MD5值常被用于验证数据的完整性,嵌入式开发时经常用到。md5sum命令可以求MD5码,下面介绍如何用C语言实现MD5功能。
一、求字符串MD5值
1、md5sum命令
$ echo -n "12345678" | md5sum //获取"12345678"字符串的md5值
结果:25d55ad283aa400af464c76d713c07ad
![]()
2、C语言实现
- md5.h文件介绍
先看一下md5.h文件,定义了MDString() 、MDFile() 这2个函数计算字符串和文件的MD5值。
下载链接:https://download.csdn.net/download/hinewcc/89165146
#ifndef _MD5_H_
#define _MD5_H_#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>#define MD 5/* PROTOTYPES should be set to one if and only if the compiler supports
function argument prototyping.
The following makes PROTOTYPES default to 0 if it has not already
been defined with C compiler flags.
*/
#ifndef PROTOTYPES
#define PROTOTYPES 0
#endif/* POINTER defines a generic pointer type */
typedef unsigned char *POINTER;/* UINT2 defines a two byte word */
typedef unsigned short int UINT2;/* UINT4 defines a four byte word */
//typedef unsigned long int UINT4;
typedef unsigned int UINT4;/* PROTO_LIST is defined depending on how PROTOTYPES is defined above.
If using PROTOTYPES, then PROTO_LIST returns the list, otherwise it
returns an empty list.
*/
#if PROTOTYPES
#define PROTO_LIST(list) list
#else
#define PROTO_LIST(list) ()
#endif/* Length of test block, number of test blocks.
*/
#define TEST_BLOCK_LEN 1000
#define TEST_BLOCK_COUNT 1000/* Constants for MD5Transform routine.
*/
#define S11 7
#define S12 12
#define S13 17
#define S14 22
#define S21 5
#define S22 9
#define S23 14
#define S24 20
#define S31 4
#define S32 11
#define S33 16
#define S34 23
#define S41 6
#define S42 10
#define S43 15
#define S44 21char* MDString PROTO_LIST ((char *));
char* MDFile PROTO_LIST ((char *));
char* hmac_md5(char* text, char* key);typedef struct {
UINT4 state[4]; /* state (ABCD) */
UINT4 count[2]; /* number of bits, modulo 2^64 (lsb first) */
unsigned char buffer[64]; /* input buffer */
} MD5_CTX;/*void MD5Init PROTO_LIST ((MD5_CTX *));
void MD5Update PROTO_LIST
((MD5_CTX *, unsigned char *, unsigned int));
void MD5Final PROTO_LIST ((unsigned char [16], MD5_CT X *));static void MD5Transform PROTO_LIST ((UINT4 [4], unsigned char [64]));
static void Encode PROTO_LIST
((unsigned char *, UINT4 *, unsigned int));
static void Decode PROTO_LIST
((UINT4 *, unsigned char *, unsigned int));
static void MD5_memcpy PROTO_LIST ((POINTER, POINTER, unsigned int));
static void MD5_memset PROTO_LIST ((POINTER, int, unsigned int));
*/
static unsigned char PADDING[64] = {
0x80, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
};/* F, G, H and I are basic MD5 functions.
*/
#define F(x, y, z) (((x) & (y)) | ((~x) & (z)))
#define G(x, y, z) (((x) & (z)) | ((y) & (~z)))
#define H(x, y, z) ((x) ^ (y) ^ (z))
#define I(x, y, z) ((y) ^ ((x) | (~z)))/* ROTATE_LEFT rotates x left n bits.
*/
#define ROTATE_LEFT(x, n) (((x) << (n)) | ((x) >> (32-(n))))/* FF, GG, HH, and II transformations for rounds 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Rotation is separate from addition to prevent recomputation.
