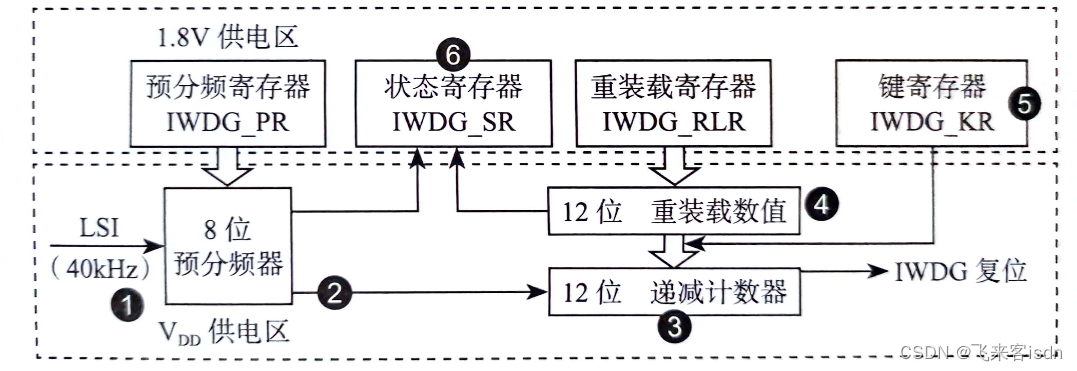
实现一个字符串类String,为其提供可接受C风格字符串的构造函数、析构函数、拷贝构造函数和拷贝赋值函数。
声明依赖文件
其中ostream库用于打印标准输入输出,cstring库为C风格的字符串库
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>声明命名空间
using namespace std;构造String类
声明私有的字符串指针成员
private:char * str;C风格构造函数
构造函数的参数为const类型的字符串指针。
构造函数的内容根据字符串的长度来向堆申请空间,随后将str的字符串内容拷贝给strcpy。
String(const char *str)
{this->str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];strcpy(this->str,str);
}拷贝构造函数
参数为String类对象的引用,根据对象的str的长度来向堆申请空间,随后将str的字符串内容拷贝给strcpy。
String(const String&that)
{str = new char[strlen(that.str) + 1];strcpy(str,that.str);
}深拷贝赋值函数
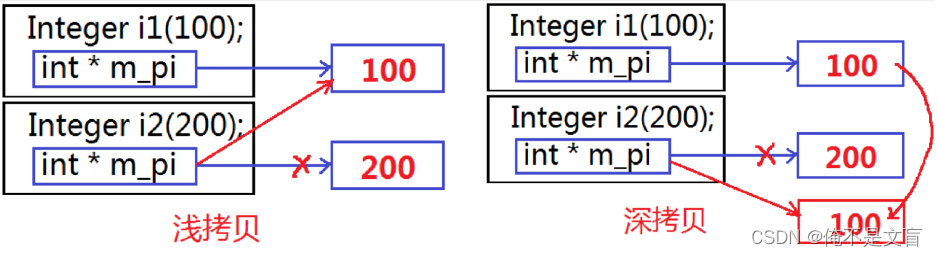
当两对象进行赋值操作时,比如“i2=i1”编译器会将其处理为“i2.operator=(i1) 的成员函数调用形式”,
其中“operator=”称为拷贝赋值操作符函数,由该函数完成赋值运算,返回结果就是表达式的结果。
如果没有自己定义拷贝赋值操作符函数,编译器会为该类提供缺省的拷贝赋值操作符函数,用于完成两个对象的赋值操作。
但是编译器提供的缺省拷贝赋值函数,和缺省拷贝构造函数类似,也是浅拷贝,有“double free”和“内存泄漏”的问题,这时需要自定义深拷贝赋值函数。
String & operator = (const String & that)
{if(this != &that){/*释放掉this对象原来的堆空间*/delete [] str;str = new char[strlen(that.str) + 1];strcpy(str,that.str);}return *this;
}完整代码
class String
{
public:String(const char *str){this->str = new char[strlen(str) + 1];strcpy(this->str,str);}String(const String&that){str = new char[strlen(that.str) + 1];strcpy(str,that.str);}void print(void){cout << str << endl;}String & operator = (const String & that){if(this != &that){/*释放掉this对象原来的堆空间*/delete [] str;str = new char[strlen(that.str) + 1];strcpy(str,that.str);}return *this;}~String(){delete []str;}const char * c_str(){return str;}
private:char * str;
};测试
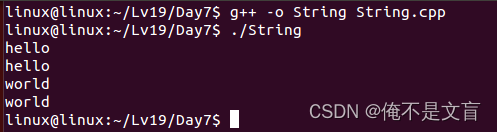
接下来编写main函数进行测试。
int main(void)
{String s1 = "hello";s1.print();String s2 = s1;s2.print();String s3 = "world";s2 = s3;s2.print();cout << s3.c_str() << endl;return 0;
}
s2在构造时调用拷贝构造函数 ,所以先打印为hello,
后面进行了s2=s3,为深拷贝构造函数,s2的str成员内容变为"world\0"。