友元分为两部分内容
- 友元函数
- 友元类
友元函数
问题:当我们尝试去重载operator<<,然后发现没办法将operator<<重载成成员函数。因为cout的输出流对象和隐含的this指针在抢占第一个参数的位置。this指针默认是第一个参数也就是左操作
数了。但是实际使用中cout需要是第一个形参对象,才能正常使用。所以要将operator<<重载成全局函数。但又会导致类外没办法访问成员,此时就需要友元来解决。operator>>同理。
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
// d1 << cout; -> d1.operator<<(&d1, cout); 不符合常规调用
// 因为成员函数第一个参数一定是隐藏的this,所以d1必须放在<<的左侧
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout)
{
_cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
return _cout;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
友元函数可以直接访问类的私有成员,它是定义在类外部的普通函数,不属于任何类,但需要在类的内部声明,声明时需要加friend关键字。
class Date
{
//友元声明 这个声明你放在公有还是私有都是不影响的,它只是一个声明
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& _cin, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& _cin, Date& d)
{
_cin >> d._year;
_cin >> d._month;
_cin >> d._day;
return _cin;
}
int main()
{
Date d;
cin >> d;
cout << d << endl;
return 0;
}
特征:
- 友元声明放在
public还是private,还是两个都不放 都是不影响的 - 友元函数不是类的成员函数
- 友元函数不能用const修饰,(提一嘴:静态成员也不能用const修饰,因为没有this 指针)
- 一个函数可以是多个类的友元函数
- 友元函数的调用与普通函数的调用原理相同
友元类
友元类的所有成员函数都可以是另一个类的友元函数,都可以访问另一个类中的非公有成员。
- 友元关系是单向的,不具有交换性。
比如下面描述Time类和Date类,在Time类中声明Date类为其友元类,那么可以在Date类中直接访问Time类的私有成员变量,但想在Time类中访问Date类中私有的成员变量则不行。 - 友元关系不能传递
- 如果C是B的友元, B是A的友元,则不能说明C时A的友元。
友元关系不能继承,在继承位置再给大家详细介绍。
class Time
{
