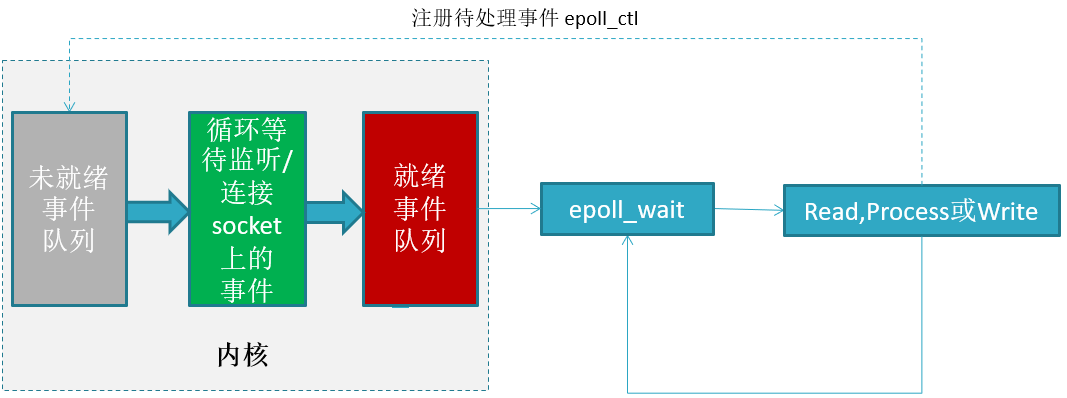
在Android中,只有在UIThread(主线程)中才能直接更新界面,
在Android中,长时间的工作联网都需要在workThread(分线程)中执行
在分线程中获取服务器数据后,需要立即到主线程中去更新UI来显示数据,
所以,如何实现线程间的通信(消息机制)?
消息机制原理
消息机制原理 尚硅谷

handler发送消息到 MessageQueue 消息队列中,消息队列内部是一个链表的结构,Looper会取出消息队列中待处理的消息,调用handler的dispatchMessage()分发消息,handler中处理消息的方法有三种,最常用的是第三种
Message的callback
handler的callback
handler的handleMessage方法
消息机制相关API
Message 消息
可理解为线程间通信的数据单元,可通过message携带需要的数据
创建对象:Message.obtain()、new Message()
Message.obtain()使用了Message中的消息池,比直接new一个对象更高效
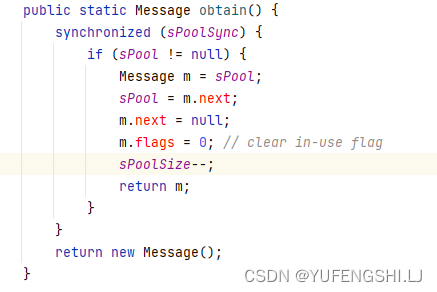
常用参数:
- what: id标识,用以区分来自哪个线程
- arg1/arg2: 子线程需要向主线程传递整型参数
- obj: Object 任意对象
Handler 处理器
handler并不是只能用在处理message上,定时循环调度等工作也能使用它。
Handler 是Message 的处理器,也负责消息的发送和移除工作。
- 发送即时消息
public final boolean sendMessage(@NonNull Message msg),实际上调用了sendMessageDelayed()发送一个延迟时间为0的消息public final boolean sendMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);}public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(@NonNull Message msg, long delayMillis) {if (delayMillis < 0) {delayMillis = 0;}return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);}
- 发送延时消息,并不是指延时发送,而是延时处理
public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(@NonNull Message msg, long delayMillis)public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(@NonNull Message msg, long delayMillis) {if (delayMillis < 0) {delayMillis = 0;}return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);}
- 发送空消息
public final boolean sendEmptyMessage(int what){return sendEmptyMessageDelayed(what, 0);}public final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) {Message msg = Message.obtain();msg.what = what;return sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis);}public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(@NonNull Message msg, long delayMillis) {if (delayMillis < 0) {delayMillis = 0;}return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);}不管是发送什么消息,最后都要调用 sendMessageAtTime 方法
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(@NonNull Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {MessageQueue queue = mQueue;if (queue == null) {RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);return false;}return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);}private boolean enqueueMessage(@NonNull MessageQueue queue, @NonNull Message msg,long uptimeMillis) {msg.target = this;msg.workSourceUid = ThreadLocalWorkSource.getUid();if (mAsynchronous) {msg.setAsynchronous(true);}return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);}
- 处理消息 (回调方法) 在主线程中执行
public interface Callback {/*** @param msg A {@link android.os.Message Message} object* @return True if no further handling is desired*/boolean handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg);}
- 移除未处理消息,比如发送的延时消息:让消息队列调用 removeMessages 方法移除消息
public final void removeCallbacks(@NonNull Runnable r) {mQueue.removeMessages(this, r, null);}
MessageQueue 消息队列
它是一个按Message的when(被处理时间)排序的优先级队列,用来存放通过 Handler 发送的消息。
实例
创建Handler对象,并重写 handleMessage 方法
在主/分线程创建Message对象,利用handler对象发送消息
在 handleMessage 中处理消息
-
创建Handler对象,并重写 handleMessage 方法
只要 handle 发了消息,就一定会触发 handleMessage 方法,并传入一个 Message 对象,根据Message 对象的what属性判断属于哪个线程。