*/
#define FF(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) { \
(a) += F((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); \
(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); \
(a) += (b); \
}
#define GG(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) { \
(a) += G ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); \
(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); \
(a) += (b); \
}
#define HH(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) { \
(a) += H ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); \
(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); \
(a) += (b); \
}
#define II(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) { \
(a) += I ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); \
(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); \
(a) += (b); \
}
void MD5Init (MD5_CTX *context);
void MD5Update(MD5_CTX *context, unsigned char *input,unsigned int inputLen);void MD5Final (unsigned char digest[16], MD5_CTX *context);
static void MD5Transform (UINT4 [4], unsigned char [64]) ;
static void Encode(unsigned char *, UINT4 *, unsigned int);
static void Decode (UINT4 *, unsigned char *, unsigned int);
static void MD5_memcpy(POINTER, POINTER, unsigned int);
static void MD5_memset(POINTER, int, unsigned int);/* MD5 initialization. Begins an MD5 operation, writing a new context.
*/
void MD5Init (MD5_CTX *context)
/* context */
{context->count[0] = context->count[1] = 0;
/* Load magic initialization constants.
*/context->state[0] = 0x67452301;context->state[1] = 0xefcdab89;context->state[2] = 0x98badcfe;context->state[3] = 0x10325476;
}/* MD5 block update operation. Continues an MD5 message-digest
operation, processing another message block, and updating the
context.
*/
void MD5Update (MD5_CTX *context, unsigned char *input,unsigned int inputLen )
/* context */
/* input block */
/* length of input block */
{unsigned int i, index, partLen;/* Compute number of bytes mod 64 */index = (unsigned int)((context->count[0] >> 3) & 0x3F);/* Update number of bits */if ((context->count[0] += ((UINT4)inputLen << 3)) < ((UINT4)inputLen << 3))context->count[1]++;context->count[1] += ((UINT4)inputLen >> 29);partLen = 64 - index;/* Transform as many times as possible.
*/if (inputLen >= partLen) {MD5_memcpy((POINTER)&context->buffer[index], (POINTER)input, partLen);MD5Transform (context->state, context->buffer);for (i = partLen; i + 63 < inputLen; i += 64)MD5Transform (context->state, &input[i]);index = 0;}elsei = 0;/* Buffer remaining input */MD5_memcpy((POINTER)&context->buffer[index], (POINTER)&input[i],inputLen-i);
}/* MD5 finalization. Ends an MD5 message-digest operation, writing the
the message digest and zeroizing the context.
*/
void MD5Final (unsigned char digest[16], MD5_CTX *context)
/* message digest */
/* context */
{unsigned char bits[8];unsigned int index, padLen;/* Save number of bits */Encode (bits, context->count, 8);/* Pad out to 56 mod 64.
*/index = (unsigned int)((context->count[0] >> 3) & 0x3f);padLen = (index < 56) ? (56 - index) : (120 - index);MD5Update (context,(unsigned char*) PADDING, padLen);/* Append length (before padding) */MD5Update (context, bits, 8);
/* Store state in digest */Encode (digest, context->state, 16);/* Zeroize sensitive information.
*/MD5_memset ((POINTER)context, 0, sizeof (*context));
}/* MD5 basic transformation. Transforms state based on block.
*/
