前言:对于采用机器学习去研究聚合物的防污性能,以及或者其他性质。目前根据我的了解我认为最困难的点有三条:
-
其一:数据,对于将要训练的数据必须要有三点要求,1.数据要多,也就是大数据,通过大量的数据更能发现某些共性的规律。而且数据量大之后对于某些误差数据的干扰就会减少。2.数据要准,其实对于某些文章的实验数据我报有很大的怀疑态度。最好的数据来源就是亲身计算的数据或者某些知名数据库的数据。3.数据类型要丰富,数据类型越丰富,可以描述的性质越多,可能或者对于所研究的性质关联性越强。
- 其二:描述符,对于描述符的选取也十分重要,好的描述符能够准确简洁的描述好想要研究的性质,不会出现过拟合或者欠拟合的状态。
- 其三:拟合函数。拟合函数也不是越复杂越好,一个合适的拟合函数,能够准确的描述想要研究的性质,最好具有迁移性以及扩展性。
如果能够准确的解决以上三个重点,发一篇好的文章肯定是志在必得的事情。
一、数据
数据质量是ML模型的基石,它直接影响模型的性能和应用。因此,在ML建模之前收集可靠的数据非常重要。数据集通常由因变量和自变量组成。因变量是指聚合物的目标特性,可以从实验、数据库、出版物、第一性原理计算或分子动力学模拟中获得。用实验数据构建的ML模型可以帮助研究人员更直观地指导实验,同时牺牲相对较高的经济性、劳动力和时间成本。从数据库中收集数据是在短时间内获取大量数据的一种非常方便的方法。
收集可用的聚合物数据库
Materials Project Computed properties of known and hypothetical materials https://materialsproject.org Protein Data Bank (PDB) 3D structures of proteins, nucleic acids, and complex assemblies http://www.wwpdb.org Citrination Computed and experimental properties of materials https://citrination.com Polymer Genome An informatics platform for polymer property prediction and design https://www.polymergenome.org PoLyInfo Various data required for polymeric material design https://polymer.nims.go.jp NanoMine An open-source data resource for members of the nanocomposites community materialsmine Polymer Property Predictor and Database Flory–Huggins χ parameters and glass transition temperatures for various polymers https://pppdb.uchicago.edu Physical Properties of Polymers Various physical properties and characterization techniques of polymers by J. Mark, K. Ngai, W. Graessley, L. Mandelkern, E. Samulski, J. Koenig and G. Wignall ACD/Labs NMR Databases Polymer NMR spectra ACD/Labs | Software for R&D | Chemistry Softwareproducts/dbs/nmr_db Polymer Science Learning Center Spectral Database Polymer IR and NMR spectra https://pslc. uwsp.edu NIST Synthetic Polymer MALDI Recipes Database Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry on a wide variety of synthetic polymers https://maldi. nist.gov CROW Polymer Properties Database A multitude of polymer properties http://polymerdatabase.com MATWEB Material Property Data Material properties of thermoplastic and thermoset polymers http://www.matweb.com Material Properties Database Engineering material properties that emphasize ease of comparison https://www.makeitfrom.com
1 聚合物基因组 Polymer Genome: Predict 高分子材料的计算或实验特性数据库以及用于快速预测的相应机器学习模型。 2 PoLy信息 高分子データベース(PoLyInfo) - DICE :: 国立研究開発法人物質・材料研究機構 PoLyInfo 从学术文献中提供有关高分子材料的 ≈100 性质、化学结构和合成方法的信息。 3 聚合物性能预测器和数据库 Polymer Property Predictor and Database 用于结构和多功能应用的聚合物材料的Flory-Huggins χ参数和玻璃化转变温度。 4 材料属性数据库 MakeItFrom.com: Material Properties Database 该数据库提供聚合物材料的机械、热学和电学性能。 5 CROW聚合物特性数据库 iPage 高分子科学数据库,包括高分子材料的结构、性能和应用。 6 PI1M GitHub - RUIMINMA1996/PI1M: A benchmark dataset for polymer informatics. 100万种聚合物用于聚合物信息学。 7 UniProt的 UniProt UniProt 提供全面、高质量且可免费访问的蛋白质序列和功能信息资源。
二、描述符
传统的分子描述符主要包括组成、结构、工艺参数和光谱信息。
