二叉树
- 一.快速创建一颗二叉树
- 二.二叉树的遍历
- 1.前序、中序、后序遍历(深度优先遍历DFS)
- 2.层序遍历(广度优先遍历BFS)
- 三.二叉树节点的个数
- 四.二叉树叶子节点的个数
- 五.二叉树的高度
- 六.二叉树第k层节点个数
- 七.二叉树查找值为x的节点
- 八.判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
- 九.二叉树的递归创建
- 十.二叉树的销毁
- 十一.二叉树必做OJ题
- 十二.了解高级树
一.快速创建一颗二叉树
-
回顾⼆叉树的概念,⼆叉树分为空树和非空⼆叉树,非空⼆叉树由根结点、根结点的左子树、根结点的右子树组成的
-
根结点的左子树和右子树分别又是由子树结点、子树结点的左子树、子树结点的右子树组成的,因此
⼆叉树定义是递归式的,后序链式⼆叉树的操作中基本都是按照该概念实现的。

typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{BTDataType data;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));if (node == NULL){perror("malloc fail!");return;}node->data = x;node->left = node->right = NULL;return node;
}BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);node1->left = node2;node1->right = node4;node2->left = node3;node4->left = node5;node4->right = node6;return node1;
}int main()
{BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();return 0;
}
二.二叉树的遍历
1.前序、中序、后序遍历(深度优先遍历DFS)
按照规则,⼆叉树的遍历有:前序/中序/后序的递归结构遍历:
-
前序遍历:访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前;访问顺序为:根结点、左子树、右子树
-
