🔥博客主页: 我要成为C++领域大神
🎥系列专栏:【C++核心编程】 【计算机网络】 【Linux编程】 【操作系统】
❤️感谢大家点赞👍收藏⭐评论✍️本博客致力于知识分享,与更多的人进行学习交流

访问互斥
引起互斥常见的原因:多线程访问全局资源或静态资源,多线程访问文件数据,多线程使用共享数据引发异常
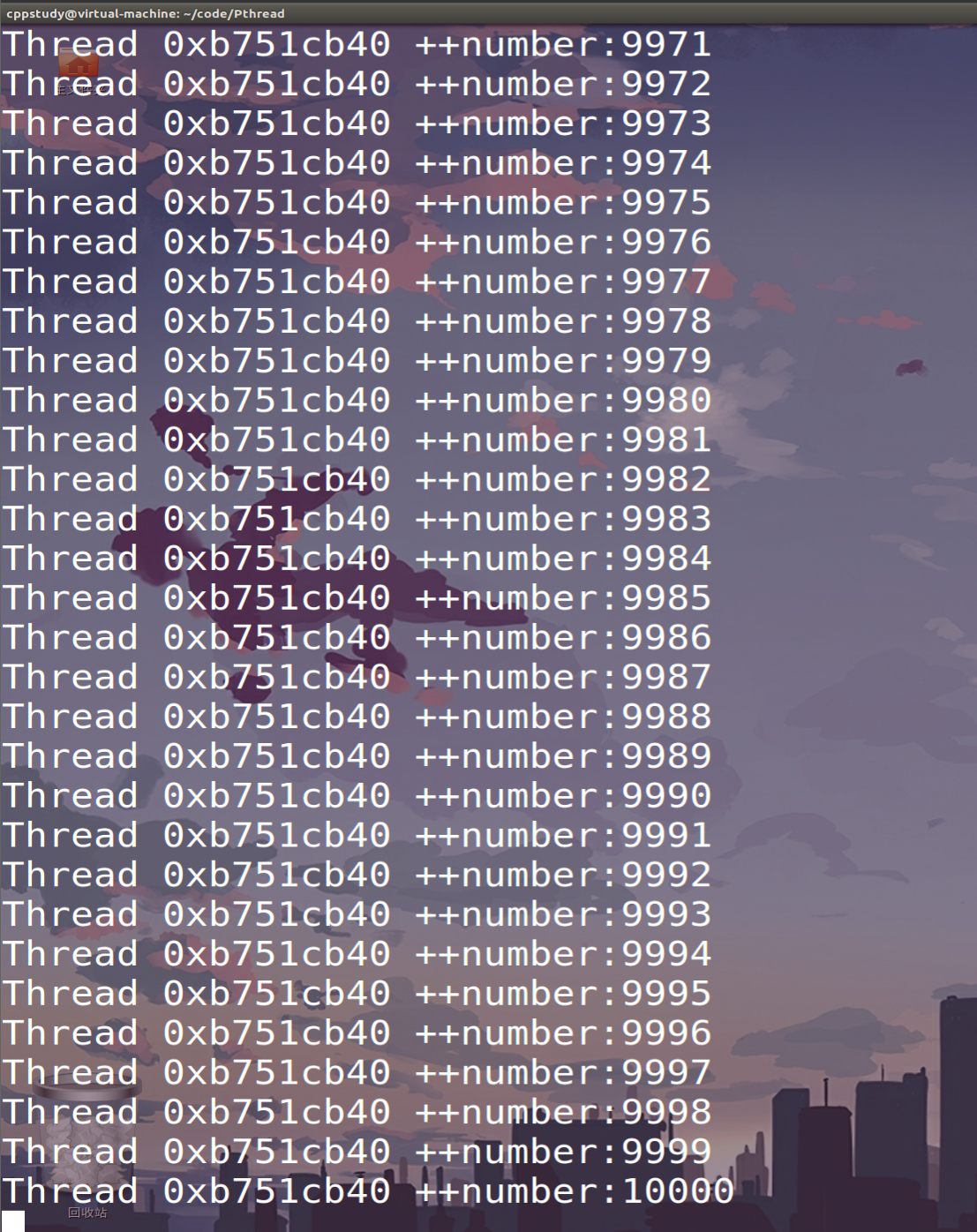
例如两个线程都在对一个全局变量num=0执行加法操作。执行加法需要有三步操作,从寄存器中取出操作数,在算术逻辑单元进行加1,将结果写回寄存器。如果让两个线程执行加法操作,当其中一个线程A的从寄存器中取出了操作数,另外一个线程B已经完成了加1,此时线程A对操作数完成加1,再放回寄存器仍是1。这就会导致两个线程访问全局资源产生互斥。
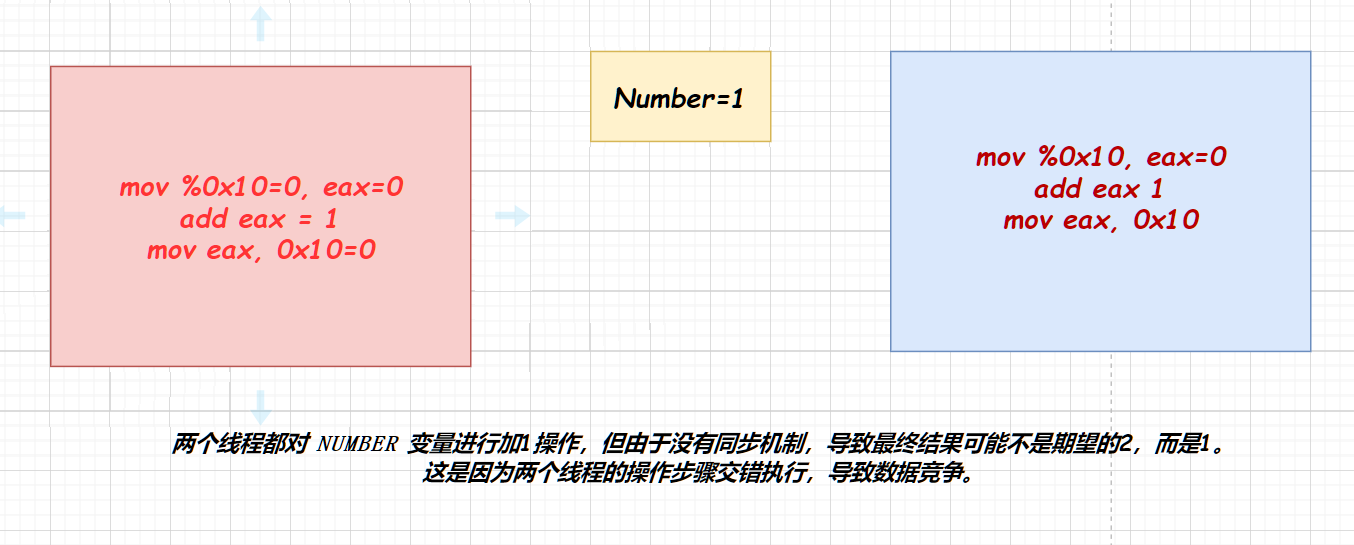
通过下面一个代码可以观察到这一现象:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>int number;
void * thread_job(void * arg)
{int tmp;for(int i=0;i<5000;++i){tmp=number;printf("Thread 0x%x ++number:%d\n",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),++tmp);number=tmp;}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_job,NULL);pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_job,NULL);while(1) sleep(1);return 0;
}
两个线程各对一个全局变量执行5000次加法,结果不可控
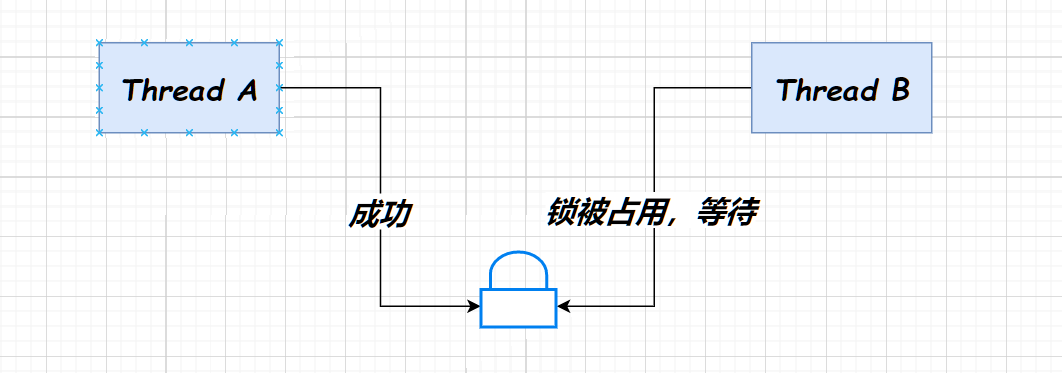
锁
互斥锁
互斥锁可以避免多线程同时访问资源,避免资源异常,结果异常。在读写全局数据时加上锁,读写完成后解锁。
pthread_mutex_t lock 互斥锁的数据类型
关于锁常用的函数:
pthread_mutex_init(&lock,NULL)互斥锁初始化
phtread_mutex_lock(&lock)上锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock)解锁
pthread_mutex_destory(&lock)释放互斥锁
两个线程如果同时使用一个锁,会发送锁被占用,一个线程挂起等待。
加锁的位置很重要,可能改变线程执行流程
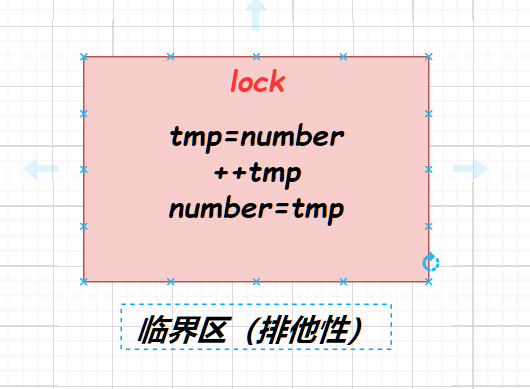
通常情况是全局资源读写时需要上锁
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>pthread_mutex_t lock;//锁需要定义成全局变量,才会对多线程生效
int number;
void * thread_job(void * arg)
