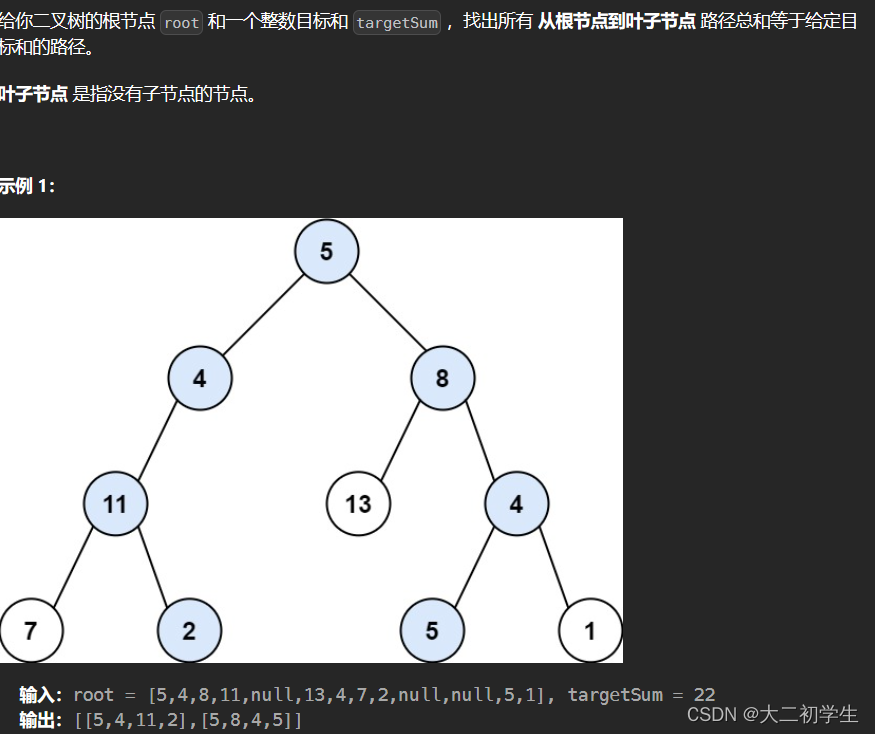
文章目录
- 一、NIO介绍
- 二、NIO原理
- 三、Buffer
- 1、Buffer原理介绍
- 2、Buffer实现类
- 3、示例
- 4、NIO和BIO的比较
- 四、Channel
- 1、介绍
- 2、FileChannel介绍
- 3、Buffer和Channel的注意事项
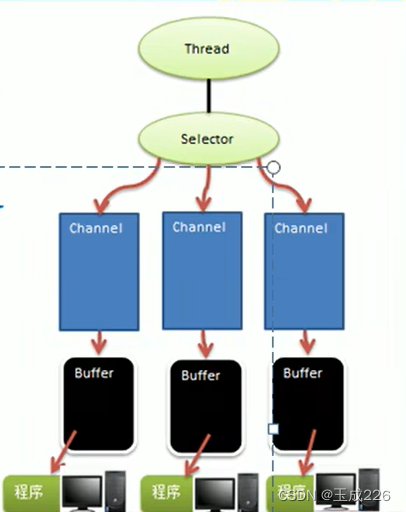
- 五、Selector
- 六、Selector、Channel和Buffer关系
一、NIO介绍
NIO介绍
二、NIO原理
-
NIO有三大核心部分: 通道(Channel)、缓冲区(Buffer)和选择器(Selector)。Channel是对原I/O体系中流的模拟,可以通过Channel完成数据的读/写操作;Buffer则用于存储数据,它是NIO与普通I/O的主要区别之一;而Selector则用于监听多个Channel的状态,以实现多路复用。
-
在NIO的工作过程中,数据首先从Channel读取到Buffer中,或者从Buffer写入到Channel中。这个过程是异步的,因此不会阻塞线程。同时,Selector会不断地轮询注册的Channel,查看是否有已经就绪的I/O操作(例如读或写),如果有,就通知相应的线程进行处理。
-
Java NIO的非阻塞模式,是一个线程从某通道发送请求或者读取数据,但是它仅能得到目前可用的数据,如果目前没有数据可用时,就什么都不会获取,而不是保持线程阻塞,所以知道数据变的可以读取之前,该线程可以继续做其他的事情。非阻塞写也是如此,一个线程请求写入一些数据到某通道,但不需要等待它完全写入,这个线程同时可以去做别的事情。
-
通俗理解:NIO是可以做到用一个线程来处理多个操作的。假设有10000个请求过来,根据实际情况,可以分配50或100个线程来处理。不像之前的阻塞 IO那样,非得分配10000个线程。
-
HTT2.0使用了多路复用的技术,做到同一个链接并发处理多个请求,而且并发请求的数量比HTTP1.1大了好几个数量级。
总的来说,NIO通过非阻塞I/O操作和事件驱动机制,提高了系统的并发性能和响应速度,使得处理大量连接和I/O操作变得更加高效。因此,NIO已经被越来越多地应用到大型应用服务器中,成为解决高并发与大量连接、I/O处理问题的有效方式。
三、Buffer
1、Buffer原理介绍
Java NIO的Buffer类是一个用于特定基本数据类型的容器。它是一个对象,包含一些要写入或者要读出的数据。在NIO中,所有的数据都是用Buffer处理的。在数据读写之前,需要先放入Buffer,或者从Buffer中取出。Buffer对象中提供了一组方法,可以轻松的使用内存块,此外缓冲区对象那中内置了一些机制,能够追踪和记录缓冲区的状态变化情况。
以下是Java NIO Buffer的基本使用步骤:
- 分配Buffer:首先,你需要通过调用allocate()方法(对于ByteBuffer,CharBuffer,DoubleBuffer,FloatBuffer,IntBuffer,LongBuffer,ShortBuffer等)在JVM的堆中分配一个新的Buffer。例如,以下代码分配一个新的ByteBuffer:
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);
- 写入数据到Buffer:调用Buffer类的put()方法将数据写入Buffer。例如:
buffer.put((byte) 10);
buffer.put((byte) 20);
- 切换Buffer的读写模式:在写数据到Buffer后,需要调用flip()方法将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式。调用flip()方法会将position设回0,并将limit设置成之前position的值。换句话说,limit现在表示的是之前写进Buffer的元素的个数。现在Buffer准备好从写模式切换到读模式:
buffer.flip();
- 从Buffer中读取数据:从Buffer中读取数据,你可以使用get()方法。读取数据直到hasRemaining()返回false。这表示已经到达Buffer的末尾:
while(buffer.hasRemaining()){ byte b = buffer.get(); // do something with b
}
- 清除Buffer:当读完Buffer中的数据后,需要清除它以便下次使用。有两种方式可以清除Buffer:调用clear()或compact()方法。clear()方法会清除整个Buffer。compact()方法只会清除已经读过的数据。任何未读的数据都被移到Buffer的起始处,新写入的数据将放到Buffer的未读数据后面。
buffer.clear(); // 清除整个Buffer
或者
buffer.compact(); // 只清除已读数据
注意,在使用Buffer时,要时刻注意Buffer的容量(capacity),位置(position)和限制(limit)。容量是Buffer能够容纳的数据元素的最大数量;位置是下一个要被读或写的元素的索引;限制是第一个不应该被读或写的元素的索引。这些值可以通过调用Buffer的相应方法来获取或设置。
以上就是Java NIO Buffer的基本使用方法。通过合理地使用Buffer,你可以有效地处理大量的数据读写操作,提高程序的性能。
2、Buffer实现类
-
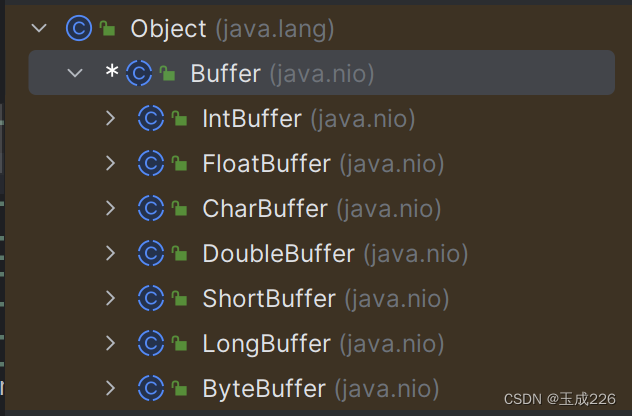
在NIO中,Buffer是一个顶层父类,它是一个抽象类,类的层级关系下图:
-
ByteBuffer:存储字节数据到缓冲区。

-
ShortBuffer:存储字符串数据到缓冲区。
-
CharBuffer:存储字符数据到缓冲区。
-
IntBuffer:存储整数数据到缓冲区。
-
LongBuffer:存储长整型数据到缓冲区。
-
DoubleBuffer:存储小数到缓冲区。
-
FloatBuffer:存储小数到缓冲区。
-
-
Buffer类定义了所有缓冲区都具有的四个属性,来提供其所包含的数据元素的信息:
| 属性 |描述 |
|–|–|
|capacity | 容量,即可以容纳的最大数据量;在缓冲区创建是被设定并且不能改变 |
|Limit| 表示缓冲区的当前终点,不能对缓冲区超过极限的位置进行操作。且极限是可以修改的|
|position| 位置,下一个要被读或写的元素的索引,每次读写缓冲区数据时都会改变,为下次读写做准备|
|mark| 标记| -
Buffer类相关的方法:
//JDK1.4,引入的api
public final int capacity(); //返回此缓冲区的容量
public final int position(); //返回此缓冲区的位置
public final Buffer position(int newPosition); //设置此缓冲区的位置
public final int limit(); //返回此缓冲区的限制
public final Buffer limit(int newLimit); //设置此缓冲区的限制
public final Buffer mark(); //在此缓冲区的位置设置标记
public final Buffer reset(); //将此缓冲区的位置重置为以前标记的位置
public final clear(); //清除此缓冲区,即将各个标记恢复到初始化状态,但是数据并没有真正擦除。
public final Buffer flip(); //反转此缓冲区
public final Buffer rewind(); //重绕此缓冲区
public final int remaining(); //返回当前位置与限制之间的元素数
public final boolean hasRemaining(); //告知当前位置和限制之间是否有元素
public final boolean isReadOnly(); //告知此缓冲区是否为只读缓冲区//JDK1.6 引入的api
public abstract boolean hasArray(); //告知此缓冲区是否具有访问的底层实现数组
public abstract Object array(); //返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组
public abstract int arrayOffset(); //返回此缓冲区的底层实现数组中第一个缓冲区元素的偏移量
public abastract boolean isDirect(); //告知此缓冲区是否为直接缓冲区
3、示例
package test.nio;import java.nio.IntBuffer;
public class BasicBuffer {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个buffer, 容量大小为5,即可以存放5个intIntBuffer buffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);//向buffer中存放数据for (int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i++) {buffer.put(i * 2);}//从buffer中读取数据buffer.flip();while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {int i = buffer.get();System.out.println(i);}}
}运行结果:
0
2
4
6
8Process finished with exit code 0
4、NIO和BIO的比较
- BIO以流的方式处理数据,而NIO以块的方式处理数据,块I/O的效率比流I/O高很多。
- BIO是阻塞的,NIO则是非阻塞的。
- BIO基于字节流和字符流进行操作,而NIO基于Channel(通道)和Buffer(缓冲区)进行操作,数据总是从通道读取到缓冲区中,或者从缓存区写入到通道中。Selector(选择器)用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接请求,数据到达等),因此使用单个线程就可以监听多个客户端通道。
四、Channel
1、介绍
-
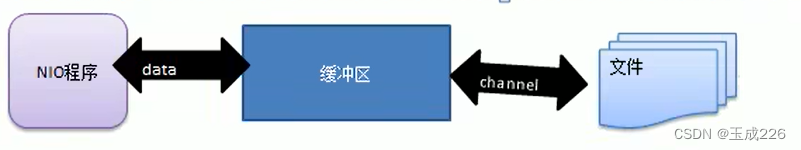
Channel提供从文件、网络读取数据的渠道,但是读取或写入的数据都必须经由Buffer。
-
NIO的通道类似于流,有如下区别:
- 通道可以同时进行读写,而流只能读或者只能写。
- 通道可以实现异步读写数据。
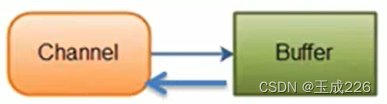
- 通道可以从缓冲读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲:
- BIO中的stream是单向的,例如FileInputStream对象只能进行读取数据的操作。
-
BIO中的stream是单向的,例如FileInputStream对象只能进行读取数据的操作,而NIO中的通道(Channel)是双向的,可以读操作,也可以写操作。