public class HandleActivity extends AppCompatActivity {TextView textView ;String httpDate = "";@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_handle);}// 利用 handller 处理// 1.实例化一个 HandlerHandler handler = new Handler(// 只要 handle 发了消息,就一定会触发 handleMessage 方法,并传入一个 Message 对象new Handler.Callback() {@Override// 3.由handle对象接收消息并处理,在Handler的内部类中处理public boolean handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {Log.e("handler 处理消息", "这是handler发送的消息,此时是空");// 根据 Message 的 what 属性,区分来源于哪个线程if (msg.what == 1) {textView1 = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView1.setText(httpDate);} else if (msg.what == 2) {textView2 = findViewById(R.id.t2);textView2.setText(httpDate);} else if (msg.what == 3) {textView3 = findViewById(R.id.t3);textView3.setText("msg.what = "+msg.what+"\n"+msg.obj.toString());}return false;}});
}- 在主/分线程创建Message对象,利用handler对象发送消息
当消息没有包含数据时,可以使用handler.sendEmptyMessage(int what) 发送一个空消息
new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp();// 当 handler 需要传送数据时,需要使用到 Message,使用 sendMessage 方法Message message = new Message();message.what = 3;DataBean dataBean = new DataBean(1,"157181@qq.com","ybr","scl","asiudh");message.obj = dataBean;handler.sendMessage(message);}}.start();- 设置一个网络操作方法
// 网络操作private void getHttp() {try {// 1. 实例化一个 URL 对象URL url = new URL("https://reqres.in/api/users");// 2. 获取 HttpURLConnection 实例,使用URL的HttpURLConnection httpURLConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();// 3. 设置请求相关属性httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("GET"); // 请求方法httpURLConnection.setConnectTimeout(6000); // 超时时间// 4. 获取响应码 200 成功 404 未请求到指定资源 500 服务器异常(此时已经发起请求)// 5. 判断响应码并获取响应数据(响应的正文)if (httpURLConnection.getResponseCode() == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) {InputStream inputStream = httpURLConnection.getInputStream(); // 获取了服务器返回的输入流byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; // bytes 数组,每次最多可以存放 1024 个字节ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();// 存储从输入流中读取的数据int len = 0;while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) > -1) {// 将字节数组中的内容写入到缓存流/* 参数1:要存入的字节数组* 参数2:起点* 参数3:要存入的长度*/byteArrayOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);}httpDate = new String(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());Log.e("GET返回的数据", httpDate);}} catch (ProtocolException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);} catch (MalformedURLException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);} catch (IOException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);}}全部代码
package com.example.androidstudiostudy;import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.example.androidstudiostudy.data.DataBean;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.ProtocolException;
