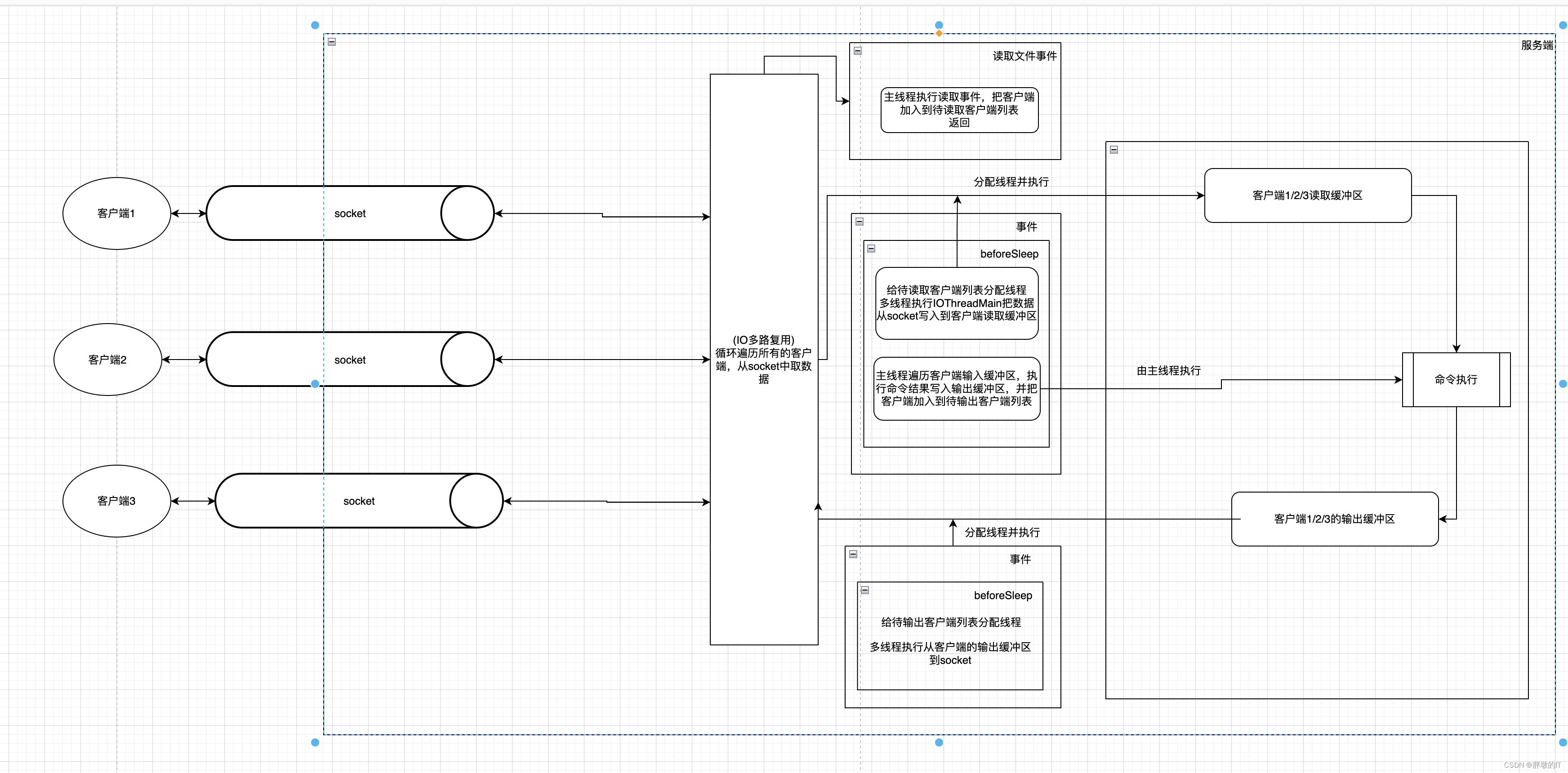
redis支持开启多线程,只有从socket到读取缓冲区和从输出缓冲区到socket这两段过程是多线程,而命令的执行还是单线程,并且是由主线程执行
借鉴:【Redis】事件驱动框架源码分析(多线程)
- 一、main启动时初始化多线程
- 二、多线程(非主线程)执行函数IOThreadMain
- 三、主线程会把客户端放入到两个等待客户端列表
- 1、开启多线程后主线程执行读取事件,如果当前多线程状态是空闲,会把客户端放入等待写入客户端列表并返回
- 2、开启多线程后,主线程执行完命令把数据写回客户端输出缓冲区并且把此客户端写入等待输出客户端列表
- 四、给两个等待客户端端列表分配多线程执行
- 1、给等待写入客户端列表分配线程后,多线程只执行到把数据从socket写入到客户端输出缓冲区,不会执行客户端输入缓冲区命令,当多线程都执行完毕后,由主线程执行各个客户端输入缓冲区的命令
- (1)多线程只执行到从socket到客户端的输入缓冲区
- (2) 多线程之后完毕后,主线程执行客户端的缓冲区的命令
- 2、给等待输出客户端列表分配线程后,多线程(包含主线程)开始执行把从客户端输出缓冲区写入到socket,如果没有写完,还会注册文件事件,让aeMain执行,
一、main启动时初始化多线程
int main(int argc, char **argv) {//.....删除干扰代码//里面有初始化IO多线程的方法InitServerLast();//.....删除干扰代码
}
void InitServerLast(void) {//.....删除干扰代码//初始化IO多线程initThreadedIO();//.....删除干扰代码
}
下面initThreadedIO函数中通过pthread_create创建线程,其中IOThreadMain是线程的执行函数
typedef struct __attribute__((aligned(CACHE_LINE_SIZE))) threads_pending {redisAtomic unsigned long value;
} threads_pending;
//存储创建的线程,和io_threads_list数组的下标对应
pthread_t io_threads[IO_THREADS_MAX_NUM];
//存储每个线程要等待处理的客户端个数,和io_threads下标对应,每一个元素中有原子类型value,代表此线程有多少等待处理的客户端
threads_pending io_threads_pending[IO_THREADS_MAX_NUM];
//多线程的状态,比如如果是read,所有的多线程都是read,如果是write,则所有的多线程都是write
int io_threads_op; /* IO_THREADS_OP_IDLE, IO_THREADS_OP_READ or IO_THREADS_OP_WRITE. */ // TODO: should access to this be atomic??!/* This is the list of clients each thread will serve when threaded I/O is* used. We spawn io_threads_num-1 threads, since one is the main thread* itself. */
//存储每一个线程要处理的客户端,io_threads_list是数组,通过下标标志不同的线程,0是主线程,数组每一个元素是某一个线程可以处理的客户端集合,
list *io_threads_list[IO_THREADS_MAX_NUM];
void initThreadedIO(void) {server.io_threads_active = 0; /* We start with threads not active. *//* Indicate that io-threads are currently idle *///设置IO线程当前状态为空闲io_threads_op = IO_THREADS_OP_IDLE;/* Don't spawn any thread if the user selected a single thread:* we'll handle I/O directly from the main thread. *///如果IO线程为1,即只需要主线程,直接返回即可if (server.io_threads_num == 1) return;//如果IO线程超过最大线程,即128,则报错退出if (server.io_threads_num > IO_THREADS_MAX_NUM) {serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Fatal: too many I/O threads configured. ""The maximum number is %d.", IO_THREADS_MAX_NUM);exit(1);}/* Spawn and initialize the I/O threads. *///根据设置的线程数初始化线程数组io_threads_list,for (int i = 0; i < server.io_threads_num; i++) {/* Things we do for all the threads including the main thread. */io_threads_list[i] = listCreate();//如果i=0代表当前创建的线程是主线程,可以跳过if (i == 0) continue; /* Thread 0 is the main thread. *//* Things we do only for the additional threads. */pthread_t tid;pthread_mutex_init(&io_threads_mutex[i],NULL);//设置线程的待处理客户端为0,原因是刚启动,没有一个客户端连接setIOPendingCount(i, 0);pthread_mutex_lock(&io_threads_mutex[i]); /* Thread will be stopped. *///创建线程,线程的运行函数是IOThreadMain,pthread_create是创建线程的函数,并且在创建线程时就执行IOThreadMain方法,不需要再单独启动if (pthread_create(&tid,NULL,IOThreadMain,(void*)(long)i) != 0) {serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Fatal: Can't initialize IO thread.");exit(1);}//把创建的线程标识加入io_threads,tid这个指针变量可以指向创建的线程io_threads[i] = tid;}
