特杰帕尔·库马瓦特
一、说明
DeepWalk 是一种基于图的机器学习算法,可为给定图生成节点嵌入。它由纽约大学的 Bryan Perozzi、Rami Al-Rfou 和 Steven Skiena 于 2014 年开发。
该算法的目标是通过分析图中每个节点的局部邻域来学习图中每个节点的表示。 DeepWalk应用了skip-gram的概念(也用于自然语言处理)来为每个节点生成向量嵌入。这个想法是将图上的随机游走视为句子,并将每个节点视为句子中的一个单词。
DeepWalk 在各个领域都有应用,包括网络分析、推荐系统和生物信息学。它广泛用于社区检测、链接预测和节点分类任务。
研究 Node2Vec 和 DeepWalk 以从图中提取嵌入
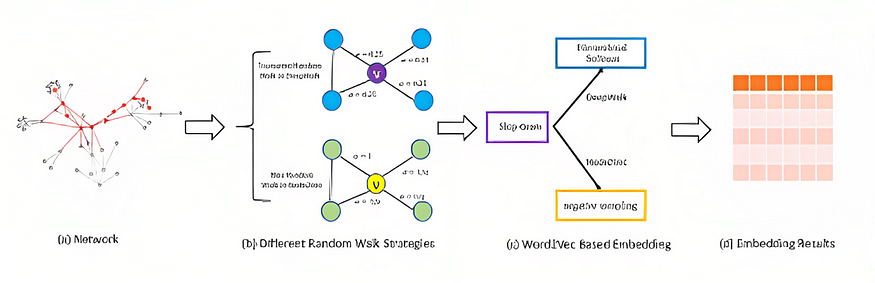
二、图综合知识
G = (V, E),其中 V 是节点的集合,E 是边的列表,可用于定义图形。两个节点之间的链接称为边。例如,边连接节点 A 和 D。同样重要的是要记住,图形可以是有向的,也可以是无向的。例如,下图是无向的,因为 A 和 D 链接在一起,反之亦然。另一个问题是,图形可以具有各种节点和边缘质量,尽管对于我们今天的目的来说,两者都不重要。
2.1 为什么我们需要节点嵌入
- 在社交网络中,用户相互通信,我们必须预测两个用户何时链接。用户由节点表示,而个人之间的关系由边缘表示。我们需要在引文网络中预测每篇研究文章的主题(链接预测任务)。
- 出版物由节点表示,而出版物之间的引文由边缘表示。(节点预测任务)
- 有特定的蛋白质属于酶和非酶的类别。氨基酸由节点表示,如果两个节点相距小于6埃,则它们通过边缘连接。(图形分类任务)
2.2 DeepWalk深度漫步
DeepWalk由石溪大学的研究人员在论文“DeepWalk:社会表征的在线学习”(2014)中提出。
DeepWalk是一种学习图中节点表示的方法。DeepWalk背后的主要思想是在图中生成随机游走,并使用这些随机游走来学习使用Word2Vec算法的节点表示。
更详细地说,给定一个图形,DeepWalk 首先生成一组从图形中的每个节点开始的随机漫游。每个随机游走只是一系列节点,从特定节点开始,并在每一步移动到其邻居之一。这些随机游走捕获图的局部结构,并提供一种方法来学习捕获其与附近节点关系的节点表示。
接下来,Word2Vec 算法用于根据生成的随机游走学习节点的表示。Word2Vec是一种流行的算法,用于学习自然语言处理中的单词表示,但它也可以应用于学习图中节点的表示。Word2Vec背后的基本思想是学习一个神经网络,该神经网络预测给定上下文(即出现在其前后的单词)的单词的概率。
在DeepWalk的情况下,从图中生成的随机游走充当“句子”,图中的节点充当“单词”。然后使用 Word2Vec 算法来学习神经网络,该神经网络预测节点在给定图形中的邻居的情况下出现在随机游走中的概率。然后,学习到的节点表示可用于各种下游任务,例如节点分类或链路预测。
总体而言,DeepWalk是一种功能强大且广泛使用的方法,用于学习图中节点的表示,以捕获图形的局部结构。
import networkx as nx
import random
import numpy as np
from typing import List
from tqdm import tqdm
from gensim.models.word2vec import Word2Vecclass DeepWalk:def __init__(self, window_size: int, embedding_size: int, walk_length: int, walks_per_node: int):""":param window_size: window size for the Word2Vec model:param embedding_size: size of the final embedding:param walk_length: length of the walk:param walks_per_node: number of walks per node"""self.window_size = window_sizeself.embedding_size = embedding_sizeself.walk_length = walk_lengthself.walk_per_node = walks_per_nodedef random_walk(self, g: nx.Graph, start: str, use_probabilities: bool = False) -> List[str]:"""Generate a random walk starting on start:param g: Graph:param start: starting node for the random walk:param use_probabilities: if True take into account the weights assigned to each edge to select the next candidate:return:"""walk = [start]for i in range(self.walk_length):neighbours = g.neighbors(walk[i])neighs = list(neighbours)if use_probabilities:probabilities = [g.get_edge_data(walk[i], neig)["weight"] for neig in neighs]sum_probabilities = sum(probabilities)probabilities = list(map(lambda t: t / sum_probabilities, probabilities))p = np.random.choice(neighs, p=probabilities)else:p = random.choice(neighs)walk.append(p)return walkdef get_walks(self, g: nx.Graph, use_probabilities: bool = False) -> List[List[str]]:"""Generate all the random walks:param g: Graph:param use_probabilities::return:"""random_walks = []for _ in range(self.walk_per_node):random_nodes = list(g.nodes)random.shuffle(random_nodes)for node in tqdm(random_nodes):random_walks.append(self.random_walk(g=g, start=node, use_probabilities=use_probabilities))return random_walksdef compute_embeddings(self, walks: List[List[str]]):"""Compute the node embeddings for the generated walks:param walks: List of walks:return:"""model = Word2Vec(sentences=walks, window=self.window_size, vector_size=self.embedding_size)return model.wv2.3 节点2Vec