中序遍历:访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树中间;访问顺序为:左子树、根结点、右子树
-
后序遍历:访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后;访问顺序为:左子树、右子树、根结点
参考如下:

代码如下:
//前序遍历
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}printf("%d ", root->data);PrevOrder(root->left);PrevOrder(root->right);
}//中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}InOrder(root->left);printf("%d ", root->data);InOrder(root->right);
}//后序遍历
void PosOrder(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL){printf("NULL ");return;}PosOrder(root->left);PosOrder(root->right);printf("%d ", root->data);
}int main()
{BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();PrevOrder(root);printf("\n");InOrder(root);printf("\n");PosOrder(root);printf("\n");return 0;
}
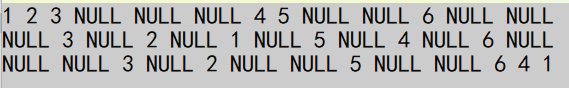
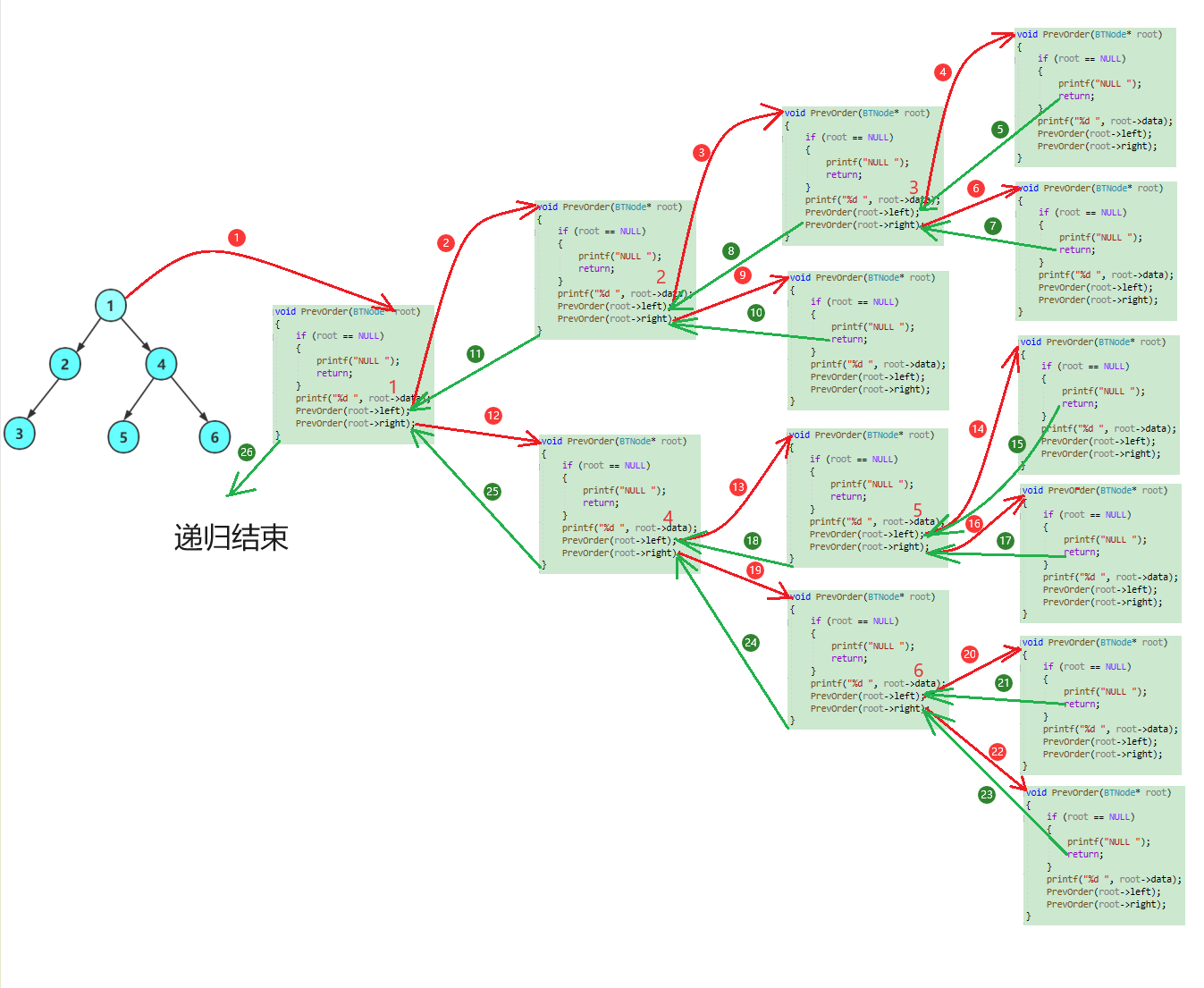
前序遍历递归图解:

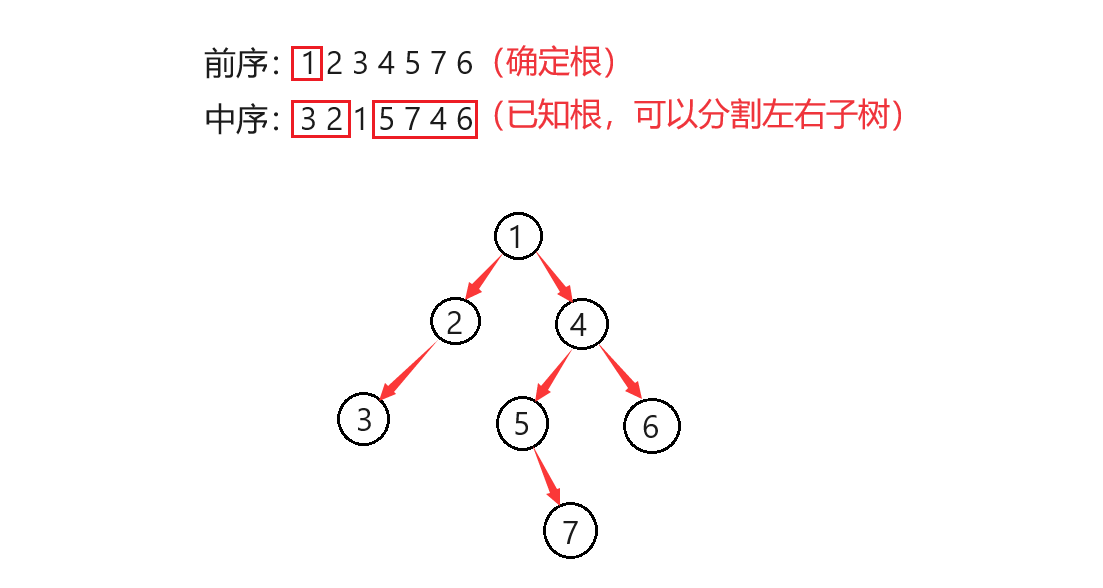
注意:已知二叉树的前序和中序,后序和中序就可以推导出二叉树的形状,但是只知道前序和后序则无法推导出二叉树的形状。
2.层序遍历(广度优先遍历BFS)