-
Channel在NIO中是一个接口
public interface Channel extends Closeable
- 常用的Channel类有:FileChannel、DatagramChannel、ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel(ServerSocketChannel类似ServerSocket、SocketChannel类似Socket)。
- FileChannel用于文件的数据读写,DatagramChannel用于UDP的数据读写,ServerSocketChannel
2、FileChannel介绍
-
FileChannel主要用来对本地文件进行IO操作,常见的方法有:
- public int read(ByteBuffer dst),从通道读取数据并放到缓冲区中。
- public int write(ByteBuffer src),把缓冲区的数据写到通道中。
- public long transferForm(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count),从目标通道中复制数据到当前通道。
- public long transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target),把数据从当前通道复制给目标通道。
-
通过channel向文件中写数据。

package test.nio;import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;public class NIOFileChannel {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "hello world 今天是星期日";try {//创建一个输出流->channelFileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file01.txt");//通过fileOutputStream获取对应的FileChannel//这个fileChannel真实类型是FileChannelImplFileChannel channel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();//创建一个缓冲区ByteBufferByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);//将str放入byteBufferbyteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());//对byteBuffer进行flipbyteBuffer.flip();//将byteBuffer,数据写入到fileChannelchannel.write(byteBuffer);fileOutputStream.close();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}- 通过Channel读取本地文件数据。
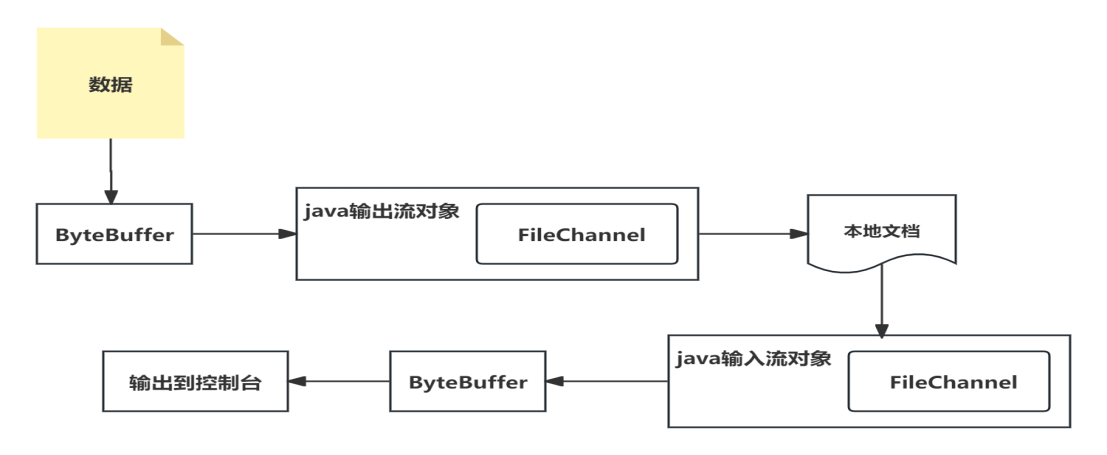
package test.nio;import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File file = new File("d:\\file01.txt");FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();//创建一个缓冲区ByteBufferByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int)file.length());//将通道的数据读入到Bufferint read = channel.read(byteBuffer);//将byteBuffer的字节数据转成StringbyteBuffer.flip();String str = new String(byteBuffer.array());System.out.println(str);fileInputStream.close();}
}结果展示:
hello world 今天是星期日Process finished with exit code 0
- 使用一个Buffer完成文件的读取
package test.nio;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class NIOFileChannel02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\file01.txt");FileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\file02.txt");FileChannel channel1 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);while (Boolean.TRUE) {byteBuffer.clear();int read = channel.read(byteBuffer);System.out.println("read = " + read);if (read == -1) {break;}byteBuffer.flip();channel1.write(byteBuffer);}fileInputStream.close();fileOutputStream.close();}