{int tmp;for(int i=0;i<5000;++i){pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);tmp=number;printf("Thread 0x%x ++number:%d\n",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),++tmp);number=tmp;pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);}
}int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_mutex_init(&lock,NULL);pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_job,NULL);pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_job,NULL);while(1) sleep(1);return 0;
}
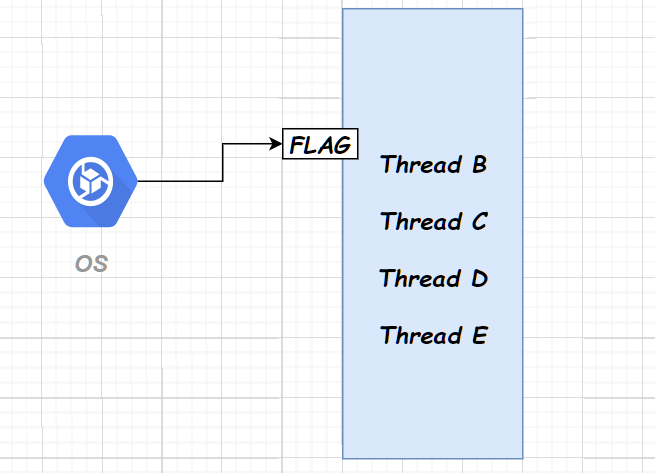
惊群问题
多线程争抢资源,因资源有限,未抢到的线程付出了无意义的系统开销
当一个线程的互斥锁使用完毕后,其他线程都会争抢这个锁, 被唤醒并争夺资源 ,从挂起态回到运行态。当其中一个线程争抢到锁后,其余线程又回到挂起态。造成了无意义的资源浪费和系统开销。
互斥锁等待队列是操作系统和线程库中用于管理等待互斥锁的线程的一个数据结构。它主要解决多线程环境中对共享资源的竞争问题,确保只有一个线程在某一时刻可以访问共享资源,从而避免数据竞争和不一致性。
对优先级高的线程使用标志标记
但是如果正在使用锁的线程释放锁后仍有时间片,它还会占用锁
旋转锁
提高锁的利用率,当多个进程需要同时使用锁时,其他线程不会挂起等待,一直处于运行态R。
读写锁
互斥锁不允许多个线程同时访问资源,资源的利用率较低,读写锁可以解决这个问题,它支持一个线程写资源,多个线程可以同时读资源,提高资源利用率。
特点:读共享,写独占,读写互斥
pthread_rwlock_tlock; 读写锁
pthread_rwlock_init(&lock,NULL)读写锁初始化
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&lock)释放锁
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&lock)读锁上锁
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&lock)写锁上锁
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock)解锁
下面是读写锁使用的demo程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>int number;
pthread_rwlock_t lock;
void *thread_read(void *arg)
{while(1){pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&lock);printf("Read Thread 0x%x Num=%d\n",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),number);pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock);usleep(100000);}}void *thread_write(void *arg)
