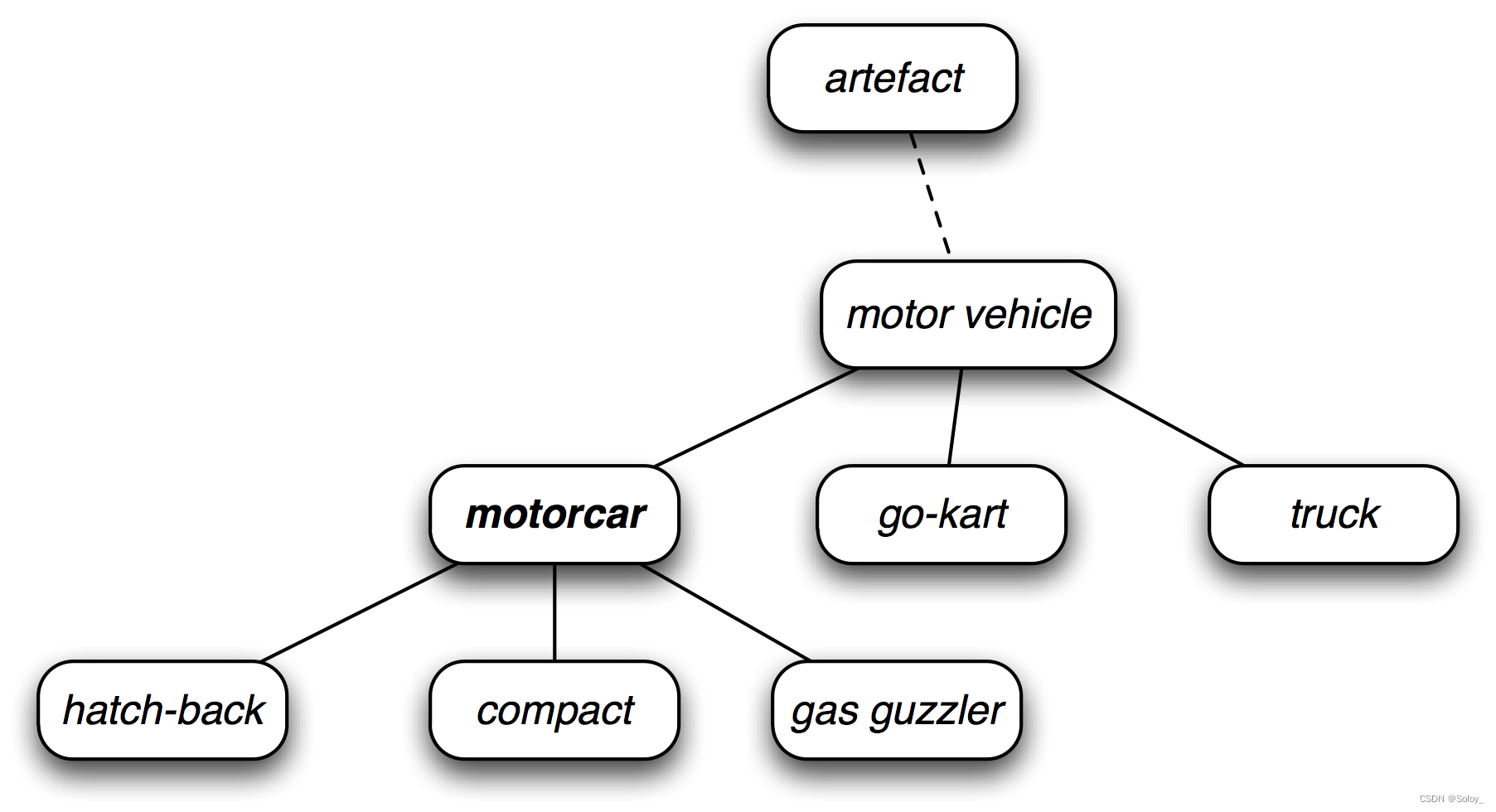
文章目录
- 一、主语
- 1、名词、代词和动词做主语
- 2、主语从句做主语,谓语动词用单数
- 3、主语从句练习
- 二、谓语动词
- 1、谓语动词种类
- 2、主谓一致
- 三、宾语
- 1、单宾语
- 2、双宾语
- 3、复合宾语
- 4、宾语从句
- 四、定语
- 1、定语从句
- 2、定语从句的翻译
- 五、状语
- 1、分词做状语
- 2、独立主格结构
- 3、With复合结构
- 4、状语从句
一、主语
定义:执行句子中动作或行为的主体
例:我吃饭 她爱我
1、名词、代词和动词做主语
1、名词或代词(主格)
例:The car is very beautiful
He is my brother
-
分清主格代词、宾格代词和物主代词。做主语的是主格代词

例:He likes playing basketball
Him likes playing basketball(错) -
名词前需要加修饰词
冠词:a an the
指示代词: this that these those
2、动词不定式做主语
注意:表示一次性,具体的动作
To finish the job is very difficult
To master two foreign languages is necessary
重点:1、谓语动词做单数
2、通常用it做形式主语,to do不定式放在后面
例:It is very difficult to finish the job
3、动词短语做主语
Learning English is very important to our life
注意:1.表示经常性的动作
Reading English aloud in the morning will do you a lot of good
2.谓语动词用单数
Cheating on the exam ruins one`s character
3.动名词的否定:在动词前面加not
Not knowing English brings a lot of trouble to us
4.动名词的逻辑主语
名词所有格和形容词性物主代词放在动名词前面
例: Their coming to help was a great encouragement to us.