层序遍历:除了先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历外,还可以对二叉树进行层序遍历。设二叉树的根结点所在层数为1,层序遍历就是从所在二叉树的根结点出发,首先访问第一层的树根结点,然后从左到右访问第2层上的结点,接着是第三层的结点,以此类推,自上而下,自左至右逐层访问树的结点的过程就是层序遍历。
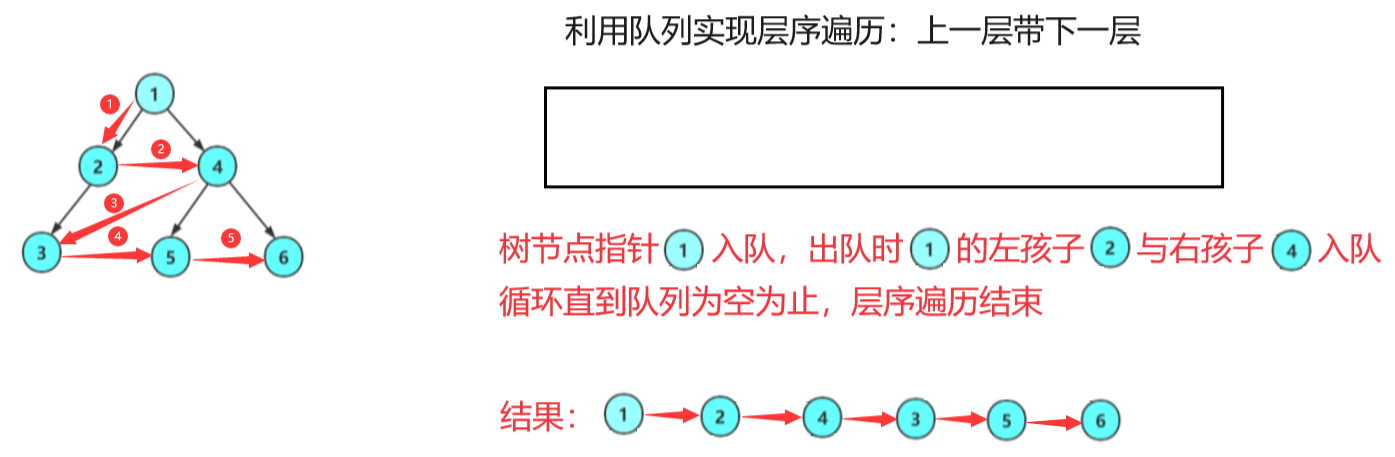
实现层序遍历需要用到队列,拷贝Queue.h与Queue.c文件到本地。
void TreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if(root)QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);printf("%d ", front->val);// NULL无需入队列if(front->left)QueuePush(&q, front->left);if (front->right)QueuePush(&q, front->right);}QueueDestory(&q);
}
三.二叉树节点的个数
错误写法:

改进方法:


最好的方法:分治法(大问题化为多个小问题、小问题再化为多个小问题…直到不能再分为止)
- 空:0个
- 非空:左子树+右子树+1
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;return TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
四.二叉树叶子节点的个数
- 空:0个
- 非空:若左子树和右子树同时为空返回1,否则左子树叶子节点+右子树叶子节点
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)return 1;return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
五.二叉树的高度
- 空:0个
- 非空:MAX {左子树高度,右子树高度} + 1
//未记录高度导致重复大量的递归效率极低
//int TreeHeight1(BTNode* root)
//{
// if (root == NULL)
// return 0;
//
// return TreeHeight(root->left) > TreeHeight(root->right) ?