{while(1){pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&lock);printf("Write Thread 0x%x Num=%d\n",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),++number);pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock);usleep(100000);}
}
int main()
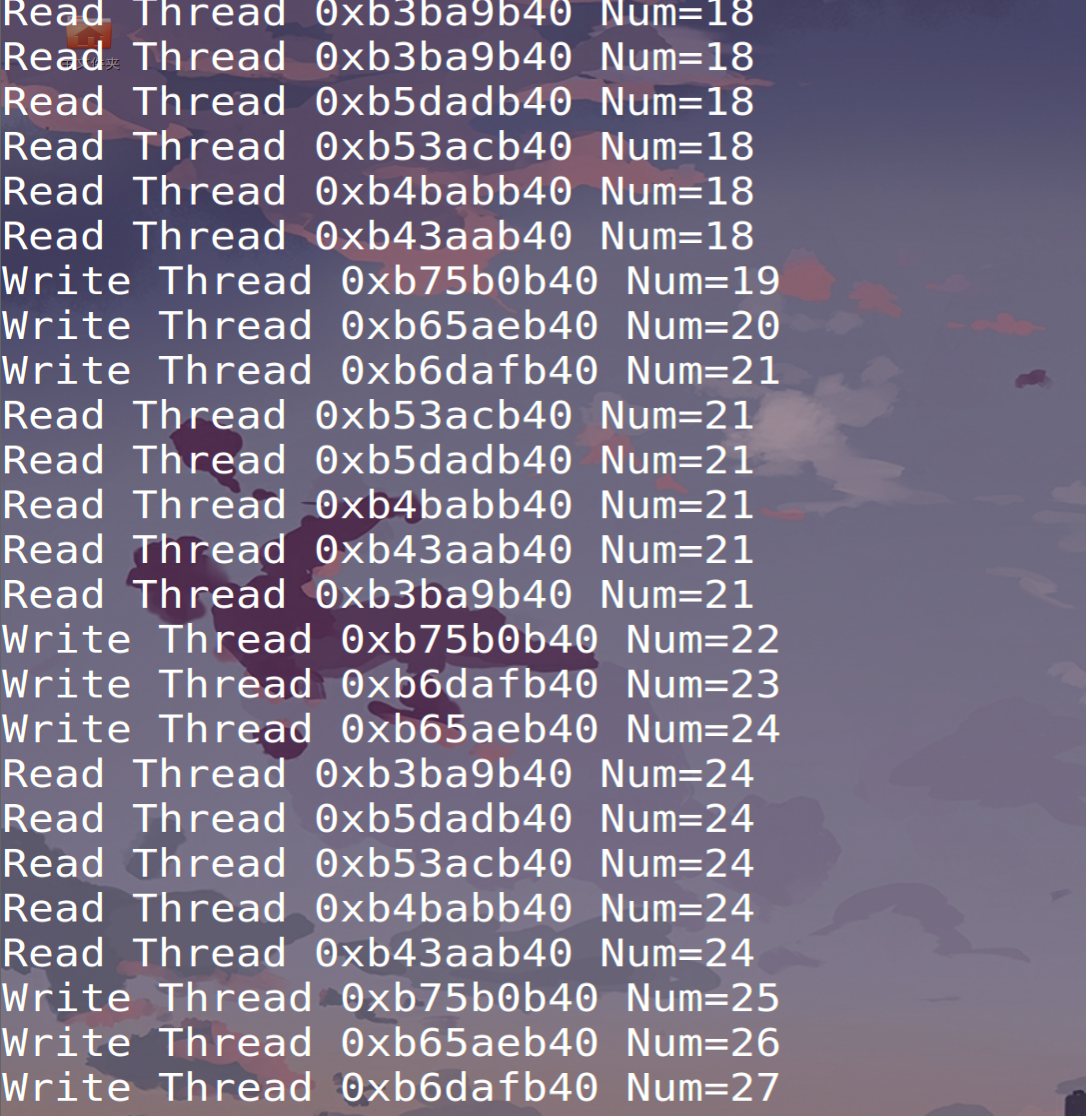
{pthread_t tids[8];pthread_rwlock_init(&lock,NULL);int i;for(i=0;i<3;++i){pthread_create(&tids[i],NULL,thread_write,NULL);}for(i;i<8;++i){pthread_create(&tids[i],NULL,thread_read,NULL);}while(i--){pthread_join(tids[i],NULL);}pthread_rwlock_destroy(&lock);exit(0);}运行结果:写的结果各不相同,读的结果都相同
进程互斥锁
通过修改互斥锁属性可以将线程互斥锁变为进程互斥锁,在进程间使用。
pthread_mutexattr_t互斥锁属性类型,默认情况下属性中均为线程互斥锁
pthread_mutexattr_setpshared(pthread_mutexattr_t* attr,PTHREAD_PROCESS_PRIVATE | PTHREAD_PROCESS_SHARED)修改锁属性中的成员
下面是多进程共享内存,使用了互斥锁来保护共享资源的demo程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <pthread.h>typedef struct {int number;pthread_mutex_t lock;
} shared_t;int main(void) {int fd;fd = open("PROCESS_LOCK", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, 0664);ftruncate(fd, sizeof(shared_t)); // 扩展文件大小shared_t *ptr = NULL;ptr = mmap(NULL, sizeof(shared_t), PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);pid_t pid;// 初始化共享资源ptr->number = 0;pthread_mutexattr_t attr;// 初始化互斥锁属性pthread_mutexattr_init(&attr);// 设为进程间共享互斥锁pthread_mutexattr_setpshared(&attr, PTHREAD_PROCESS_SHARED);// 用属性初始化互斥锁pthread_mutex_init(&ptr->lock, &attr);pid = fork();if (pid > 0) {// 