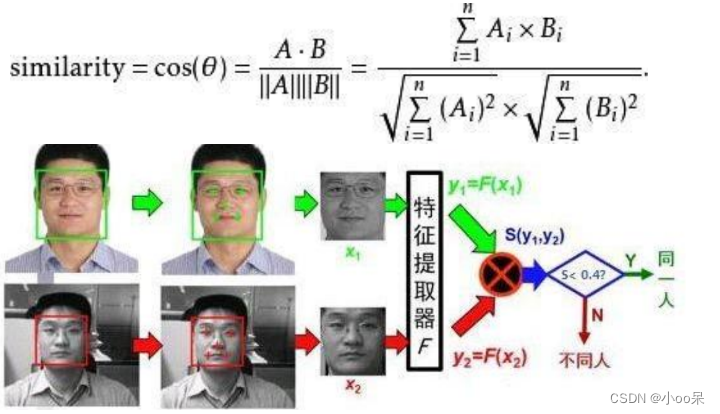
在深度学习和神经网络中,反向传播算法是一种至关重要的技术,它使得网络能够通过学习不断调整自身的参数以优化性能。作为训练神经网络的核心机制,反向传播通过计算损失函数对模型参数的梯度,并据此更新网络权重,从而逐步减少预测值与真实值之间的差距。这一过程是神经网络实现自适应学习、提升预测精度的关键步骤,为现代机器学习应用提供了强大的支持。
在神经网络中,每个神经元的输出是通过将输入数据应用于一系列函数(如权重相乘、加偏置、激活函数等)计算得到的。每一层的输出会成为下一层的输入。这种层层嵌套的函数结构可以被看作是一系列复合函数。
反向传播算法的过程如下:
1.前向传播💥
输入数据通过网络的每一层前向传播,直到最后一层产生输出。
2.计算损失💥
网络的输出与真实值之间的差异通过损失函数计算出来,得到一个损失值,它衡量了当前网络的性能。
3.反向传播💥
通过链式法则从输出层反向逐层计算损失函数对每个参数(权重和偏置)的梯度。这涉及到对损失函数关于网络输出的导数,以及网络输出关于网络参数的导数的计算。
4.参数更新💥
一旦计算出损失函数关于所有参数的梯度,就使用梯度下降或其他优化算法来更新网络的权重和偏置,以减少损失。
神经网络反向传播
#定义输入值和期望输出
x_1 = 40.0
x_2 = 80.0
expected_output = 60.0
初始化
#定义权重
w_1_11 = 0.5
w_1_12 = 0.5
w_1_13 = 0.5
w_1_21 = 0.5
w_1_22 = 0.5
w_1_23 = 0.5
w_2_11 = 1.0
w_2_21 = 1.0
w_2_31 = 1.0
# 前向传播
z_1 = x_1 *w_1_11 +x2*w1_21
z_2 = x_1 * w_1_12 + x_2 * w_1_22
Z_3 = x_1 * w_1_13 + X_2 * w_1_23
y_pred = z_1 * w_2_11+ z_2 * w_2_21+ z_3 * w_2_31
# print(z_1,z_2,z_3,y_pred)
print("前向传播预测值为:", y_pred)
#计算损失函数值(L2损失)
loss = 0.5 *( expected_output - y_pred)**2
print("当前的loss值为: ",loss)#计算输出层关于损失函数的梯度
d_loss_predicted_output = -( expected_output - y_pred) #计算权重关于损失函数的梯度
d_loss_w_2_11 = d_loss_predicted_output * z_1
d_loss_w_2_21 = d_loss_predicted_output * z_2
d_loss_w_2_31 = d_loss_predicted_output * z_3 print(d_loss_w_2_11,d_loss_w_2_21,d_loss_w_2_31)
d_loss_w_1_11 = d_loss_predicted_output *w_2_11 *x_1
d_loss_w_1_21 = d_loss_predicted_output * w_2_11 *x_2
d_loss_w_1_12 = d_loss_predicted_output * w_2_21 *x_1
d_loss_w_1_22 = d_loss_predicted_output * w_2_21 * x_2
d_loss_w_1_13 = d_loss_predicted_output*w_2_31 *x_1#使用梯度下降法更新权重
learning_rate = 1e-5
w_2_11 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_2_11
w_2_21 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_2_21
w_2_31 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_2_31
w_1_11 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_1_11
w_1_12 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_1_12
w_1_13 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_1_13
w_1_21 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_1_21
w_1_22 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_1_22
w_1_23 -= learning_rate * d_loss_w_1_23# 前向传播
z_1 = x_1 * w_1_11 + x_2 * w_1_21
z_2 = x_1 * w_1_12+ x_2* w_1_22
Z_3 = x_1 * w_1_13+ x_2 * w_1_23
y_pred = z_1 * w_2_11 + z_2 * w_2_21 + z_3 * w_2_31
print("Final: ",y_pred)
# print("前向传播预测值为:“, y_pred)
loss = 0.5 *(expected_output - y_pred)**2
print("当前的loss值为: ", loss)前向传播预测值为: 180.0
当前的loss值为:7200.0
Final:140.3136
当前的loss值为:3225.1371724800006
制作梯度下降求最小值的动画
为了展示梯度下降算法寻找函数最小值的过程,我们可以使用Python的matplotlib库来可视化这个过程。以下是一个简单的案例,使用梯度下降算法来寻找一个二次函数(例如 (f(x) = x^2))的最小值,并先静态地显示梯度下降的过程,然后将其制作成动画。
第一步:静态显示梯度下降
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def f(x): return x ** 2 def df(x): return 2 * x def gradient_descent(x_start, learning_rate, epochs): x = x_start history = [] for i in range(epochs): grad = df(x) x -= learning_rate * grad history.append(x) return history # 初始值、学习率和迭代次数
x_start = 5.0
