491. 非递减子序列
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出并返回所有该数组中不同的递增子序列,递增子序列中 至少有两个元素 。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
数组中可能含有重复元素,如出现两个整数相等,也可以视作递增序列的一种特殊情况。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [4,6,7,7] 输出:[[4,6],[4,6,7],[4,6,7,7],[4,7],[4,7,7],[6,7],[6,7,7],[7,7]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [4,4,3,2,1] 输出:[[4,4]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 15-100 <= nums[i] <= 100
思路:
本题和求子集相似,要求取有序子集,但子集不能重复,所以就不能将原数组排序后取子集实现去重,本题也是同一父节点下的同层上使用过的元素就不能再使用了

递归三部曲:
1.确定返回值和参数的类型
定义两个全局变量
List<List<Integer>> result;记录所有结点
List<Integer> node;记录当前结点
返回值为void,在递归过程中更高全局变量
2.确定递归结束条件
本题其实类似求子集问题,也是要遍历树形结构找每一个节点,但本题收集结果有所不同,题目要求递增子序列大小至少为2
if(startIndex>nums.length)
return;
这行代码可以省略,因为startIndex在递归过程中会加1,不会无限递归下去(进不去for循环)
3.确定单层逻辑
同一父节点下的同层上使用过的元素就不能再使用了,我们使用set对本层元素去重,注意set只负责本层,所以进入下一层需要清空
将个数大于1的node加入到result
对本层元素去重
递归找到所有node
代码参考:
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<>();List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {backTracking(nums,0);return result;}public void backTracking(int[] nums,int startIndex){if(path.size()>1)result.add(new LinkedList<>(path));if(startIndex == nums.length){return;}Set<Integer> hashSet= new HashSet<>();for(int i=startIndex;i<nums.length;i++){if(!path.isEmpty()&&nums[i]<path.get(path.size()-1)||hashSet.contains(nums[i])){continue;} hashSet.add(nums[i]);path.add(nums[i]);backTracking(nums,i+1);path.removeLast();}}}
46. 全排列
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1] 输出:[[0,1],[1,0]]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1] 输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 6-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有整数 互不相同
思路:
思路:用回溯法收集叶节点,用uesd数组记录路径上哪些数字已经使用,实现路径去重,这里就不是树层去重了
递归三部曲:
1.确定返回值和参数的类型
定义两个全局变量List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<>();记录结果集
List<Integer>path=new LinkedList<>();记录递归路径,也就是全排列的过程
返回值为void,传入需要排列 的数组nums,和数组used(记录递归过程中哪些数被用掉了,实现路径去重)
2.确定递归结束条件
if(nums.length==path.size()){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
nums.length==path.size()时到达叶节点,也就是找到一组全排列了
3.确定单层逻辑
将路径上没用过的数加入路径

代码:
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<>();List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];backTracking(nums,used);return result;}public void backTracking(int[] nums,boolean[] used){if(path.size()==nums.length){result.add(new LinkedList(path));}for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){if(used[i]){continue;}path.add(nums[i]);used[i]=true;backTracking(nums,used);used[i]=false;path.removeLast();}}
}47. 全排列 II
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2] 输出: [[1,1,2],[1,2,1],[2,1,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 8-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
思路:本题与上一题区别在于,序列nums包含重复数字, 本题该如何去重 呢?
先将数组排序,让相同的数字排在一起,实现树层去重,利用used数组实现路径去重
i>0&&nums[i-1]==nums[i]&&!used[i-1]:说明在同一层使用了,注意这里的used[i-1]必须为false,只有这样两个相同的数才会出现在同一层
used[i]:说明该数在路径中已经使用了,不能再使用了
代码:
if(i>0&&nums[i-1]==nums[i]&&!used[i-1]||used[i]){
continue;
}