His being elected our president made us very surprised.
2、主语从句做主语,谓语动词用单数
1.当主语从句是陈述句时,用that引导,且不能省略。谓语动词用单数
He finished the job in such a short time surprised us all.(错)
That he finished the job in such a short time surprised us all(对)
2.常常用it 做形式主语
例:That the driver could not control the car was obvious
It is obvious that the driver could not control the car
3.whether 引导的主语从句
注意:一般用whether,不用if
Whether we will go to Beijing is still a problem
Whether it is true remains a question
4.特殊疑问词引导的从句做主语
1)用陈述语序
2)特殊疑问词在从句中做成分
3)从句的意义相当于名词
例:What we need is time.
Why he make the mistake is unknown
3、主语从句练习
1.他还活着,真是个奇迹(wonder)
It is a wonder that he is still alive
2.你要来伦敦,是一个好消息
It is a good news that you are coming to London
3.他们是否支持我们,仍然是一个问题
Whether they would support us was a problem
4.我们何时去北京,还没有定下来
When we shall go to Beijing is not decided
5.这个问题如何解决的,是一个秘密
How this problem was solved was a secret
二、谓语动词
定义:表示主语的行为、动作和状态
例:We study English
They plant trees
1、谓语动词种类
- 行为动词:包括及物动词和不及物动词
及物动词:后面必须跟宾语意义才完整,用vt代替
例:We plant trees around our school
不及物动词:本身意义完整,可以独立使用,或后面加介词后方可跟宾语
例:My watch stopped
we go to Beijing - 系动词:be(am,is,are)
例:He is a teacher - 情态动词:
can/could/may/must/might/should/will/would等+do 构成复合谓语动词
例:He can play football
They will help me - 助动词:do/does/did
例:He didn’t finish the job yesterday
You do know a lot about the Internet
2、主谓一致
- 语法原则:即语法上要一致,主语是单数,谓语动词也是单数;主语是复数,谓语动词是复数。
例:The students are very young
She looks very beautiful - 意义原则:即从意义上处理主谓一致关系
例:This pair of trousers costs 100 yuan
My family are watching TV now - 就近原则
例:There is a book and some cakes on the table
Neither my grandsons nor their father is coming
常用作单数:
- 不定代词做主语,谓语动词用单数。
例:Someone is knocking at the door.
Nothing is important than life. - many a 或more than one +单数名词,谓语动词用单数
- 非谓语动词做主语,用单数。
三、宾语
定义:宾语即谓语动词作用的对象
例:我吃饭 他喜欢女孩 l like apples
1、单宾语
-
名词做宾语
例:Show your passport,please -
代词做宾语(包括不定代词和宾格代词)
例:He didn’t say anything
All of the girls like him -
数词做宾语
例:How many do you want ? l want two -
名词化得形容词,即the+形容词(表示一类人)做宾语
例:They sent the injured to the hospital
The government should pay more attention to the poor -
不定式或动名词做宾语
例:They want to play basketball
They enjoy playing basketball
2、双宾语
定义:有些动词可以连接两个宾语,即指人的间接宾语和物的直接宾语
常用句型为:及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语
例:Give me a cup of tea=Give a cup of tea to me
有时间接宾语可以改成由to 或for引起的短语
例:She passed him the salt=She passed the salt to him
下面几种情况通常用to或for引起的短语:
1.当直接宾语是人称代词(it或them)时。
例如:The watch is Lilei`s. Please give it to him.
