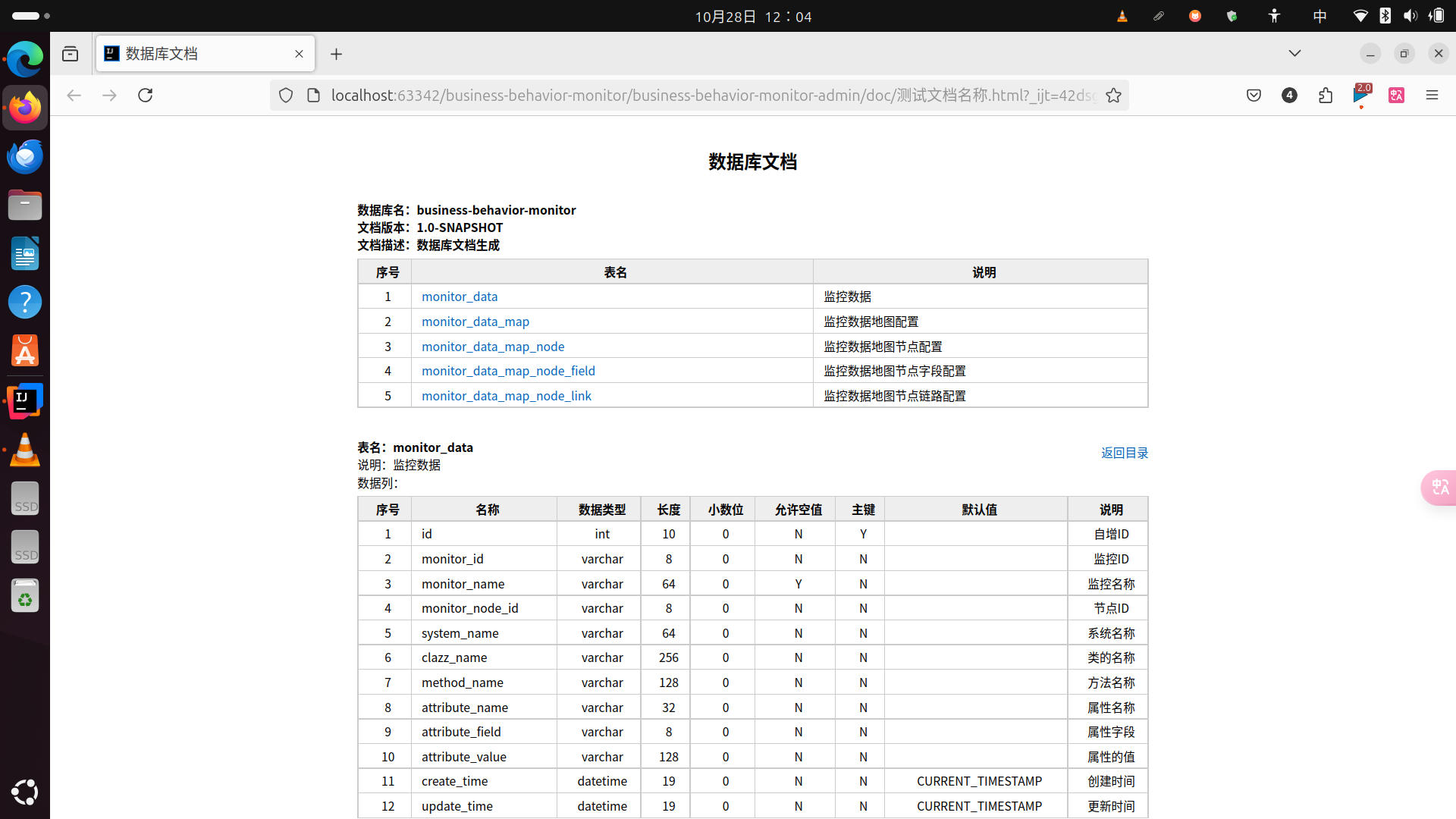
文章目录
- 一、Apply Family
- 二、`apply()`: rows or columns of a matrix or data frame
- 三、Applying a custom function
- 四、Applying a custom function "on-the-fly"
- 五、Applying a function that takes extra arguments
- 六、What's the return argument?