// TreeHeight(root->left) + 1 : TreeHeight(root->right) + 1;
//}int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);return leftHeight > rightHeight ?leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
六.二叉树第k层节点个数
- 空:0个
- 非空且k==1:返回1
- 非空且k>1:左子树的k-1层节点个数+右子树的k-1层节点个数
int TreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{if (root == NULL)return 0;if (k == 1)return 1;return TreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + TreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
七.二叉树查找值为x的节点
- 空:返回NULL
- 非空且data==x:返回root
- 非空且data!=x:递归左子树+递归右子树,注意:
要保存递归的结果层层返回
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{if (root == NULL)return NULL;if (root->data == x)return root;BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);if (ret1)return ret1;BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);if (ret2)return ret2;return NULL;
}
八.判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
注意:满二叉树可以利用树的高度,和节点的个数判断,但是完全二叉树前k-1层是满二叉树,最后一层不是满的,该方法就不行了。
可以利用层序遍历解决,方法如下:
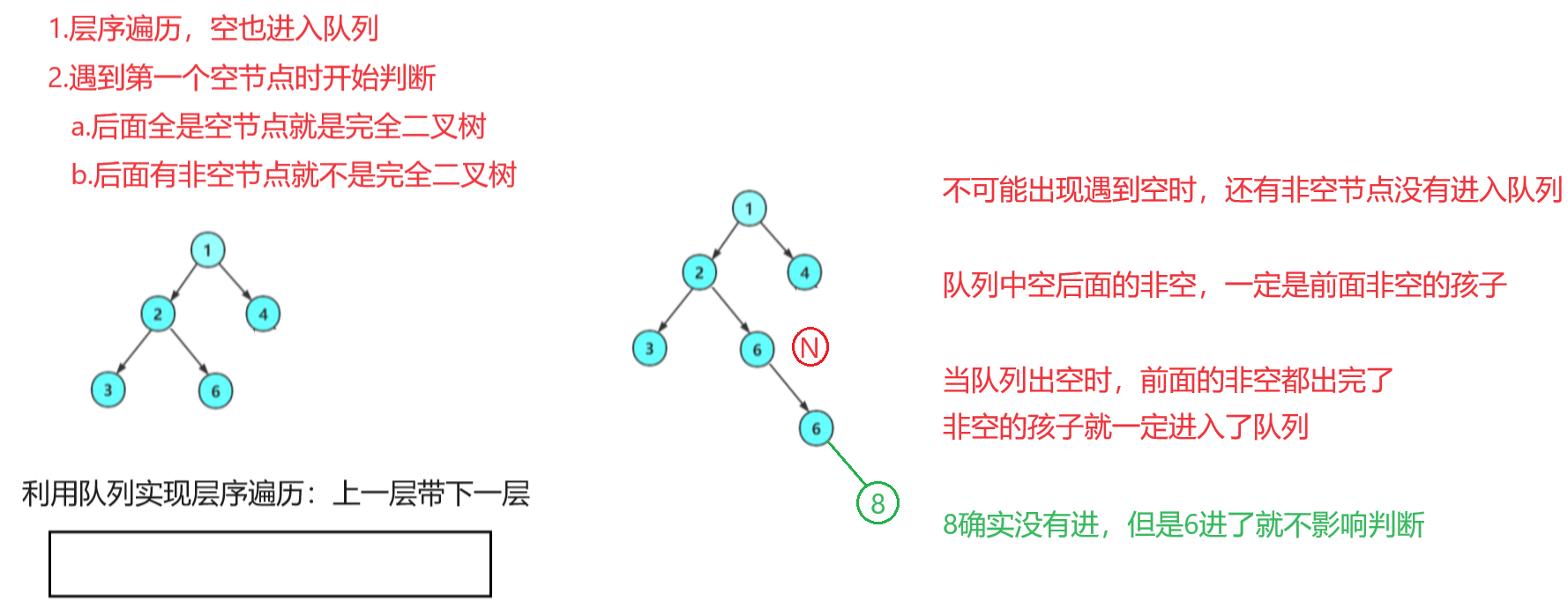
bool TreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{Queue q;QueueInit(&q);if(root)QueuePush(&q, root);while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//遇到第一个空,开始判断if (front == NULL)break;QueuePush(&q, front->left);QueuePush(&q, front->right);}while (!QueueEmpty(&q)){BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);QueuePop(&q);//队列中还有非空节点,就不是完全二叉树if (front){QueueDestory(&q);return false;} }//队列中没有非空节点,就是完全二叉树QueueDestory(&q);return true;
}
九.二叉树的递归创建
题目:已知前序遍历结果:abc##de#g##f###(其中#是NULL)
输出:中序遍历的结果(不包含NULL)
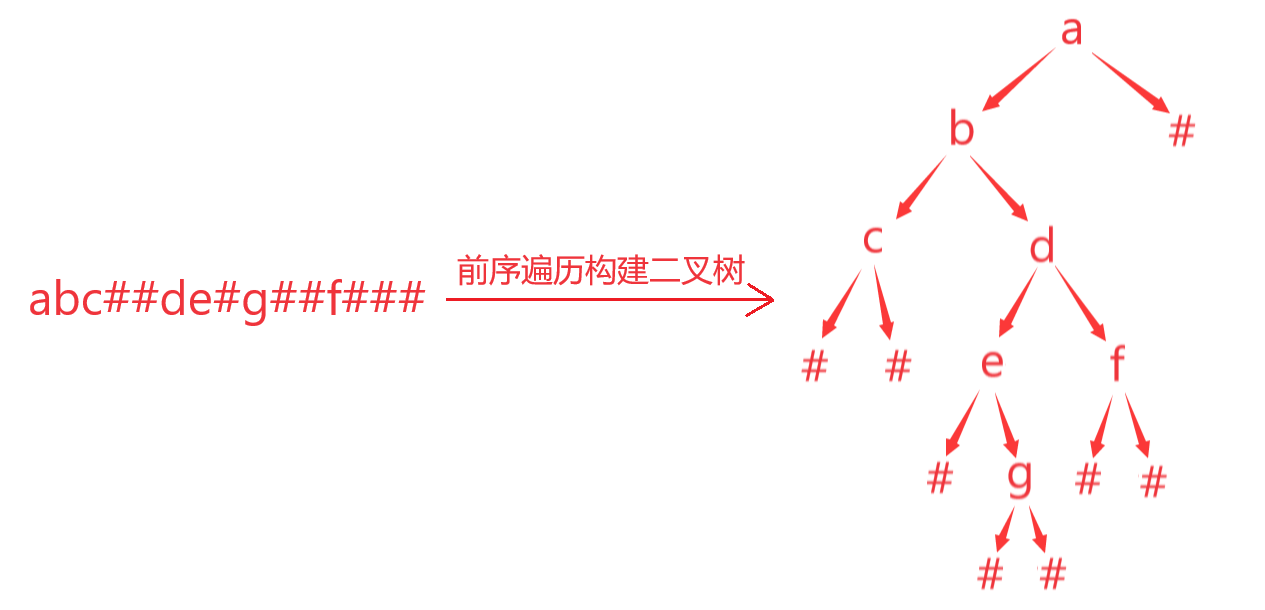
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{char val;struct BinaryTreeNode* left;struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;BTNode* CreateTree(char* a, int* pi)
