一、链表的常见技巧总结
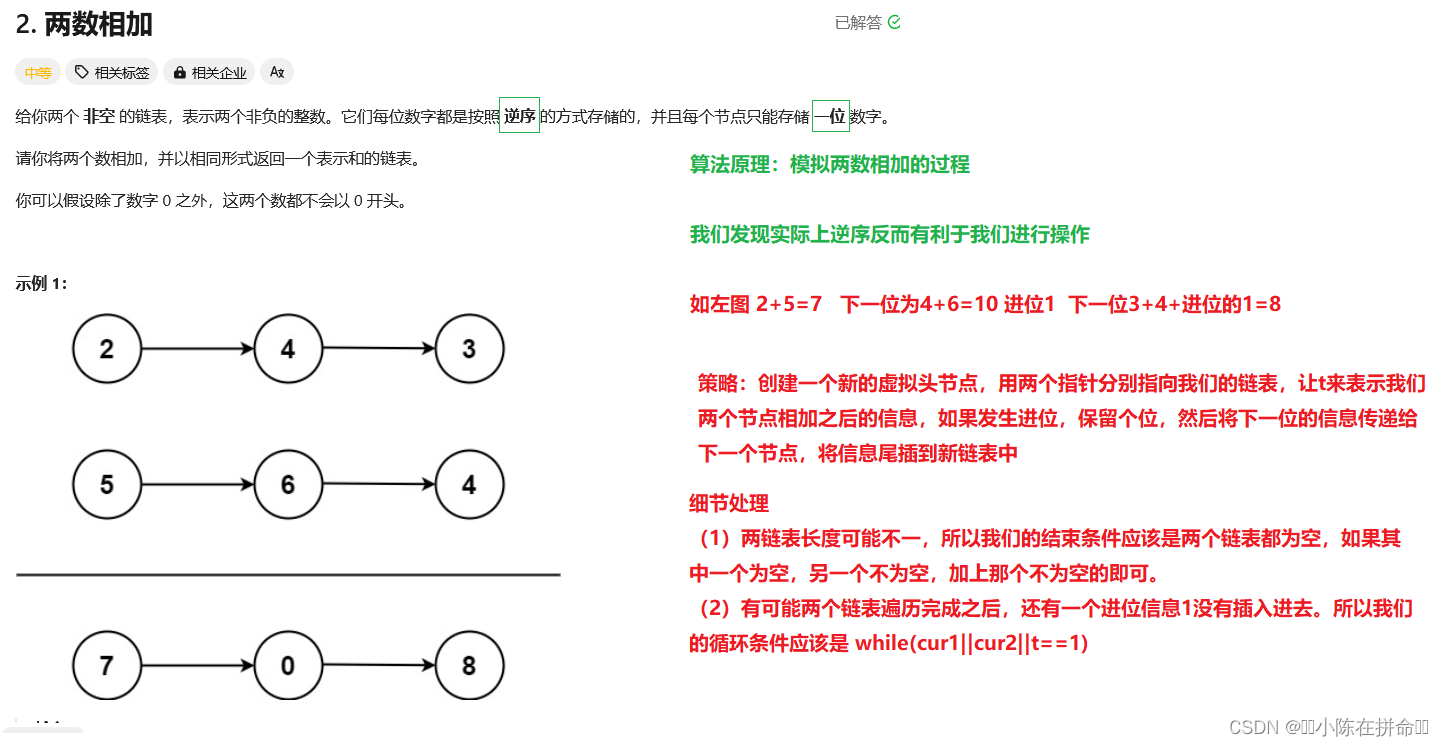
 二、两数相加
二、两数相加
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {//利用t来存进位信息int t=0;ListNode*newhead=new ListNode(0);//创建一个哨兵节点,方便尾插ListNode*ptail=newhead;//ptail方便尾插ListNode* cur1=l1,*cur2=l2;while(cur1||cur2||t==1)//t==1防止后面有进位没加上{if(cur1) {t+=cur1->val; cur1=cur1->next;}if(cur2) {t+=cur2->val;cur2=cur2->next;}ptail->next=new ListNode(t%10);ptail=ptail->next;t/=10;}ListNode*ret=newhead->next;delete newhead;return ret;}
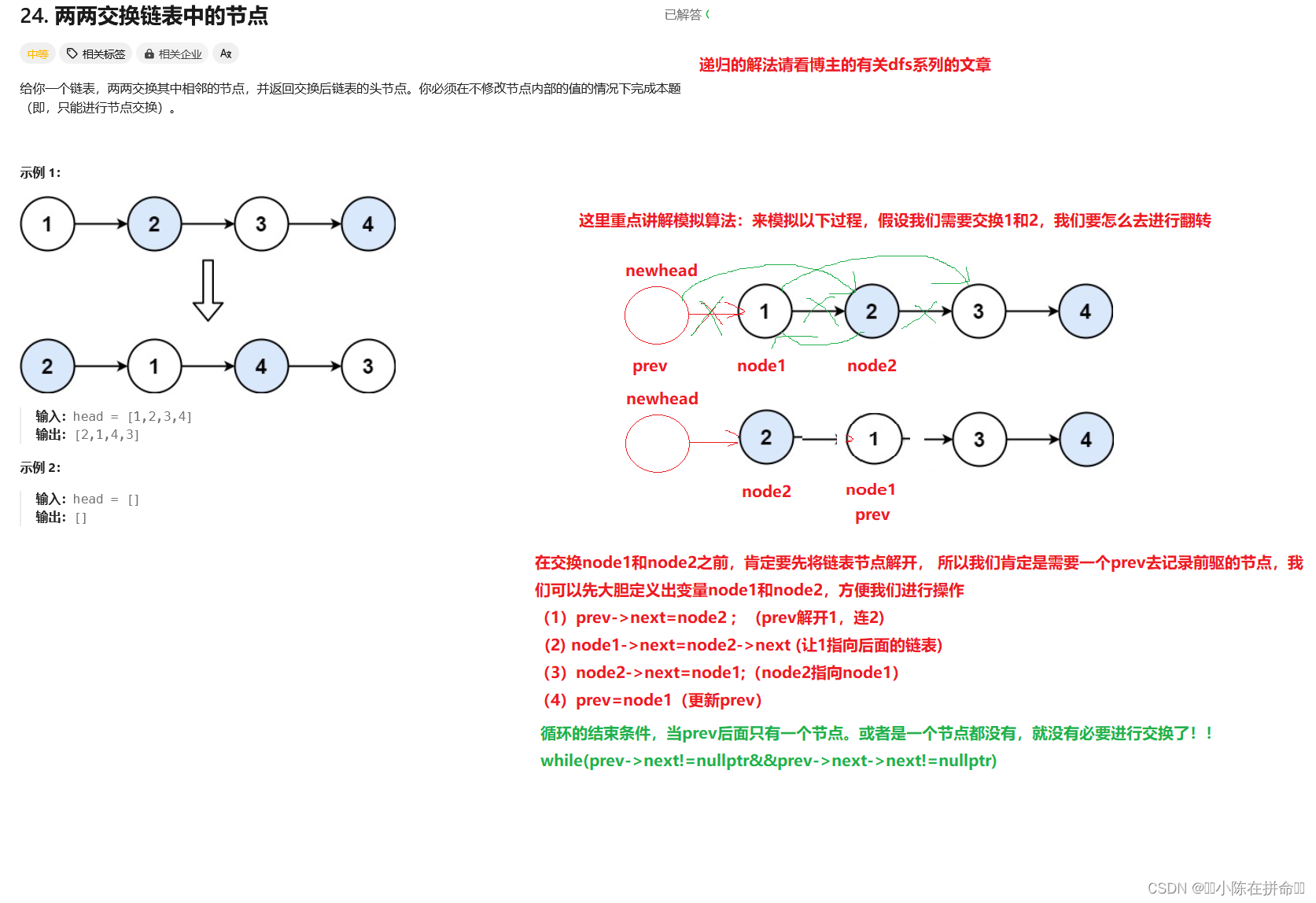
};三、两两交换链表中的节点
四、重排链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:void reorderList(ListNode* head) {//方法1,利用一个数据结构将每个节点存起来,通过下标去访问//方法2, (1)利用快慢指针,找中点 (2) 拆开链表 从中点开始往后翻转 (3)进行合并成新链表if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr||head->next->next==nullptr) return;ListNode*mid=midnode(head);//找到中间节点//断开链表ListNode*l1=head;ListNode*l2=mid->next;mid->next=nullptr;//然后反转2l2=reverseList(l2);//合并链表mergeList(l1,l2);}ListNode*midnode(ListNode* head){ListNode*fast=head;ListNode*slow=head;while(fast->next!=nullptr&&fast->next->next!=nullptr)//确保后面两步能走{fast=fast->next->next;slow=slow->next;}return slow;//此时慢指针指向的就是最小的节点}ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head){ListNode*p1=nullptr;ListNode*p2=head;ListNode*p3=head->next;//记录下一个要遍历的点while(p2){p2->next=p1;p1=p2;p2=p3;if(p3) p3=p3->next ;}return p1;}void mergeList(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){ListNode* temp1,*temp2;while(l1!=nullptr&&l2!=nullptr){temp1=l1->next;temp2=l2->next;l1->next=l2;l1=temp1;//回到原链表0l2->next=l1;l2=temp2;//回到原链表}}