}- 拷贝文件transferFrom方法
要求:使用FileChannel(通道)和方法transferFrom,完成文件的拷贝。
package test.nio;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;public class NIOFileChannel03 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//创建相关的流FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\star.png");FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\ab.png");//获取各个流对应的fileChannelFileChannel channel = fileInputStream.getChannel();FileChannel channel1 = fileOutputStream.getChannel();//使用transform完成拷贝channel1.transferFrom(channel, 0, channel.size());//关闭相关通道和流channel.close();channel1.close();fileInputStream.close();fileOutputStream.close();}
}3、Buffer和Channel的注意事项
- ByteBuffer支持类型化的put和get,put放入什么数据类型,get就应该使用相应的数据类型来取出,否则可能有BufferUnderflowException异常。
package test.nio;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class NIOByteBufferPutGet {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个bufferByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);//类型化方式放入数据allocate.putInt(100);allocate.putLong(9);allocate.putChar('a');allocate.putShort((short)4);//取出allocate.flip();System.out.println(allocate.getInt());System.out.println(allocate.getLong());System.out.println(allocate.getChar());System.out.println(allocate.getLong());}
}- 可以将一个普通Buffer转成只读Buffer。
package test.nio;import java.nio.ByteBuffer;public class ReadOnlyBuffer {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个bufferByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);System.out.println("capacity = " + allocate.capacity());for (int i = 0; i < allocate.capacity(); i++) {allocate.put((byte)i);}//读取allocate.flip();//得到一个只读的BufferByteBuffer readOnlyBuffer = allocate.asReadOnlyBuffer();System.out.println(readOnlyBuffer.getClass());//读取while(readOnlyBuffer.hasRemaining()) {System.out.println(readOnlyBuffer.get());}}
}- NIO还提供了MappedByteBuffer,可以让文件直接在内存(堆外的内存)中进行修改,而如何同步到文件由NIO来完成。
- NIO支持通过多个Buffer(即Buffer数组)完成读写操作,即Scattering和Gattering。
package test.nio;import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Arrays;/*** Scattering: 将数据写入到buffer时,可以采用buffer数组,依次写入。* Gathering:从buffer读取数据时,可以采用buffer数组,依次读。**/