{//遇到#返回NULLif(a[*pi] == '#'){(*pi)++;return NULL;}//创建根节点BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));root->val = a[(*pi)++];//递归构建左子树root->left = CreateTree(a, pi);//递归构建右子树root->right = CreateTree(a, pi);//返回根节点return root;
}void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{if(root == NULL)return;InOrder(root->left);printf("%c ", root->val);InOrder(root->right);
}int main() {char a[100];scanf("%s", a);int i = 0;BTNode* root = CreateTree(a, &i); //注意:要传入地址InOrder(root);
}
十.二叉树的销毁
- 空:返回NULL
- 非空:后序遍历销毁节点
void TreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{if (root == NULL)return;TreeDestory(root->left);TreeDestory(root->right);free(root);
}
十一.二叉树必做OJ题
- 单值二叉树
- 相同的树
- 对称二叉树
- 二叉树的前序遍历
- 二叉树的中序遍历
- 二叉树的后序遍历
- 另一棵树的子树
- 二叉树遍历
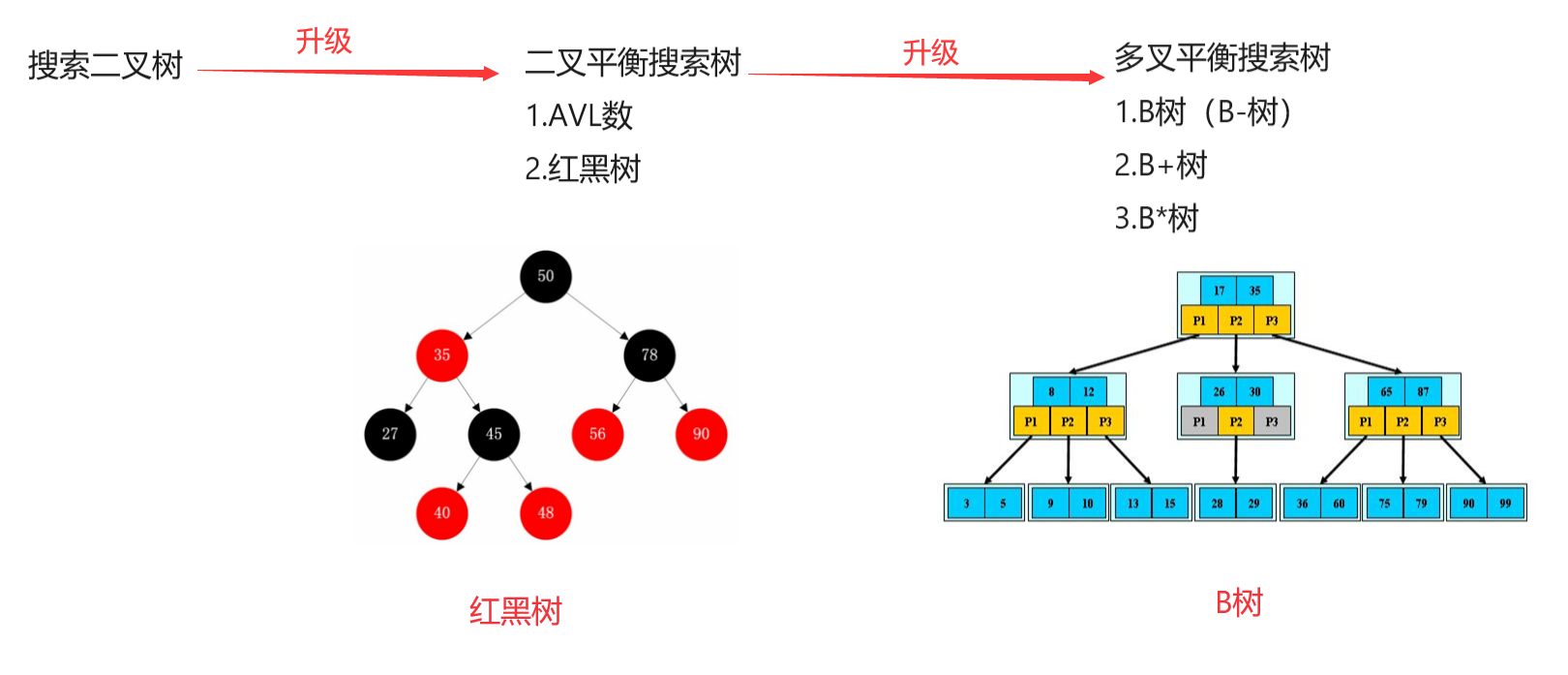
十二.了解高级树










![Python入门级[ 基础语法 函数... ] 笔记 例题较多](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/b86fedcf0cab4a289afacace4215ec56.png)