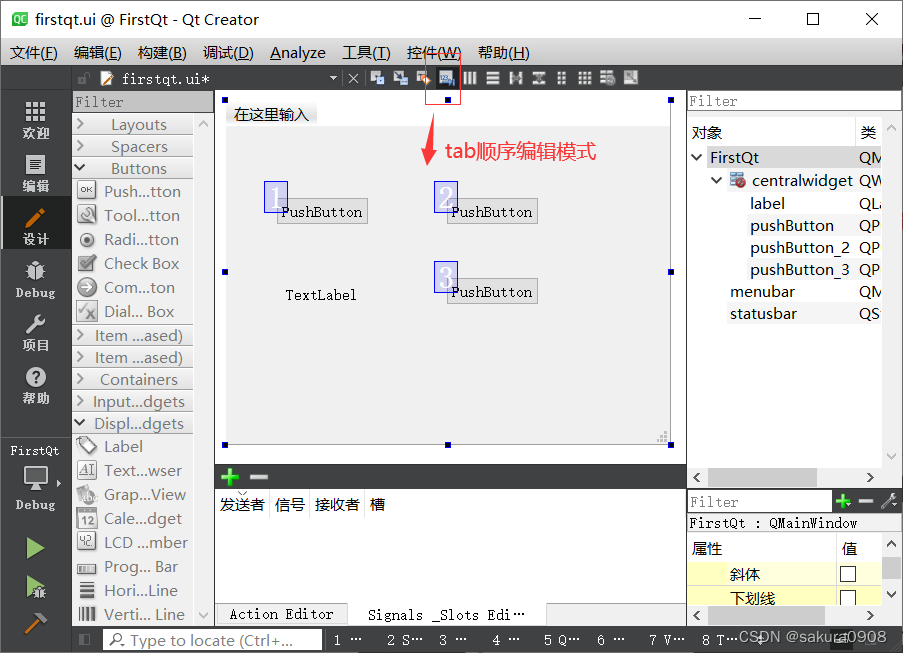
gromacs能在win上运行,还是个开源的软件,这都很值得入手学习
记录下gromacs教程的练习情况:
Lysozyme in water
水中的溶菌酶,嗯,估计就是把蛋白处理后放在显试溶剂里跑MD这个模拟。
1、文件的准备:
1、先到PDB数据库下载1AKI的蛋白文件
2、用文本编辑器将water去掉,在VMD或者pymol里查看分子的结构,看是否有结构的缺失。
3、用gmx的pdb2gmx生成需要的文件:
- 一个拓扑文件
- 一个限制坐标信息文件
- 一个坐标结构(预进程的结构)文件
拓扑文件(*.top)包含的信息:非键参数(原子类型和电荷信息)、键参数(键、键角和二面角)
gmx pdb2gmx -f .\1aki_delwat.pdb -o 1aki_processed.gro -water spce#-f 后接pdb文件
#-water 选择要使用的水模型:none, spc, spce, tip3p, tip4p, tip5p,tips3p
#-o 输出的结构文件,gro格式
#-p 输出的拓扑文件
按下回车后,跳出系列力场进行选择
教程里选择15的all-atom OPLS力场,所以这里在光标处输入15,按下回车
然后结构文件gro、拓扑文件top就生成了
教程里介绍的几个gmx2pdb的关键字:
-ignh: #忽略pdb文件里的H原子,不去除,一般这种情况是需要pdb里H原子的坐标信息,但需要手动修改H原子的名字,让其符合gromacs的格式
-ter: #交互式地为N端和C端分配电荷状态。
-inter: #交互式地为 Glu、Asp、Lys、Arg 和 His 分配电荷状态;选择哪些Cys参与二硫键2、检查拓扑文件:
略
3、定义盒子和填充溶剂:
这里主要的两个步骤:
- 1、定义盒子的维度,通过editconf模块
- 2、给盒子填上溶剂,使用solvate模块
使用命令:
gmx editconf -f 1AKI_processed.gro -o 1AKI_newbox.gro -c -d 1.0 -bt cubic-f -o:#输入、输出坐标文件(*.gro)
-c: #让蛋白质放置在盒子中央(center)
-d:#指出盒子的尺寸,1nm
-bt:#指出盒子的类型,立方体到盒子边缘的距离是一个重要的参数。由于我们将使用周期性边界条件,因此必须满足最小图像约定。也就是说,蛋白质永远不应该看到它的周期性图像,否则计算出的力将是虚假的。指定 1.0 nm 的溶质盒距离意味着蛋白质的任何两个周期图像之间至少有 2.0 nm。这个距离对于模拟中常用的任何截止方案来说都足够了。
gmx solvate -cp 1AKI_newbox.gro -cs spc216.gro -o 1AKI_solv.gro -p topol.top-cp: #上一步editconf输出的gro文件
-cs: #gromacs自带的水模型,spc216.gro,这是一个通用的平衡3点溶剂模型。您可以使用它作为SPC、SPC/E 或TIP3P水的溶剂配置,因为它们都是三点水模型。-o:#输出的更新的坐标文件
-p:#输出的更新的拓扑文件检查拓扑文件的[moleucles]模块,里面的内容出现更新:
[ molecules ]
; Compound #mols
Protein_A 1
SOL 10832 4、增加离子:
在拓扑文件中检查体系的电荷(蛋白的电荷)
在[atom]区域的信息里,有qtot的字眼,是原子电荷累计的总和,查看最后列的qtot数值就是体系的整体电荷。这个体系是8个正电荷。
Gromacs里增加离子的模块是genion
再用genion添加离子前,需要用grompp模块生成一个*.tpr文件
tpr是一个包含结构信息、拓扑信息和模拟参数的二进制输入文件
而用grompp之前,需要准备如下的*.mdp (molecular dynamics parameter file) 文件
