Springboot3
Spring Boot 3是Spring Boot框架的一个主要版本,它基于Spring Framework 6构建,引入了对最新Java版本(如Java 17及以上)的支持,并提供了许多新特性和改进。Spring Boot 3旨在简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程,通过提供自动配置、起步依赖管理和微服务支持,使得开发者能够快速构建生产级别的基于Spring的应用程序。这个版本强化了对响应式编程和现代云原生应用的支持,同时继续提升性能和可维护性,为构建下一代企业级应用提供了坚实的基础。
Springboot能帮助我们简单、快捷的创建一个独立的、生产级别的spring应用(springboot底层就是spring)
大多数 SpringBoot 应用只需要编写少量配置即可快速整合 Spring 平台以及第三方技术
● 快速创建独立 Spring 应用
○ SSM:导包、写配置、启动运行
● 直接嵌入Tomcat、Jetty or Undertow(无需部署 war 包)【Servlet容器】
○ linux java tomcat mysql: war 放到 tomcat 的 webapps下
○ jar: java环境; java -jar
● 重点:提供可选的starter,简化应用整合
○ 场景启动器(starter):web、json、邮件、oss(对象存储)、异步、定时任务、缓存…
○ 导包一堆,控制好版本。
○ 为每一种场景准备了一个依赖; web-starter。mybatis-starter
● 重点:按需自动配置 Spring 以及 第三方库
○ 如果这些场景我要使用(生效)。这个场景的所有配置都会自动配置好。
○ 约定大于配置:每个场景都有很多默认配置。
○ 自定义:配置文件中修改几项就可以
● 提供生产级特性:如 监控指标、健康检查、外部化配置等
○ 监控指标、健康检查(k8s)、外部化配置
● 无代码生成、无xml
总结:简化开发,简化配置,简化整合,简化部署,简化监控,简化运维。
快速体验
场景:浏览器发送/hello请求,返回"Hello,Spring Boot 3!"
<!-- 所有springboot项目都必须继承自 spring-boot-starter-parent --><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>3.0.5</version></parent>
导入场景:场景启动器
<dependencies>
<!-- web开发的场景启动器 --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency></dependencies>主程序
@SpringBootApplication //这是一个SpringBoot应用
public class MainApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);}
}
业务
@RestController
public class HelloController {@GetMapping("/hello")public String hello(){return "Hello,Spring Boot 3!";}}
测试
默认启动访问: localhost:8080
打包
<!-- SpringBoot应用打包插件--><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId></plugin></plugins></build>
mvn clean package把项目打成可执行的jar包
java -jar demo.jar启动项目
场景一导入,万物皆就绪
无需编写任何配置,直接开发业务
简化配置
application.properties:
● 集中式管理配置。只需要修改这个文件就行 。
● 配置基本都有默认值
● 能写的所有配置都在: spring官方文档
简化部署
打包为可执行的jar包。linux服务器上有java环境。
简化运维
修改配置(外部放一个application.properties文件)、监控、健康检查。
Spring Initializr 创建向导

只扫描主程序所在包的文件(及子包)
主程序:BootApplication
所在包:boot
boot包之外的不会被扫描
依赖管理机制
为什么导入的starter-web所有相关依赖都导入进来?
● 开发什么场景,导入什么场景启动器。
● maven依赖传递原则。A-B-C: A就拥有B和C
● 导入 场景启动器。 场景启动器 自动把这个场景的所有核心依赖全部导入进来
为什么版本号都不用写?
● 每个boot项目都有一个父项目spring-boot-starter-parent
● parent的父项目是spring-boot-dependencies
● 父项目 版本仲裁中心,把所有常见的jar的依赖版本都声明好了。
● 比如:mysql-connector-j
3、自定义版本号
● 利用maven的就近原则
○ 直接在当前项目properties标签中声明父项目用的版本属性的key
○ 直接在导入依赖的时候声明版本
4、第三方的jar包
● boot父项目没有管理的需要自行声明好
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>druid</artifactId><version>1.2.16</version>
</dependency>

自动配置机制
● 自动配置的 Tomcat、SpringMVC 等
○ 导入场景,容器中就会自动配置好这个场景的核心组件。
○ 以前:DispatcherServlet、ViewResolver、CharacterEncodingFilter…
○ 现在:自动配置好的这些组件
○ 验证:容器中有了什么组件,就具有什么功能
public static void main(String[] args) {//java10: 局部变量类型的自动推断var ioc = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);//1、获取容器中所有组件的名字String[] names = ioc.getBeanDefinitionNames();//2、挨个遍历:// dispatcherServlet、beanNameViewResolver、characterEncodingFilter、multipartResolver// SpringBoot把以前配置的核心组件现在都给我们自动配置好了。for (String name : names) {System.out.println(name);}}
● 默认的包扫描规则
○ @SpringBootApplication 标注的类就是主程序类
○ SpringBoot只会扫描主程序所在的包及其下面的子包,自动的component-scan功能
○ 自定义扫描路径
■ @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = “com.atguigu”)
■ @ComponentScan(“com.atguigu”) 直接指定扫描的路径
● 配置默认值
○ 配置文件的所有配置项是和某个类的对象值进行一一绑定的。
○ 绑定了配置文件中每一项值的类: 属性类。
○ 比如:
■ ServerProperties绑定了所有Tomcat服务器有关的配置
■ MultipartProperties绑定了所有文件上传相关的配置
■ …参照官方文档:或者参照 绑定的 属性类
● 按需加载自动配置
○ 导入场景spring-boot-starter-web
○ 场景启动器除了会导入相关功能依赖,导入一个spring-boot-starter,是所有starter的starter,基础核心starter
○ spring-boot-starter导入了一个包 spring-boot-autoconfigure。包里面都是各种场景的AutoConfiguration自动配置类
○ 虽然全场景的自动配置都在 spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包,但是不是全都开启的。
■ 导入哪个场景就开启哪个自动配置
总结: 导入场景启动器、触发 spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包的自动配置生效、容器中就会具有相关场景的功能
完整流程
思考:
1、SpringBoot怎么实现导一个starter、写一些简单配置,应用就能跑起来,我们无需关心整合
2、为什么Tomcat的端口号可以配置在application.properties中,并且Tomcat能启动成功?
3、导入场景后哪些自动配置能生效?

自动配置流程细节梳理
1、导入starter-web:导入了web开发场景
● 1、场景启动器导入了相关场景的所有依赖:starter-json、starter-tomcat、springmvc
● 2、每个场景启动器都引入了一个spring-boot-starter,核心场景启动器。
● 3、核心场景启动器引入了spring-boot-autoconfigure包。
● 4、spring-boot-autoconfigure里面囊括了所有场景的所有配置。
● 5、只要这个包下的所有类都能生效,那么相当于SpringBoot官方写好的整合功能就生效了。
● 6、SpringBoot默认却扫描不到 spring-boot-autoconfigure下写好的所有配置类。(这些配置类给我们做了整合操作),默认只扫描主程序所在的包。
2、主程序:@SpringBootApplication
● 1、@SpringBootApplication由三个注解组成@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan
● 2、SpringBoot默认只能扫描自己主程序所在的包及其下面的子包,扫描不到 spring-boot-autoconfigure包中官方写好的配置类
● 3、@EnableAutoConfiguration:SpringBoot 开启自动配置的核心。
○ 1. 是由@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)提供功能:批量给容器中导入组件。
○ 2. SpringBoot启动会默认加载 142个配置类。
○ 3. 这142个配置类来自于spring-boot-autoconfigure下 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件指定的
○ 项目启动的时候利用 @Import 批量导入组件机制把 autoconfigure 包下的142 xxxxAutoConfiguration类导入进来(自动配置类)
○ 虽然导入了142个自动配置类
● 4、按需生效:
○ 并不是这142个自动配置类都能生效
○ 每一个自动配置类,都有条件注解@ConditionalOnxxx,只有条件成立,才能生效
3、xxxxAutoConfiguration自动配置类
● 1、给容器中使用@Bean 放一堆组件。
● 2、每个自动配置类都可能有这个注解@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class),用来把配置文件中配的指定前缀的属性值封装到 xxxProperties属性类中
● 3、以Tomcat为例:把服务器的所有配置都是以server开头的。配置都封装到了属性类中。
● 4、给容器中放的所有组件的一些核心参数,都来自于xxxProperties。xxxProperties都是和配置文件绑定。
● 只需要改配置文件的值,核心组件的底层参数都能修改
4、写业务,全程无需关心各种整合(底层这些整合写好了,而且也生效了)
核心流程总结:
1、导入starter,就会导入autoconfigure包。
2、autoconfigure 包里面 有一个文件 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports,里面指定的所有启动要加载的自动配置类
3、@EnableAutoConfiguration 会自动的把上面文件里面写的所有自动配置类都导入进来。xxxAutoConfiguration 是有条件注解进行按需加载
4、xxxAutoConfiguration给容器中导入一堆组件,组件都是从 xxxProperties中提取属性值
5、xxxProperties又是和配置文件进行了绑定

核心技能
常用注解
springboot摒弃XML方式,改为全注解驱动。
1. 组件注册
@Configuration(替代以前的配置类,配置类也是容器中的组件)、@SpringBootConfiguration(与configuration没有什么区别,可任意使用)
@Bean(替代以前的bean注解,默认的是组件在容器中的名字是所在类名)、@Scope(放的是单实例还是多实例的)

@Controller、 @Service、@Repository、@Component
@Import
需要将第三方包的类放到ioc容器中:
方法1:在配置类中定义方法加上Bean标签
方法2:在配置类上面使用@import(需要导入的类.class)
注意:@Bean导入的组件默认用的是方法名,@Import导入的组件,组件的名字是全类名
@ComponentScan
步骤:
1、@Configuration 编写一个配置类
2、在配置类中,自定义方法给容器中注册组件。配合@Bean
3、或使用@Import 导入第三方的组件
2. 条件注解
如果注解指定的条件成立,则触发指定行为。
@ConditionalOnXxx
@ConditionalOnClass:如果类路径中存在这个类,则触发指定行为
@ConditionalOnMissingClass:如果类路径中不存在这个类,则触发指定行为
@ConditionalOnBean:如果容器中存在这个Bean(组件),则触发指定行为
@ConditionalOnMissingBean:如果容器中不存在这个Bean(组件),则触发指定行为

场景:
● 如果存在FastsqlException这个类,给容器中放一个Cat组件,名cat01,
● 否则,就给容器中放一个Dog组件,名dog01
● 如果系统中有dog01这个组件,就给容器中放一个 User组件,名zhangsan
● 否则,就放一个User,名叫lisi
@ConditionalOnBean(value=组件类型,name=组件名字):判断容器中是否有这个类型的组件,并且名字是指定的值
3. 属性绑定
@ConfigurationProperties: 声明组件的属性和配置文件哪些前缀开始项进行绑定
@EnableConfigurationProperties:快速注册注解:
● 场景:SpringBoot默认只扫描自己主程序所在的包。如果导入第三方包,即使组件上标注了 @Component、@ConfigurationProperties 注解,也没用。因为组件都扫描不进来,此时使用这个注解就可以快速进行属性绑定并把组件注册进容器
将容器中任意组件(Bean)的属性值和配置文件的配置项的值进行绑定
● 1、给容器中注册组件(@Component、@Bean)
● 2、使用@ConfigurationProperties 声明组件和配置文件的哪些配置项进行绑定
YAML配置文件
痛点:SpringBoot 集中化管理配置,application.properties
问题:配置多以后难阅读和修改,层级结构辨识度不高
YAML 是 “YAML Ain’t a Markup Language”(YAML 不是一种标记语言)。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:“Yet Another Markup Language”(是另一种标记语言)。
● 设计目标,就是方便人类读写
● 层次分明,更适合做配置文件
● 使用.yaml或 .yml作为文件后缀
基本语法
● 大小写敏感
● 使用缩进表示层级关系,k: v,使用空格分割k,v
● 缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格。换行
● 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
● # 表示注释,从这个字符一直到行尾,都会被解析器忽略。
支持的写法:
● 对象:键值对的集合,如:映射(map)/ 哈希(hash) / 字典(dictionary)
● 数组:一组按次序排列的值,如:序列(sequence) / 列表(list)
● 纯量:单个的、不可再分的值,如:字符串、数字、bool、日期
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") //和配置文件person前缀的所有配置进行绑定
@Data //自动生成JavaBean属性的getter/setter
//@NoArgsConstructor //自动生成无参构造器
//@AllArgsConstructor //自动生成全参构造器
public class Person {private String name;private Integer age;private Date birthDay;private Boolean like;private Child child; //嵌套对象private List<Dog> dogs; //数组(里面是对象)private Map<String,Cat> cats; //表示Map
}@Data
public class Dog {private String name;private Integer age;
}@Data
public class Child {private String name;private Integer age;private Date birthDay;private List<String> text; //数组
}@Data
public class Cat {private String name;private Integer age;
}
properties表示法
person.name=张三
person.age=18
person.birthDay=2010/10/12 12:12:12
person.like=true
person.child.name=李四
person.child.age=12
person.child.birthDay=2018/10/12
person.child.text[0]=abc
person.child.text[1]=def
person.dogs[0].name=小黑
person.dogs[0].age=3
person.dogs[1].name=小白
person.dogs[1].age=2
person.cats.c1.name=小蓝
person.cats.c1.age=3
person.cats.c2.name=小灰
person.cats.c2.age=2
yaml表示法
person:name: 张三age: 18birthDay: 2010/10/10 12:12:12like: truechild:name: 李四age: 20birthDay: 2018/10/10text: ["abc","def"]dogs:- name: 小黑age: 3- name: 小白age: 2cats:c1:name: 小蓝age: 3c2: {name: 小绿,age: 2} #对象也可用{}表示
细节
● birthDay 推荐写为 birth-day
● 文本:
○ 单引号不会转义【\n 则为普通字符串显示】
○ 双引号会转义【\n会显示为换行符】
● 大文本
○ |开头,大文本写在下层,保留文本格式,换行符正确显示
○ >开头,大文本写在下层,折叠换行符
● 多文档合并
○ 使用—可以把多个yaml文档合并在一个文档中,每个文档区依然认为内容独立
小技巧:lombok
简化JavaBean 开发。自动生成构造器、getter/setter、自动生成Builder模式等
<dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
3. 日志配置