- 七、Optimized functions for special tasks
- 八、`lapply`: elements of a list or vector
- 九、`sapply()`: elements of a list or vector
- 十、`tapply()`: levels of a factor vector
- 十一、`split()`: split by levels of a factor
一、Apply Family
R offers a family of apply functions, which allow you to apply a function across different chunks of data. Offers an alternative to explicit iteration using for() loop; can be simpler and faster, though not always. Summary of functions:
apply(): apply a function to rows or columns of a matrix or data framelapply(): apply a function to elements of a list or vectorsapply(): same as the above, but simplify the output (if possible)tapply(): apply a function to levels of a factor vector
二、apply(): rows or columns of a matrix or data frame
The apply() function takes inputs of the following form:
apply(x, MARGIN=1, FUN=my.fun), to applymy.fun()across rows of a matrix or data framexapply(x, MARGIN=2, FUN=my.fun), to applymy.fun()across columns of a matrix or data framex
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=sum) # Minimum entry in each column
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 212321.00 221790.00 58.50 3543.93 368.90 2655.40
## Frost Area
## 5223.00 3536794.00colSums(state.x77)
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 212321.00 221790.00 58.50 3543.93 368.90 2655.40
## Frost Area
## 5223.00 3536794.00
- When output of the function passed to
FUNis a single value,apply()output a vector across the columns/rows
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=which.max) # Index of the max in each column
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 5 2 18 11 1 44
## Frost Area
## 28 2
- When output of the function passed to
FUNis a vector,apply()output a matrix across the columns/rows
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=summary)

三、Applying a custom function
For a custom function, we can just define it before hand, and the use apply() as usual
# Our custom function: second largest value
second.max = function(v) { sorted.v = sort(v,decreasing = T)return(sorted.v[2])
}apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=second.max)
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 18076.00 5348.00 2.40 72.96 13.90 66.70
## Frost Area
## 186.00 262134.00apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=max)
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 21198.0 6315.0 2.8 73.6 15.1 67.3
## Frost Area
## 188.0 566432.0
四、Applying a custom function “on-the-fly”
Instead of defining a custom function before hand, we can define it “on-the-fly”.
# Compute trimmed means, defining this on-the-fly
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=function(v) { sorted.v = sort(v,decreasing = T)return(sorted.v[2])
})## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 18076.00 5348.00 2.40 72.96 13.90 66.70
## Frost Area
## 186.00 262134.00
- When the custom function is simple, this can be more convenient
# Compute trimmed means, defining this on-the-fly
apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=function(v) {sort(v,decreasing = T)[2]})## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 18076.00 5348.00 2.40 72.96 13.90 66.70
## Frost Area
## 186.00 262134.00
五、Applying a function that takes extra arguments
Can tell apply() to pass extra arguments to the function in question. E.g., can use: apply(x, MARGIN=1, FUN=my.fun, extra.arg.1, extra.arg.2), for two extra arguments extra.arg.1, extra.arg.2 to be passed to my.fun()
# Our custom function: trimmed mean, with user-specified percentiles
kth.max = function(v,k) { sorted.v = sort(v,decreasing = T)return(sorted.v[k])
}apply(state.x77, MARGIN=2, FUN=kth.max, k=10)
## Population Income Illiteracy Life Exp Murder HS Grad
## 5814.00 4903.00 1.80 72.13 11.10 59.90
## Frost Area
## 155.00 96184.00
六、What’s the return argument?