父进程for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {pthread_mutex_lock(&ptr->lock);printf("Parent pid %d: number = %d\n", getpid(), ++(ptr->number));pthread_mutex_unlock(&ptr->lock);}wait(NULL);} else if (pid == 0) {// 子进程for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {pthread_mutex_lock(&ptr->lock);printf("Child pid %d: number = %d\n", getpid(), ++(ptr->number));pthread_mutex_unlock(&ptr->lock);}exit(0);} else {perror("fork call failed");exit(0);}close(fd);pthread_mutexattr_destroy(&attr);pthread_mutex_destroy(&ptr->lock);munmap(ptr, sizeof(shared_t));return 0;
}

文件读写锁
1把写锁,n把读锁,读共享,写互斥,读写互斥
通过修改文件结构体里的文件锁结构体属性来实现上锁和解锁效果。用户需要自定义锁结构体并赋值,而后对文件默认锁结构题=体进行替换,实现文件上锁效果
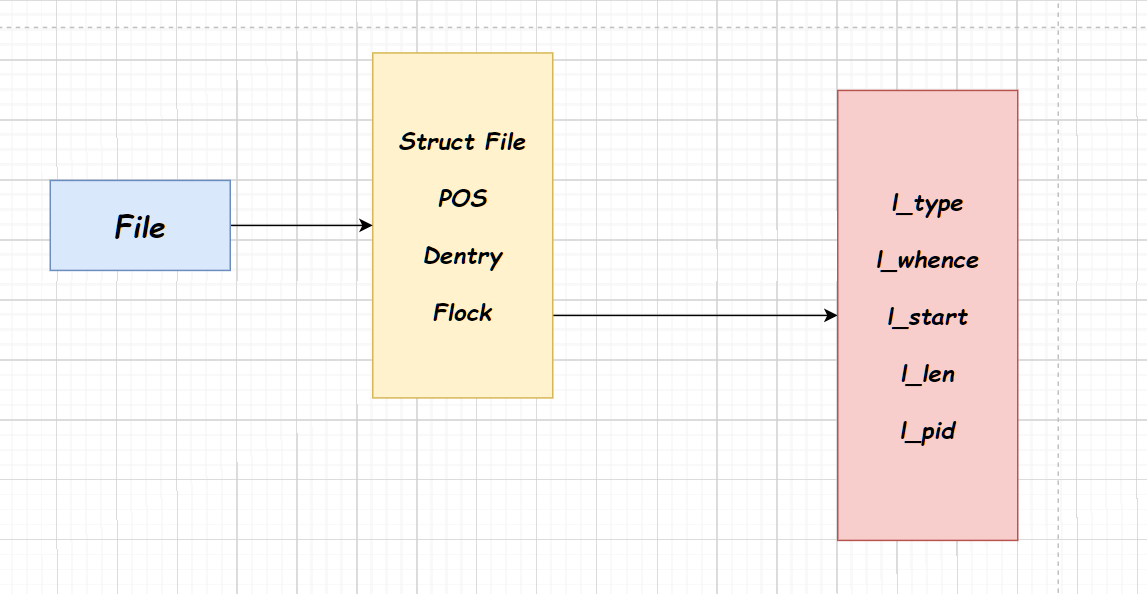

通过查看手册,l_type是锁的类型,有读锁,写锁,未上锁三种状态
l_whence是设置开始加锁的位置(相对于文件整个文件的位置)
l_start是在加锁位置的偏移量
l_len是加锁的长度
l_pid是当前使用锁的进程pid
使用下面这个函数可以设置锁的状态和得到锁的状态,根据第二个参数来判断是得到锁还是上锁。
fcntl(fd,F_GETLK, struct flock * lock)将文件默认的锁结构体传出到lock变量中
fcntl(fd,F_SETLK, struct flock * newlock)将自定义的newlock替换文件原有的锁结构体,实现上锁效果。F_SETLK是非阻塞上锁,F_SETLKW是阻塞上锁关键字,如果文件锁被占用,则会挂起等待。
下面是对文件进行上锁的demo程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>int main()
{int fd=open("file_test",O_RDWR);struct flock old;fcntl(fd,F_GETLK,&old);//if(old.l_type==F_UNLCK)//{printf("file_test lock status:F_UNLOCK\n");struct flock newlock;newlock.l_type=F_WRLCK;newlock.l_whence=SEEK_SET;newlock.l_start=0;newlock.l_len=0;fcntl(fd,F_SETLKW,&newlock);printf("Process A %d set file_test lock status:F_WRLCK\n",getpid());sleep(10);newlock.l_type=F_UNLCK;fcntl(fd,F_SETLKW,&newlock);printf("Process A %d set file_test lock status:F_UNLCK\n",getpid());//}//else//printf("file_test lock status:F_WRLCK\n");return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>int main()
