💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
🌈4 Matlab代码&Simulink仿真实现
💥1 概述
要在Simulink中实现具有吸引子的非线性系统,可以按照以下步骤进行操作:
1. 打开Simulink并创建一个新的模型。
2. 在模型中添加非线性系统的表示。可以使用Math Function块、Lookup Table块或者自定义的S函数来表示非线性系统的动态行为。根据你所建模的具体系统,选择合适的模块来表示非线性函数。
3. 在系统中添加具有吸引子效应的元素。这可以包括非线性函数中的非线性项、延迟项、反馈或者其他非线性特征。根据具体的吸引子效应,调整系统中的参数和配置。
4. 设置系统的初始条件。使用Initial Condition块来设置模型初始条件。这些初始条件可以影响系统的稳定性和吸引子的形成。
5. 运行模型并观察吸引子效应。使用Simulink模拟器运行模型,并观察系统的行为。通过调整吸引子参数和系统的其他特性,可以进一步探索系统的响应。
请注意,具体的建模和设置步骤会根据你所研究的非线性系统和吸引子特性而有所不同。以上步骤提供了一个一般的指导,具体实现还需要根据你的问题进行调整和定制。
📚2 运行结果
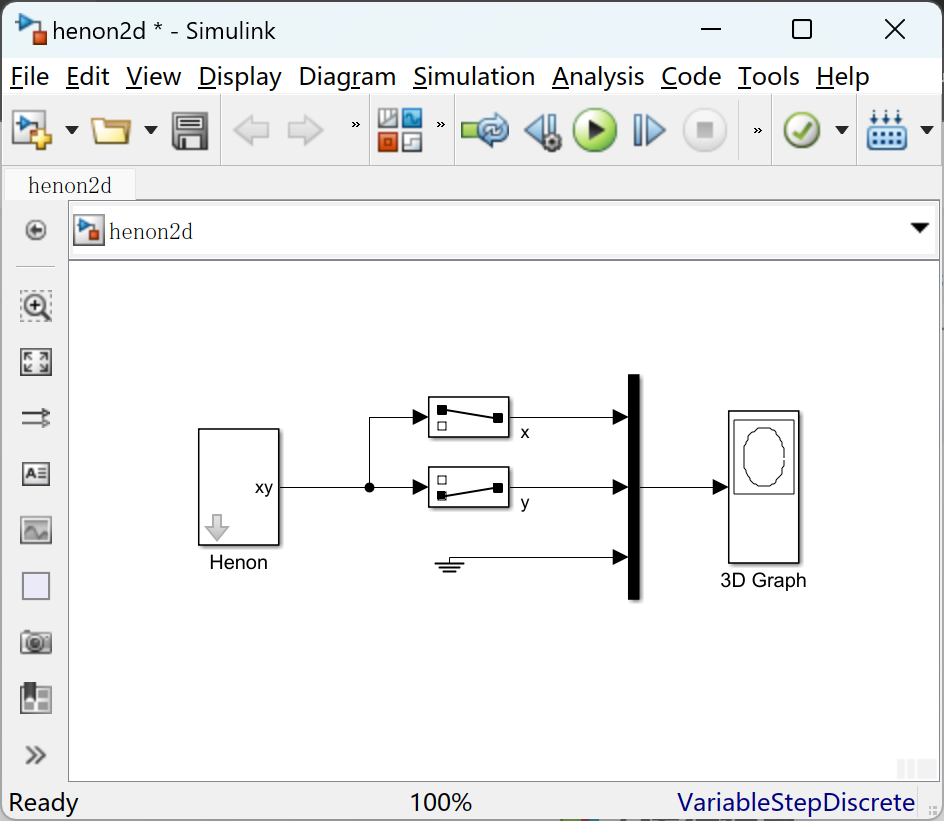
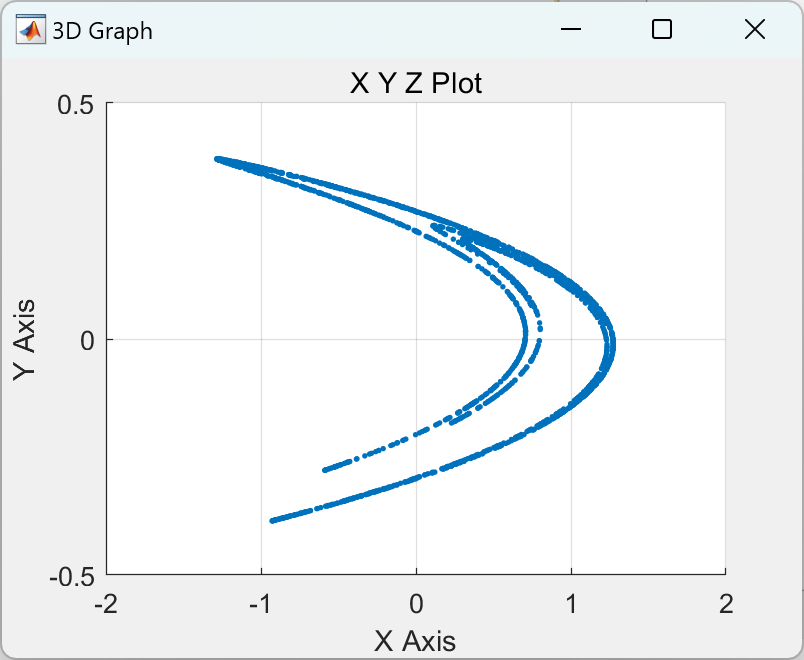
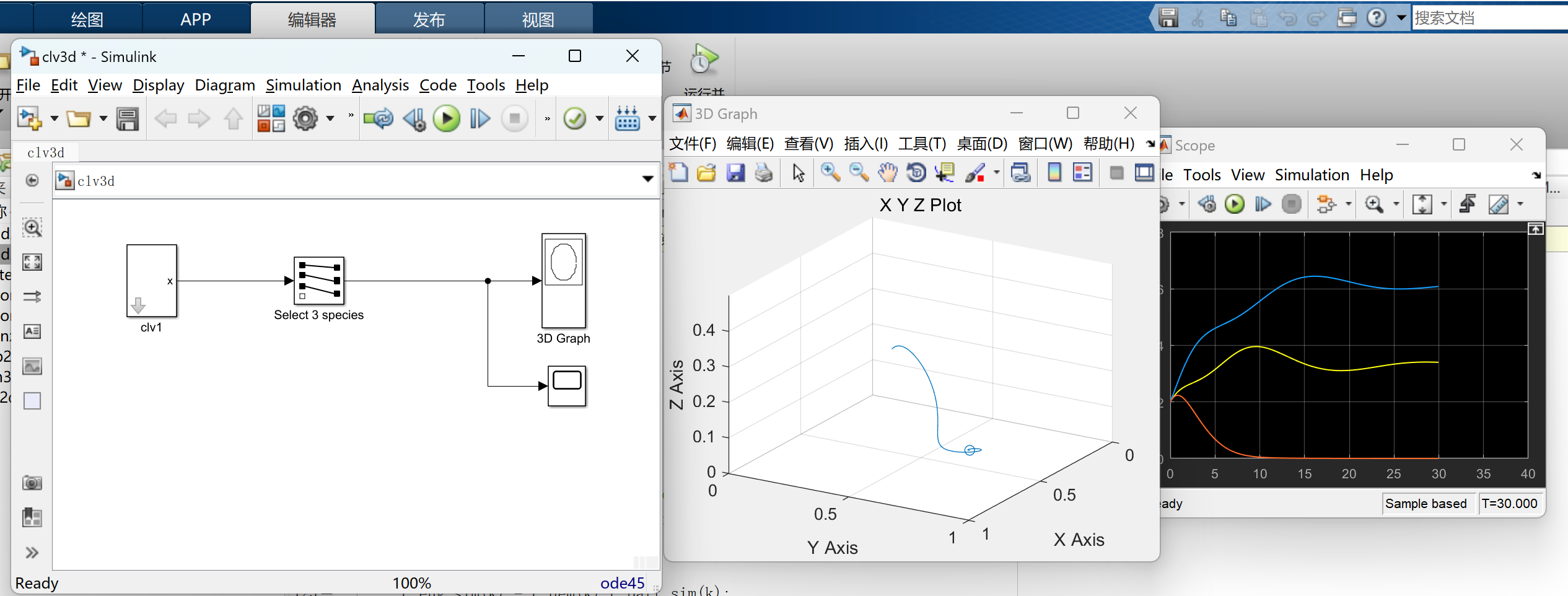
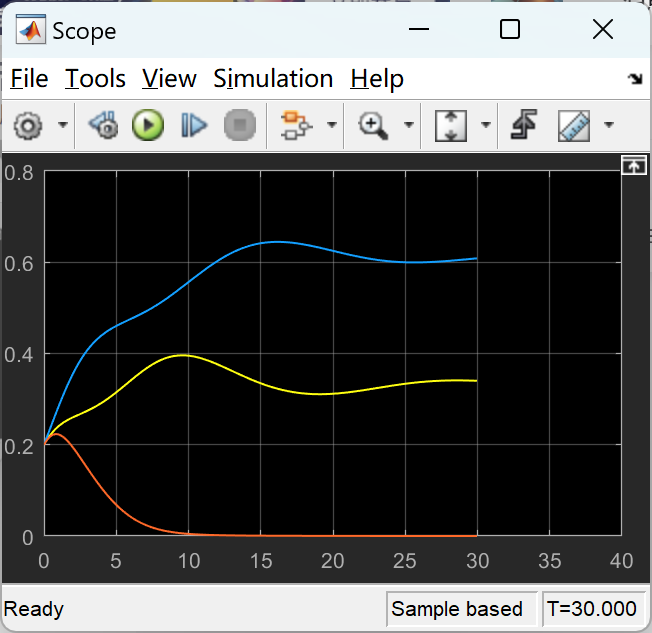
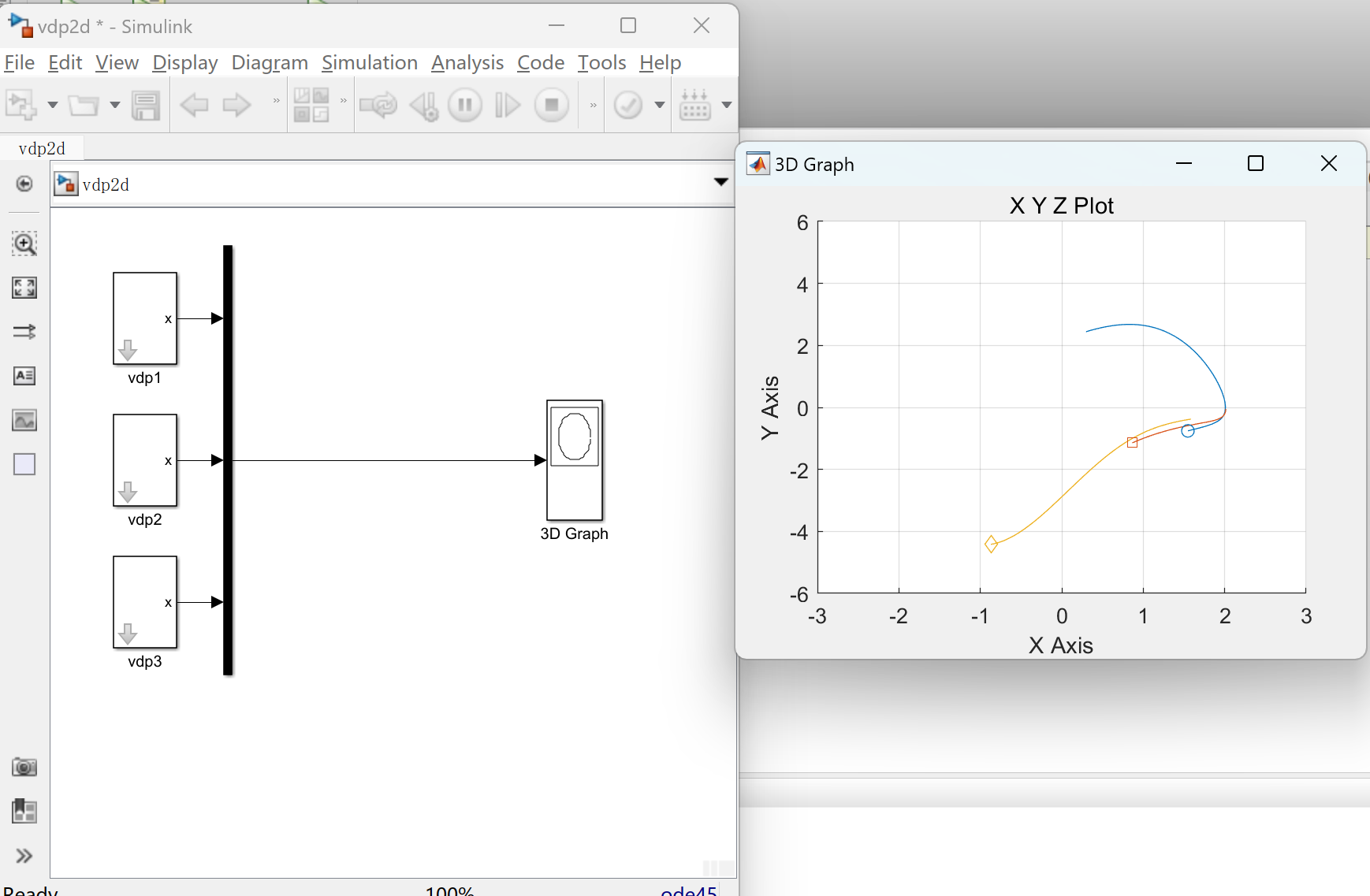
部分代码:
% ax was there in sfunxy, for everything else there's varargin
if length(ax)~=6, error('Axes limits must be defined.'); end
% get number of moving points (i.e. number of lines) to be plotted
if nargin>6, nmax=fix(varargin{2}); else nmax=1; end
sizes=simsizes; % this initializes size vector to zero
sizes.NumInputs = 3*nmax; % input vector size at runtime
sizes.NumSampleTimes = 1; % fill number of sample times
% get sample time
if nargin>5, ts=[varargin{1} 0]; else ts=[0.01 0]; end
% return initialization values to simulink as function outputs
sys=simsizes(sizes);x0=[];str=[];
% get the active figure parameter (toolbar and menubar)
if nargin>13 && varargin{9}, tb='figure'; else tb='none'; end
% do the figure initialization
FigHandle=get_param(gcbh,'UserData');
if isempty(FigHandle) || ~ishandle(FigHandle)
% the figure doesn't exist, create one
FigHandle = figure(...
'Units', 'pixel',...
'Position', [100 100 400 300],...
'Name', get_param(gcbh,'Name'),...
'Tag', 'SIMULINK_3DGRAPH_FIGURE',...
'NumberTitle', 'off',...
'IntegerHandle', 'off',...
'Toolbar', tb,...
'Menubar', tb);
else
% otherwise clear it
clf(FigHandle);
end
% get number of moving points, camera position, and grid switch
if nargin>7, CPos=varargin{3}; else CPos=[3 2 1]*100; end
if nargin>8 && varargin{4}, GdSw='On'; else GdSw='Off'; end
% Note: the structure pd contains all the plot data and will be
% later stored in the figure's userdata!
% create axes
pd.XYZAxes = axes('Parent',FigHandle);
cord=get(pd.XYZAxes,'ColorOrder');
set(pd.XYZAxes,'Visible','on','Xlim', ax(1:2),'Ylim', ax(3:4),'Zlim', ax(5:6),'CameraPosition',CPos,'XGrid',GdSw,'YGrid',GdSw,'ZGrid',GdSw);
% get LineStyle string, Marker string, and max num of line points
if nargin>9, ls=varargin{5}; else ls='-'; end
if nargin>10, mk=varargin{6}; else mk='none'; end
if nargin>11, mx=varargin{7}; else mx=1e5; end
% create a vector of animatedline objects
pd.XYZLine = [];
for n=1:nmax
pd.XYZLine = [pd.XYZLine animatedline('Parent',pd.XYZAxes,'LineStyle',ls,'Marker',mk,'MaximumNumPoints',mx,'Color',cord(1+mod(n-1,size(cord,1)),:))];
end
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1]刘博伦. 具有隐藏吸引子的非线性系统混沌特性研究[D].华北电力大学(北京),2020.DOI:10.27140/d.cnki.ghbbu.2020.001358.
[2]董二女. 粉末注射成形动力系统的混沌吸引子形态研究[D].中南大学,2011.





![[mongo]应用场景及选型](https://github.com/tutengdihuang/image/assets/31843331/0ac362e8-7916-4764-8c3d-c256fef60bcd)