2. 日志格式
2023-03-31T13:56:17.511+08:00 INFO 4944 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2023-03-31T13:56:17.511+08:00 INFO 4944 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/10.1.7]
默认输出格式:
● 时间和日期:毫秒级精度
● 日志级别:ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, or TRACE.
● 进程 ID
● —: 消息分割符
● 线程名: 使用[]包含
● Logger 名: 通常是产生日志的类名
● 消息: 日志记录的内容
注意: logback 没有FATAL级别,对应的是ERROR
默认值:参照:spring-boot包additional-spring-configuration-metadata.json文件
默认输出格式值:%clr(%d{KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 55: …H:mm:ss.SSSXXX}}̲){faint} %clr({LOG_LEVEL_PATTERN:-%5p}) %clr( P I D : − ) m a g e n t a {PID:- }){magenta} %clr(---){faint} %clr([%15.15t]){faint} %clr(%-40.40logger{39}){cyan} %clr(:){faint} %m%n PID:−)magenta{LOG_EXCEPTION_CONVERSION_WORD:-%wEx}
可修改为:‘%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level [%thread] %logger{15} ===> %msg%n’
3. 记录日志
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());或者使用Lombok的@Slf4j注解
4. 日志级别
● 由低到高:ALL,TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR,FATAL,OFF;
○ 只会打印指定级别及以上级别的日志
○ ALL:打印所有日志
○ TRACE:追踪框架详细流程日志,一般不使用
○ DEBUG:开发调试细节日志
○ INFO:关键、感兴趣信息日志
○ WARN:警告但不是错误的信息日志,比如:版本过时
○ ERROR:业务错误日志,比如出现各种异常
○ FATAL:致命错误日志,比如jvm系统崩溃
○ OFF:关闭所有日志记录
● 不指定级别的所有类,都使用root指定的级别作为默认级别
● SpringBoot日志默认级别是 INFO
- 在application.properties/yaml中配置logging.level.=指定日志级别
- level可取值范围:TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, or OFF,定义在 LogLevel类中
- root 的logger-name叫root,可以配置logging.level.root=warn,代表所有未指定日志级别都使用 root 的 warn 级别
5. 日志分组
比较有用的技巧是:
将相关的logger分组在一起,统一配置。SpringBoot 也支持。比如:Tomcat 相关的日志统一设置
logging.group.tomcat=org.apache.catalina,org.apache.coyote,org.apache.tomcat
logging.level.tomcat=trace

6. 文件输出
SpringBoot 默认只把日志写在控制台,如果想额外记录到文件,可以在application.properties中添加logging.file.name or logging.file.path配置项。

文件归档与滚动切割
归档:每天的日志单独存到一个文档中。
切割:每个文件10MB,超过大小切割成另外一个文件。
- 每天的日志应该独立分割出来存档。如果使用logback(SpringBoot 默认整合),可以通过application.properties/yaml文件指定日志滚动规则。
- 如果是其他日志系统,需要自行配置(添加log4j2.xml或log4j2-spring.xml)
- 支持的滚动规则设置如下

8. 自定义配置
通常我们配置 application.properties 就够了。当然也可以自定义。比如:

如果可能,我们建议您在日志配置中使用-spring 变量(例如,logback-spring.xml 而不是 logback.xml)。如果您使用标准配置文件,spring 无法完全控制日志初始化。
最佳实战:自己要写配置,配置文件名加上 xx-spring.xml
9. 切换日志组合
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、SpringBoot3-Web开发
1. Web场景
1. 自动配置
1、整合web场景
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency>
2、引入了 autoconfigure功能
3、@EnableAutoConfiguration注解使用@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)批量导入组件
4、加载 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 文件中配置的所有组件
5、所有自动配置类如下
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration
====以下是响应式web场景和现在的没关系======
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveMultipartAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebSessionIdResolverAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration
================以上没关系=================
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
6、绑定了配置文件的一堆配置项
● 1、SpringMVC的所有配置 spring.mvc
● 2、Web场景通用配置 spring.web
● 3、文件上传配置 spring.servlet.multipart
● 4、服务器的配置 server: 比如:编码方式
2. 默认效果
默认配置:
- 包含了 ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 和 BeanNameViewResolver 组件,方便视图解析
- 默认的静态资源处理机制: 静态资源放在 static 文件夹下即可直接访问
- 自动注册了 Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter组件,适配常见数据类型转换和格式化需求
- 支持 HttpMessageConverters,可以方便返回json等数据类型
- 注册 MessageCodesResolver,方便国际化及错误消息处理
- 支持 静态 index.html
- 自动使用ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer,实现消息处理、数据绑定、类型转化、数据校验等功能
重要:
● 如果想保持 boot mvc 的默认配置,并且自定义更多的 mvc 配置,如:interceptors, formatters, view controllers 等。可以使用@Configuration注解添加一个 WebMvcConfigurer 类型的配置类,并不要标注 @EnableWebMvc
● 如果想保持 boot mvc 的默认配置,但要自定义核心组件实例,比如:RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, 或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,给容器中放一个 WebMvcRegistrations 组件即可
● 如果想全面接管 Spring MVC,@Configuration 标注一个配置类,并加上 @EnableWebMvc注解,实现 WebMvcConfigurer 接口
WebMvcAutoConfiguration原理
生效条件
@AutoConfiguration(after = { DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,ValidationAutoConfiguration.class }) //在这些自动配置之后
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET) //如果是web应用就生效,类型SERVLET、REACTIVE 响应式web
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class) //容器中没有这个Bean,才生效。默认就是没有
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)//优先级
@ImportRuntimeHints(WebResourcesRuntimeHints.class)//一个标志性注解不用管
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
}
2. 效果
- 放了两个Filter:
a. HiddenHttpMethodFilter;页面表单提交Rest请求(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE)
b. FormContentFilter: 表单内容Filter,GET(数据放URL后面)、POST(数据放请求体)请求可以携带数据,PUT、DELETE 的请求体数据会被忽略 - 给容器中放了WebMvcConfigurer组件;给SpringMVC添加各种定制功能
a. 所有的功能最终会和配置文件进行绑定
b. WebMvcProperties: spring.mvc配置文件
c. WebProperties: spring.web配置文件
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class) //额外导入了其他配置@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class })@Order(0)public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware{}
3. WebMvcConfigurer接口
提供了配置SpringMVC底层的所有组件入口

4. 静态资源规则源码
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");return;}//1、addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getWebjarsPathPattern(),"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> {registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());if (this.servletContext != null) {ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION);registration.addResourceLocations(resource);}});
}
- 规则一:访问: /webjars/**路径就去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/下找资源.
a. maven 导入依赖 - 规则二:访问: /**路径就去 静态资源默认的四个位置找资源
a. classpath:/META-INF/resources/
b. classpath:/resources/
c. classpath:/static/
d. classpath:/public/ - 规则三:静态资源默认都有缓存规则的设置
a. 所有缓存的设置,直接通过配置文件: spring.web
b. cachePeriod: 缓存周期; 多久不用找服务器要新的。 默认没有,以s为单位
c. cacheControl: HTTP缓存控制;https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Caching
d. useLastModified:是否使用最后一次修改。配合HTTP Cache规则
如果浏览器访问了一个静态资源 index.js,如果服务这个资源没有发生变化,下次访问的时候就可以直接让浏览器用自己缓存中的东西,而不用给服务器发请求
registration.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod()));
registration.setCacheControl(this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl());
registration.setUseLastModified(this.resourceProperties.getCache().isUseLastModified());
3. 欢迎页
欢迎页规则在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 中进行了定义:
- 在静态资源目录下找 index.html
- 没有就在 templates下找index模板页
6.EnableWebMvcConfiguration 源码
//SpringBoot 给容器中放 WebMvcConfigurationSupport 组件。
//我们如果自己放了 WebMvcConfigurationSupport 组件,Boot的WebMvcAutoConfiguration都会失效。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(WebProperties.class)
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration implements ResourceLoaderAware
{}
- HandlerMapping: 根据请求路径 /a 找那个handler能处理请求
a. WelcomePageHandlerMapping:
ⅰ. 访问 /**路径下的所有请求,都在以前四个静态资源路径下找,欢迎页也一样
ⅱ. 找index.html:只要静态资源的位置有一个 index.html页面,项目启动默认访问
为什么容器中放一个WebMvcConfigurer就能配置底层行为 - WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是一个自动配置类,它里面有一个 EnableWebMvcConfiguration
- EnableWebMvcConfiguration继承与 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration,这两个都生效
- DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration利用 DI 把容器中 所有 WebMvcConfigurer 注入进来
- 别人调用
DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration的方法配置底层规则,而它调用所有 WebMvcConfigurer的配置底层方法
7. WebMvcConfigurationSupport
提供了很多的默认设置。
判断系统中是否有相应的类:如果有,就加入相应的HttpMessageConverter
jackson2Present = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper", classLoader) &&ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator", classLoader);
jackson2XmlPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.xml.XmlMapper", classLoader);
jackson2SmilePresent = ClassUtils.isPresent("com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.smile.SmileFactory", classLoader);
4. Favicon
在静态资源目录下找 favicon.ico
缓存实验
server.port=9000#1、spring.web:
# 1.配置国际化的区域信息
# 2.静态资源策略(开启、处理链、缓存)#开启静态资源映射规则
spring.web.resources.add-mappings=true#设置缓存
#spring.web.resources.cache.period=3600
##缓存详细合并项控制,覆盖period配置:
## 浏览器第一次请求服务器,服务器告诉浏览器此资源缓存7200秒,7200秒以内的所有此资源访问不用发给服务器请求,7200秒以后发请求给服务器
spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.max-age=7200
#使用资源 last-modified 时间,来对比服务器和浏览器的资源是否相同没有变化。相同返回 304
spring.web.resources.cache.use-last-modified=true
** 自定义静态资源规则**
自定义静态资源路径、自定义缓存规则
** 配置方式**
spring.mvc: 静态资源访问前缀路径
spring.web:
● 静态资源目录
● 静态资源缓存策略
#1、spring.web:
# 1.配置国际化的区域信息
# 2.静态资源策略(开启、处理链、缓存)#开启静态资源映射规则
spring.web.resources.add-mappings=true#设置缓存
spring.web.resources.cache.period=3600
##缓存详细合并项控制,覆盖period配置:
## 浏览器第一次请求服务器,服务器告诉浏览器此资源缓存7200秒,7200秒以内的所有此资源访问不用发给服务器请求,7200秒以后发请求给服务器
spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.max-age=7200
## 共享缓存
spring.web.resources.cache.cachecontrol.cache-public=true
#使用资源 last-modified 时间,来对比服务器和浏览器的资源是否相同没有变化。相同返回 304
spring.web.resources.cache.use-last-modified=true#自定义静态资源文件夹位置
spring.web.resources.static-locations=classpath:/a/,classpath:/b/,classpath:/static/#2、 spring.mvc
## 2.1. 自定义webjars路径前缀
spring.mvc.webjars-path-pattern=/wj/**
## 2.2. 静态资源访问路径前缀
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/**
代码方式
● 容器中只要有一个 WebMvcConfigurer 组件。配置的底层行为都会生效
● @EnableWebMvc //禁用boot的默认配置
@Configuration //这是一个配置类
public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {//保留以前规则//自己写新的规则。registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/a/","classpath:/b/").setCacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(1180, TimeUnit.SECONDS));}
}
代码方式
● 容器中只要有一个 WebMvcConfigurer 组件。配置的底层行为都会生效
● @EnableWebMvc //禁用boot的默认配置
@Configuration //这是一个配置类
public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {//保留以前规则WebMvcConfigurer.super.addResourceHandlers(registry);//自己写新的规则。registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/a/","classpath:/b/").setCacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(1180, TimeUnit.SECONDS));}
}
@Configuration //这是一个配置类,给容器中放一个 WebMvcConfigurer 组件,就能自定义底层
public class MyConfig /*implements WebMvcConfigurer*/ {@Beanpublic WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){return new WebMvcConfigurer() {@Overridepublic void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/a/", "classpath:/b/").setCacheControl(CacheControl.maxAge(1180, TimeUnit.SECONDS));}};}}
路径匹配
Spring5.3 之后加入了更多的请求路径匹配的实现策略;
以前只支持 AntPathMatcher 策略, 现在提供了 PathPatternParser 策略。并且可以让我们指定到底使用那种策略。
Ant风格路径用法
Ant 风格的路径模式语法具有以下规则:
● :表示任意数量的字符。
● ?:表示任意一个字符。
● **:表示任意数量的目录。
● {}:表示一个命名的模式占位符。
● []:表示字符集合,例如[a-z]表示小写字母。
例如:
● .html 匹配任意名称,扩展名为.html的文件。
● /folder1//.java 匹配在folder1目录下的任意两级目录下的.java文件。
● /folder2/**/.jsp 匹配在folder2目录下任意目录深度的.jsp文件。
● /{type}/{id}.html 匹配任意文件名为{id}.html,在任意命名的{type}目录下的文件。
注意:Ant 风格的路径模式语法中的特殊字符需要转义,如:
● 要匹配文件路径中的星号,则需要转义为\。
● 要匹配文件路径中的问号,则需要转义为\?。
模式切换
AntPathMatcher 与 PathPatternParser
● PathPatternParser 在 jmh 基准测试下,有 6~8 倍吞吐量提升,降低 30%~40%空间分配率
● PathPatternParser 兼容 AntPathMatcher语法,并支持更多类型的路径模式
● PathPatternParser “**” 多段匹配的支持仅允许在模式末尾使用
@GetMapping("/a*/b?/{p1:[a-f]+}")public String hello(HttpServletRequest request, @PathVariable("p1") String path) {log.info("路径变量p1: {}", path);//获取请求路径String uri = request.getRequestURI();return uri;}
总结:
● 使用默认的路径匹配规则,是由 PathPatternParser 提供的
● 如果路径中间需要有 **,替换成ant风格路径
# 改变路径匹配策略:
# ant_path_matcher 老版策略;
# path_pattern_parser 新版策略;
spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy=ant_path_matcher
4. 内容协商
后端给前端返回的数据格式,默认使用的是Json