}
二、多线程(非主线程)执行函数IOThreadMain
void *IOThreadMain(void *myid) {/* The ID is the thread number (from 0 to server.io_threads_num-1), and is* used by the thread to just manipulate a single sub-array of clients. */long id = (unsigned long)myid;char thdname[16];snprintf(thdname, sizeof(thdname), "io_thd_%ld", id);redis_set_thread_title(thdname);redisSetCpuAffinity(server.server_cpulist);makeThreadKillable();//下面是死循环while(1) {/* Wait for start */for (int j = 0; j < 1000000; j++) {//如果当前线程有需要读取或者输出的客户端,则跳出这个for循环,执行下面的操作if (getIOPendingCount(id) != 0) break;}/* Give the main thread a chance to stop this thread. *///如果上面的for循环是正常执行结束,不是break的,不能后续的操作,通过continue重新回到上面for循环继续等待if (getIOPendingCount(id) == 0) {pthread_mutex_lock(&io_threads_mutex[id]);pthread_mutex_unlock(&io_threads_mutex[id]);continue;}serverAssert(getIOPendingCount(id) != 0);/* Process: note that the main thread will never touch our list* before we drop the pending count to 0. */listIter li;listNode *ln;//把当前线程可以处理的客户端放入到迭代列表中listRewind(io_threads_list[id],&li);while((ln = listNext(&li))) {client *c = listNodeValue(ln);//多线程的状态是输出,从输出缓冲区输出到客户端的socketif (io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_WRITE) {writeToClient(c,0);} else if (io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_READ) {//多线程的状态是读取,从客户端的socket中读取数据到输入缓冲区readQueryFromClient(c->conn);} else {serverPanic("io_threads_op value is unknown");}}listEmpty(io_threads_list[id]);setIOPendingCount(id, 0);}
}
三、主线程会把客户端放入到两个等待客户端列表
通过下面的代码,知道等待写入客户端列表和等待输出客户端列表是全局变量
struct redisServer {// 省略...//list类型,记录待处理输出的客户端集合list *clients_pending_write; /* There is to write or install handler. *///list类型,记录待处理读取的客户端集合list *clients_pending_read; /* Client has pending read socket buffers. */// 省略...
}
1、开启多线程后主线程执行读取事件,如果当前多线程状态是空闲,会把客户端放入等待写入客户端列表并返回
在前面的文章中,主线程通过
readQueryFromClient函数来执行从客户端socket中得到数据写入输入缓冲区
void readQueryFromClient(connection *conn) {//省略。。。。/* Check if we want to read from the client later when exiting from* the event loop. This is the case if threaded I/O is enabled. */if (postponeClientRead(c)) return;//省略。。。。
}
/* Return 1 if we want to handle the client read later using threaded I/O.* This is called by the readable handler of the event loop.* As a side effect of calling this function the client is put in the* pending read clients and flagged as such. */
int postponeClientRead(client *c) {if (server.io_threads_active &&// I/O 线程是否活跃,活跃表示激活了IO多线程server.io_threads_do_reads &&//I/O 线程是否执行读操作,表示IO多线程可以针对待读取客户端列表的执行读取操作//不在阻塞期间处理事件,为了避免读取RDB或AOF文件时阻塞无法及时处理请求,processEventsWhileBlokced函数在执行时,待读取客户端列表不能读取。!ProcessingEventsWhileBlocked &&// 客户端标志位不包含 MASTER、SLAVE 或 BLOCKED,解释:CLIENT_MASTER、CLIENT_SLAVE表示是用于主从复制的客户端, CLIENT_BLOCKED表示客户端是阻塞状态 !(c->flags & (CLIENT_MASTER|CLIENT_SLAVE|CLIENT_BLOCKED)) &&// I/O 线程操作为 IDLE(空闲)说明执行到这的是主线程执行读取事件,只需要把客户端放入server.clients_pending_read, io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_IDLE) {listAddNodeHead(server.clients_pending_read,c);// 如果满足条件,将客户端添加到待读取客户端列表的头部c->pending_read_list_node = listFirst(server.clients_pending_read);return 1;//表示此客户端的放入了待读取客户端列表,主线程应该返回,不再执行后续的操作} else {return 0;//表示此客户端没有放入待读取客户端列表,可以由主线程继续执行后续的操作}