import java.net.URL;public class HandleActivity extends AppCompatActivity {TextView textView1, textView2, textView3;String httpDate = "";// 利用 handller 处理// 1.实例化一个 HandlerHandler handler = new Handler(// 只要 handle 发了消息,就一定会触发 handleMessage 方法,并传入一个 Message 对象new Handler.Callback() {@Override// 3.由handle对象接收消息并处理,在Handler的内部类中处理public boolean handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {Log.e("handler 处理消息", "这是handler发送的消息,此时是空");// 根据 Message 的 what 属性,区分来源于哪个线程if (msg.what == 1) {textView1 = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView1.setText(httpDate);} else if (msg.what == 2) {textView2 = findViewById(R.id.t2);textView2.setText(httpDate);} else if (msg.what == 3) {textView3 = findViewById(R.id.t3);textView3.setText("msg.what = "+msg.what+"\n"+msg.obj.toString());}return false;}});@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_handle);}// 此时有两个线程,这两线程发送的消息都能被 Handle接收,但如何区分不同线程发送的消息从而做不同处理呢?public void getDate(View view) {int id = view.getId();// 第一个线程if (id == R.id.handle1) {new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp();// 此时会报错:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views./*TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView.setText(httpDate);*/// 解决办法 1 runOnUiThread 方法 ==> 相当于在主线程中跑 (初学阶段)/*runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView.setText(httpDate);}});*/// 解决办法 2 利用 Handle 处理// 2.在子线程中发送(空)消息,此时发送的是空消息handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);}}.start();}// 第二个线程else if (id == R.id.handle2) {new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp();httpDate = httpDate + "\n第2个线程";handler.sendEmptyMessage(2);}}.start();}// 第三个线程else if (id == R.id.handle3) {new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp();// 当 handler 需要传送数据时,需要使用到 Message,使用 sendMessage 方法/* 1. 实例化一个 Message* 2. 参数** what:用于区分 handler 发送消息的不同线程来源** arg1/arg2: 子线程需要向主线程传递整型参数** obj: Object 任意对象*/Message message = new Message();message.what = 3;DataBean dataBean = new DataBean(1,"157181@qq.com","ybr","scl","asiudh");message.obj = dataBean;handler.sendMessage(message);}}.start();}}// 网络操作private void getHttp() {try {// 1. 实例化一个 URL 对象URL url = new URL("https://reqres.in/api/users");// 2. 获取 HttpURLConnection 实例,使用URL的HttpURLConnection httpURLConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();// 3. 设置请求相关属性httpURLConnection.setRequestMethod("GET"); // 请求方法httpURLConnection.setConnectTimeout(6000); // 超时时间// 4. 获取响应码 200 成功 404 未请求到指定资源 500 服务器异常(此时已经发起请求)// 5. 判断响应码并获取响应数据(响应的正文)if (httpURLConnection.getResponseCode() == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) {InputStream inputStream = httpURLConnection.getInputStream(); // 获取了服务器返回的输入流byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; // bytes 数组,每次最多可以存放 1024 个字节ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();// 存储从输入流中读取的数据int len = 0;while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) > -1) {// 将字节数组中的内容写入到缓存流/* 参数1:要存入的字节数组* 参数2:起点* 参数3:要存入的长度*/byteArrayOutputStream.write(bytes, 0, len);}httpDate = new String(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());Log.e("GET返回的数据", httpDate);}} catch (ProtocolException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);} catch (MalformedURLException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);} catch (IOException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);}}
}Looper 循环器
- 负责循环取出 MessageQueue 中当前需要处理的Message
- 交给对应的handler进行处理
- 处理完后,将Message缓存到消息池中,以备复用
每个线程都可以有一个关联的Looper对象,用于处理该线程的消息队列。主要功能是接收来自消息队列的消息并将其分发给对应的Handler处理。
在Android中,主线程已经自动创建了一个Looper对象,并启动了消息循环,我们可以在主线程中方便地使用Handler来处理UI事件。
而对于其他线程,如果需要处理消息,就需要手动创建一个Looper对象,并调用Looper.loop()方法来启动消息循环。