public class ScatteringAndGatheringTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//使用ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannelServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000);//绑定端口到Socket,并启动serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);//创建buffer数组ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);int messageLength = 8; //从客户端接收8个字节//等待客户端连接(telnet)SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();//循环的读取while (Boolean.TRUE) {int byteRead = 0;while(byteRead < messageLength) {long read = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);byteRead += read; //累计读取的字节数System.out.println("byteRead = " + byteRead);//使用流打印,看看当前的这个buffer的position和limitArrays.asList(byteBuffers).stream().map(buffer -> "position = " + buffer.position() + ", limit = " + buffer.limit()).forEach(System.out::println);}//将所有的buffer进行flipArrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(buffer -> buffer.flip());//将数据读出显示到客户端long byteWrite = 0;while(byteWrite < messageLength) {long l = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);byteWrite += l;}//将所有的buffer进行clearArrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(buffer -> buffer.clear());System.out.println("byteRead:= " + byteRead + " byteWrite= " + byteWrite + " messageLenght= " + messageLength);}}
}五、Selector
六、Selector、Channel和Buffer关系
- 每个channel都会对应一个Buffer。
- Selector对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个channel(连接)。
- 程序切换到那个Channel是由事件决定的,Event就是一个总要的概念。
- Selector会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换。
- Buffer就是一个内存块,底层是一个数组。
- 数据的读取写入是通过Buffer。BIO中要么是输入流要么是输出流,不能双向。但是NIO的Buffer是可以读也可以写的,需要调用flip方法切换。
- channel是双向的,可以返回底层操作系统的情况,比如Linux,底层的操作系统通道就是双向的。
package test.nio;import java.nio.IntBuffer;
public class BasicBuffer {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个buffer, 容量大小为5,即可以存放5个intIntBuffer buffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);for (int j = 0; j < 5; j ++) {//向buffer中存放数据for (int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i++) {buffer.put(i * 2);}//从buffer中读取数据buffer.flip();while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {int i = buffer.get();System.out.println(i);}System.out.println("==============================================================================");buffer.flip();}}
}输出结果:
0
2
4
6
8
==============================================================================
0
2
4
6
8
==============================================================================
0
2
4
6
8
==============================================================================
0
2
4
6
8
==============================================================================
0
2
4
6
8
==============================================================================Process finished with exit code 0