代码参考:
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> result= new LinkedList<>();List<Integer> path= new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];Arrays.sort(nums);backTracking(nums,used);return result;}public void backTracking(int[] nums,boolean[] used){if(nums.length==path.size()){result.add(new LinkedList<>(path));return;}for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){if(i>0&&nums[i-1]==nums[i]&&!used[i-1]||used[i]){continue;}used[i]=true;path.add(nums[i]);backTracking(nums,used);used[i]=false;path.removeLast();}}
}332. 重新安排行程
给你一份航线列表 tickets ,其中 tickets[i] = [fromi, toi] 表示飞机出发和降落的机场地点。请你对该行程进行重新规划排序。
所有这些机票都属于一个从 JFK(肯尼迪国际机场)出发的先生,所以该行程必须从 JFK 开始。如果存在多种有效的行程,请你按字典排序返回最小的行程组合。
- 例如,行程
["JFK", "LGA"]与["JFK", "LGB"]相比就更小,排序更靠前。
假定所有机票至少存在一种合理的行程。且所有的机票 必须都用一次 且 只能用一次。
示例 1:

输入:tickets = [["MUC","LHR"],["JFK","MUC"],["SFO","SJC"],["LHR","SFO"]] 输出:["JFK","MUC","LHR","SFO","SJC"]
示例 2:

输入:tickets = [["JFK","SFO"],["JFK","ATL"],["SFO","ATL"],["ATL","JFK"],["ATL","SFO"]] 输出:["JFK","ATL","JFK","SFO","ATL","SFO"] 解释:另一种有效的行程是 ["JFK","SFO","ATL","JFK","ATL","SFO"] ,但是它字典排序更大更靠后。
提示:
1 <= tickets.length <= 300tickets[i].length == 2fromi.length == 3toi.length == 3fromi和toi由大写英文字母组成fromi != toi
思路:
本题用回溯法,遍历所有的票的使用顺序,由于所有机票至少存在一种合理的行程,我们先将票按照起始位置的开头字母小的排序,递归过程中找到其中一种合理行程就返回,该行程一定是字典排序更小的行程。
递归三部曲:
1.确定返回值和参数的类型
使用全局变量保存结果 ,参数传入所有的票(List<List<String>> tickets),和每张票的使用情况(used[])
由于只取第一个结果,所有返回值类型设置为boolean类型,当找到第一个结果时,就返回true
List<String> path=new LinkedList<>();
List<String> result;
boolean travel(List<List<String>> tickets,boolean used[])
2.确定递归结束条件
当记录路径的数组的长度==票的长度+1,说明合理用完了所有票,找到了合理旅游路径,结束递归
if(path.size()==tickets.size()+1){
result=new ArrayList<>(path);
return true;
}
3.单层递归逻辑
递归找到所有方案
for(int i=0;i<tickets.size();i++){
if(!used[i]&&path.get(path.size()-1).equals(tickets.get(i).get(0))){
path.add(tickets.get(i).get(1));
used[i]=true;
//找到第一个方案,结束递归
if( travel(tickets,used))return true;
path.remove(path.size()-1);
used[i]=false;
}
}
return false;
总体代码:
class Solution {List<String> path=new LinkedList<>();List<String> result;public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) {boolean[] used=new boolean[tickets.size()];//给票排序Collections.sort(tickets,(a,b)->a.get(1).compareTo(b.get(1)));path.add("JFK");travel(tickets,used);return result;}boolean travel(List<List<String>> tickets,boolean used[]){if(path.size()==tickets.size()+1){result=new ArrayList<>(path);return true;}for(int i=0;i<tickets.size();i++){if(!used[i]&&path.get(path.size()-1).equals(tickets.get(i).get(0))){path.add(tickets.get(i).get(1));used[i]=true;//找到第一个方案,结束递归if( travel(tickets,used))return true;path.remove(path.size()-1);used[i]=false;}}return false;}
}使用本方法因为排序的原因会出现超时
改进方法:
用Map<出发机场, Map<到达机场, 航班次数>> map来记录车票,Map<到达机场, 航班次数>为升序TreeMap
class Solution {private Deque<String> path = new LinkedList<>();//双端队列,用来存储飞行路径private Map<String,Map<String,Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();//hashmap存储一个其他到其他地方的票数public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) {for(int i=0;i<tickets.size();i++){//统计每个出发地到目的地的票数if(map.containsKey(tickets.get(i).get(0))){Map<String,Integer> temp= map.get(tickets.get(i).get(0));//获取目的地们与其对应的票数temp.put(tickets.get(i).get(1),temp.getOrDefault(tickets.get(i).get(1),0)+1);map.put(tickets.get(i).get(0),temp);}else{Map temp = new TreeMap<>();temp.put(tickets.get(i).get(1),1);map.put(tickets.get(i).get(0),temp);}}path.add("JFK");backTracking(tickets.size());return new LinkedList( path);}public boolean backTracking(int tickets){if(path.size()==tickets+1){return true;}String start = path.getLast();//取出同一出发地点的各个机票的目的地和对应的票数if(map.get(start)!=null)for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> target : map.get(start).entrySet()){int times= target.getValue();if(times>0){path.add(target.getKey());target.setValue(times-1);if( backTracking(tickets)){return true;}path.removeLast();target.setValue(times);}}return false;}
}51. N 皇后
按照国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击与之处在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上的棋子。
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例 1:
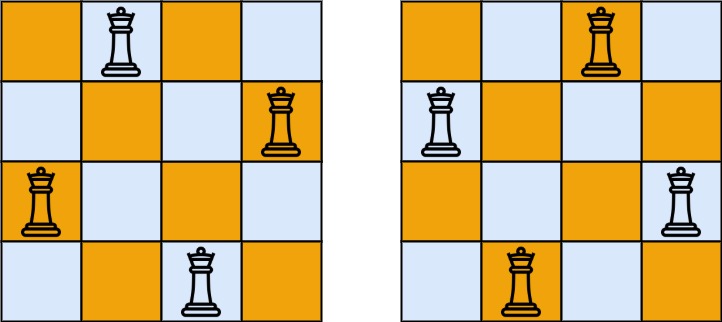
输入:n = 4 输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]] 解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:[["Q"]]
提示:
1 <= n <= 9
皇后们的约束条件:
- 不能同行
- 不能同列
- 不能同斜线
思路:用回溯法,遍历出所有可以放置的可能性
递归三部曲:
1.确定返回值和参数类型
要把所有能摆放的位置都得出,用全局变量public List<List<String>> result=new ArrayList<>();记录所有合理的棋盘,返回值为void,传入棋盘(char[][] chessboard),要放置的皇后在哪一行(int row),棋盘的宽度(n);
public void backTracking(int n,int row,char[][] chessboard)
2.确定递归结束条件
当row==n时,说明所有行都放置了皇后,找到了一种合理放法,将该棋盘存入result中,递归结束
if(row==n){
List<String> temp= array2List(chessboard);
result.add(temp);
return;
}
3.确定单层递归逻辑
遍历该行的每一个位置并检查其合理性,如果合理,进入下一行棋盘的摆放
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
//如果当前位置合法,就递归放下一行
if(isVaild(chessboard,row,i,n)){
chessboard[row][i]='Q';
backTracking(n,row+1,chessboard);
chessboard[row][i]='.';
}
}
class Solution {List<List<String>> result = new LinkedList<>();List<String> board = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {char[][] chessboard = new char[n][n];for(char[] c:chessboard){Arrays.fill(c,'.');}backTracking(n,0,chessboard);return result;}public void backTracking(int n,int row,char[][] chessboard){if(row==chessboard.length){List<String> temp= array2List(chessboard);result.add(temp);return;}for(int i=0;i<chessboard.length;i++){if(isVaild(n,chessboard,row,i)){chessboard[row][i]='Q';backTracking(n,row+1,chessboard);chessboard[row][i]='.';}}}//将数组转为listList<String> array2List(char[][] chessboard){List<String> result=new ArrayList<>();for(int i=0;i<chessboard.length;i++){StringBuilder temp=new StringBuilder();for(int j=0;j<chessboard[0].length;j++){temp.append(chessboard[i][j]);}result.add(temp.toString());}return result;}public boolean isVaild(int n,char[][] chessboard,int row,int col){//检查列for(int i=row;i>=0;i--){if(chessboard[i][col]=='Q'){return false;}}//45°角for(int i=row-1,j=col+1;i>=0&&j<n;i--,j++){if(chessboard[i][j]=='Q'){return false;}}//135°for(int i=row-1,j=col-1;i>=0&&j>=0;i--,j--){if(chessboard[i][j]=='Q'){return false;}}return true;}
}