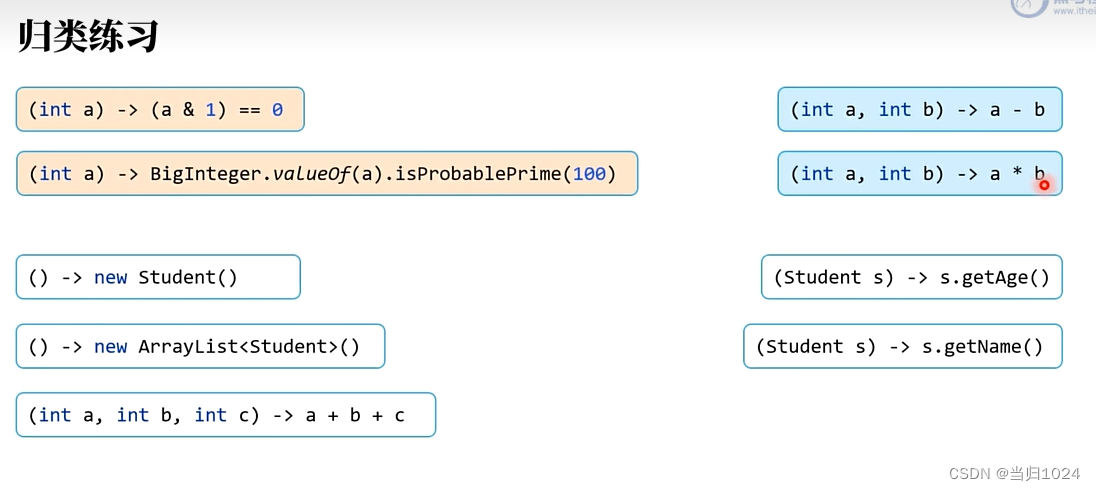
目录
1. 栈
1.1 栈的概念和结构
1.2 栈的实现
1.2.1 栈的顺序储存结构
1.2.2 栈的基本操作
1.3 有效的括号
1. 栈
1.1 栈的概念和结构
堆栈又名栈(stack),它是一种运算受限的线性表。
限定仅在表尾进行插入和删除操作的线性表。这一端被称为栈顶,相对地,把另一端称为栈底。
向一个栈插入新元素又称作进栈、入栈或压栈,它是把新元素放到栈顶元素的上面,使之成为新的栈顶元素;
从一个栈删除元素又称作出栈或退栈,它是把栈顶元素删除掉,使其相邻的元素成为新的栈顶元素。
入数据在栈顶,出数据也在栈顶。

1.2 栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表来实现,两者相比较的话,数组的结构实现更优。
1.2.1 栈的顺序储存结构
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;
1.2.2 栈的基本操作
(1)初始化
//Stack.h//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);//Stack.cvoid STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}
注意:这里 top 的值可以是0,或者是-1。
两种写法的区别在于:

这两种写法没有好坏之分。
(2)销毁
//Stack.h//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);//Stack.cvoid STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}(3)入栈
//Stack.h//入栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);//Stack.cvoid STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);//如果栈满,扩容if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newcapacity; //更新栈的容量}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++; //将元素x插入栈中,并且将栈顶指针上移一位
}(4)出栈
//Stack.h//出栈
void STPop(ST* ps);//Stack.cvoid STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps)); //栈不为空ps->top--; //栈顶指针向后移一位
}(5)读取栈顶元素
//Stack.h//读取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
//Stack.cSTDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));return ps->a[ps->top - 1]; //因为前面定义的 top = 0
}(6)返回栈的长度
//Stack.h//返回栈的长度
int STSize(ST* ps);
//Stack.cint STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}(7)判断栈是否为空
//Stack.h//判断栈是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
//Stack.cbool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);if(ps->top == 0)return true;elsereturn false;
}1.3 有效的括号
示例代码:
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* a;int top;int capacity;
}ST;//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);//入栈
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//出栈
void STPop(ST* ps);//读取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);//栈的大小
int STSize(ST* ps);//判断栈是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);void STInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");return;}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newcapacity;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}void STPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!STEmpty(ps));return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}int STSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}bool isValid(char* s) {ST st;STInit(&st);while(*s){if (*s == '(' || *s == '[' || *s == '{'){STPush(&st, *s);}else{//右括号比左括号多if(STEmpty(&st)){STDestroy(&st);return false;}char top = STTop(&st);STPop(&st);//符号不匹配if((*s == ']' && top != '[')|| (*s == ')' && top != '(')|| (*s == '}' && top != '{')){STDestroy(&st);return false;}}++s;}//左括号比右括号多,栈不为空bool ret = STEmpty(&st);STDestroy(&st);return ret;
}