** 多端内容适配**
默认规则
- SpringBoot 多端内容适配。
1.1. 基于请求头内容协商:(默认开启)
1.1.1. 客户端向服务端发送请求,携带HTTP标准的Accept请求头。
1.1.1.1. Accept: application/json、text/xml、text/yaml
1.1.1.2. 服务端根据客户端请求头期望的数据类型进行动态返回
1.2. 基于请求参数内容协商:(需要开启)
1.2.1. 发送请求 GET /projects/spring-boot?format=json
1.2.2. 匹配到 @GetMapping(“/projects/spring-boot”)
1.2.3. 根据参数协商,优先返回 json 类型数据【需要开启参数匹配设置】
1.2.4. 发送请求 GET /projects/spring-boot?format=xml,优先返回 xml 类型数据
效果演示
请求同一个接口,可以返回json和xml不同格式数据 - 引入支持写出xml内容依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId><artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
标注注解
@JacksonXmlRootElement // 可以写出为xml文档
@Data
public class Person {private Long id;private String userName;private String email;private Integer age;
}
开启基于请求参数的内容协商
# 开启基于请求参数的内容协商功能。 默认参数名:format。 默认此功能不开启
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-parameter=true
# 指定内容协商时使用的参数名。默认是 format
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.parameter-name=type

** 内容协商原理-HttpMessageConverter**
● HttpMessageConverter 怎么工作?合适工作?
● 定制 HttpMessageConverter 来实现多端内容协商
● 编写WebMvcConfigurer提供的configureMessageConverters底层,修改底层的MessageConverter
@ResponseBody由HttpMessageConverter处理
标注了@ResponseBody的返回值 将会由支持它的 HttpMessageConverter写给浏览器
- 如果controller方法的返回值标注了 @ResponseBody 注解
1.1. 请求进来先来到DispatcherServlet的doDispatch()进行处理
1.2. 找到一个 HandlerAdapter 适配器。利用适配器执行目标方法
1.3. RequestMappingHandlerAdapter来执行,调用invokeHandlerMethod()来执行目标方法
1.4. 目标方法执行之前,准备好两个东西
1.4.1. HandlerMethodArgumentResolver:参数解析器,确定目标方法每个参数值
1.4.2. HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler:返回值处理器,确定目标方法的返回值改怎么处理
1.5. RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 里面的invokeAndHandle()真正执行目标方法
1.6. 目标方法执行完成,会返回返回值对象
1.7. 找到一个合适的返回值处理器 HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler
1.8. 最终找到 RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor能处理 标注了 @ResponseBody注解的方法
1.9. RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 调用writeWithMessageConverters ,利用MessageConverter把返回值写出去
上面解释:@ResponseBody由HttpMessageConverter处理 - HttpMessageConverter 会先进行内容协商
2.1. 遍历所有的MessageConverter看谁支持这种内容类型的数据
2.2. 默认MessageConverter有以下

2.4. 最终因为要json所以MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter支持写出json
2.5. jackson用ObjectMapper把对象写出去
WebMvcAutoConfiguration提供几种默认HttpMessageConverters
● EnableWebMvcConfiguration通过 addDefaultHttpMessageConverters添加了默认的MessageConverter;如下:
○ ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter: 支持字节数据读写
○ StringHttpMessageConverter: 支持字符串读写
○ ResourceHttpMessageConverter:支持资源读写
○ ResourceRegionHttpMessageConverter: 支持分区资源写出
○ AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter:支持表单xml/json读写
○ MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter: 支持请求响应体Json读写

系统提供默认的MessageConverter 功能有限,仅用于json或者普通返回数据。额外增加新的内容协商功能,必须增加新的HttpMessageConverter
自定义内容返回
增加yaml返回支持
导入依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId><artifactId>jackson-dataformat-yaml</artifactId>
</dependency>
把对象写出成YAML
public static void main(String[] args) throws JsonProcessingException {Person person = new Person();person.setId(1L);person.setUserName("张三");person.setEmail("aaa@qq.com");person.setAge(18);YAMLFactory factory = new YAMLFactory().disable(YAMLGenerator.Feature.WRITE_DOC_START_MARKER);ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(factory);String s = mapper.writeValueAsString(person);System.out.println(s);}
编写配置
#新增一种媒体类型
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.yaml=text/yaml
增加HttpMessageConverter组件,专门负责把对象写出为yaml格式
@Beanpublic WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){return new WebMvcConfigurer() {@Override //配置一个能把对象转为yaml的messageConverterpublic void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {converters.add(new MyYamlHttpMessageConverter());}};}
思考:如何增加其他
● 配置媒体类型支持:
○ spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.media-types.yaml=text/yaml
● 编写对应的HttpMessageConverter,要告诉Boot这个支持的媒体类型
○ 按照3的示例
● 把MessageConverter组件加入到底层
○ 容器中放一个WebMvcConfigurer 组件,并配置底层的MessageConverter
HttpMessageConverter的示例写法
public class MyYamlHttpMessageConverter extends AbstractHttpMessageConverter<Object> {private ObjectMapper objectMapper = null; //把对象转成yamlpublic MyYamlHttpMessageConverter(){//告诉SpringBoot这个MessageConverter支持哪种媒体类型 //媒体类型super(new MediaType("text", "yaml", Charset.forName("UTF-8")));YAMLFactory factory = new YAMLFactory().disable(YAMLGenerator.Feature.WRITE_DOC_START_MARKER);this.objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(factory);}@Overrideprotected boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {//只要是对象类型,不是基本类型return true;}@Override //@RequestBodyprotected Object readInternal(Class<?> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException {return null;}@Override //@ResponseBody 把对象怎么写出去protected void writeInternal(Object methodReturnValue, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {//try-with写法,自动关流try(OutputStream os = outputMessage.getBody()){this.objectMapper.writeValue(os,methodReturnValue);}}
}
5. 模板引擎
● 由于 SpringBoot 使用了嵌入式 Servlet 容器。所以 JSP 默认是不能使用的。
● 如果需要服务端页面渲染,优先考虑使用 模板引擎。

模板引擎页面默认放在 src/main/resources/templates
SpringBoot 包含以下模板引擎的自动配置
● FreeMarker
● Groovy
● Thymeleaf
● Mustache
Thymeleaf官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head><title>Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</title><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /><link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" media="all" th:href="@{/css/gtvg.css}" />
</head>
<body><p th:text="#{home.welcome}">Welcome to our grocery store!</p>
</body
</html>
Thymeleaf整合
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
自动配置原理
- 开启了 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration 自动配置
- 属性绑定在 ThymeleafProperties 中,对应配置文件 spring.thymeleaf 内容
- 所有的模板页面默认在 classpath:/templates文件夹下
- 默认效果
a. 所有的模板页面在 classpath:/templates/下面找
b. 找后缀名为.html的页面
2. 基础语法
1. 核心用法
th:xxx:动态渲染指定的 html 标签属性值、或者th指令(遍历、判断等)
● th:text:标签体内文本值渲染
○ th:utext:不会转义,显示为html原本的样子。
● th:属性:标签指定属性渲染
● th:attr:标签任意属性渲染
● th:ifth:each…:其他th指令
● 例如:
<p th:text="${content}">原内容</p>
<a th:href="${url}">登录</a>
<img src="../../images/gtvglogo.png" th:attr="src=@{/images/gtvglogo.png},title=#{logo},alt=#{logo}" />
表达式:用来动态取值
● :变量取值;使用 m o d e l 共享给页面的值都直接用 {}:变量取值;使用model共享给页面的值都直接用 :变量取值;使用model共享给页面的值都直接用{}
● @{}:url路径;
● #{}:国际化消息
● ~{}:片段引用
● {}:变量选择:需要配合th:object绑定对象
系统工具&内置对象:详细文档
● param:请求参数对象
● session:session对象
● application:application对象
● #execInfo:模板执行信息
● #messages:国际化消息
● #uris:uri/url工具
● #conversions:类型转换工具
● #dates:日期工具,是java.util.Date对象的工具类
● #calendars:类似#dates,只不过是java.util.Calendar对象的工具类
● #temporals: JDK8+ java.time API 工具类
● #numbers:数字操作工具
● #strings:字符串操作
● #objects:对象操作
● #bools:bool操作
● #arrays:array工具
● #lists:list工具
● #sets:set工具
● #maps:map工具
● #aggregates:集合聚合工具(sum、avg)
● #ids:id生成工具
2. 语法示例
表达式:
● 变量取值:${…}
● url 取值:@{…}
● 国际化消息:#{…}
● 变量选择:{…}
● 片段引用: ~{…}
常见:
● 文本: ‘one text’,‘another one!’,…
● 数字: 0,34,3.0,12.3,…
● 布尔:true、false
● null: null
● 变量名: one,sometext,main…
文本操作:
● 拼串: +
● 文本替换:| The name is ${name} |
布尔操作:
● 二进制运算: and,or
● 取反:!,not
比较运算:
● 比较:>,<,<=,>=(gt,lt,ge,le)
● 等值运算:==,!=(eq,ne)
条件运算:
● if-then: (if)?(then)
● if-then-else: (if)?(then):(else)
● default: (value)?:(defaultValue)
特殊语法:
● 无操作:
'User is of type ' + (${user.isAdmin()} ? 'Administrator' : (${user.type} ?: 'Unknown'))
遍历
语法: th:each=“元素名,迭代状态 : ${集合}”
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}"><td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td><td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td><td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr><tr th:each="prod,iterStat : ${prods}" th:class="${iterStat.odd}? 'odd'"><td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td><td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td><td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr>
iterStat 有以下属性:
● index:当前遍历元素的索引,从0开始
● count:当前遍历元素的索引,从1开始
● size:需要遍历元素的总数量
● current:当前正在遍历的元素对象
● even/odd:是否偶数/奇数行
● first:是否第一个元素
● last:是否最后一个元素
判断
th:if
<ahref="comments.html"th:href="@{/product/comments(prodId=${prod.id})}"th:if="${not #lists.isEmpty(prod.comments)}">view</a
th:switch
<div th:switch="${user.role}"><p th:case="'admin'">User is an administrator</p><p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a manager</p><p th:case="*">User is some other thing</p>
</div>
属性优先级
● 片段
● 遍历
● 判断