}
2、开启多线程后,主线程执行完命令把数据写回客户端输出缓冲区并且把此客户端写入等待输出客户端列表
在前面的文章中,知道从输出(回复)缓冲区到socket是通过
addReply函数
//将结果返回到回复缓冲区
void addReply(client *c, robj *obj) {if (prepareClientToWrite(c) != C_OK) return;//主线程将数据写入输出缓冲区if (sdsEncodedObject(obj)) {_addReplyToBufferOrList(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr));} else if (obj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INT) {/* For integer encoded strings we just convert it into a string* using our optimized function, and attach the resulting string* to the output buffer. */char buf[32];size_t len = ll2string(buf,sizeof(buf),(long)obj->ptr);_addReplyToBufferOrList(c,buf,len);} else {serverPanic("Wrong obj->encoding in addReply()");}
}
int prepareClientToWrite(client *c) { /* Schedule the client to write the output buffers to the socket, unless* it should already be setup to do so (it has already pending data).** If CLIENT_PENDING_READ is set, we're in an IO thread and should* not put the client in pending write queue. Instead, it will be* done by handleClientsWithPendingReadsUsingThreads() upon return.*///调用了clientHasPendingReplies函数判断输出缓冲区是否有还有数据等待写回到客户端//如果当前客户端输出缓冲区没有数据了,并且线程还处于空闲状态,则执行putClientInPendingWriteQueue把当前客户端放入待输出客户端列表if (!clientHasPendingReplies(c) && io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_IDLE)putClientInPendingWriteQueue(c);/* Authorize the caller to queue in the output buffer of this client. */return C_OK;
}
void putClientInPendingWriteQueue(client *c) {/* Schedule the client to write the output buffers to the socket only* if not already done and, for slaves, if the slave can actually receive* writes at this stage. */if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE) && //客户端标识不是CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE(c->replstate == REPL_STATE_NONE || //(客户端未在进行主从复制||(客户端是主从复制的从节点,但全量复制的 RDB 文件已经传输完成,客户端可以接收请求))(c->replstate == SLAVE_STATE_ONLINE && !c->repl_start_cmd_stream_on_ack))){/* Here instead of installing the write handler, we just flag the* client and put it into a list of clients that have something* to write to the socket. This way before re-entering the event* loop, we can try to directly write to the client sockets avoiding* a system call. We'll only really install the write handler if* we'll not be able to write the whole reply at once. *///将客户端的表示设置为等待输出c->flags |= CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE;//把当前客户端加入server.clients_pending_writelistLinkNodeHead(server.clients_pending_write, &c->clients_pending_write_node);}
}
四、给两个等待客户端端列表分配多线程执行
通过以前的文章,知道redis集群的事件都是通过