- 必须确保在创建Handler对象之前,在线程中调用了Looper.prepare()方法创建Looper对象并初始化。
- 通过调用Looper.loop()方法,线程会进入一个无限循环,不断地从消息队列中取出消息,并将其分发给对应的Handler进行处理。当调用Looper.quit()方法时,消息循环会停止,线程会退出循环。
Handler handler2;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_handle);// 开一个新的线程,用于接收主线程向子线程传递消息new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {// 系统会自动为主线程开启消息循环(自动调用这句代码),与此同时创建一个 Looper 对象,不断的从 MessageQue中读取消息,交给主线程处理Looper.prepare(); // 准备开启一个消息循环handler2 = new Handler(new Handler.Callback() {@Overridepublic boolean handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {Log.e("主线程向子线程中发送消息", "" + msg.what + "" + msg.arg1);return false;}});Looper.loop(); //开始消息循环,相当于 while(true) ,在这里等待消息}}).start();}// 此时有两个线程,这两线程发送的消息都能被 Handle接收,但如何区分不同线程发送的消息从而做不同处理呢?public void getDate(View view) {int id = view.getId();// 第一个线程if (id == R.id.handle1) {new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp();// 此时会报错:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views./*TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView.setText(httpDate);*/// 解决办法 1 runOnUiThread 方法 ==> 相当于在主线程中跑 (初学阶段)/*runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView.setText(httpDate);}});*/// 解决办法 2 利用 Handle 处理// 2.在子线程中发送(空)消息,此时发送的是空消息handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);}}.start();}// 第二个线程else if (id == R.id.handle2) {new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp();httpDate = httpDate + "\n第2个线程";handler.sendEmptyMessage(2);}}.start();}// 第三个线程else if (id == R.id.handle3) {new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp(); Message message = new Message();message.what = 3;DataBean dataBean = new DataBean(1, "157181@qq.com", "ybr", "scl", "asiudh");message.obj = dataBean;handler.sendMessage(message);}}.start();}// 第四个线程- 主线程向子线程发送消息else if (id == R.id.handle4) {Message message2 = new Message();message2.what = 999;message2.arg1 = 1234;handler2.sendMessage(message2);}}线程中更新UI
runOnUiThread 方法
==> 相当于在主线程中跑 (初学阶段)
public void getDate() {new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp();// 此时会报错:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views./*TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView.setText(httpDate);*/// 解决办法 1 runOnUiThread 方法 ==> 相当于在主线程中跑 (初学阶段)runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView.setText(httpDate);}});}}.start();}利用Handler
new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();getHttp();// 此时会报错:Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views.// 2.在子线程中发送(空)消息,此时发送的是空消息handler.sendEmptyMessage(1);}
}.start();Handler handler = new Handler(new Handler.Callback() {@Override// 3.由handle对象接收消息并处理,在Handler的内部类中处理public boolean handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {Log.e("handler 处理消息", "这是handler发送的消息,此时是空");textView = findViewById(R.id.t1);textView.setText(httpDate);return false;}});什么是异步任务?
逻辑上:以多线程的方式完成的功能需求
API上:指AsyncTask类
在没有 AsyncTask 前,我们可以使用 Thread+Handler 实现异步任务,而 AsyncTask 是对Thread+Handler 功能的封装,使用更简洁,效率更高效
AsyncTask 是一个抽象类,需要指定3个泛型参数
public abstract class AsyncTask<Params, Progress, Result>- Params: 这个泛型指定的是我们传递给异步任务执行时的参数的类型。
- Progress: 这个泛型指定的是我们的异步任务在执行的时候将执行的进度返回给UI线程的参数的类型。
- Result: 这个泛型指定的异步任务执行完后返回给UI线程的结果的类型。
而 AsyncTask目前已被弃用