符表达式
public class DirectionNode extends AbstractNode {private String direction;public DirectionNode(String direction) {this.direction = direction;}//方向表达式的解释操作public String interpret() {if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("up")) {return "向上";} else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("down")) {return "向下";} else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("left")) {return "向左";} else if (direction.equalsIgnoreCase("right")) {return "向右";} else {return "无效指令";}}
}//动作解释:终结符表达式
public class ActionNode extends AbstractNode {private String action;public ActionNode(String action) {this.action = action;}//动作(移动方式)表达式的解释操作public String interpret() {if (action.equalsIgnoreCase("move")) {return "移动";} else if (action.equalsIgnoreCase("run")) {return "快速移动";} else {return "无效指令";}}
}//距离解释:终结符表达式
public class DistanceNode extends AbstractNode {private String distance;public DistanceNode(String distance) {this.distance = distance;}//距离表达式的解释操作public String interpret() {return this.distance;}
}
工具类InstructionHandler用于对输入指令进行处理,将输入指令分割为字符串数组,将第1个、第2个和第3个单词组合成一个句子,并存入栈中;如果发现有单词“and”,则将“and”后的第1个、第2个和第3个单词组合成一个新的句子作为“and”的右表达式,并从栈中取出原先所存句子作为左表达式,然后组合成一个And节点存入栈中,依此类推,直到整个指令解析结束。
import java.util.Stack;//指令处理类:工具类
public class InstructionHandler {private AbstractNode node;public void handle(String instruction) {AbstractNode left = null, right = null;AbstractNode direction = null, action = null, distance = null;//声明一个栈对象用于存储抽象语法树Stack stack = new Stack();//以空格分隔指令字符串String[] words = instruction.split(" ");for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {if (words[i].equalsIgnoreCase("and")) {//弹出栈顶表达式作为左表达式left = (AbstractNode) stack.pop();String word1 = words[++i];direction = new DirectionNode(word1);String word2 = words[++i];action = new ActionNode(word2);String word3 = words[++i];distance = new DistanceNode(word3);right = new SentenceNode(direction, action, distance); //右表达式stack.push(new AndNode(left, right)); //将新表达式压入栈中} else {//如果是从头开始进行解释,则将前三个单词组成一个简单句子SentenceNode并将该句子压入栈中String word1 = words[i];direction = new DirectionNode(word1);String word2 = words[++i];action = new ActionNode(word2);String word3 = words[++i];distance = new DistanceNode(word3);left = new SentenceNode(direction, action, distance);//将新表达式压入栈中stack.push(left);}}this.node = (AbstractNode) stack.pop(); //将全部表达式从栈中弹出}public String output() {return node.interpret();}
}
客户端类
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {String instruction = "up move 5 and down run 10 and left move 5";InstructionHandler handler = new InstructionHandler();handler.handle(instruction);String outString;outString = handler.output();System.out.println(outString);}
}