aeMain循环执行的,其中执行函数aeProcessEvents中beforeSleep会给多线程分配要处理的客户端
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {eventLoop->stop = 0;while (!eventLoop->stop) {aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);}
}
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{//省略....if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL && (flags & AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP))eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);//省略....
}
void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {/* We should handle pending reads clients ASAP after event loop.我们应该在事件循环后尽快处理挂起的读取客户端 */// 调用了handleClientsWithPendingReadsUsingThreads为等待读取客户端列表中的客户端分配线程执行 */handleClientsWithPendingReadsUsingThreads();/* Handle writes with pending output buffers. *///处理具有挂起输出缓冲区的写入。//调用了handleClientsWithPendingWritesUsingThreads为等待输出客户端列表的分配线程handleClientsWithPendingWritesUsingThreads();
}
1、给等待写入客户端列表分配线程后,多线程只执行到把数据从socket写入到客户端输出缓冲区,不会执行客户端输入缓冲区命令,当多线程都执行完毕后,由主线程执行各个客户端输入缓冲区的命令
在分配线程后,到全部线程都执行完从
socket写入到客户端缓冲区之前,io_threads_op都是read状态,不是空闲状态,多线程之后完毕后,io_threads_op改为空闲,由主线程执行命令,这些环节都在beforeSleep函数中
int handleClientsWithPendingReadsUsingThreads(void) {//如果没有开启多线程或者不是读取线程状态,直接返回if (!server.io_threads_active || !server.io_threads_do_reads) return 0;// 从server.clients_pending_read获取等待读取操作的客户端int processed = listLength(server.clients_pending_read);//如果没有等待读取操作的客户端,直接返回if (processed == 0) return 0;/* Distribute the clients across N different lists. */listIter li;listNode *ln;//获得延迟读取操作客户端的迭代列表lilistRewind(server.clients_pending_read,&li);int item_id = 0;//下面根据取余把待读取客户端列表分配线程,包括主线程while((ln = listNext(&li))) {//获取每一个待处理的客户端clientclient *c = listNodeValue(ln);//item_id表示每个客户端的序号,从0开始,int target_id = item_id % server.io_threads_num;listAddNodeTail(io_threads_list[target_id],c);//每处理一个客户端就增1item_id++;}/* Give the start condition to the waiting threads, by setting the* start condition atomic var. *///设置多线程的状态为读取状态io_threads_op = IO_THREADS_OP_READ;for (int j = 1; j < server.io_threads_num; j++) {int count = listLength(io_threads_list[j]);setIOPendingCount(j, count);}/* Also use the main thread to process a slice of clients. *///因为其他线程有IOThreadMain执行,,而主线程是排除在外的,所以这里单独针对主线程和它可以操作的客户端做readlistRewind(io_threads_list[0],&li);while((ln = listNext(&li))) {client *c = listNodeValue(ln);//这个是从socket到客户端读取缓冲区的执行函数,并且注意这时候io_threads_op不是空闲,是read状态readQueryFromClient(c->conn);}listEmpty(io_threads_list[0]);/* Wait for all the other threads to end their work. *///等待所有其他线程结束其工作。while(1) {unsigned long pending = 0;for (int j = 1; j < server.io_threads_num; j++)pending += getIOPendingCount(j);if (pending == 0) break;}//设置多线程的状态为空闲io_threads_op = IO_THREADS_OP_IDLE;/* Run the list of clients again to process the new buffers. */// /* 再次判断server.clients_pending_read是否有待处理的客户端*///主线程执行各个客户端缓冲区的命令while(listLength(server.clients_pending_read)) {ln = listFirst(server.clients_pending_read);client *c = listNodeValue(ln);// 删除节点listDelNode(server.clients_pending_read,ln);c->pending_read_list_node = NULL;//省略。。。。。。