learning_rate = 0.1
epochs = 50 # 执行梯度下降
history = gradient_descent(x_start, learning_rate, epochs) # 绘制函数图像和梯度下降的轨迹
x_values = np.linspace(-10, 10, 400)
y_values = [f(x) for x in x_values] plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(x_values, y_values, label="f(x) = x^2")
plt.scatter(history, [f(x) for x in history], color='red', label="Gradient Descent Path")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("f(x)")
plt.title("Gradient Descent to Find Minimum of f(x) = x^2")
plt.legend()
plt.show()第二步:动画显示
为了实现动画效果,我们可以使用matplotlib.animation模块。以下是一个示例代码,展示了如何使用动画来可视化梯度下降的过程:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6)) x_values = np.linspace(-10, 10, 400)
y_values = [f(x) for x in x_values]
ax.plot(x_values, y_values, label="f(x) = x^2")
line, = ax.plot([], [], 'ro', animated=True)
ax.set_xlim(-10, 10)
ax.set_ylim(0, 100)
ax.set_xlabel("x")
ax.set_ylabel("f(x)")
ax.set_title("Gradient Descent Animation for f(x) = x^2") def init(): line.set_data([], []) return line, def animate(i): x = x_start - i * learning_rate * df(x_start - i * learning_rate) y = f(x) line.set_data(x, y) return line, ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init, frames=epochs, interval=100, blit=True) plt.show()- 注意:在实际运行动画代码之前,请确保已经安装了必要的库,并且你的环境支持动画的显示。
实现三维平面的梯度下降
在三维空间中实现梯度下降算法的可视化会稍微复杂一些,因为我们需要处理三个维度。为了简化问题,我们可以选择一个简单的三维函数,比如 (f(x, y) = x2 + y2),这是一个碗状的三维曲面,其最小值在原点 (0, 0)。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation # 定义目标函数和它的梯度
def f(x, y): return x**2 + y**2 def grad_f(x, y): dfdx = 2 * x dfdy = 2 * y return np.array([dfdx, dfdy]) # 梯度下降算法
def gradient_descent(x_start, y_start, learning_rate, epochs): path = [] x, y = x_start, y_start for _ in range(epochs): grad = grad_f(x, y) x, y = x - learning_rate * grad[0], y - learning_rate * grad[1] path.append((x, y, f(x, y))) return np.array(path) # 初始参数设置
x_start, y_start = 1.5, 1.5
learning_rate = 0.1
epochs = 50 # 执行梯度下降算法并记录路径
path = gradient_descent(x_start, y_start, learning_rate, epochs) # 设置3D图形
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') # 绘制3D曲面
X = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100)
Y = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = f(X, Y)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='viridis', alpha=0.8) # 绘制梯度下降的路径
x_vals, y_vals, z_vals = path[:, 0], path[:, 1], path[:, 2]
ax.plot(x_vals, y_vals, z_vals, 'r-', label='Gradient Descent Path') # 图形装饰
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
ax.set_title('Gradient Descent in 3D')
ax.legend() # 显示图形
plt.show()- 首先定义了一个目标函数 (f(x, y)) 和它的梯度函数
grad_f(x, y)。然后,gradient_descent函数执行梯度下降算法,并记录每一步的路径。最后,我们使用matplotlib的3D功能来绘制函数曲面和梯度下降的路径。
在深入探讨神经网络反向传播算法之后,我们可以清晰地认识到这一机制在现代深度学习领域中的核心地位。反向传播不仅为神经网络提供了自我学习和优化的能力,更是推动了人工智能技术的飞速发展。通过不断地迭代和调整网络参数,反向传播使得神经网络能够逐渐逼近复杂的非线性函数,从而在各种应用场景中展现出强大的性能。未来,随着计算能力的提升和算法的不断改进,反向传播算法将继续引领神经网络的发展,为人工智能的普及和应用奠定坚实基础。



![[学习笔记] VFX Silhouette](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/cf52362fd9fd4785a9d00dc06f3edb3d.png)