2.当强调间接宾语时。
例:Mother cooks breakfast for us everyday.
3.当间接宾语比直接宾语长时
例:On the bus, he often gives the seat to an old person.
3、复合宾语
常用句型为:主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语
定义:在英语中,有些及物动词接宾语后,需要接补足语来补充说明宾语的有关情况,这样意思才完整。宾语和宾语补足语称为复合宾语
判断标准:如果宾语与其后的成分存在逻辑上的主谓或主表关系,则该动词就是接的复合宾语,否则就是双宾语
例:We call them mooncakes(名词)
At first, I found English hard.(形容词)
In the country, he can hear birds singing.(分词)
She often helps her mother to do homework(不定式)
The boy found his pen on the floor.(介词短语)
4、宾语从句
宾语从句就是一个句子来构成的宾语,并有一个连词引导
那些句子可以做宾语?
- 陈述句 he is famous basketball player
- 一般疑问句 will our teachers attend the meeting
- 特殊疑问句 which coat did you want
1.当宾语从句是陈述句时(包括肯定句和否定句),连词由that引导,因为that在从句中不作任何成分,也没有任何具体意思,因此在口语或非正式文体中常省略
She says(that)she won’t take part in the sports meeting
2.一般疑问句做宾语

宾语从句必须用陈述语序:陈述语序即:主语+谓语/主语+系动词
由if或者whether(or not)引导一般疑问句的宾语从句
if和whether在句中的意思是“是否”
注意:只用whether不用if情况
1.whether引导的从句常可以与or not 直接连用,如:Let me know whether you can come or not
2.当宾语从句提到句首时,只能用whether引导,如:Whether it is true or not,l can’t tell
3.whether引导to 的不定时,如:l don’t know whether to accept or refuse
4.whether及其引导的成分可放于介词之后,做介词的宾语
l worry about whether l hurt her feelings
3.特殊疑问句做宾语从句

四、定语
1、介词短语做后置定语
The weather in Beijing is colder than that in Shanghai
(地点)
His love for his country is very great
(动宾)
2、形容词做后置定语
He looked at the street full of cars
他看着车辆拥挤的街道
3、现在分词短语做后置定语
They built a highway leading into the mountains
他们修建了一条通往山里的公路
4、过去分词短语做后置定语
What’s the languages spoken in that area
那个地区讲什么语言
5、动词不定式做后置定语
(1)表示动宾关系
动词不定式 to do 做修饰语的逻辑谓语
被修饰的名词为动词不定式to do的直接宾语
例:l have a lot of work to do today
我今天有很多活要干
(2)表示主谓关系
被修饰的名字表示逻辑主语
修饰它的动词不定式结构表示逻辑谓语
例:He’s always the first to come
1、定语从句
-
先行词:定语从句修饰的词
例:The car which was stolen has been found
The house whose windows are broken is empty -
关系词:
1)起连接作用,引导定语从句
2)关系代词:that which who whom whose as
关系副词:when where why
3)在定语从句中做成分:主语 宾语 定语 状语 表语

(1)who和that:当先行词是指代人的名词或代词,且在定语从句中做主语时
例:They boy who is standing there is Tom
(2)whom和that:当先行词是指代人的名词或代词,且在定语从句中做宾语时
例:This is our Chinese teacher(whom)everyone likes
(3)which或that:当先行词是物,在定语从句中做主语或宾语
例:The new house (which/that)l bought last year is very big
(4)where :先行词表示地点,在定语从句中做状语
when:先行词表示时间,在定语从句中做状语
why:先行词表示原因
关系副词=介词+which why=for which
例:This is the classroom where we study
This is the classroom in which we study
This is the reason why l like Tom
This is the reason for which l like Tom
We will never forget the days when we spent with our teacher
We will never forget the days in which we spent with our teacher
特殊用法:
1.只用关系代词that,不用which,who 或 whom的几种情况
1)当先行词是all,everything,nothing,something,anything,little,none,few等时,如:All that you want are here
2)当先行词被all,no,some,any,every,a few ,a little ,much,only,very 等修饰时。如:There is no person that doesn’t make mistake
3)当先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。如: This is the best film that l have ever seen
4)当出现两个人或两个以上的先行词,并同时兼指人和物时。如:We are talking about the people and countries that we have visited
2.介词+which/whom结构中,介词的选择取决于三种情况
1)根据定义从句中谓语动词。如:
This is the college in which l am studing
2)先行词与介词的习惯搭配。如:
The speed at which the machine operates is shown on the meter
仪表上显示出这台机器运转的速度。
3)当定语从句为最高级时只能用of which ;否者用其他介词。如:
l have five dictionaries of which the Longman Dictionary is the best