// 这里解析命令并执行,请看下面的(2)介绍if (processPendingCommandAndInputBuffer(c) == C_ERR) {/* If the client is no longer valid, we avoid* processing the client later. So we just go* to the next. */continue;}/* We may have pending replies if a thread readQueryFromClient() produced* replies and did not put the client in pending write queue (it can't).*/if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE) && clientHasPendingReplies(c))putClientInPendingWriteQueue(c);}/* Update processed count on server */server.stat_io_reads_processed += processed;return processed;
}
(1)多线程只执行到从socket到客户端的输入缓冲区
在readQueryFromClient->processInputBuffer
void readQueryFromClient(connection *conn) {//省略。。。if (processInputBuffer(c) == C_ERR)c = NULL;//省略。。。。
}
int processInputBuffer(client *c) {/* Multibulk processing could see a <= 0 length. */if (c->argc == 0) {resetClient(c);} else {/* If we are in the context of an I/O thread, we can't really* execute the command here. All we can do is to flag the client* as one that needs to process the command. */if (io_threads_op != IO_THREADS_OP_IDLE) {//多线程执行读取期间,io_threads_op的状态是read,所以直接break,后面的processCommandAndResetClient无法执行,serverAssert(io_threads_op == IO_THREADS_OP_READ);c->flags |= CLIENT_PENDING_COMMAND;break;}//执行命令/* We are finally ready to execute the command. */if (processCommandAndResetClient(c) == C_ERR) {/* If the client is no longer valid, we avoid exiting this* loop and trimming the client buffer later. So we return* ASAP in that case. */return C_ERR;}}}
(2) 多线程之后完毕后,主线程执行客户端的缓冲区的命令
上面多线程读取socket到客户端输入缓冲区后之后,即
handleClientsWithPendingReadsUsingThreads最后面,主线程while遍历了客户端,执行processPendingCommandAndInputBuffer
int processPendingCommandAndInputBuffer(client *c) {/* Notice, this code is also called from 'processUnblockedClients'.* But in case of a module blocked client (see RM_Call 'K' flag) we do not reach this code path.* So whenever we change the code here we need to consider if we need this change on module* blocked client as well */if (c->flags & CLIENT_PENDING_COMMAND) {c->flags &= ~CLIENT_PENDING_COMMAND;if (processCommandAndResetClient(c) == C_ERR) {return C_ERR;}}/* Now process client if it has more data in it's buffer.** Note: when a master client steps into this function,* it can always satisfy this condition, because its querybuf* contains data not applied. */if (c->querybuf && sdslen(c->querybuf) > 0) {return processInputBuffer(c);}return C_OK;
}
processCommandAndResetClient方法就是命令执行函数
2、给等待输出客户端列表分配线程后,多线程(包含主线程)开始执行把从客户端输出缓冲区写入到socket,如果没有写完,还会注册文件事件,让aeMain执行,
在分配线程后,到全部线程都执行完从socket写入到客户端缓冲区之前,io_threads_op都是writer状态,不是空闲状态