{int fd=open("file_test",O_RDWR);struct flock newlock;newlock.l_type=F_WRLCK;newlock.l_whence=SEEK_SET;newlock.l_start=0;newlock.l_len=0;fcntl(fd,F_SETLKW,&newlock);printf("Process B %d set file_test lock status:F_WRLCK\n",getpid());return 0;
}
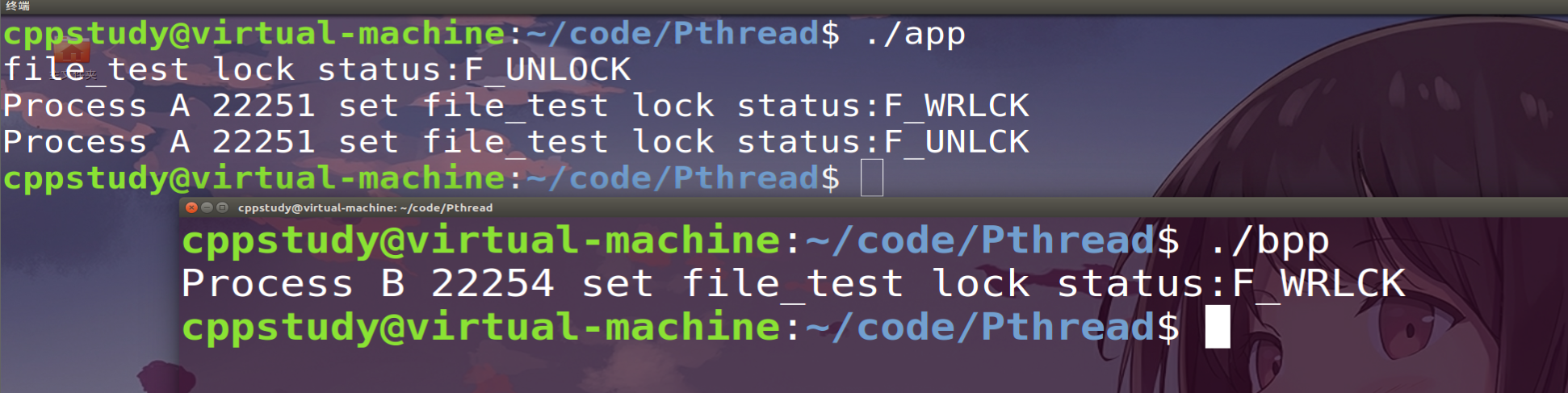
运行结果:F_SETLKW是阻塞上锁关键字,文件锁被进程A占用,进程B挂起等待

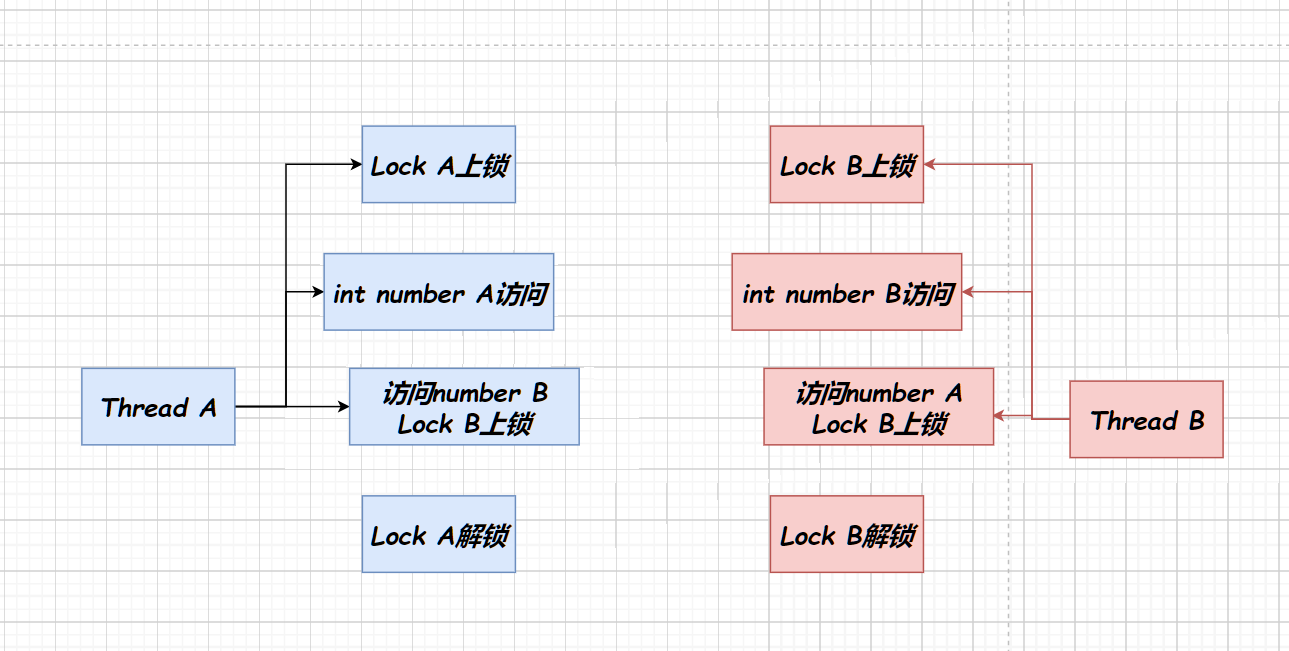
死锁问题
锁资源有限,但多线程相互请求锁资源,导致线程永久阻塞,这种现象称为死锁。
死锁发送的四个必要条件:
请求与保持条件:某个线程在占用一把锁后还要请求新锁,容易引发死锁问题
不可剥夺条件:除了占用资源的线程外,其他人无法解锁资源
互斥条件:某个线程占用锁资源后,其他线程申请则挂起等待
环路等待条件:每个线程都在等待相邻线程手中的资源,这种称为等待环路
下面是产生死锁问题的demo程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>pthread_mutex_t lockA,lockB;
int numA=5;
int numB=6;
void *thread_jobA(void* arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&lockA);printf("numA = %d\n",numA);sleep(0);pthread_mutex_lock(&lockB);printf("numA + numB = %d\n",numA+numB);pthread_mutex_unlock(&lockB);pthread_mutex_unlock(&lockA);
}void *thread_jobB(void* arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&lockB);printf("numB = %d\n",numB);sleep(0);pthread_mutex_lock(&lockA);printf("numA + numB = %d\n",numA+numB);pthread_mutex_unlock(&lockA);pthread_mutex_unlock(&lockB);
}int main()
{pthread_mutex_init(&lockA,NULL);pthread_mutex_init(&lockB,NULL);pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_jobA,NULL);pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_jobB,NULL);while(1) sleep(1);return 0;