};五、合并k个升序链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

 优先级队列:
优先级队列:
class Solution {
public://建小堆需要greaterstruct greater //构造一个仿函数{bool operator()(const ListNode*l1,const ListNode*l2){return l1->val>l2->val;}};ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {//建立优先级队列(小堆),每次将堆顶元素插入进去,然后再删除堆顶元素,插入下个位置priority_queue<ListNode*,vector<ListNode*>,greater> heap;//建立一个小堆//入堆for(auto l:lists) if(l) heap.push(l);//因为有可能里面存的是一个空链表//开始合并k个有序链表ListNode*newnode=new ListNode(0);ListNode*ptail=newnode;//用于帮助我们进行尾插while(!heap.empty()){//进行尾插ListNode*it=heap.top();ptail->next=it;ptail=it;//去到下一个位置准备尾插//删除堆顶元素并将该节点的下一个节点入堆 ,为空就不入heap.pop();if(it->next) heap.push(it->next);}//此时全部的元素都插入完成了,返回最终的链表ListNode*ret=newnode->next;delete newnode;return ret;//时间复杂度o(n*k*logk)}
};分治思想:
//策略,利用递归解决问题,结合归并排序,合并两个有序链表 (利用分治思想)
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists){int n=lists.size();return merge(lists,0,n-1);//让merge帮助我们完成整个区间的归并}ListNode* merge(vector<ListNode*>& lists,int left,int right){//首先,处理边界情况,如果不存在链表或者是只有一个链表,此时没有必要进行下去if(left>right) return nullptr;if(left==right) return lists[left];//让merge帮助我们归并左右区间int mid=(left+right)>>1;ListNode*l1=merge(lists,left,mid);ListNode*l2=merge(lists,mid+1,right);//然后开始进行合并两个有序链表return mergetwolist(l1,l2);}ListNode*mergetwolist(ListNode*l1,ListNode*l2){//考虑两个链表为空的情况if(l1==nullptr) return