int handleClientsWithPendingWritesUsingThreads(void) {//如果等待输出客户端列表没有,则直接返回int processed = listLength(server.clients_pending_write);if (processed == 0) return 0; /* Return ASAP if there are no clients. *//* If I/O threads are disabled or we have few clients to serve, don't* use I/O threads, but the boring synchronous code. *///没有开启多线程,由主线程直接执行handleClientsWithPendingWrites返回if (server.io_threads_num == 1 || stopThreadedIOIfNeeded()) {return handleClientsWithPendingWrites();}/* Start threads if needed. */if (!server.io_threads_active) startThreadedIO();/* Distribute the clients across N different lists. */listIter li;listNode *ln;//获取待写回客户端列表clients_pending_write加入到迭代链表中listRewind(server.clients_pending_write,&li);int item_id = 0;// 遍历待写的客户端while((ln = listNext(&li))) {client *c = listNodeValue(ln);c->flags &= ~CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE;/* Remove clients from the list of pending writes since* they are going to be closed ASAP. */if (c->flags & CLIENT_CLOSE_ASAP) {listUnlinkNode(server.clients_pending_write, ln);continue;}/* Since all replicas and replication backlog use global replication* buffer, to guarantee data accessing thread safe, we must put all* replicas client into io_threads_list[0] i.e. main thread handles* sending the output buffer of all replicas. */if (getClientType(c) == CLIENT_TYPE_SLAVE) {listAddNodeTail(io_threads_list[0],c);continue;}//根据线程数取余,分配线程int target_id = item_id % server.io_threads_num;listAddNodeTail(io_threads_list[target_id],c);item_id++;}/* Give the start condition to the waiting threads, by setting the* start condition atomic var. *///设置多线程状态为写入状态io_threads_op = IO_THREADS_OP_WRITE;for (int j = 1; j < server.io_threads_num; j++) {int count = listLength(io_threads_list[j]);setIOPendingCount(j, count);}//0是主线程,主线程单独遍历它所获取的待写入客户端列表,执行writeToClient//因为非主线程,有IOThreadMain函数/* Also use the main thread to process a slice of clients. */listRewind(io_threads_list[0],&li);while((ln = listNext(&li))) {client *c = listNodeValue(ln);//里面有_writeToClient函数执行客户端输出缓冲区到socketwriteToClient(c,0);}listEmpty(io_threads_list[0]);//这个是主线程等待其他线程都写完/* Wait for all the other threads to end their work. */while(1) {unsigned long pending = 0;for (int j = 1; j < server.io_threads_num; j++)pending += getIOPendingCount(j);if (pending == 0) break;}//多线程状态设置为空闲io_threads_op = IO_THREADS_OP_IDLE;/* Run the list of clients again to install the write handler where* needed. */// 再次获取server.clients_pending_write所有待写的客户端listRewind(server.clients_pending_write,&li);while((ln = listNext(&li))) {client *c = listNodeValue(ln);/* Update the client in the mem usage after we're done processing it in the io-threads */updateClientMemUsageAndBucket(c);/* Install the write handler if there are pending writes in some* of the clients. *///如果缓冲区数据未全部写回调用installClientWriteHandler注册可写事件,回调函数为sendReplyToClientif (clientHasPendingReplies(c)) {installClientWriteHandler(c);}}while(listLength(server.clients_pending_write) > 0) {listUnlinkNode(server.clients_pending_write, server.clients_pending_write->head);}/* Update processed count on server */server.stat_io_writes_processed += processed;return processed;
}