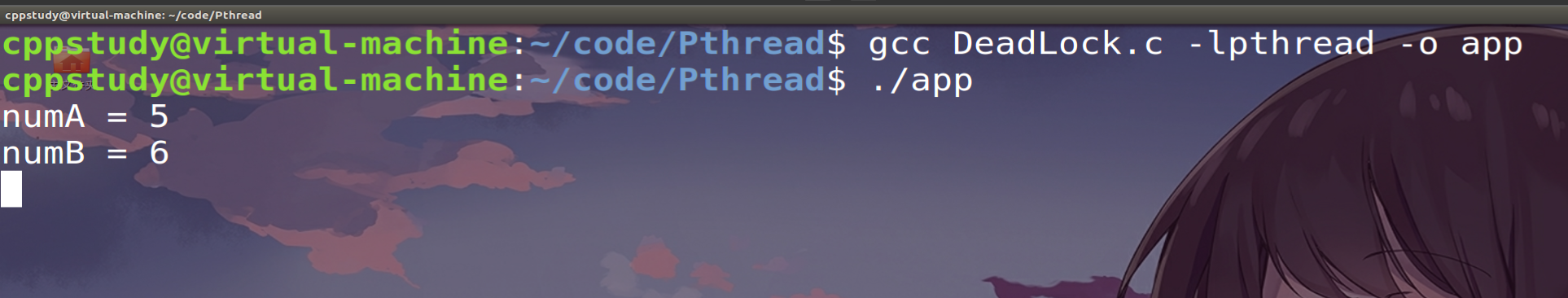
}线程A因线程B占用锁而挂起,线程B因线程A占用锁而挂起。两个线程都没有打印第二行输出。
死锁处理
产生死锁后,杀死死锁线程,解除死锁,而后再创建(死锁频繁,创建销毁线程开销较大)
死锁检测
有向图检测
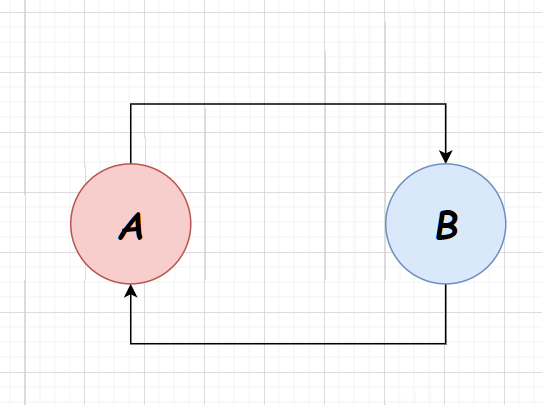
可以通过图的遍历算法检测出图中是否出现环路,如果是则已发生死锁,可以通过杀死线程的方式杀死某个节点,解除死锁。
死锁预防
哲学家就餐问题
有五个哲学家,他们围坐在一张圆桌旁,桌上摆放着五个盘子和五根筷子。哲学家们的生活方式是交替进行思考和进餐。为了进餐,哲学家需要两根筷子,因此每个哲学家必须同时从自己左右两侧拿起筷子才能进餐。哲学家放下筷子时,思考开始。
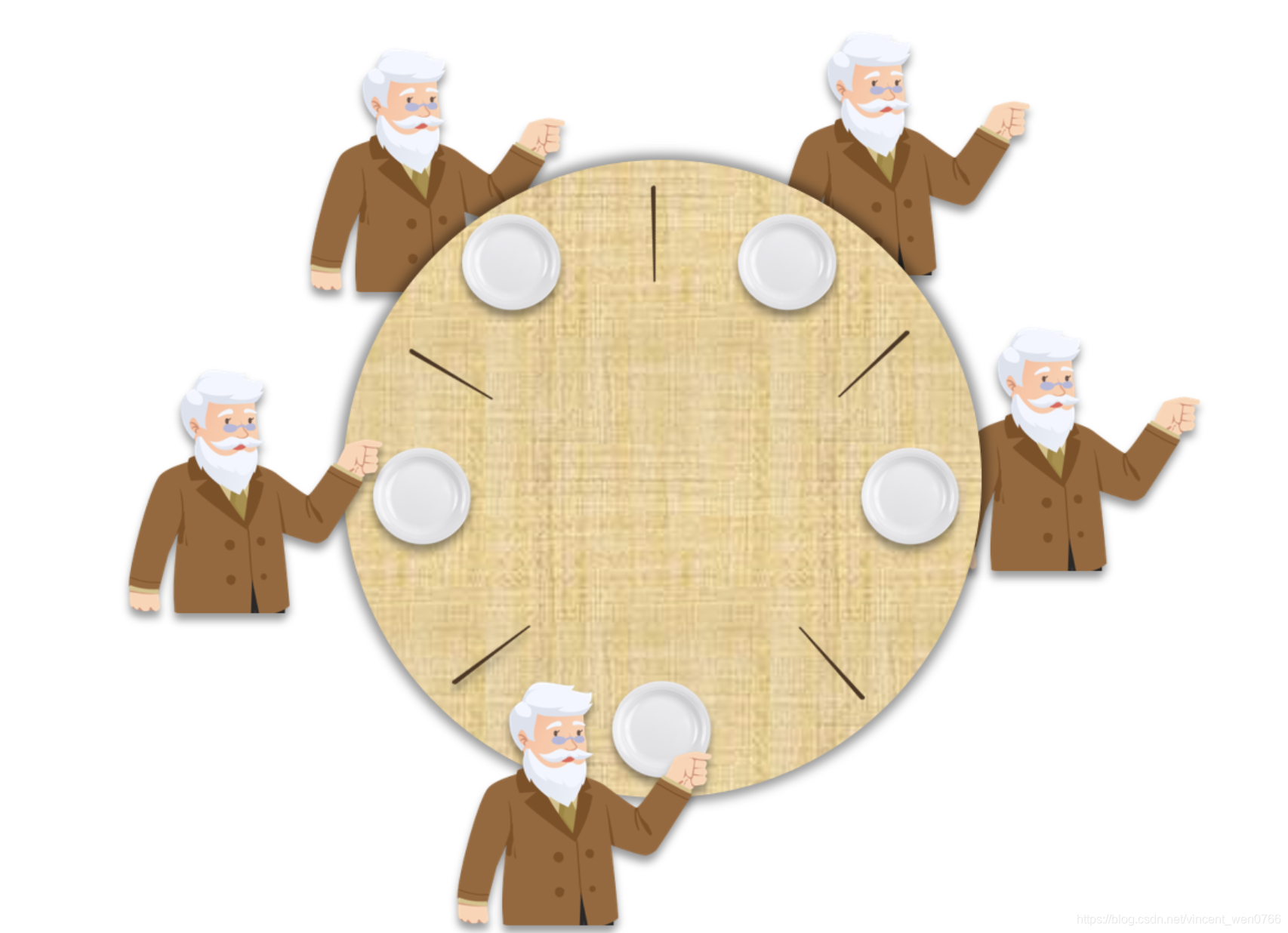
死锁:如果每个哲学家拿起自己右边的筷子,并等待左边的筷子,那么他们将永远等待下去,这就形成了死锁。
饥饿:某个哲学家可能一直无法得到两根筷子进餐,导致饿死。
资源竞争:哲学家们同时拿筷子的动作需要同步,以防止出现竞争条件。
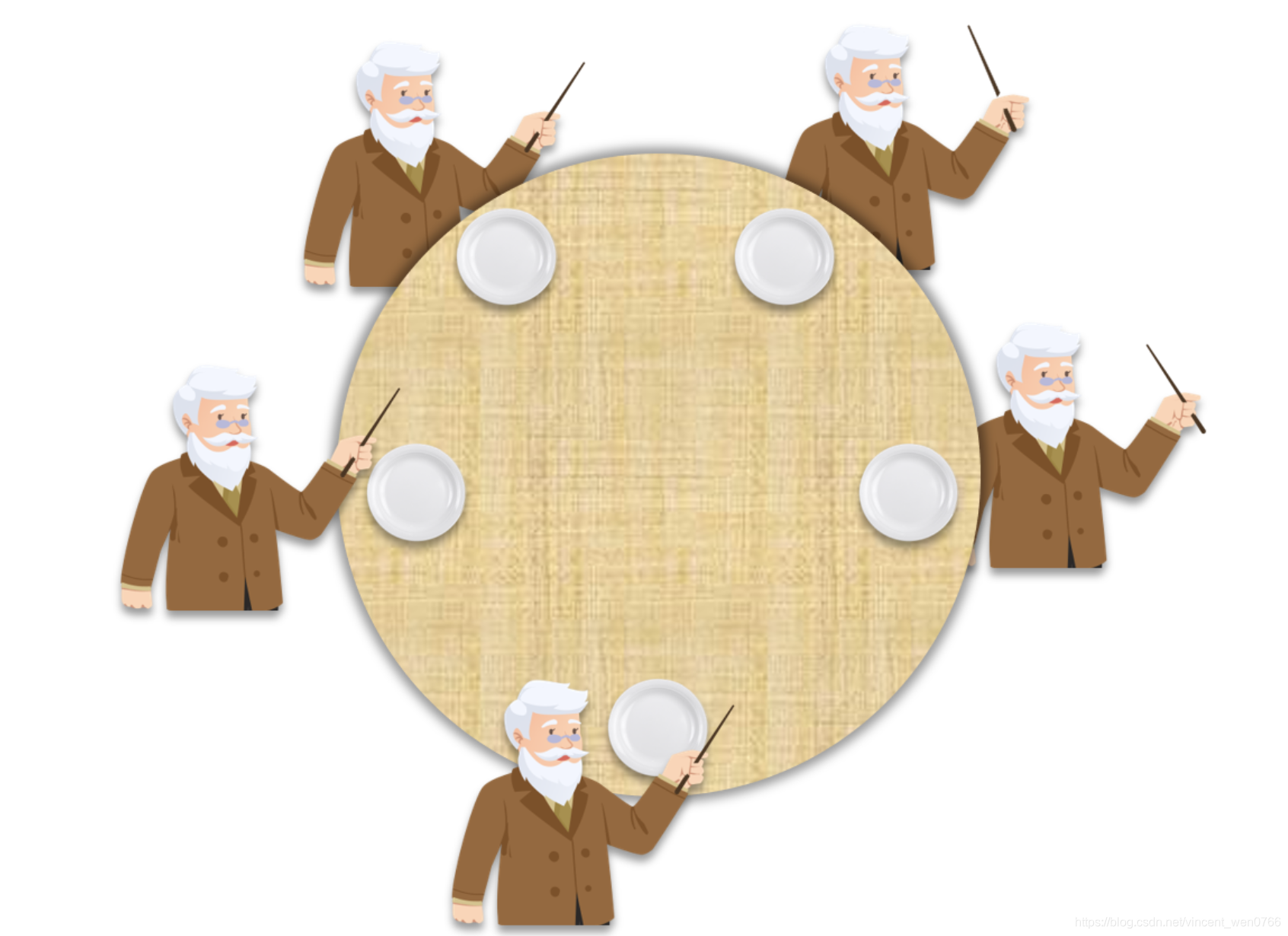
解锁死锁问题的方法
礼貌策略:当某个哲学家拿起左手的资源,发现无法获取右手的资源,它会放下左手资源,让其他人就餐
活锁问题:如果哲学家同时频繁触发礼貌机制,导致所有哲学家拿起放下餐具,无法进食,饿死
高权级策略:选中一名哲学家提高权限,此哲学家要进餐时,向相邻哲学家发送通知,让其放下资源
高权策略:由于优先级转换,可能导致多数时间,只有超级哲学家在就餐
银行家算法
银行家算法是一种避免死锁的算法,它通过模拟资源分配,检查在给定资源分配之后,系统是否会进入安全状态。如果会进入安全状态,则分配资源,否则不分配。
银行家算法将资源都抽象为银行资产,每个用户借款,银行进行借款风险评估,如果风险超出阈值,禁止放款
线程控制(条件变量)
条件变量技术实现线程的挂起和唤醒。为线程指定执行条件,按执行条件挂起和唤醒线程。
条件变量类型 pthread_cond_t 线程可以在条件变量上挂起,也可以从中唤醒。
相关函数
pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *cd,NULL)初始化条件变量
pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t* cd,NULL)销毁条件变量
pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t* cd, pthread_mutex_t *lock)
两次执行:
线程第一次执行wait函数,挂起线程的同时解锁互斥锁。
线程被唤醒的同时执行wait,上锁互斥锁
pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t * cd)唤醒一个挂起在cd中的线程
pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t * cd)唤醒所有挂起在cd中的线程