l2;if(l2==nullptr) return l1;//此时两个链表必然不为空,开始进行合并ListNode*newhead=new ListNode(0);//哨兵节点ListNode*ptail=newhead;//帮助我们进行尾插ListNode*cur1=l1,*cur2=l2;//两个指针分别指向两个链表while(cur1&&cur2)//当两个都不为空的时候{if(cur1->val<cur2->val) {//此时要尾插cur1ptail->next=cur1;ptail=cur1;//更新到下一个位置cur1=cur1->next;//继续去下一个节点遍历}else{ptail->next=cur2;ptail=cur2;//更新到下一个位置cur2=cur2->next;//继续去下一个节点遍历}}//可能有的链表没有遍历完if(cur1) ptail->next=cur1;if(cur2) ptail->next=cur2;//此时返回到目标的位置ListNode*ret=newhead->next;delete newhead;return ret;}
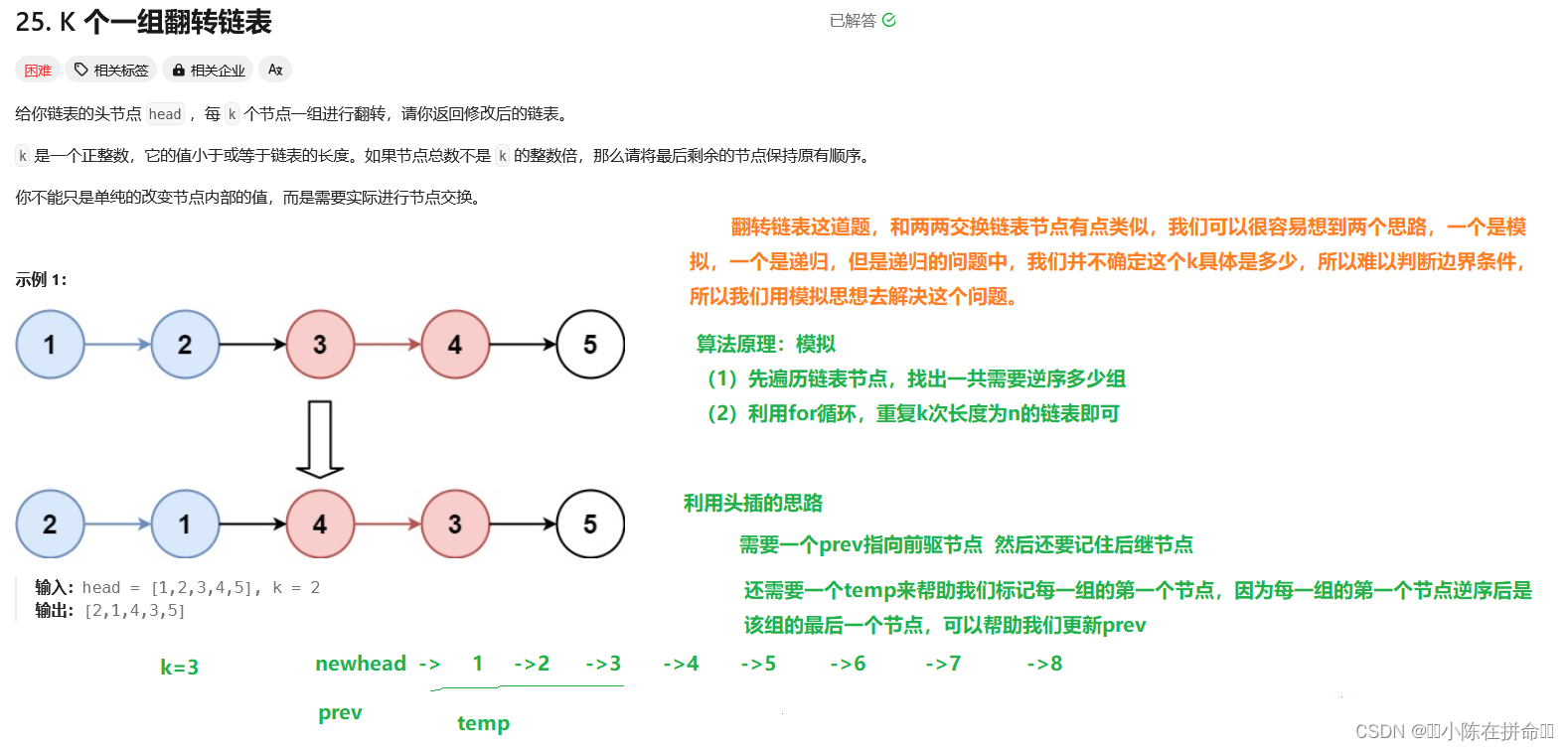
};六、k个一组翻转链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {int n=0;//记录总数ListNode*cur=head;while(cur)//统计节点个数,并推测有多少组{cur=cur->next;++n;}n/=k;//看看一共需要几组ListNode*newhead=new ListNode(0);//创建一个哨兵节点ListNode*prev=newhead;//记住被头插的点cur=head;//从head开始进行头插//翻转n组,每组翻转k个for(int i=0;i<n;++i){ListNode*temp=cur;for(int j=0;j<k;++j){//用头插的逻辑ListNode*next=cur->next;;cur->next=prev->next;prev->next=cur;cur=next;//继续去链表的下一个点}prev=temp;//更新prev}//循环结束后,将后面的不需要逆序的部分接上prev->next=cur;ListNode*ret=newhead->next;delete newhead;return ret;}
};七、旋转链表
. - 力扣(LeetCode)

思路1:截断再连接
class Solution {
public:ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {//让链表成环(闭合成环),然后在指定位置断开if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr||k==0) return head;int count=1;//数节点数量ListNode*ptail=head;while(ptail->next!