static void MD5Transform (UINT4 state[4],unsigned char block[64]){UINT4 a = state[0], b = state[1], c = state[2], d = state[3], x[16];Decode (x, block, 64);/* Round 1 */FF (a, b, c, d, x[ 0], S11, 0xd76aa478); /* 1 */FF (d, a, b, c, x[ 1], S12, 0xe8c7b756); /* 2 */FF (c, d, a, b, x[ 2], S13, 0x242070db); /* 3 */FF (b, c, d, a, x[ 3], S14, 0xc1bdceee); /* 4 */FF (a, b, c, d, x[ 4], S11, 0xf57c0faf); /* 5 */FF (d, a, b, c, x[ 5], S12, 0x4787c62a); /* 6 */FF (c, d, a, b, x[ 6], S13, 0xa8304613); /* 7 */FF (b, c, d, a, x[ 7], S14, 0xfd469501); /* 8 */FF (a, b, c, d, x[ 8], S11, 0x698098d8); /* 9 */FF (d, a, b, c, x[ 9], S12, 0x8b44f7af); /* 10 */FF (c, d, a, b, x[10], S13, 0xffff5bb1); /* 11 */FF (b, c, d, a, x[11], S14, 0x895cd7be); /* 12 */FF (a, b, c, d, x[12], S11, 0x6b901122); /* 13 */FF (d, a, b, c, x[13], S12, 0xfd987193); /* 14 */FF (c, d, a, b, x[14], S13, 0xa679438e); /* 15 */FF (b, c, d, a, x[15], S14, 0x49b40821); /* 16 *//* Round 2 */GG (a, b, c, d, x[ 1], S21, 0xf61e2562); /* 17 */GG (d, a, b, c, x[ 6], S22, 0xc040b340); /* 18 */GG (c, d, a, b, x[11], S23, 0x265e5a51); /* 19 */GG (b, c, d, a, x[ 0], S24, 0xe9b6c7aa); /* 20 */GG (a, b, c, d, x[ 5], S21, 0xd62f105d); /* 21 */GG (d, a, b, c, x[10], S22, 0x2441453); /* 22 */GG (c, d, a, b, x[15], S23, 0xd8a1e681); /* 23 */GG (b, c, d, a, x[ 4], S24, 0xe7d3fbc8); /* 24 */GG (a, b, c, d, x[ 9], S21, 0x21e1cde6); /* 25 */GG (d, a, b, c, x[14], S22, 0xc33707d6); /* 26 */GG (c, d, a, b, x[ 3], S23, 0xf4d50d87); /* 27 */GG (b, c, d, a, x[ 8], S24, 0x455a14ed); /* 28 */GG (a, b, c, d, x[13], S21, 0xa9e3e905); /* 29 */GG (d, a, b, c, x[ 2], S22, 0xfcefa3f8); /* 30 */GG (c, d, a, b, x[ 7], S23, 0x676f02d9); /* 31 */GG (b, c, d, a, x[12], S24, 0x8d2a4c8a); /* 32 *//* Round 3 */HH (a, b, c, d, x[ 5], S31, 0xfffa3942); /* 33 */HH (d, a, b, c, x[ 8], S32, 0x8771f681); /* 34 */HH (c, d, a, b, x[11], S33, 0x6d9d6122); /* 35 */HH (b, c, d, a, x[14], S34, 0xfde5380c); /* 36 */HH (a, b, c, d, x[ 1], S31, 0xa4beea44); /* 37 */HH (d, a, b, c, x[ 4], S32, 0x4bdecfa9); /* 38 */HH (c, d, a, b, x[ 7], S33, 0xf6bb4b60); /* 39 */HH (b, c, d, a, x[10], S34, 0xbebfbc70); /* 40 */HH (a, b, c, d, x[13], S31, 0x289b7ec6); /* 41 */HH (d, a, b, c, x[ 0], S32, 0xeaa127fa); /* 42 */HH (c, d, a, b, x[ 3], S33, 0xd4ef3085); /* 43 */HH (b, c, d, a, x[ 6], S34, 0x4881d05); /* 44 */HH (a, b, c, d, x[ 9], S31, 0xd9d4d039); /* 45 */HH (d, a, b, c, x[12], S32, 0xe6db99e5); /* 46 */HH (c, d, a, b, x[15], S33, 0x1fa27cf8); /* 47 */HH (b, c, d, a, x[ 2], S34, 0xc4ac5665); /* 48 *//* Round 4 */II (a, b, c, d, x[ 0], S41, 0xf4292244); /* 49 */II (d, a, b, c, x[ 7], S42, 0x432aff97); /* 50 */II (c, d, a, b, x[14], S43, 0xab9423a7); /* 51 */II (b, c, d, a, x[ 5], S44, 0xfc93a039); /* 52 */II (a, b, c, d, x[12], S41, 0x655b59c3); /* 53 */II (d, a, b, c, x[ 3], S42, 0x8f0ccc92); /* 54 */II (c, d, a, b, x[10], S43, 0xffeff47d); /* 55 */II (b, c, d, a, x[ 1], S44, 0x85845dd1); /* 56 */II (a, b, c, d, x[ 8], S41, 0x6fa87e4f); /* 57 */II (d, a, b, c, x[15], S42, 0xfe2ce6e0); /* 58 */II (c, d, a, b, x[ 6], S43, 0xa3014314); /* 59 */II (b, c, d, a, x[13], S44, 0x4e0811a1); /* 60 */II (a, b, c, d, x[ 4], S41, 0xf7537e82); /* 61 */II (d, a, b, c, x[11], S42, 0xbd3af235); /* 62 */II (c, d, a, b, x[ 2], S43, 0x2ad7d2bb); /* 63 */II (b, c, d, a, x[ 9], S44, 0xeb86d391); /* 64 */state[0] += a;state[1] += b;state[2] += c;state[3] += d;/* Zeroize sensitive information.