** 行内写法**
[[…]] or [(…)]
<p>Hello, [[${session.user.name}]]!</p>
变量选择
<div th:object="${session.user}"><p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p><p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p><p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
<div><p>Name: <span th:text="${session.user.firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p><p>Surname: <span th:text="${session.user.lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p><p>Nationality: <span th:text="${session.user.nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div
9. 模板布局
● 定义模板: th:fragment
● 引用模板:~{templatename::selector}
● 插入模板:th:insert、th:replace
<footer th:fragment="copy">© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer><body><div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}"></div><div th:replace="~{footer :: copy}"></div>
</body>
<body>结果:<body><div><footer>© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer></div><footer>© 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</footer></body>
</body>
devtools
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId></dependency>
修改页面后;ctrl+F9刷新效果;
java代码的修改,如果devtools热启动了,可能会引起一些bug,难以排查
国际化
国际化的自动配置参照MessageSourceAutoConfiguration
实现步骤:
- Spring Boot 在类路径根下查找messages资源绑定文件。文件名为:messages.properties
- 多语言可以定义多个消息文件,命名为messages_区域代码.properties。如:
a. messages.properties:默认
b. messages_zh_CN.properties:中文环境
c. messages_en_US.properties:英语环境 - 在程序中可以自动注入 MessageSource组件,获取国际化的配置项值
- 在页面中可以使用表达式 #{}获取国际化的配置项值
@Autowired //国际化取消息用的组件MessageSource messageSource;@GetMapping("/haha")public String haha(HttpServletRequest request){Locale locale = request.getLocale();//利用代码的方式获取国际化配置文件中指定的配置项的值String login = messageSource.getMessage("login", null, locale);return login;}
错误处理
- 默认机制
错误处理的自动配置都在ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration中,两大核心机制:
● 1. SpringBoot 会自适应处理错误,响应页面或JSON数据
● 2. SpringMVC的错误处理机制依然保留,MVC处理不了,才会交给boot进行处理

发生错误以后,转发给/error路径,SpringBoot在底层写好一个 BasicErrorController的组件,专门处理这个请求
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) //返回HTMLpublic ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));response.setStatus(status.value());ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);}@RequestMapping //返回 ResponseEntity, JSONpublic ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {return new ResponseEntity<>(status);}Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);}
错误页面是这么解析到
//1、解析错误的自定义视图地址
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
//2、如果解析不到错误页面的地址,默认的错误页就是 error
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
容器中专门有一个错误视图解析器
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(DispatcherServlet.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ErrorViewResolver.class)
DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() {return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext, this.resources);
}
SpringBoot解析自定义错误页的默认规则
@Overridepublic ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);}return modelAndView;}private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName,this.applicationContext);if (provider != null) {return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);}return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);}private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {for (String location : this.resources.getStaticLocations()) {try {Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");if (resource.exists()) {return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model);}}catch (Exception ex) {}}return null;}
容器中有一个默认的名为 error 的 view; 提供了默认白页功能
@Bean(name = "error")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "error")
public View defaultErrorView() {return this.defaultErrorView;
}
封装了JSON格式的错误信息
@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorAttributes.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {return new DefaultErrorAttributes();}
规则:
-
解析一个错误页
a. 如果发生了500、404、503、403 这些错误
ⅰ. 如果有模板引擎,默认在 classpath:/templates/error/精确码.html
ⅱ. 如果没有模板引擎,在静态资源文件夹下找 精确码.html
b. 如果匹配不到精确码.html这些精确的错误页,就去找5xx.html,4xx.html模糊匹配
ⅰ. 如果有模板引擎,默认在 classpath:/templates/error/5xx.html
ⅱ. 如果没有模板引擎,在静态资源文件夹下找 5xx.html -
如果模板引擎路径templates下有 error.html页面,就直接渲染
2. 自定义错误响应 -
自定义json响应
使用@ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler 进行统一异常处理 -
自定义页面响应
根据boot的错误页面规则,自定义页面模板 -
最佳实战
● 前后分离
○ 后台发生的所有错误,@ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler进行统一异常处理。
● 服务端页面渲染
○ 不可预知的一些,HTTP码表示的服务器或客户端错误
■ 给classpath:/templates/error/下面,放常用精确的错误码页面。500.html,404.html
■ 给classpath:/templates/error/下面,放通用模糊匹配的错误码页面。 5xx.html,4xx.html
○ 发生业务错误
■ 核心业务,每一种错误,都应该代码控制,跳转到自己定制的错误页。
■ 通用业务,classpath:/templates/error.html页面,显示错误信息。
页面,JSON,可用的Model数据如下
 嵌入式容器
嵌入式容器
在 Spring Boot 支持的嵌入式容器中只有 Tomcat 支持使用 JSP,Undertow 和 Jetty 均不支持!
Servlet容器:管理、运行Servlet组件(Servlet、Filter、Listener)的环境,一般指服务器
自动配置原理
● SpringBoot 默认嵌入Tomcat作为Servlet容器。
● 自动配置类是ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration
● 自动配置类开始分析功能。xxxxAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@ConditionalOnClass(ServletRequest.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
@Import({ ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class,ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class,ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedJetty.class,ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedUndertow.class })
public class ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration {}
- ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 自动配置了嵌入式容器场景
- 绑定了ServerProperties配置类,所有和服务器有关的配置 server
- ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration 导入了 嵌入式的三大服务器 Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow
a. 导入 Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow 都有条件注解。系统中有这个类才行(也就是导了包)
b. 默认 Tomcat配置生效。给容器中放 TomcatServletWebServerFactory
c. 都给容器中 ServletWebServerFactory放了一个 web服务器工厂(造web服务器的)
d. web服务器工厂 都有一个功能,getWebServer获取web服务器
e. TomcatServletWebServerFactory 创建了 tomcat。 - ServletWebServerFactory 什么时候会创建 webServer出来。
- ServletWebServerApplicationContextioc容器,启动的时候会调用创建web服务器
- Spring容器刷新(启动)的时候,会预留一个时机,刷新子容器。onRefresh()
- refresh() 容器刷新 十二大步的刷新子容器会调用 onRefresh();
@Overrideprotected void onRefresh() {super.onRefresh();try {createWebServer();}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);}}
Web场景的Spring容器启动,在onRefresh的时候,会调用创建web服务器的方法。
Web服务器的创建是通过WebServerFactory搞定的。容器中又会根据导了什么包条件注解,启动相关的 服务器配置,默认EmbeddedTomcat会给容器中放一个 TomcatServletWebServerFactory,导致项目启动,自动创建出Tomcat。
. 自定义

<properties><servlet-api.version>3.1.0</servlet-api.version>
</properties>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId><exclusions><!-- Exclude the Tomcat dependency --><exclusion><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- Use Jetty instead -->
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
最佳实践
用法:
● 修改server下的相关配置就可以修改服务器参数
● 通过给容器中放一个ServletWebServerFactory,来禁用掉SpringBoot默认放的服务器工厂,实现自定义嵌入任意服务器。
全面接管SpringMVC
● SpringBoot 默认配置好了 SpringMVC 的所有常用特性。
● 如果我们需要全面接管SpringMVC的所有配置并禁用默认配置,仅需要编写一个WebMvcConfigurer配置类,并标注 @EnableWebMvc 即可
● 全手动模式
○ @EnableWebMvc : 禁用默认配置
○ WebMvcConfigurer组件:定义MVC的底层行为
WebMvcAutoConfiguration 到底自动配置了哪些规则
SpringMVC自动配置场景给我们配置了如下所有默认行为
- WebMvcAutoConfigurationweb场景的自动配置类
1.1. 支持RESTful的filter:HiddenHttpMethodFilter
1.2. 支持非POST请求,请求体携带数据:FormContentFilter
1.3. 导入EnableWebMvcConfiguration:
1.3.1. RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
1.3.2. WelcomePageHandlerMapping: 欢迎页功能支持(模板引擎目录、静态资源目录放index.html),项目访问/ 就默认展示这个页面.
1.3.3. RequestMappingHandlerMapping:找每个请求由谁处理的映射关系
1.3.4. ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver:默认的异常解析器
1.3.5. LocaleResolver:国际化解析器
1.3.6. ThemeResolver:主题解析器
1.3.7. FlashMapManager:临时数据共享
1.3.8. FormattingConversionService: 数据格式化 、类型转化
1.3.9. Validator: 数据校验JSR303提供的数据校验功能
1.3.10. WebBindingInitializer:请求参数的封装与绑定
1.3.11. ContentNegotiationManager:内容协商管理器
1.4. WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter配置生效,它是一个WebMvcConfigurer,定义mvc底层组件
1.4.1. 定义好 WebMvcConfigurer 底层组件默认功能;所有功能详见列表
1.4.2. 视图解析器:InternalResourceViewResolver
1.4.3. 视图解析器:BeanNameViewResolver,视图名(controller方法的返回值字符串)就是组件名
1.4.4. 内容协商解析器:ContentNegotiatingViewResolver
1.4.5. 请求上下文过滤器:RequestContextFilter: 任意位置直接获取当前请求
1.4.6. 静态资源链规则
1.4.7. ProblemDetailsExceptionHandler:错误详情
1.4.7.1. SpringMVC内部场景异常被它捕获:
1.5. 定义了MVC默认的底层行为: WebMvcConfigurer
** @EnableWebMvc 禁用默认行为** - @EnableWebMvc给容器中导入 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration组件,
他是 WebMvcConfigurationSupport - WebMvcAutoConfiguration有一个核心的条件注解, @ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class),容器中没有WebMvcConfigurationSupport,WebMvcAutoConfiguration才生效.
- @EnableWebMvc 导入 WebMvcConfigurationSupport 导致 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 失效。导致禁用了默认行为
● @EnableWebMVC 禁用了 Mvc的自动配置
● WebMvcConfigurer 定义SpringMVC底层组件的功能类