因此,如何使用ML快速高效地从出版物中提取数据也成为研究热点。近年来,第一性原理计算和分子动力学模拟在预测目标性质方面得到了快速发展。但是,在ML过程中传输的计算中也存在不可避免的错误,从而降低了模型的鲁棒性。自变量是指影响因变量的因素,也称为特征或描述符。这些描述符包括化学成分、原子参数、结构参数或过程参数,可以从领域知识或描述符生成软件中获得。
聚合物指纹
尼龙-6的重复单元可以看作是1-NH-,5-CH的连接2- 和 1-CO 块。构成重复单元的这些构建块称为聚合物指纹
常用的聚合物指纹图谱包括摩根指纹图谱(MF)、分子嵌入图谱(ME)和分子图谱(MG)除了最常用的MF、ME和MG指纹作为聚合物表示外,还有其他指纹也可以用来表示聚合物,如原子对指纹、拓扑扭转指纹、分层指纹等。
结构的描述符
聚合物指纹图谱更侧重于重复单元的组成信息,而基于结构的描述符不仅反映了重复单元的组成信息,还表征了结构信息。根据分子结构的维度,基于结构的描述符可分为二维描述符和三维描述符
2D 和 3D 描述符可以通过专业的描述符生成软件获得,例如 Dragon;或开源工具包,例如 Mordred 和 RDKit 中的其他工具包。
使用最广泛的基于 2D 的结构描述符是 SMILES 表示。SMILES 的全称是 Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System,
基于 3D 结构的描述符可以通过 Mordred 和 Dragon 等描述符生成软件获得。
2.1 描述符的评估
根据描述符和目标之间的冗余和相关性,特征可以分为四个基本子集:不相关特征、冗余特征、弱相关但非冗余特征和强相关特征。不相关和冗余的特征往往会降低模型的评估指标,使模型性能更差。适当的特征选择算法应在不丢失任何重要信息的情况下降低输入空间的维数。根据评估策略与建模算法的关系,特征选择技术可分为滤波器、包装器和嵌入式。
滤波方法旨在通过原始数据集计算特征与目标之间的相关性,并通过设置阈值来选择关键特征,以消除相关性较弱的特征。[88]滤波方法的主要特点在于特定判别模型的独立性以及对特征之间潜在相关性的无知。[89、90]Wrapper 方法从所有特征组合中尽可能地选择最优特征组合,将特征选择过程视为搜索最优任务。[91]过滤法和包装法的区别在于建模算法是否在特征选择过程中引入。
因此,这种方法基本上通过特征选择来封装分类或预测结果,一次评估一次变量的组合。表3显示了高分子材料中常用的过滤器和包装器类型的特征选择算法。嵌入式方法是筛选出特定算法的重要特征子集,在构建分类或回归模型时,可以给出每个特征的评价分数。该方法结合偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)、随机森林(RF)和惩罚回归等不同算法,可以提高整体预测精度。
高分子材料中的常见特征选择算法
1 CFS Filter CFS estimates the performance of a subset of features rather than a single feature. It introduces a forward search strategy to select strongly correlated non-redundant features. 2 mRMR Filter mRMR uses incremental search to select features, which can maximize the correlation between features and categories as well as minimize the redundancy between features. 3 Markov blanket Filter Markov blankets can perform feature redundancy analysis. In the feature space, the detailed information of the target variable can be obtained from its Markov blanket, and the non-Markov blanket can be regarded as redundant features of the target variable to reduce the feature dimension. 4 Genetic algorithm Wrapper Genetic algorithm uses an evolution-based method to determine the optimal set. After the algorithm runs for a certain number of generations, the optimal member of the group is the selected feature. 5 Backward elimination Wrapper All independent variables are selected into the model and then the partial F test is performed on each independent variable. The smallest F value is recorded as FL and compared with the pre-specified significance level F0. If FL < F0, the variable is eliminated, and refit the regression model with the remaining variables. 5 Forward selection Wrapper Forward selection method is a method of independent variable selection of a regression model. Its characteristic is to introduce the candidate independent variables into the regression equation one by one to test the significance of the regression coefficient, and to decide whether to introduce the independent variable into the model.