signal函数的误唤醒,如果系统是多核处理器CPU,signal函数可能唤醒多个CPU,导致误唤醒。
下面这段demo程序实现了条件控制线程交替工作
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>int day_night;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t cond;void * threadA_job(void *arg)
{while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);while(day_night==0){pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&lock);}printf("Thread A TID 0x%x is working,working state:%d\n",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),day_night);--day_night;pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);pthread_cond_signal(&cond);}
}void * threadB_job(void *arg)
{while(1){pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);while(day_night){pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&lock);}printf("Thread B TID 0x%x is working,working state:%d\n",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),day_night);++day_night;pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);pthread_cond_signal(&cond);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid,NULL,threadA_job,NULL);pthread_create(&tid,NULL,threadB_job,NULL);while(1) sleep(1);return 0;
}
生产者消费者
经典的数据传递或任务传递模型
生产者:任务队列为满挂起,非满则添加数据
生产者生产任务后,通知一个消费者,让它获取任务
消费者:任务队列为空挂起,非空则获取任务执行
消费者获取任务后,唤醒一个生产者
需要两个条件变量
Not_Full Not_Null
遍历时使用环形队列实现

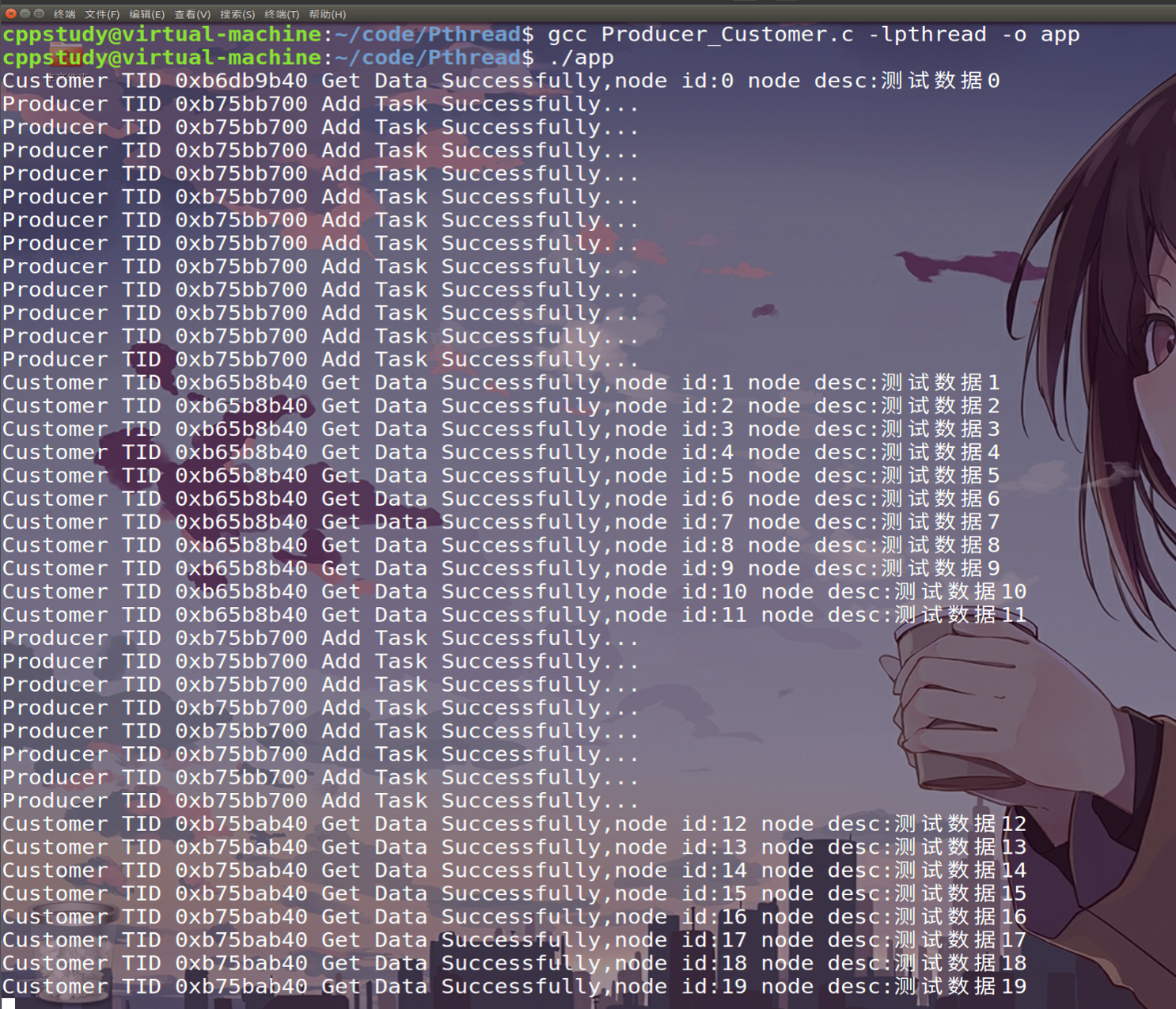
下面是实现生产者消费者的demo程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t Not_Full;
pthread_cond_t Not_Empty;typedef struct
{int id;char desc[1024];
}data_t;typedef struct