=nullptr) //找到尾节点,并统计节点数{ptail=ptail->next;++count;}int add=count-k%count;//看看具体是翻转几次if(add==count) return head;//避免不需要翻转的情况//截断重连ListNode*cur=head;while(--add) cur=cur->next; //找到被截断的位置ListNode*ret=cur->next;cur->next=nullptr;//断开cur=ret;while(cur->next!=nullptr) cur=cur->next;//找到尾节点cur->next=head;//连接return ret; }
};思路2:链表成环,指定位置截断
class Solution {
public:ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {//让链表成环,然后在指定位置断开if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr||k==0) return head;int count=1;//数节点数量ListNode*ptail=head;while(ptail->next!=nullptr) //找到尾节点,并统计节点数{ptail=ptail->next;++count;}int add=count-k%count;//看看具体是翻转几次ptail->next=head;//头尾相连while(add--) ptail=ptail->next;ListNode*ret=ptail->next;ptail->next=nullptr;return ret; }
};思路3:逆置前n-k个,再逆置后k个,最后整体逆置
class Solution {
public:ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr||k==0) return head;//先逆置前n-k个,再逆置后k个,再整体逆置int count=1;//数节点数量ListNode*ptail=head;while(ptail->next!=nullptr) //找到尾节点,并统计节点数{ptail=ptail->next;++count;}int add=count-k%count;//看看具体是翻转几次if(add==count) return head;//开始找前n-k个节点ListNode*cur=head;while(--add) cur=cur->next;ListNode*l2=cur->next;//第二个链表cur->next=nullptr;//断开ListNode* l1=reverse(head);l2=reverse(l2);head->next=ptail;//连接起来return reverse(l1);//然后整体翻转}ListNode*reverse(ListNode* head){ //只有一个节点,没什么好逆置的if(head==nullptr||head->next==nullptr) return head;ListNode*p1=nullptr,*p2=head,*p3=head->next;while(p2){p2->next=p1;p1=p2;p2=p3;if(p3) p3=p3->next;}return p1;}
};