三、ML算法
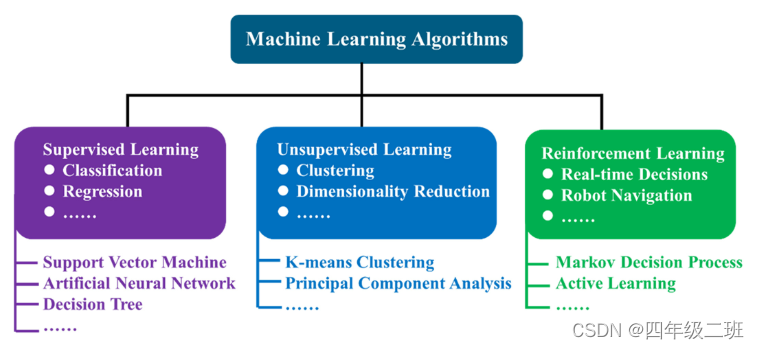
监督学习:训练数据包含输出标签以实现数据分类或回归
支持向量机,人工神经
无监督学习:无输出标签
K均值聚类和主成分分析
强化学习:迭代方法,其中智能体采取行动改变其状态并与环境交互以最大化其目标奖励值
马尔可夫决策过程和主动学习
算法:支持向量机(SVM) 图神经网络 (GNN)、高斯过程回归 (GPR)、主动学习和支持向量机 (SVM)人工神经网络(ANN)深度学习 迁移学习 遗传算法(GA)贝叶斯算法。
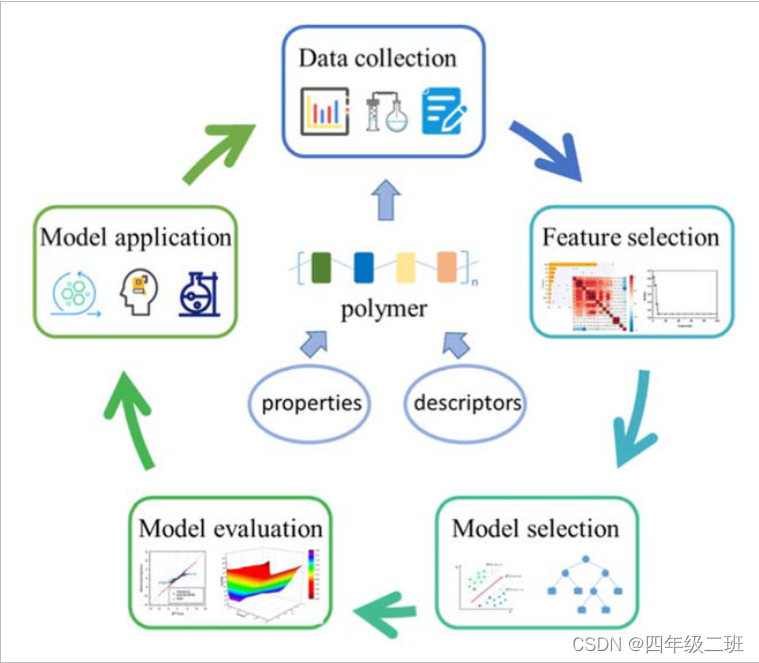
四、实际流程