{data_t * container;int Front;int Rear;int Max;int Cur;
}queue_t;queue_t * Create_queue(int Max)
{queue_t * que=(queue_t *)malloc(sizeof(queue_t));que->Front=0;que->Rear=0;que->Max=Max;que->Cur=0;que->container=(data_t*)malloc(sizeof(data_t)*Max);return que;
}void * Customer_job(void * arg)
{pthread_detach(pthread_self());queue_t *que=(queue_t*)arg;data_t node;while(1){while(que->Cur==0){pthread_cond_wait(&Not_Empty,&lock);}node=que->container[que->Rear];printf("Customer TID 0x%x Get Data Successfully,node id:%d node desc:%s\n",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),node.id,node.desc);--(que->Cur);que->Rear=(que->Rear+1)%que->Max;pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);pthread_cond_signal(&Not_Full);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main()
{pthread_t tid[3];if(pthread_mutex_init(&lock,NULL)!=0 || pthread_cond_init(&Not_Empty,NULL)!=0 || pthread_cond_init(&Not_Full,NULL)!=0){printf("init failed\n");exit(0);}queue_t * que=Create_queue(100);data_t node;for(int i=0;i<3;++i){pthread_create(&tid[i],NULL,Customer_job,(void*)que);}//生产者循环添加任务for(int i=0;i<20;++i){node.id=i;bzero(node.desc,sizeof(node.desc));sprintf(node.desc,"测试数据%d",i);pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);que->container[que->Front]=node;que->Front=(que->Front+1)%que->Max;++que->Cur;pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);pthread_cond_signal(&Not_Empty);printf("Producer TID 0x%x Add Task Successfully...\n",(unsigned int)pthread_self());}while(1)sleep(1);return 0;
}