** Web新特性**
RFC 7807: https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7807
错误信息返回新格式
原理
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
//配置过一个属性 spring.mvc.problemdetails.enabled=true
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc.problemdetails", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true")
static class ProblemDetailsErrorHandlingConfiguration {@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ResponseEntityExceptionHandler.class)ProblemDetailsExceptionHandler problemDetailsExceptionHandler() {return new ProblemDetailsExceptionHandler();}}
- ProblemDetailsExceptionHandler 是一个 @ControllerAdvice集中处理系统异常
- 处理以下异常。如果系统出现以下异常,会被SpringBoot支持以 RFC 7807规范方式返回错误数据
@ExceptionHandler({HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class, //请求方式不支持HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException.class,HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException.class,MissingPathVariableException.class,MissingServletRequestParameterException.class,MissingServletRequestPartException.class,ServletRequestBindingException.class,MethodArgumentNotValidException.class,NoHandlerFoundException.class,AsyncRequestTimeoutException.class,ErrorResponseException.class,ConversionNotSupportedException.class,TypeMismatchException.class,HttpMessageNotReadableException.class,HttpMessageNotWritableException.class,BindException.class})
效果:
默认响应错误的json。状态码 405
{"timestamp": "2023-04-18T11:13:05.515+00:00","status": 405,"error": "Method Not Allowed","trace": "org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException: Request method 'POST' is not supported\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.handleNoMatch(RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.java:265)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.lookupHandlerMethod(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java:441)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.getHandlerInternal(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java:382)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getHandlerInternal(RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.java:126)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getHandlerInternal(RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.java:68)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.AbstractHandlerMapping.getHandler(AbstractHandlerMapping.java:505)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.getHandler(DispatcherServlet.java:1275)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doDispatch(DispatcherServlet.java:1057)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doService(DispatcherServlet.java:974)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.processRequest(FrameworkServlet.java:1011)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.doPost(FrameworkServlet.java:914)\r\n\tat jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:563)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.service(FrameworkServlet.java:885)\r\n\tat jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:631)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:205)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsFilter.doFilter(WsFilter.java:53)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:174)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.RequestContextFilter.doFilterInternal(RequestContextFilter.java:100)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:116)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:174)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.FormContentFilter.doFilterInternal(FormContentFilter.java:93)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:116)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:174)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter.doFilterInternal(CharacterEncodingFilter.java:201)\r\n\tat org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:116)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:174)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:149)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve.invoke(StandardWrapperValve.java:166)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve.invoke(StandardContextValve.java:90)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase.invoke(AuthenticatorBase.java:493)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.invoke(StandardHostValve.java:115)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve.invoke(ErrorReportValve.java:93)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve.invoke(StandardEngineValve.java:74)\r\n\tat org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.service(CoyoteAdapter.java:341)\r\n\tat org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Processor.service(Http11Processor.java:390)\r\n\tat org.apache.coyote.AbstractProcessorLight.process(AbstractProcessorLight.java:63)\r\n\tat org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$ConnectionHandler.process(AbstractProtocol.java:894)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint$SocketProcessor.doRun(NioEndpoint.java:1741)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SocketProcessorBase.run(SocketProcessorBase.java:52)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1191)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:659)\r\n\tat org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable.run(TaskThread.java:61)\r\n\tat java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:833)\r\n","message": "Method 'POST' is not supported.","path": "/list"
}
开启ProblemDetails返回, 使用新的MediaType
Content-Type: application/problem+json+ 额外扩展返回
{"type": "about:blank","title": "Method Not Allowed","status": 405,"detail": "Method 'POST' is not supported.","instance": "/list"
}
函数式Web
SpringMVC 5.2 以后 允许我们使用函数式的方式,定义Web的请求处理流程。
函数式接口
Web请求处理的方式:
- @Controller + @RequestMapping:耦合式 (路由、业务耦合)
- 函数式Web:分离式(路由、业务分离)
场景
场景:User RESTful - CRUD
● GET /user/1 获取1号用户
● GET /users 获取所有用户
● POST /user 请求体携带JSON,新增一个用户
● PUT /user/1 请求体携带JSON,修改1号用户
● DELETE /user/1 删除1号用户
核心类
● RouterFunction 定义路由信息。发什么请求,谁来处理
● RequestPredicate 定义请求规则:请求谓语。请求方式(GET/POST)、请求参数
● ServerRequest 封装请求完整数据
● ServerResponse 封装响应完整数据
示例
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.RequestPredicate;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.RouterFunction;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.ServerResponse;import static org.springframework.web.servlet.function.RequestPredicates.accept;
import static org.springframework.web.servlet.function.RouterFunctions.route;@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class MyRoutingConfiguration {private static final RequestPredicate ACCEPT_JSON = accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);@Beanpublic RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routerFunction(MyUserHandler userHandler) {return route().GET("/{user}", ACCEPT_JSON, userHandler::getUser).GET("/{user}/customers", ACCEPT_JSON, userHandler::getUserCustomers).DELETE("/{user}", ACCEPT_JSON, userHandler::deleteUser).build();}}
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.ServerRequest;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.function.ServerResponse;@Component
public class MyUserHandler {public ServerResponse getUser(ServerRequest request) {...return ServerResponse.ok().build();}public ServerResponse getUserCustomers(ServerRequest request) {...return ServerResponse.ok().build();}public ServerResponse deleteUser(ServerRequest request) {...return ServerResponse.ok().build();}}
SpringBoot3-数据访问
整合SSM场景
SpringBoot 整合 Spring、SpringMVC、MyBatis 进行数据访问场景开发
1. 创建SSM整合项目
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency><groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
2. 配置数据源
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.200.100:3306/demo
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.type=com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
3. 配置MyBatis
#指定mapper映射文件位置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mapper/*.xml
#打开驼峰命名规则
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
CRUD编写
● 编写Bean
● 编写Mapper
● 使用mybatisx插件,快速生成MapperXML
● 测试CRUD
5. 自动配置原理
SSM整合总结:
- 导入 mybatis-spring-boot-starter
- 配置数据源信息
- 配置mybatis的mapper接口扫描与xml映射文件扫描
- 编写bean,mapper,生成xml,编写sql 进行crud。事务等操作依然和Spring中用法一样
- 效果:
a. 所有sql写在xml中
b. 所有mybatis配置写在application.properties下面
● jdbc场景的自动配置:
○ mybatis-spring-boot-starter导入 spring-boot-starter-jdbc,jdbc是操作数据库的场景
○ Jdbc场景的几个自动配置
■ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration
● 数据源的自动配置
● 所有和数据源有关的配置都绑定在DataSourceProperties
● 默认使用 HikariDataSource
■ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration
● 给容器中放了JdbcTemplate操作数据库
■ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration
■ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration
● 基于XA二阶提交协议的分布式事务数据源
■ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration
● 支持事务
○ 具有的底层能力:数据源、JdbcTemplate、事务
● MyBatisAutoConfiguration:配置了MyBatis的整合流程
○ mybatis-spring-boot-starter导入 mybatis-spring-boot-autoconfigure(mybatis的自动配置包),
○ 默认加载两个自动配置类:
■ org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration
■ org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration
● 必须在数据源配置好之后才配置
● 给容器中SqlSessionFactory组件。创建和数据库的一次会话
● 给容器中SqlSessionTemplate组件。操作数据库
○ MyBatis的所有配置绑定在MybatisProperties
○ 每个Mapper接口的代理对象是怎么创建放到容器中。详见@MapperScan原理:
■ 利用@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)批量给容器中注册组件。解析指定的包路径里面的每一个类,为每一个Mapper接口类,创建Bean定义信息,注册到容器中。
如何分析哪个场景导入以后,开启了哪些自动配置类。
找:classpath:/META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件中配置的所有值,就是要开启的自动配置类,但是每个类可能有条件注解,基于条件注解判断哪个自动配置类生效了。
快速定位生效的配置
#开启调试模式,详细打印开启了哪些自动配置
debug=true
# Positive(生效的自动配置) Negative(不生效的自动配置)
扩展:整合其他数据源
- Druid 数据源
暂不支持 SpringBoot3
● 导入druid-starter
● 写配置
● 分析自动配置了哪些东西,怎么用
Druid官网:https://github.com/alibaba/druid
#数据源基本配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.200.100:3306/demo
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource# 配置StatFilter监控
spring.datasource.druid.filter.stat.enabled=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.stat.db-type=mysql
spring.datasource.druid.filter.stat.log-slow-sql=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.stat.slow-sql-millis=2000
# 配置WallFilter防火墙
spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall.enabled=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall.db-type=mysql
spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall.config.delete-allow=false
spring.datasource.druid.filter.wall.config.drop-table-allow=false
# 配置监控页,内置监控页面的首页是 /druid/index.html
spring.datasource.druid.stat-view-servlet.enabled=true
spring.datasource.druid.stat-view-servlet.login-username=admin
spring.datasource.druid.stat-view-servlet.login-password=admin
spring.datasource.druid.stat-view-servlet.allow=*# 其他 Filter 配置不再演示
# 目前为以下 Filter 提供了配置支持,请参考文档或者根据IDE提示(spring.datasource.druid.filter.*)进行配置。
# StatFilter
# WallFilter
# ConfigFilter
# EncodingConvertFilter
# Slf4jLogFilter
# Log4jFilter
# Log4j2Filter
# CommonsLogFilter
4、SpringBoot3-基础特性
1. SpringApplication
1.1. 自定义 banner
- 类路径添加banner.txt或设置spring.banner.location就可以定制 banner
- 推荐网站:Spring Boot banner 在线生成工具,制作下载英文 banner.txt,修改替换 banner.txt 文字实现自定义,个性化启动 banner-bootschool.net
spring.main.banner-mode可以修改banner输出在控制台,或者日志或者关闭
1.2. 自定义 SpringApplication
import org.springframework.boot.Banner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(MyApplication.class);application.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);application.run(args);}}
1.3. FluentBuilder API
new SpringApplicationBuilder().sources(Parent.class).child(Application.class).bannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF).run(args);
2. Profiles
环境隔离能力;快速切换开发、测试、生产环境
步骤:
- 标识环境:指定哪些组件、配置在哪个环境生效
- 切换环境:这个环境对应的所有组件和配置就应该生效
2.1. 使用
2.1.1 指定环境
● Spring Profiles 提供一种隔离配置的方式,使其仅在特定环境生效;
● 任何@Component, @Configuration 或 @ConfigurationProperties 可以使用 @Profile 标记,来指定何时被加载。【容器中的组件都可以被 @Profile标记】
2.2. Profile 分组
创建prod组,指定包含db和mq配置
spring.profiles.group.prod[0]=db
spring.profiles.group.prod[1]=mq
使用–spring.profiles.active=prod ,就会激活prod,db,mq配置文件
2.3. Profile 配置文件
● application-{profile}.properties可以作为指定环境的配置文件。
● 激活这个环境,配置就会生效。最终生效的所有配置是
○ application.properties:主配置文件,任意时候都生效
○ application-{profile}.properties:指定环境配置文件,激活指定环境生效
profile优先级 > application

3. 外部化配置
场景:线上应用如何快速修改配置,并应用最新配置?
● SpringBoot 使用 配置优先级 + 外部配置 简化配置更新、简化运维。
● 只需要给jar应用所在的文件夹放一个application.properties最新配置文件,重启项目就能自动应用最新配置
3.1. 配置优先级
Spring Boot 允许将配置外部化,以便可以在不同的环境中使用相同的应用程序代码。
我们可以使用各种外部配置源,包括Java Properties文件、YAML文件、环境变量和命令行参数。
@Value可以获取值,也可以用@ConfigurationProperties将所有属性绑定到java object中
以下是 SpringBoot 属性源加载顺序。后面的会覆盖前面的值。由低到高,高优先级配置覆盖低优先级
- 默认属性(通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的)
- @PropertySource指定加载的配置(需要写在@Configuration类上才可生效)
- 配置文件(application.properties/yml等)
- RandomValuePropertySource支持的random.*配置(如:@Value(“${random.int}”))
- OS 环境变量
- Java 系统属性(System.getProperties())
- JNDI 属性(来自java:comp/env)
- ServletContext 初始化参数
- ServletConfig 初始化参数
- SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON属性(内置在环境变量或系统属性中的 JSON)
- 命令行参数
- 测试属性。(@SpringBootTest进行测试时指定的属性)
- 测试类@TestPropertySource注解
- Devtools 设置的全局属性。($HOME/.config/spring-boot)
结论:配置可以写到很多位置,常见的优先级顺序:
● 命令行> 配置文件> springapplication配置
配置文件优先级如下:(后面覆盖前面)
- jar 包内的application.properties/yml
- jar 包内的application-{profile}.properties/yml
- jar 包外的application.properties/yml
- jar 包外的application-{profile}.properties/yml
建议:用一种格式的配置文件。如果.properties和.yml同时存在,则.properties优先
结论:包外 > 包内; 同级情况:profile配置 > application配置
所有参数均可由命令行传入,使用–参数项=参数值,将会被添加到环境变量中,并优先于配置文件。
比如java -jar app.jar --name=“Spring”,可以使用@Value(“${name}”)获取
演示场景:
● 包内: application.properties server.port=8000
● 包内: application-dev.properties server.port=9000
● 包外: application.properties server.port=8001
● 包外: application-dev.properties server.port=9001
启动端口?:命令行 > 9001 > 8001 > 9000 > 8000
3.2. 外部配置
SpringBoot 应用启动时会自动寻找application.properties和application.yaml位置,进行加载。顺序如下:(后面覆盖前面)
- 类路径: 内部
a. 类根路径
b. 类下/config包 - 当前路径(项目所在的位置)
a. 当前路径
b. 当前下/config子目录
c. /config目录的直接子目录
最终效果:优先级由高到低,前面覆盖后面
● 命令行 > 包外config直接子目录 > 包外config目录 > 包外根目录 > 包内目录
● 同级比较:
○ profile配置 > 默认配置
○ properties配置 > yaml配置