*/MD5_memset ((POINTER)x, 0, sizeof (x));
}/* Encodes input (UINT4) into output (unsigned char). Assumes len is
a multiple of 4.
*/
static void Encode (unsigned char *output, UINT4 *input,unsigned int len){unsigned int i, j;for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) {output[j] = (unsigned char)(input[i] & 0xff);output[j+1] = (unsigned char)((input[i] >> 8) & 0xff);output[j+2] = (unsigned char)((input[i] >> 16) & 0xff);output[j+3] = (unsigned char)((input[i] >> 24) & 0xff);}
}/* Decodes input (unsigned char) into output (UINT4). Assumes len is
a multiple of 4.
*/
static void Decode (UINT4 *output,unsigned char *input,unsigned int len){unsigned int i, j;for (i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4)output[i] = ((UINT4)input[j]) | (((UINT4)input[j+1]) << 8) | (((UINT4)input[j+2]) << 16) | (((UINT4)input[j+3]) << 24);
}/* Note: Replace "for loop" with standard memcpy if possible.
*/
static void MD5_memcpy (POINTER output,POINTER input, unsigned int len){unsigned int i;for (i = 0; i < len; i++)output[i] = input[i];
}/* Note: Replace "for loop" with standard memset if possible.
*/
static void MD5_memset (POINTER output, int value, unsigned int len){unsigned int i;for (i = 0; i < len; i++)((char *)output)[i] = (char)value;
}/* Digests a string and prints the result.
*/
char* MDString (char *string){MD5_CTX context;unsigned char digest[16];char output1[32];static char output[33]={""};unsigned int len = strlen (string);int i;MD5Init (&context);MD5Update (&context, (unsigned char*)string, len);MD5Final (digest, &context);for (i = 0; i < 16; i++){sprintf(&(output1[2*i]),"%02x",(unsigned char)digest[i]);sprintf(&(output1[2*i+1]),"%02x",(unsigned char)(digest[i]<<4));}for(i=0;i<32;i++)output[i]=output1[i];return output;
}/* Digests a file and prints the result.
*/
char* MDFile (char *filename){static char output[33]={""};FILE *file;MD5_CTX context;int len;unsigned char buffer[1024], digest[16];int i;char output1[32];if ((file = fopen (filename, "rb")) == NULL){printf ("%s can't be openedn", filename);return 0;} else {MD5Init (&context);while ((len = fread (buffer, 1, 1024, file)))MD5Update (&context, buffer, len);MD5Final (digest, &context);fclose (file);for (i = 0; i < 16; i++){sprintf(&(output1[2*i]),"%02x",(unsigned char)digest[i]);sprintf(&(output1[2*i+1]),"%02x",(unsigned char)(digest[i]<<4));}for(i=0;i<32;i++)output[i]=output1[i];return output;}
}char* hmac_md5(char* text,char* key){char digest[16];char output1[32];static char output[33]={""};MD5_CTX context;unsigned char k_ipad[65]; /* inner padding -
* key XORd with ipad
*/unsigned char k_opad[65]; /* outer padding -
* key XORd with opad
*/unsigned char tk[16];int i;int text_len = strlen (text);int key_len=strlen(key);
/* if key is longer than 64 bytes reset it to key=MD5(key) */if (key_len > 64) {MD5_CTX tctx;MD5Init(&tctx);MD5Update(&tctx,(unsigned char*) key, key_len);MD5Final(tk, &tctx);key = (char*)tk;key_len = 16;}/*