3.限制性定语从句与非限制性定语从句区别
限定性定语从句和先行词之间没有逗号,表示对先行词起修饰限定作用;而非限定性定语从句和先行词之间有逗号分开,是对先行词进行补充说明,相当于并列句。如:
He is the man who has a strong personality
他是一个个性很强的人(限定性定语从句)
My brother,who works abroad,is coming next week
我哥哥在国外工作,他下周将回来(非限制性定语从句)
注:1)非限定性定语从句不能用that来引导,一般用which,as或who(指人)。用which或as引导时,既可以修饰主句的部分内容,也可修饰主句的全部内容。如:
He spoke confidently, which impressed me most. (which指代整个主句,在从句中作主语)
2)as引导的非限定性定语从句可以放在主句之前,也可以放在主句之后,但which或who引导的非限定性定语从句不能放在主句之前。如:
As we all know the moon is a satellite of the earth
3)在限定性定语从句中,关系代词做宾语可以省略;但在非限定性定语从句中,关系代词做宾语时不能省略。如:
The film (which)l saw last night is about a young teacher(which可以省略)
She introduced to her husband,whom l hadn’t met before(whom不可省略)
练习:
1.愿意参加聚会的人请在这儿签名。
Those who are willing to attend the party please sign here
2.这是那个值得参观的地方。
This is the place worth visiting
3.众所周知,地球是圆的,不是平的。
As we all know,the earth is round,not flat
4.这是那个房子被烧毁的男人
This is the man whose house was burned down
5.在我们学校有一个外教,他的父母都生活在美国。
In our school,there is foreign teacher whose parent live in the US
2、定语从句的翻译
(一)前置法
把英语原文的定语从句翻译成带“的”的定语词组,放置于被修饰的词之前,将英语原文的复合句翻译成汉语的简单句,这种方法一般用于限制性定语从句比较短的情况。
一些较短的具有述性的非限制性定语从句也可采用前置法,但没有限制性定语从句使用得普遍。
The people who worked for him lived in Shanghai
在他手下工作的人在威海居住
(1)The sun,which had hidden all day,now came out in all its splendor
那个整天躲在云层里的太阳,现在又光芒四射地露面了
(2)But Miggle‘s laugh ,which was very infectious,broke the silence
但米格尔的富有感染力的笑声打破了静默
(二)后置法
当定语从句较长时,如果翻译成前置的定语,就会不符合汉语的表达习惯,在这种情况下,往往把该定语从句翻译成并列的分句,放置于原来它所修饰词的后面。翻译时可以用三种方法来处理
1)译成并列分句,重复先行词
l told the story to John,who told it to his brother
我把这件事告诉了约翰,约翰又告诉了他弟弟
2)译成并列分句,省略先行词
lt is he who received the letter that announced the death of your uncle
3)译成独立句(非限制性定从)
He had talked to Vice-President Nixon,who assured him that everything that could be done would be done
他和副总统尼克松谈过话。副总统向他保证凡是能过做到的他都将竭尽全力去做
(三)融合法
融合法是指翻译时把主句和定语从句融合在一起译成一个简单句。由于限制性定语从句与主句关系较紧密,所以融合法多用于翻译限制性定语从句,尤其是“there be ”结构带有定语从句的句型
There are many people who want to see the film
许多人要看这部电影
五、状语
定义:修饰谓语中心词,说明谓语中心词发生的状态
状语的作用:状语说明地点、时间、原因、目的、结果、条件、方向、程度、方式和伴随状况等
状语的分类:状语按其修饰的功能不同可分为九大类–时间状语、原因状语、目的状语、结果状语、条件状语、地点状语、比较状语、让步状语和方式状语
1、分词做状语
分词(包括现在分词和过去分词)做状语,通常表示主语在做的另一个动作(次要动作),用来对谓语动词表示的动作进行修饰,它可以表时间、原因、结果、条件、让步、方式和伴随,相当于状语从句
关键:当分词与主语是主动关系时,用现在分词,当分词与主语是被动关系时用过去分词。注意只有一个主语
例:Working hard,you will succeed=if you work hard,you will succeed
Seen from the mountain,the school is very beautiful=If it is seen from the mountain,the shool is very beautiful
- 分词的一般态:v+ing或v+ed
表示分词的动作与主句的动作时间不分先后,几乎同时发生
例:He sat at the table,reading a book - 分词的完成态:having done
当分词表示的动作,在主句谓语动词表示的动作之前就已经完成,用分词的完成态
例:Having finished all the work,they had a good rest - 现在分词的否定式:not doing ;被动态的否定式:not being done
例:不知道做什么,她坐到那里哭了起来
Not knowing what to do,she sat there crying - 连词+分词做状语
例:当比较不同的文化时,我们常常感到非常惊讶。
When compared different cultures,we often are very surprised
2、独立主格结构
- 由名词或代词加上分词或分词短语构成的一种独立结构,用于修饰整个句子
- 特点:
1️⃣独立主格结构的逻辑主语与句子的主语不同,它独立存在
2️⃣名词或代词与后面的分词,形容词,副词,不定式,介词等是主谓关系
3️⃣独立主格结构一般有逗号与主句分开 - 基本构成形式
1)名词(代词)+现在分词(主动关系:和独立结构主语)
例:The girl staring at him ,he didn’t know what to say
2)名词(代词)+过去分词(被动关系)
例:The problem solved,the quality has been increased
3)名词(代词)+不定式(分主动和被动)
Many trees to be planted,our school will look very beautiful
The four of us agreed on a division of the work, each to translate a quarter of the book.