规律:最外层的最优先。
● 命令行 > 所有
● 包外 > 包内
● config目录 > 根目录
● profile > application
配置不同就都生效(互补),配置相同高优先级覆盖低优先级
3.4. 属性占位符
配置文件中可以使用 ${name:default}形式取出之前配置过的值。
app.name=MyApp
app.description=${app.name} is a Spring Boot application written by ${username:Unknown}
4. 单元测试-JUnit5
4.1. 整合
SpringBoot 提供一系列测试工具集及注解方便我们进行测试。
spring-boot-test提供核心测试能力,spring-boot-test-autoconfigure 提供测试的一些自动配置。
我们只需要导入spring-boot-starter-test 即可整合测试
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
spring-boot-starter-test 默认提供了以下库供我们测试使用
● JUnit 5
● Spring Test
● AssertJ
● Hamcrest
● Mockito
● JSONassert
● JsonPath
4.2. 测试
4.2.0 组件测试
JUnit5的注解与JUnit4的注解有所变化
https://junit.org/junit5/docs/current/user-guide/#writing-tests-annotations
● @Test :表示方法是测试方法。但是与JUnit4的@Test不同,他的职责非常单一不能声明任何属性,拓展的测试将会由Jupiter提供额外测试
● @ParameterizedTest :表示方法是参数化测试,下方会有详细介绍
● @RepeatedTest :表示方法可重复执行,下方会有详细介绍
● @DisplayName :为测试类或者测试方法设置展示名称
● @BeforeEach :表示在每个单元测试之前执行
● @AfterEach :表示在每个单元测试之后执行
● @BeforeAll :表示在所有单元测试之前执行
● @AfterAll :表示在所有单元测试之后执行
● @Tag :表示单元测试类别,类似于JUnit4中的@Categories
● @Disabled :表示测试类或测试方法不执行,类似于JUnit4中的@Ignore
● @Timeout :表示测试方法运行如果超过了指定时间将会返回错误
● @ExtendWith :为测试类或测试方法提供扩展类引用
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.fail;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions.assumeTrue;import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;class StandardTests {@BeforeAllstatic void initAll() {}@BeforeEachvoid init() {}@DisplayName("😱")@Testvoid succeedingTest() {}@Testvoid failingTest() {fail("a failing test");}@Test@Disabled("for demonstration purposes")void skippedTest() {// not executed}@Testvoid abortedTest() {assumeTrue("abc".contains("Z"));fail("test should have been aborted");}@AfterEachvoid tearDown() {}@AfterAllstatic void tearDownAll() {}}

4.2.3 嵌套测试
JUnit 5 可以通过 Java 中的内部类和@Nested 注解实现嵌套测试,从而可以更好的把相关的测试方法组织在一起。在内部类中可以使用@BeforeEach 和@AfterEach 注解,而且嵌套的层次没有限制
@DisplayName("A stack")
class TestingAStackDemo {Stack<Object> stack;@Test@DisplayName("is instantiated with new Stack()")void isInstantiatedWithNew() {new Stack<>();}@Nested@DisplayName("when new")class WhenNew {@BeforeEachvoid createNewStack() {stack = new Stack<>();}@Test@DisplayName("is empty")void isEmpty() {assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());}@Test@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when popped")void throwsExceptionWhenPopped() {assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::pop);}@Test@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when peeked")void throwsExceptionWhenPeeked() {assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, stack::peek);}@Nested@DisplayName("after pushing an element")class AfterPushing {String anElement = "an element";@BeforeEachvoid pushAnElement() {stack.push(anElement);}@Test@DisplayName("it is no longer empty")void isNotEmpty() {assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());}@Test@DisplayName("returns the element when popped and is empty")void returnElementWhenPopped() {assertEquals(anElement, stack.pop());assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());}@Test@DisplayName("returns the element when peeked but remains not empty")void returnElementWhenPeeked() {assertEquals(anElement, stack.peek());assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());}}}
}
4.2.4 参数化测试
参数化测试是JUnit5很重要的一个新特性,它使得用不同的参数多次运行测试成为了可能,也为我们的单元测试带来许多便利。
利用@ValueSource等注解,指定入参,我们将可以使用不同的参数进行多次单元测试,而不需要每新增一个参数就新增一个单元测试,省去了很多冗余代码。
@ValueSource: 为参数化测试指定入参来源,支持八大基础类以及String类型,Class类型
@NullSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个null的入参
@EnumSource: 表示为参数化测试提供一个枚举入参
@CsvFileSource:表示读取指定CSV文件内容作为参数化测试入参
@MethodSource:表示读取指定方法的返回值作为参数化测试入参(注意方法返回需要是一个流)
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = {"one", "two", "three"})
@DisplayName("参数化测试1")
public void parameterizedTest1(String string) {System.out.println(string);Assertions.assertTrue(StringUtils.isNotBlank(string));
}@ParameterizedTest
@MethodSource("method") //指定方法名
@DisplayName("方法来源参数")
public void testWithExplicitLocalMethodSource(String name) {System.out.println(name);Assertions.assertNotNull(name);
}static Stream<String> method() {return Stream.of("apple", "banana");
}
5、SpringBoot3-核心原理
1. 事件和监听器
1. 生命周期监听
监听器-SpringApplicationRunListener
- 自定义SpringApplicationRunListener来监听事件;
1.1. 编写SpringApplicationRunListener 实现类
1.2. 在 META-INF/spring.factories 中配置 org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=自己的Listener,还可以指定一个有参构造器,接受两个参数(SpringApplication application, String[] args)
1.3. springboot 在spring-boot.jar中配置了默认的 Listener,如下

/*** Listener先要从 META-INF/spring.factories 读到** 1、引导: 利用 BootstrapContext 引导整个项目启动* starting: 应用开始,SpringApplication的run方法一调用,只要有了 BootstrapContext 就执行* environmentPrepared: 环境准备好(把启动参数等绑定到环境变量中),但是ioc还没有创建;【调一次】* 2、启动:* contextPrepared: ioc容器创建并准备好,但是sources(主配置类)没加载。并关闭引导上下文;组件都没创建 【调一次】* contextLoaded: ioc容器加载。主配置类加载进去了。但是ioc容器还没刷新(我们的bean没创建)。* =======截止以前,ioc容器里面还没造bean呢=======* started: ioc容器刷新了(所有bean造好了),但是 runner 没调用。* ready: ioc容器刷新了(所有bean造好了),所有 runner 调用完了。* 3、运行* 以前步骤都正确执行,代表容器running。*/

事件触发时机
2. 各种回调监听器
● BootstrapRegistryInitializer: 感知特定阶段:感知引导初始化
○ META-INF/spring.factories
○ 创建引导上下文bootstrapContext的时候触发。
○ application.addBootstrapRegistryInitializer();
○ 场景:进行密钥校对授权。
● ApplicationContextInitializer: 感知特定阶段: 感知ioc容器初始化
○ META-INF/spring.factories
○ application.addInitializers();
● ApplicationListener: 感知全阶段:基于事件机制,感知事件。 一旦到了哪个阶段可以做别的事
○ @Bean或@EventListener: 事件驱动
○ SpringApplication.addListeners(…)或 SpringApplicationBuilder.listeners(…)
○ META-INF/spring.factories
● SpringApplicationRunListener: 感知全阶段生命周期 + 各种阶段都能自定义操作; 功能更完善。
○ META-INF/spring.factories
● ApplicationRunner: 感知特定阶段:感知应用就绪Ready。卡死应用,就不会就绪
○ @Bean
● CommandLineRunner: 感知特定阶段:感知应用就绪Ready。卡死应用,就不会就绪
○ @Bean
最佳实战:
● 如果项目启动前做事: BootstrapRegistryInitializer 和 ApplicationContextInitializer
● 如果想要在项目启动完成后做事:ApplicationRunner和 CommandLineRunner
● 如果要干涉生命周期做事:SpringApplicationRunListener
● 如果想要用事件机制:ApplicationListener
完整触发流程
9大事件触发顺序&时机
- ApplicationStartingEvent:应用启动但未做任何事情, 除过注册listeners and initializers.
- ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent: Environment 准备好,但context 未创建.
- ApplicationContextInitializedEvent: ApplicationContext 准备好,ApplicationContextInitializers 调用,但是任何bean未加载
- ApplicationPreparedEvent: 容器刷新之前,bean定义信息加载
- ApplicationStartedEvent: 容器刷新完成, runner未调用
=以下就开始插入了探针机制==== - AvailabilityChangeEvent: LivenessState.CORRECT应用存活; 存活探针
- ApplicationReadyEvent: 任何runner被调用
- AvailabilityChangeEvent:ReadinessState.ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC就绪探针,可以接请求
- ApplicationFailedEvent :启动出错

SpringBoot 事件驱动开发
应用启动过程生命周期事件感知(9大事件)、应用运行中事件感知(无数种)。
● 事件发布:ApplicationEventPublisherAware或注入:ApplicationEventMulticaster
● 事件监听:组件 + @EventListener


事件发布者
@Service
public class EventPublisher implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware {/*** 底层发送事件用的组件,SpringBoot会通过ApplicationEventPublisherAware接口自动注入给我们* 事件是广播出去的。所有监听这个事件的监听器都可以收到*/ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;/*** 所有事件都可以发* @param event*/public void sendEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {//调用底层API发送事件applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event);}/*** 会被自动调用,把真正发事件的底层组组件给我们注入进来* @param applicationEventPublisher event publisher to be used by this object*/@Overridepublic void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;}
}
事件订阅者
@Service
public class CouponService {@Order(1)@EventListenerpublic void onEvent(LoginSuccessEvent loginSuccessEvent){System.out.println("===== CouponService ====感知到事件"+loginSuccessEvent);UserEntity source = (UserEntity) loginSuccessEvent.getSource();sendCoupon(source.getUsername());}public void sendCoupon(String username){System.out.println(username + " 随机得到了一张优惠券");}
}
**自动配置原理
- 入门理解**
应用关注的三大核心:场景、配置、组件

- 导入starter
- 依赖导入autoconfigure
- 寻找类路径下 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports文件
- 启动,加载所有 自动配置类 xxxAutoConfiguration
a. 给容器中配置功能组件
b. 组件参数绑定到 属性类中。xxxProperties
c. 属性类和配置文件前缀项绑定
d. @Contional派生的条件注解进行判断是否组件生效 - 效果:
a. 修改配置文件,修改底层参数
b. 所有场景自动配置好直接使用
c. 可以注入SpringBoot配置好的组件随时使用
SPI机制
● Java中的SPI(Service Provider Interface)是一种软件设计模式,用于在应用程序中动态地发现和加载组件。SPI的思想是,定义一个接口或抽象类,然后通过在classpath中定义实现该接口的类来实现对组件的动态发现和加载。
● SPI的主要目的是解决在应用程序中使用可插拔组件的问题。例如,一个应用程序可能需要使用不同的日志框架或数据库连接池,但是这些组件的选择可能取决于运行时的条件。通过使用SPI,应用程序可以在运行时发现并加载适当的组件,而无需在代码中硬编码这些组件的实现类。
● 在Java中,SPI的实现方式是通过在META-INF/services目录下创建一个以服务接口全限定名为名字的文件,文件中包含实现该服务接口的类的全限定名。当应用程序启动时,Java的SPI机制会自动扫描classpath中的这些文件,并根据文件中指定的类名来加载实现类。
● 通过使用SPI,应用程序可以实现更灵活、可扩展的架构,同时也可以避免硬编码依赖关系和增加代码的可维护性。
以上回答来自ChatGPT-3.5
在SpringBoot中,META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
作业:写一段java的spi机制代码