* the HMAC_MD5 transform looks like:
*
* MD5(K XOR opad, MD5(K XOR ipad, text))
*
* where K is an n byte key
* ipad is the byte 0x36 repeated 64 times
* opad is the byte 0x5c repeated 64 times
* and text is the data being protected
*//* start out by storing key in pads *//*bzero( k_ipad, sizeof k_ipad);
bzero( k_opad, sizeof k_opad);
*/for(i=0;i<65;i++)k_ipad[i]=(unsigned char)0;for(i=0;i<65;i++)k_opad[i]=(unsigned char)0;/*bcopy( key, k_ipad, key_len);
bcopy( key, k_opad, key_len);
*/for(i=0;i<key_len;i++){k_ipad[i]=(unsigned char)key[i];k_opad[i]=(unsigned char)key[i];}/* XOR key with ipad and opad values */for (i=0; i<64; i++) {k_ipad[i] ^= 0x36;k_opad[i] ^= 0x5c;}
/*
* perform inner MD5
*/MD5Init(&context); /* init context for 1st
* pass */MD5Update(&context, k_ipad, 64); /* start with inner pad */MD5Update(&context, (unsigned char*)text, text_len); /* then text of datagram*/MD5Final((unsigned char*)digest, &context); /* finish up 1st pass */
/*
* perform outer MD5
*/MD5Init(&context); /* init context for 2nd
* pass */MD5Update(&context, k_opad, 64); /* start with outer pad */MD5Update(&context,(unsigned char*) digest, 16); /* then results of 1st
* hash */MD5Final((unsigned char*)digest, &context); /* finish up 2nd pass */for (i = 0; i < 16; i++){sprintf(&(output1[2*i]),"%02x",(unsigned char)digest[i]);sprintf(&(output1[2*i+1]),"%02x",(unsigned char)(digest[i]<<4));}for(i=0;i<32;i++)output[i]=output1[i];return output;
}#endif
main.c需包含md5.h头文件,调用 MDString() 即可实现求字符串MD5码功能
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "md5.h" //包含MD5头文件#define DEBUG_PRINTF printfint main(int argc, char **argv)
{int i;char* pMd5Value = NULL;if (argc != 2) {return -1;}printf("argv[1]: %s\n", argv[1]);pMd5Value = MDString(argv[1]);printf("%s\n", pMd5Value);return 0;
}
- 编译
$ gcc -o string_md5 main.c //编译生成可执行程序 string_md5
- 测试结果
$ ./string_md5 12345678 //验证
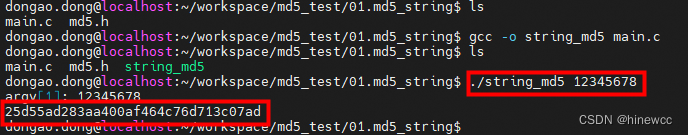
可以看到,结果与md5sum命令相同,也是 25d55ad283aa400af464c76d713c07ad
二、求文件MD5值
先准备一个文件,内容和文件名无所谓,如:file.txt
1、md5sum命令
$ md5sum file.txt //获取file.txt文件的MD5值
结果:d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
![]()
2、C语言实现
main.c需包含md5.h头文件,调用 MDFile() 求文件的MD5值。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "md5.h" //包含md5.h头文件int main(int argc, char **argv)
{int i;struct stat st;char* pMd5Value = NULL;if (argc != 2) {return -1;}printf("argv[1]: %s\n", argv[1]);if (stat(argv[1], &st) < 0) {printf("%s not exist\n", argv[1]);return -1;}pMd5Value = MDFile(argv[1]); //计算文件的MD5printf("%s\n", pMd5Value);return 0;
}
- 编译
$ gcc -o file_md5 main.c
- 测试结果
$ ./file_md5 file.txt
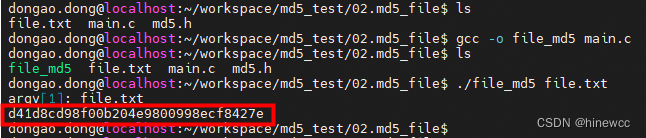
可以看到,结果与md5sum命令相同,也是 d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e




![[集群聊天项目] muduo网络库](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/394dc412c1474f5ba7483e781a92c18f.png#pic_center)