What kind of data type will apply() give us? Depends on what function we pass. Summary, say, with FUN=my.fun():
- If
my.fun()returns a single value, thenapply()will return a vector - If
my.fun()returns k values, thenapply()will return a matrix with k rows (note: this is true regardless of whetherMARGIN=1orMARGIN=2) - If
my.fun()returns different length outputs for different inputs, thenapply()will return a list - If
my.fun()returns a list, thenapply()will return a list
七、Optimized functions for special tasks
Don’t overuse the apply paradigm! There’s lots of special functions that optimized are will be both simpler and faster than using apply(). E.g.,
rowSums(),colSums(): for computing row, column sums of a matrixrowMeans(),colMeans(): for computing row, column means of a matrixmax.col(): for finding the maximum position in each row of a matrix
Combining these functions with logical indexing and vectorized operations will enable you to do quite a lot. E.g., how to count the number of positives in each row of a matrix?
x = matrix(rnorm(9), 3, 3)
# Don't do this (much slower for big matrices)
apply(x, MARGIN=1, function(v) { return(sum(v > 0)) })
## [1] 2 2 1# Do this insted (much faster, simpler)
rowSums(x > 0)
## [1] 2 2 1
八、lapply: elements of a list or vector
The lapply() function takes inputs as in: lapply(x, FUN=my.fun), to apply my.fun() across elements of a list or vector x. The output is always a list
my.list## $nums
## [1] 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
##
## $chars
## [1] "a" "b" "c" "d" "e" "f" "g" "h" "i" "j" "k" "l"
##
## $bools
## [1] TRUE FALSE FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE
lapply(my.list, FUN=mean) # Get a warning: mean() can't be applied to chars
## Warning in mean.default(X[[i]], ...): argument is not numeric or
## logical: returning NA
## $nums
## [1] 0.35
##
## $chars
## [1] NA
##
## $bools
## [1] 0.5lapply(my.list, FUN=summary)
## $nums
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.100 0.225 0.350 0.350 0.475 0.600
##
## $chars
## Length Class Mode
## 12 character character
##
## $bools
## Mode FALSE TRUE
## logical 3 3
九、sapply(): elements of a list or vector
The sapply() function works just like lapply(), but tries to simplify the return value whenever possible. E.g., most common is the conversion from a list to a vector
sapply(my.list, FUN=mean) # Simplifies the result, now a vector
## Warning in mean.default(X[[i]], ...): argument is not numeric or
## logical: returning NA
## nums chars bools
## 0.35 NA 0.50
sapply(my.list, FUN=summary) # Can't simplify, so still a list
## $nums
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.100 0.225 0.350 0.350 0.475 0.600
##
## $chars
## Length Class Mode
## 12 character character
##
## $bools
## Mode FALSE TRUE
## logical 3 3
十、tapply(): levels of a factor vector
The function tapply() takes inputs as in: tapply(x, INDEX=my.index, FUN=my.fun), to apply my.fun() to subsets of entries in x that share a common level in my.index
# Compute the mean and sd of the Frost variable, within each region
tapply(state.x77[,"Frost"], INDEX=state.region, FUN=mean)
## Northeast South North Central West
## 132.7778 64.6250 138.8333 102.1538tapply(state.x77[,"Frost"], INDEX=state.region, FUN=sd)
## Northeast South North Central West
## 30.89408 31.30682 23.89307 68.87652
十一、split(): split by levels of a factor
The function split() split up the rows of a data frame by levels of a factor, as in: split(x, f=my.index) to split a data frame x according to levels of my.index
# Split up the state.x77 matrix according to region
state.by.reg = split(data.frame(state.x77), f=state.region)class(state.by.reg) # The result is a list
## [1] "list"names(state.by.reg) # This has 4 elements for the 4 regions
## [1] "Northeast" "South" "North Central" "West"class(state.by.reg[[1]]) # Each element is a data frame
## [1] "data.frame"















![洛谷 P3130 [USACO15DEC] Counting Haybale P](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/dede9e15d9724821bf5a008519875939.png)