自定义starter
场景:抽取聊天机器人场景,它可以打招呼。
效果:任何项目导入此starter都具有打招呼功能,并且问候语中的人名需要可以在配置文件中修改
● 1. 创建自定义starter项目,引入spring-boot-starter基础依赖
● 2. 编写模块功能,引入模块所有需要的依赖。
● 3. 编写xxxAutoConfiguration自动配置类,帮其他项目导入这个模块需要的所有组件
● 4. 编写配置文件META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports指定启动需要加载的自动配置
● 5. 其他项目引入即可使用
- 业务代码
自定义配置有提示。导入以下依赖重启项目,再写配置文件就有提示
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "robot") //此属性类和配置文件指定前缀绑定
@Component
@Data
public class RobotProperties {private String name;private String age;private String email;
}<!-- 导入配置处理器,配置文件自定义的properties配置都会有提示--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId><optional>true</optional></dependency>
基本抽取
● 创建starter项目,把公共代码需要的所有依赖导入
● 把公共代码复制进来
● 自己写一个 RobotAutoConfiguration,给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件
○ 为什么这些组件默认不会扫描进去?
○ starter所在的包和 引入它的项目的主程序所在的包不是父子层级
● 别人引用这个starter,直接导入这个 RobotAutoConfiguration,就能把这个场景的组件导入进来
● 功能生效。
● 测试编写配置文件
使用@EnableXxx机制
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Documented
@Import(RobotAutoConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableRobot {}
完全自动配置
● 依赖SpringBoot的SPI机制
● META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 文件中编写好我们自动配置类的全类名即可
● 项目启动,自动加载我们的自动配置类

Docker安装
还不会docker的同学,参考【云原生实战(10~25集)】快速入门
sudo yum install -y yum-utilssudo yum-config-manager \--add-repo \https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.reposudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-pluginsudo systemctl enable docker --now#测试工作
docker ps
# 批量安装所有软件
docker compose
创建 /prod 文件夹,准备以下文件
2. prometheus.yml
global:scrape_interval: 15sevaluation_interval: 15sscrape_configs:- job_name: 'prometheus'static_configs:- targets: ['localhost:9090']- job_name: 'redis'static_configs:- targets: ['redis:6379']- job_name: 'kafka'static_configs:- targets: ['kafka:9092']
docker-compose.yml
version: '3.9'services:redis:image: redis:latestcontainer_name: redisrestart: alwaysports:- "6379:6379"networks:- backendzookeeper:image: bitnami/zookeeper:latestcontainer_name: zookeeperrestart: alwaysenvironment:ZOOKEEPER_CLIENT_PORT: 2181ZOOKEEPER_TICK_TIME: 2000networks:- backendkafka:image: bitnami/kafka:3.4.0container_name: kafkarestart: alwaysdepends_on:- zookeeperports:- "9092:9092"environment:ALLOW_PLAINTEXT_LISTENER: yesKAFKA_CFG_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT: zookeeper:2181KAFKA_OFFSETS_TOPIC_REPLICATION_FACTOR: 1networks:- backendkafka-ui:image: provectuslabs/kafka-ui:latestcontainer_name: kafka-uirestart: alwaysdepends_on:- kafkaports:- "8080:8080"environment:KAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: devKAFKA_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: kafka:9092networks:- backendprometheus:image: prom/prometheus:latestcontainer_name: prometheusrestart: alwaysvolumes:- ./prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.ymlports:- "9090:9090"networks:- backendgrafana:image: grafana/grafana:latestcontainer_name: grafanarestart: alwaysdepends_on:- prometheusports:- "3000:3000"networks:- backendnetworks:backend:name: backend
启动环境
docker compose -f docker-compose.yml up -d


测试
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;@Test
void redisTest(){redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("a","1234");Assertions.assertEquals("1234",redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("a"));
}
自动配置原理
- META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports中导入了RedisAutoConfiguration、RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration和RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration。所有属性绑定在RedisProperties中
- RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration属于响应式编程,不用管。RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration属于 JPA 操作,也不用管
- RedisAutoConfiguration 配置了以下组件
1.1. LettuceConnectionConfiguration: 给容器中注入了连接工厂LettuceConnectionFactory,和操作 redis 的客户端DefaultClientResources。
1.2. RedisTemplate<Object, Object>: 可给 redis 中存储任意对象,会使用 jdk 默认序列化方式。
1.3. StringRedisTemplate: 给 redis 中存储字符串,如果要存对象,需要开发人员自己进行序列化。key-value都是字符串进行操作··
定制化
序列化机制
@Configuration
public class AppRedisConfiguration {/*** 允许Object类型的key-value,都可以被转为json进行存储。* @param redisConnectionFactory 自动配置好了连接工厂* @return*/@Beanpublic RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);//把对象转为json字符串的序列化工具template.setDefaultSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());return template;}
}
redis客户端
RedisTemplate、StringRedisTemplate: 操作redis的工具类
● 要从redis的连接工厂获取链接才能操作redis
● Redis客户端
○ Lettuce: 默认
○ Jedis:可以使用以下切换
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>io.lettuce</groupId><artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency><!-- 切换 jedis 作为操作redis的底层客户端--><dependency><groupId>redis.clients</groupId><artifactId>jedis</artifactId></dependency>
配置参考
spring.data.redis.host=8.130.74.183
spring.data.redis.port=6379
#spring.data.redis.client-type=lettuce#设置lettuce的底层参数
#spring.data.redis.lettuce.pool.enabled=true
#spring.data.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8spring.data.redis.client-type=jedis
spring.data.redis.jedis.pool.enabled=true
spring.data.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=8
接口文档

. 整合
导入场景
<dependency><groupId>org.springdoc</groupId><artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId><version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
配置
# /api-docs endpoint custom path 默认 /v3/api-docs
springdoc.api-docs.path=/api-docs# swagger 相关配置在 springdoc.swagger-ui
# swagger-ui custom path
springdoc.swagger-ui.path=/swagger-ui.htmlspringdoc.show-actuator=true
3. 使用
常用注解

Docket配置
如果有多个Docket,配置如下
@Beanpublic GroupedOpenApi publicApi() {return GroupedOpenApi.builder().group("springshop-public").pathsToMatch("/public/**").build();}@Beanpublic GroupedOpenApi adminApi() {return GroupedOpenApi.builder().group("springshop-admin").pathsToMatch("/admin/**").addMethodFilter(method -> method.isAnnotationPresent(Admin.class)).build();}
如果只有一个Docket,可以配置如下
springdoc.packagesToScan=package1, package2
springdoc.pathsToMatch=/v1, /api/balance/**

远程过程调用:
服务提供者:
服务消费者:
通过连接对方服务器进行请求\响应交互,来实现调用效果
API/SDK的区别是什么?
api:接口(Application Programming Interface)
远程提供功能;
sdk:工具包(Software Development Kit)
导入jar包,直接调用功能即可
开发过程中,我们经常需要调用别人写的功能
如果是内部微服务,可以通过依赖cloud、注册中心、openfeign等进行调用
如果是外部暴露的,可以发送 http 请求、或遵循外部协议进行调用
SpringBoot 整合提供了很多方式进行远程调用
轻量级客户端方式
RestTemplate: 普通开发
WebClient: 响应式编程开发
Http Interface: 声明式编程
Spring Cloud分布式解决方案方式
Spring Cloud OpenFeign
第三方框架
Dubbo
gRPC
…
1. WebClient
非阻塞、响应式HTTP客户端
1.1 创建与配置
发请求:
请求方式: GET\POST\DELETE\xxxx
请求路径: /xxx
请求参数:aa=bb&cc=dd&xxx
请求头: aa=bb,cc=ddd
请求体:
创建 WebClient 非常简单:
WebClient.create()
WebClient.create(String baseUrl)
还可以使用 WebClient.builder() 配置更多参数项:
uriBuilderFactory: 自定义UriBuilderFactory ,定义 baseurl.
defaultUriVariables: 默认 uri 变量.
defaultHeader: 每个请求默认头.
defaultCookie: 每个请求默认 cookie.
defaultRequest: Consumer 自定义每个请求.
filter: 过滤 client 发送的每个请求
exchangeStrategies: HTTP 消息 reader/writer 自定义.
clientConnector: HTTP client 库设置.
//获取响应完整信息
WebClient client = WebClient.create("https://example.org");
1.2获取响应
retrieve()方法用来声明如何提取响应数据。比如
//获取响应完整信息
WebClient client = WebClient.create("https://example.org");Mono<ResponseEntity<Person>> result = client.get().uri("/persons/{id}", id).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).retrieve().toEntity(Person.class);//只获取body
WebClient client = WebClient.create("https://example.org");Mono<Person> result = client.get().uri("/persons/{id}", id).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).retrieve().bodyToMono(Person.class);//stream数据
Flux<Quote> result = client.get().uri("/quotes").accept(MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM).retrieve().bodyToFlux(Quote.class);//定义错误处理
Mono<Person> result = client.get().uri("/persons/{id}", id).accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).retrieve().onStatus(HttpStatus::is4xxClientError, response -> ...).onStatus(HttpStatus::is5xxServerError, response -> ...).bodyToMono(Person.class);
1.3定义请求体
etrieve()方法用来声明如何提取响应数据。比如
//1、响应式-单个数据
Mono<Person> personMono = ... ;Mono<Void> result = client.post().uri("/persons/{id}", id).contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).body(personMono, Person.class).retrieve().bodyToMono(Void.class);//2、响应式-多个数据
Flux<Person> personFlux = ... ;Mono<Void> result = client.post().uri("/persons/{id}", id).contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_STREAM_JSON).body(personFlux, Person.class).retrieve().bodyToMono(Void.class);//3、普通对象
Person person = ... ;Mono<Void> result = client.post().uri("/persons/{id}", id).contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).bodyValue(person).retrieve().bodyToMono(Void.class);
HTTP Interface
Spring 允许我们通过定义接口的方式,给任意位置发送 http 请求,实现远程调用,可以用来简化 HTTP 远程访问。需要webflux场景才可
2.1 导入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.2 定义接口
public interface BingService {@GetExchange(url = "/search")String search(@RequestParam("q") String keyword);
}
2.3 创建代理&测试s
@SpringBootTest
class Boot05TaskApplicationTests {@Testvoid contextLoads() throws InterruptedException {//1、创建客户端WebClient client = WebClient.builder().baseUrl("https://cn.bing.com").codecs(clientCodecConfigurer -> {clientCodecConfigurer.defaultCodecs().maxInMemorySize(256*1024*1024);//响应数据量太大有可能会超出BufferSize,所以这里设置的大一点}).build();//2、创建工厂HttpServiceProxyFactory factory = HttpServiceProxyFactory.builder(WebClientAdapter.forClient(client)).build();//3、获取代理对象BingService bingService = factory.createClient(BingService.class);//4、测试调用Mono<String> search = bingService.search("尚硅谷");System.out.println("==========");search.subscribe(str -> System.out.println(str));Thread.sleep(100000);}}
SpringBoot整合kafka
参照:https://docs.spring.io/spring-kafka/reference/
spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers=172.20.128.1:9092
消息发送
@SpringBootTest
class Boot07KafkaApplicationTests {@AutowiredKafkaTemplate kafkaTemplate;@Testvoid contextLoads() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {StopWatch watch = new StopWatch();watch.start();CompletableFuture[] futures = new CompletableFuture[10000];for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {CompletableFuture send = kafkaTemplate.send("order", "order.create."+i, "订单创建了:"+i);futures[i]=send;}CompletableFuture.allOf(futures).join();watch.stop();System.out.println("总耗时:"+watch.getTotalTimeMillis());}}
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
public class MyBean {private final KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;public MyBean(KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate) {this.kafkaTemplate = kafkaTemplate;}public void someMethod() {this.kafkaTemplate.send("someTopic", "Hello");}}
消息监听
@Component
public class OrderMsgListener {@KafkaListener(topics = "order",groupId = "order-service")public void listen(ConsumerRecord record){System.out.println("收到消息:"+record); //可以监听到发给kafka的新消息,以前的拿不到}@KafkaListener(groupId = "order-service-2",topicPartitions = {@TopicPartition(topic = "order",partitionOffsets = {@PartitionOffset(partition = "0",initialOffset = "0")})})public void listenAll(ConsumerRecord record){System.out.println("收到partion-0消息:"+record);}
}
6. 参数配置
消费者
spring.kafka.consumer.value-deserializer=org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonDeserializer
spring.kafka.consumer.properties[spring.json.value.default.type]=com.example.Invoice
spring.kafka.consumer.properties[spring.json.trusted.packages]=com.example.main,com.example.another
生产者
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer=org.springframework.kafka.support.serializer.JsonSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.properties[spring.json.add.type.headers]=false
自动配置原理
kafka 自动配置在KafkaAutoConfiguration
- 容器中放了 KafkaTemplate 可以进行消息收发
- 容器中放了KafkaAdmin 可以进行 Kafka 的管理,比如创建 topic 等
- kafka 的配置在KafkaProperties中
- @EnableKafka可以开启基于注解的模式
Spring Security 原理
1. 过滤器链架构
Spring Security利用 FilterChainProxy 封装一系列拦截器链,实现各种安全拦截功能
Servlet三大组件:Servlet、Filter、Listener