friend class Date; // 声明日期类为时间类的友元类,则在日期类中就直接访问Time类
中的私有成员变量
public:
Time(int hour = 0, int minute = 0, int second = 0)
: _hour(hour)
, _minute(minute)
, _second(second)
{}
private:
int _hour;
int _minute;
int _second;
};
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
void SetTimeOfDate(int hour, int minute, int second)
{
// 直接访问时间类私有的成员变量
_t._hour = hour;
_t._minute = minute;
_t._second = second;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
Time _t;
};
内部类
概念:如果一个类定义在另一个类的内部,这个内部类就叫做内部类。内部类是一个独立的类,它不属于外部类,更不能通过外部类的对象去访问内部类的成员。外部类对内部类没有任何优越的访问权限
特性:
- 内部类可以定义在外部类的
public、protected、private都是可以的。 - 注意内部类可以直接访问外部类中的
static成员,不需要外部类的对象/类名。 - sizeof(外部类)=外部类,和内部类没有任何关系
思考下面代码的结果:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class A
{
public://内部类class B{public:private:int _b;};private:int _a;};int main()
{cout << sizeof(A) << endl;return 0;
}
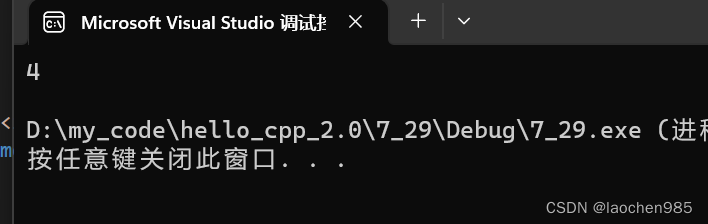
这个就可以说明:sizeof(外部类) = 外部类 与内部类没有任何关系
还需要理解的就是:
B类 和 A类 ,虽然B类在A类的内部,但实际上B类和A类 是两个独立的类,只是说,B类 要受到 A 类的 域 和 访问限定符的限制
所以可以这么说,A 对象里面 是 没有B对象的
如果内部类 是定义在public 中的 就可以通过 域作用限定符来进行访问
如果内部类 是定义在private 中的 无法通过 域作用限定符来进行访问
注意:内部类就是外部类的友元类,参见友元类的定义,内部类可以通过外部类的对象参数来访问外部类中的所有成员。但是外部类不是内部类的友元
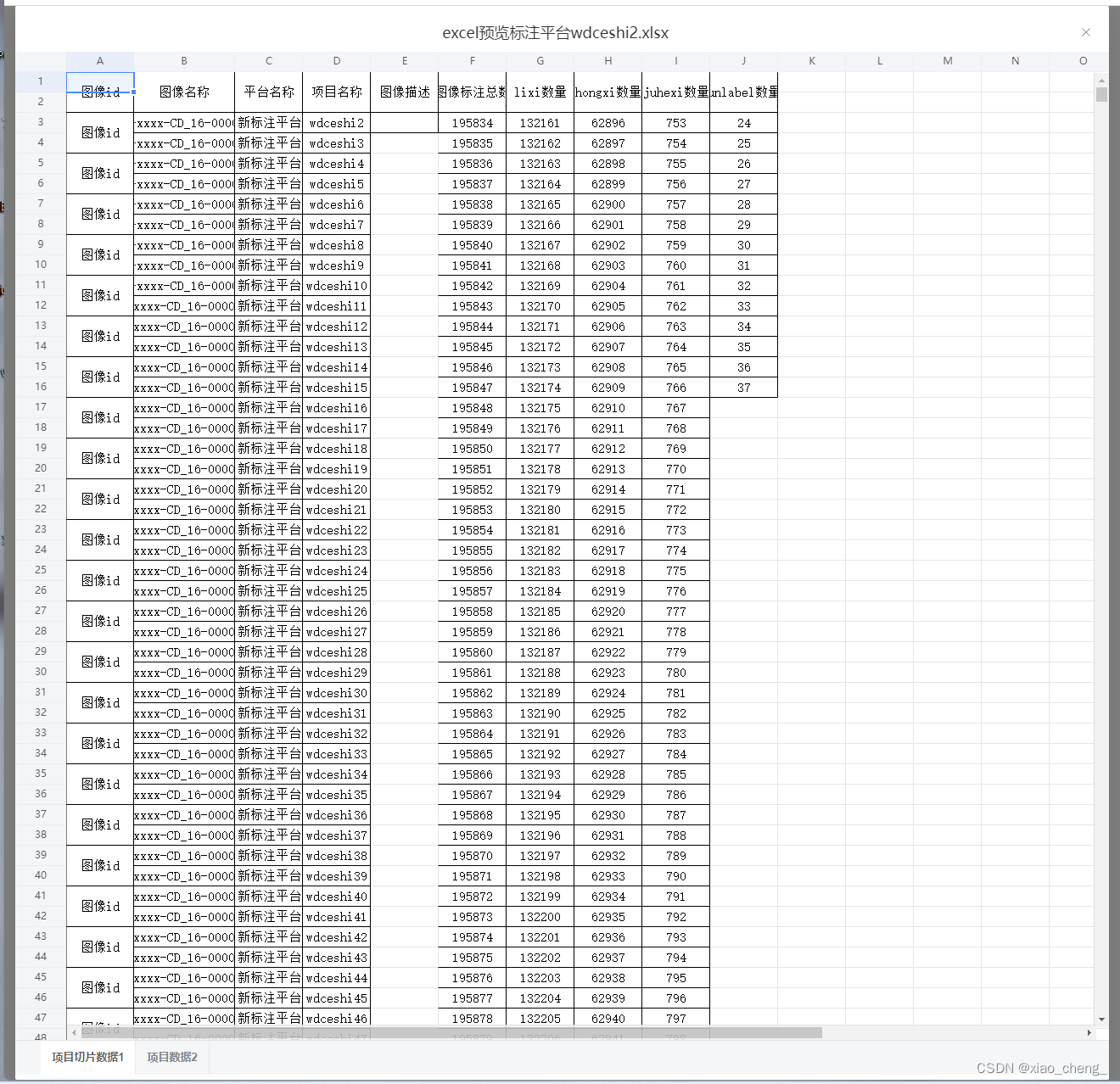
![[保研/考研机试] KY85 二叉树 北京大学复试上机题 C++实现](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2f58798bbd8f4036bc006fcc3c4a7627.png)