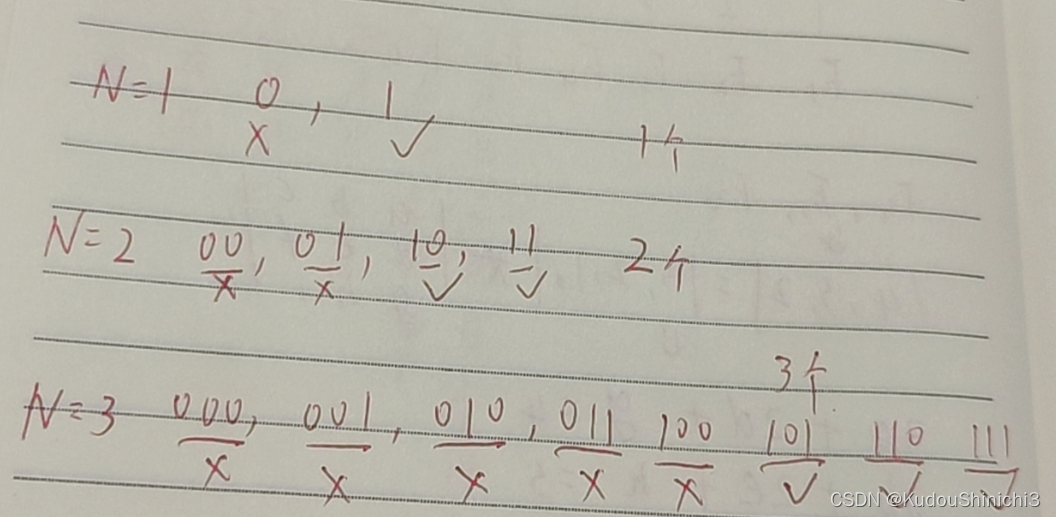文章目录
- 1. 题目来源
- 2. 题目解析
1. 题目来源
链接:3067. 在带权树网络中统计可连接服务器对数目
2. 题目解析
挺有意思的一道题目,重点是要能够读懂题目,然后结合几个图相关的处理技巧即可拿下。
- 图存储:邻接表即可。
- 无向无环图的单侧图遍历:无向图一般邻接表建立两条边,正常图遍历会有重复边。一般的处理操作就是遍历时记录一个 fa 父节点即可,即不会往父节点方向遍历,则一直会向下遍历,最终结果无重复。
- 结果处理:实际上就是每个节点作为根节点,作为服务器 C,查找子树中的所有与根节点距离能被整除的节点个数。这里计数需要使用到乘法原理,具体看下摘自灵神的这张图即可:

- 优化技巧:如果枚举的根,相邻点只有一个的话,那么结果一定是 0,因为要求 C 到 A、B 的边是不重复的。
- 时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
class Solution {
public:vector<int> countPairsOfConnectableServers(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int signalSpeed) {int n = edges.size() + 1;vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> g(n);for (auto &e : edges) {int x = e[0], y = e[1], w = e[2];g[x].push_back({y, w});g[y].push_back({x, w});}vector<int> ans(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {// 如果只有一个相邻点,则结果为 0。因为该点不能作为 C 点,题目要求没有与 a、b 的公共边if (g[i].size() == 1) {continue;}int sum = 0;for (auto &[y, wt] : g[i]) { // 递归遍历子树int cnt = dfs(y, i , wt, signalSpeed, g);ans[i] += cnt * sum;sum += cnt;}}return ans;}// dfs 统计子树中有多少节点可以被整除int dfs(int x, int fa, int sum, int signalSpeed, vector<vector<pair<int ,int >>> g) {int cnt = sum % signalSpeed == 0;for (auto &[y, wt] : g[x]) {if (y != fa) { // 不等于父节点,只计算单边树cnt += dfs(y, x, sum + wt, signalSpeed, g);}}return cnt;}
};





![[DDR4] DDR 简史](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/8d31fad7a28745eb81e253606f226423.png#pic_center)