FilterChainProxy

SecurityFilterChain

使用
1. HttpSecurity
@Configuration
@Order(SecurityProperties.BASIC_AUTH_ORDER - 10)
public class ApplicationConfigurerAdapter extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.antMatcher("/match1/**").authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/match1/user").hasRole("USER").antMatchers("/match1/spam").hasRole("SPAM").anyRequest().isAuthenticated();}
}
MethodSecurity
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class SampleSecureApplication {
}@Service
public class MyService {@Secured("ROLE_USER")public String secure() {return "Hello Security";}}
核心
● WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
● @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity: 开启全局方法安全配置
○ @Secured
○ @PreAuthorize
○ @PostAuthorize
● UserDetailService: 去数据库查询用户详细信息的service(用户基本信息、用户角色、用户权限)
. 实战1. 引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId><artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId><version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope><optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>com.mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId><scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId><optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId><artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity6</artifactId><!-- Temporary explicit version to fix Thymeleaf bug --><version>3.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId><artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
2. 页面
首页
<p>Click <a th:href="@{/hello}">here</a> to see a greeting.</p>
Hello页
<h1>Hello</h1>
登录页
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org"><head><title>Spring Security Example</title></head><body><div th:if="${param.error}">Invalid username and password.</div><div th:if="${param.logout}">You have been logged out.</div><form th:action="@{/login}" method="post"><div><label> User Name : <input type="text" name="username" /> </label></div><div><label> Password: <input type="password" name="password" /> </label></div><div><input type="submit" value="Sign In" /></div></form></body>
</html>
配置类
视图控制
package com.example.securingweb;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewControllerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;@Configuration
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {registry.addViewController("/home").setViewName("index");registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");registry.addViewController("/hello").setViewName("hello");registry.addViewController("/login").setViewName("login");}
}
Security配置
package com.atguigu.security.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;/*** @author lfy* @Description* @create 2023-03-08 16:54*/
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {@Beanpublic SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.authorizeHttpRequests((requests) -> requests.requestMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll().anyRequest().authenticated()).formLogin((form) -> form.loginPage("/login").permitAll()).logout((logout) -> logout.permitAll());return http.build();}@Beanpublic UserDetailsService userDetailsService() {UserDetails user =User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("admin").password("admin").roles("USER").build();return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user);}
}
改造Hello页
<!DOCTYPE html>
<htmlxmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org"xmlns:sec="https://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity6"
><head><title>Hello World!</title></head><body><h1 th:inline="text">Hello <span th:remove="tag" sec:authentication="name">thymeleaf</span>!</h1><form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post"><input type="submit" value="Sign Out" /></form></body>
</html>
可观测性

1. SpringBoot Actuator
1. 实战
1. 场景引入
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. 暴露指标
management:endpoints:enabled-by-default: true #暴露所有端点信息web:exposure:include: '*' #以web方式暴露
3. 访问数据
● 访问 http://localhost:8080/actuator;展示出所有可以用的监控端点
● http://localhost:8080/actuator/beans
● http://localhost:8080/actuator/configprops
● http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics
● http://localhost:8080/actuator/metrics/jvm.gc.pause
● http://localhost:8080/actuator/endpointName/detailPath
. Endpoint


2. 定制端点
● 健康监控:返回存活、死亡
● 指标监控:次数、率
1. HealthEndpoint2. 定制端点
● 健康监控:返回存活、死亡
● 指标监控:次数、率
1. HealthEndpoint
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.HealthIndicator;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
public class MyHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {@Overridepublic Health health() {int errorCode = check(); // perform some specific health checkif (errorCode != 0) {return Health.down().withDetail("Error Code", errorCode).build();}return Health.up().build();}}构建Health
Health build = Health.down().withDetail("msg", "error service").withDetail("code", "500").withException(new RuntimeException()).build();
management:health:enabled: trueshow-details: always #总是显示详细信息。可显示每个模块的状态信息
@Component
public class MyComHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {/*** 真实的检查方法* @param builder* @throws Exception*/@Overrideprotected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {//mongodb。 获取连接进行测试Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();// 检查完成if(1 == 2){
// builder.up(); //健康builder.status(Status.UP);map.put("count",1);map.put("ms",100);}else {
// builder.down();builder.status(Status.OUT_OF_SERVICE);map.put("err","连接超时");map.put("ms",3000);}builder.withDetail("code",100).withDetails(map);}
}
**MetricsEndpoint **
class MyService{Counter counter;public MyService(MeterRegistry meterRegistry){counter = meterRegistry.counter("myservice.method.running.counter");}public void hello() {counter.increment();}
}

#安装prometheus:时序数据库
docker run -p 9090:9090 -d \
-v pc:/etc/prometheus \
prom/prometheus#安装grafana;默认账号密码 admin:admin
docker run -d --name=grafana -p 3000:3000 grafana/grafana
导入依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>io.micrometer</groupId><artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId><version>1.10.6</version>
</dependency>
management:endpoints:web:exposure: #暴露所有监控的端点include: '*'
访问: http://localhost:8001/actuator/prometheus 验证,返回 prometheus 格式的所有指标
部署Java应用
#安装上传工具
yum install lrzsz#安装openjdk
# 下载openjdk
wget https://download.oracle.com/java/17/latest/jdk-17_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzmkdir -p /opt/java
tar -xzf jdk-17_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz -C /opt/java/
sudo vi /etc/profile
#加入以下内容
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/java/jdk-17.0.7
export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin#环境变量生效
source /etc/profile# 后台启动java应用
nohup java -jar boot3-14-actuator-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar > output.log 2>&1 &确认可以访问到: http://8.130.32.70:9999/actuator/prometheus
配置 Prometheus 拉取数据
## 修改 prometheus.yml 配置文件
scrape_configs:- job_name: 'spring-boot-actuator-exporter'metrics_path: '/actuator/prometheus' #指定抓取的路径static_configs:- targets: ['192.168.200.1:8001']labels:nodename: 'app-demo'
配置 Grafana 监控面板
● 添加数据源(Prometheus)
● 添加面板。可去 dashboard 市场找一个自己喜欢的面板,也可以自己开发面板;Dashboards | Grafana Labs
AOT




原生镜像:native-image(机器码、本地镜像)
● 把应用打包成能适配本机平台 的可执行文件(机器码、本地镜像)
2. GraalVM
https://www.graalvm.org/
GraalVM是一个高性能的JDK,旨在加速用Java和其他JVM语言编写的应用程序的执行,同时还提供JavaScript、Python和许多其他流行语言的运行时。
GraalVM提供了两种运行Java应用程序的方式:
● 1. 在HotSpot JVM上使用Graal即时(JIT)编译器
● 2. 作为预先编译(AOT)的本机可执行文件运行(本地镜像)。
GraalVM的多语言能力使得在单个应用程序中混合多种编程语言成为可能,同时消除了外部语言调用的成本。







附录:SpringBoot3改变 & 新特性 快速总结
1、自动配置包位置变化【参照视频:07、11】
META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
2、jakata api迁移
druid有问题
3、新特性 - 函数式Web、ProblemDetails
4、GraalVM 与 AOT
5、响应式编程全套
6、剩下变化都是版本升级,意义不大






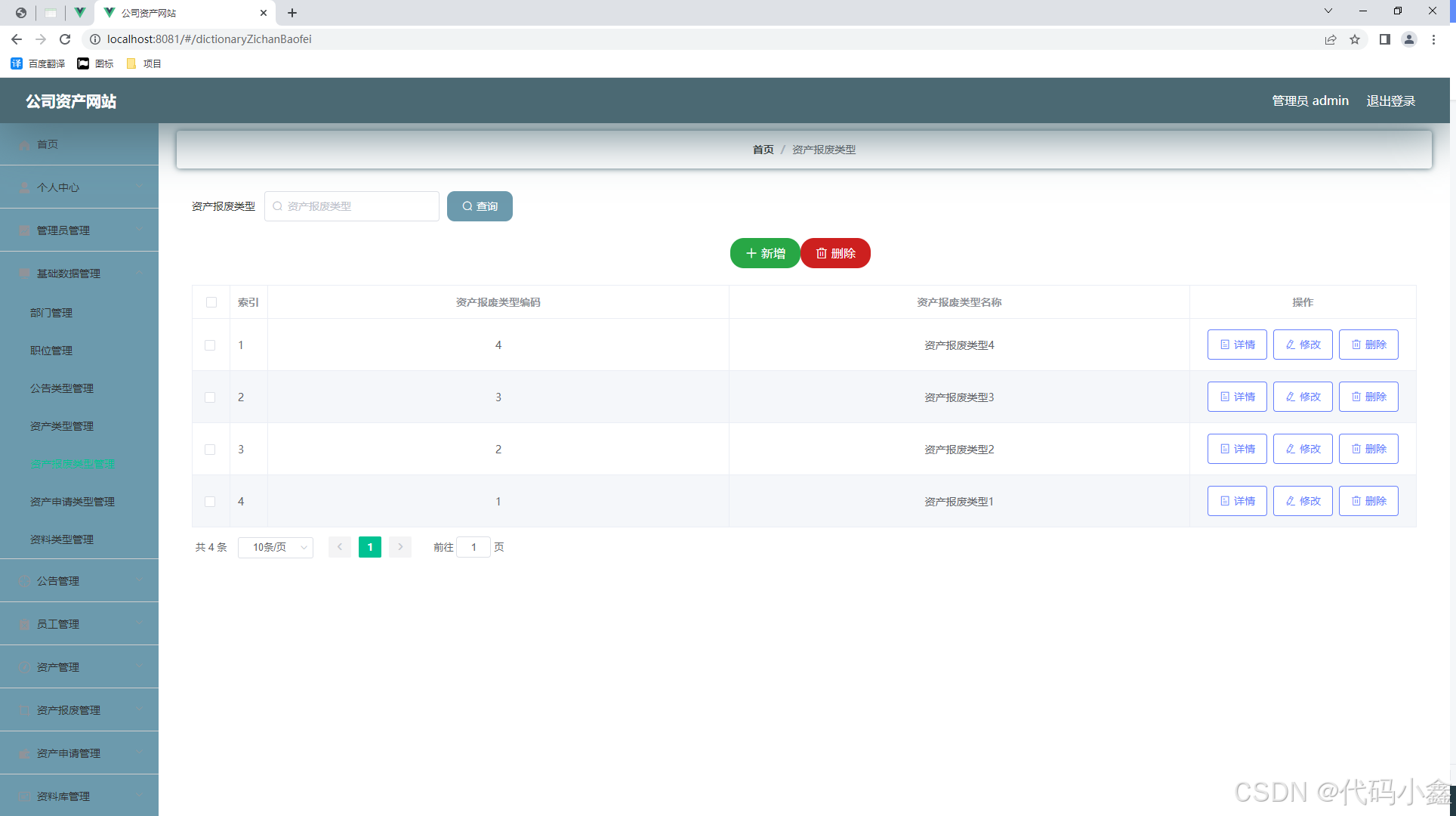






![[JAVA]有关MyBatis环境配置介绍](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6b2d13bbc9a1426e88e3439575945e55.png)