Node2Vec由斯坦福大学的研究人员在论文“node2vec:网络的可扩展特征学习”(2016)中提出。
在使用Deepwalk的一些概念时,这种方法使它们更进一步。为了提取随机游走,它结合了DFS和BFS技术。两个参数 P(返回参数)和 Q 控制这种算法组合(输入-输出参数)。
本质上,如果P很大,随机游走就会很大,所以它会探索,如果P很小,我们就会靠近家。Q表现出类似但相反的行为;如果 Q 很小,它将参与探索,而如果 Q 很大,它将保持局部。原始文件包含更多信息。
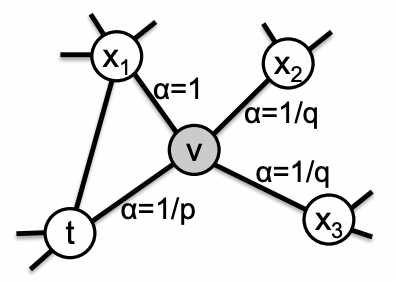
Node2vec 的采样策略接受 4 个参数: — 漫游次数:从图形中的每个节点生成的随机漫游次数 — 漫游长度:每个随机漫游中有多少个节点 — P:返回超参数 — Q:Inout 超参数以及标准的 skip-gram 参数
我们可以使用 PyTorch 几何来测试 Node2Vec。为了加快 GNN 的使用,该软件包实现了各种图形神经网络拓扑和技术。我将使用 Pytorch 几何指令的一小部分来测试它。他们为此利用了Cora数据集。Cora 数据集中的 2708 篇科学出版物分为七类。引文网络中有5429个链接。0/1 值的词向量表示字典中不存在/存在匹配的单词,用于描述数据集中的每个出版物。字典中有1433个不同的单词。
from torch_geometric.nn import Node2Vec
import os.path as osp
import torch
from torch_geometric.datasets import Planetoid
from tqdm.notebook import tqdmdataset = 'Cora'
path = osp.join('.', 'data', dataset)
dataset = Planetoid(path, dataset) # dowload or load the Cora dataset
data = dataset[0]
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu' # check if cuda is available to send the model and tensors to the GPU
model = Node2Vec(data.edge_index, embedding_dim=128, walk_length=20,context_size=10, walks_per_node=10,num_negative_samples=1, p=1, q=1, sparse=True).to(device)loader = model.loader(batch_size=128, shuffle=True, num_workers=4) # data loader to speed the train
optimizer = torch.optim.SparseAdam(list(model.parameters()), lr=0.01) # initzialize the optimizer def train():model.train() # put model in train modeltotal_loss = 0for pos_rw, neg_rw in tqdm(loader):optimizer.zero_grad() # set the gradients to 0loss = model.loss(pos_rw.to(device), neg_rw.to(device)) # compute the loss for the batchloss.backward()optimizer.step() # optimize the parameterstotal_loss += loss.item()return total_loss / len(loader)for epoch in range(1, 100):loss = train()print(f'Epoch: {epoch:02d}, Loss: {loss:.4f}')all_vectors = ""
for tensor in model(torch.arange(data.num_nodes, device=device)):s = "\t".join([str(value) for value in tensor.detach().cpu().numpy()])all_vectors += s + "\n"
# save the vectors
with open("vectors.txt", "w") as f:f.write(all_vectors)
# save the labels
with open("labels.txt", "w") as f:f.write("\n".join([str(label) for label in data.y.numpy()]))三、结论
本案例提出用G-ML的方式实现 word2vec的方式;以DeepWalk表征训练过程;在这个过程中,自然地将N-gram结合进去,有效地实现 word2vec。
四、参考
- 对于 skip-gram 和 word2vec,请参阅此视频
- [1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_theory
- [2] Graph Machine Learning: 通过应用机器学习技术和算法将图形数据提升到一个新的水平 作者:Aldo Marzullo、Claudio Stamile 和 Enrico Deusebio
- [3] node2vec · PyPI
- [4] https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.00653.pdf
Deep Walk and Node2Vec: Graph Embeddings | by Tejpal Kumawat | Medium