3、With复合结构

4、状语从句
(一)时间状语从句
1、when,while和as的用法
(1)when即可引导一个持续性动作,也可以引导一个短暂性动作,when强调主从动作有先后,如:
①When he got here,the classroom had been clean
当他到达那里时,教室已经打扫过了(主句动作发生在从句动作之前)
②He went to play football when he finished his homework
完成作业后他去踢足球了(主句动作发生在从句动作之后)
when可作并列连词用,相当于just then,at the time,前一分句多用进行时、be about to表示正在做,就在这时发生了另一件事,如:
l was reading when he suddenly come in
(2)while强调主句动作发生在从句动作所发生的时间段内,从句动作必须使延续性的动词。如:
Will you please take care of my house while l was away
(3)as引导一个持续性动作,强调主从句的动作同时发生,有“一边…一边…”的意思,也可说明两种正在发展或变化的情况,有“随着…”的意思。如:
He sang as he walked.他边走边唱。
(二)地点状语从句
1、地点状语从句可用where,wherever、anywhere、everywhere引导。地点状语从句可用于主句之前或之后
You are free to go wherever you like
你可以随心所欲地去任何地方
Where there is a will,there is a way
有志者,事竟成
2、注意区分定语从句和状语从句
where引导的地点状语从句直接修饰动词,而在定语从句中where作为副词要跟在表示地点的先行词后面
You’d better make a mark where you have any questions.(状语从句)
You’d better make a mark at the place where you have any questions.(定语从句)
(三)原因状语从句
1、引导原因状语从句的从属连词有because,as,since,now that,seeing that等,每个连词含义不尽相同
(1)because用来回答why的提问,语气最强,一般放在主句后
(2)since表示既然或已知的理由,稍加分析即可表明原因,多放在句首
(3)as多用于口语,语气比because,since弱,表示的理由是明显的或被认为是已知的,是对主句的附带说明,重点在主句,可放在句首或句尾,放在句尾时as可省略。
l can’t go,(as)l am busy
(四)目的状语从句
引导目的状语从句的从属连词有:so that, in order that, for fear that,in case, lest等。
1.in order that与so that
两个连词都意为“以便……,为了……”,引导的状语从句中需用情态动词;in order that比so that正式,引导的状语从句可置于主句之前或之后,而so that引导的从句只能置于主句之后。
I’ll speak slowly so that you can understand me.
(五)结果状语从句
1.引导结果状语从句的从属连词有: so that, so…that…,such…that…。其结构形式为:
Mike is so honest a worker that we all believe him.
(六)条件状语从句
常用引导词:if, unless,
特殊引导词:as/so long as, only if, providing/provided that, supposing that, in case that, on condition that
We’ll start our project if the president agrees.
(七)方式状语从句
引导方式状语从句的从属连词有:as, as if, as though等。方式状语从句应放在主句之后。as引导方式状语从句,意为“按照,正如”;其中as if或as though引导的从句一般用虚拟语气,但如果从句中所陈述的情况很可能实现,也可用陈述语气。
Do as you are told to, or you’ll be fired.
(八)让步状语从句
1.although/though, even though/if引导让步状语从句
although与though两者意思相同,一般可以互换,都可以与yet, still或nevertheless连用,但不能和but连用。
He is unhappy though/although he has a lot of money.
尽管他很有钱,但是他不幸福。