; ions.mdp - used as input into grompp to generate ions.tpr ; Parameters describing what to do, when to stop and what to save integrator = steep ; Algorithm (steep = steepest descent minimization) emtol = 1000.0 ; Stop minimization when the maximum force < 1000.0 kJ/mol/nm emstep = 0.01 ; Minimization step size nsteps = 50000 ; Maximum number of (minimization) steps to perform; Parameters describing how to find the neighbors of each atom and how to calculate the interactions nstlist = 1 ; Frequency to update the neighbor list and long range forces cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching ns_type = grid ; Method to determine neighbor list (simple, grid) coulombtype = cutoff ; Treatment of long range electrostatic interactions rcoulomb = 1.0 ; Short-range electrostatic cut-off rvdw = 1.0 ; Short-range Van der Waals cut-off pbc = xyz ; Periodic Boundary Conditions in all 3 dimensions
这些参数都是基于OPLS-AA力场设置的,跟换力场,参数可能不适用(来自教程的提示)。
gmx grompp -f ions.mdp -c 1AKI_solv.gro -p topol.top -o ions.tpr-f #后接复制到的mdp文件
-c -f #后面是结构和拓扑文件
-o #是输出的*.tpr文件
这样,tpr文件就生成了
gmx genion -s ions.tpr -o 1AKI_solv_ions.gro -p topol.top -pname NA -nname CL -neutral-s #加tpr文件
-o -p #更新的结构文件和拓扑文件
-pname -nname #增加的阴阳离子是什么元素
-neutral #让体系处于电中性
-conc #指出增加的离子浓度
然后选择13号组,嵌入离子
5、进行能量最小化(EM):
5.1、操作:
这一步和增加离子类似,要用grompp生成一个*.tpr文件,然后用gromacs的MD引擎mdrun进行能量最小化。
将上一步增加离子的ions.mdp拷贝一件,重命名为minim.mdp
gmx grompp -f minim.mdp -c 1AKI_solv_ions.gro -p topol.top -o em.tpr-f: #后接模拟参数信息,这里的信息和增加离子的类似
-c -p: #后接结构、拓扑文件
-o: #后是输出的以上信息的组装的二进制文件没有出错,接下来就是EM:
gmx mdrun -v -deffnm em-v: #将细节输出到终端里
-deffnm: #后接所有的文件名(包括输出和输入)
-s: #后接输入文件,就是em.tpr这里会得到系列输出文件,如果EM结束
- em.log:文本文件,EM进程的日志文件
- em.edr: 二进制的能量文件
- em.trr: 二进制的精确的轨迹文件
- em.gro: 能量最小化的结构
5.2、如何判断一个EM是否成功:
看两个因素:
①体系的势能Epot,对于一个水中的蛋白质,能量最小化后,其Epot应该在105-106之间。
②Fmax,在minim.mdp文件中,设置了一个参数:emtol = 1000.0,意思就是要Fmax<1000.0 kJ mol-1 nm-1
成功的最小化,要满足这两个条件。
提取em中的能量变化,进行分析:
gmx energy -f em.edr -o potential.xvg输入命令后,会出现系列选项,这里选择10的potential
因为可以多选,在末尾输入0再回车
终端会返回poteintial的均值,和产生一个potential.xvg文件
xvg文件绘制图形,势能降至105-106kj/mol,说明最小化成功,可进行下一步的模拟。

6、平衡模拟:
EM保证一个合理的起始结构(建立的体系中水分子和蛋白的位置是人为放置的,原子间可能存在很近的,不合理的距离,从而产生极大的、不稳定的、不合理的能量),EM的目的就是解决这个。
在正式模拟(成品模拟)之前,体系中没有建立真实的密度,需要提高温度、再给予压力,让体系达到真实的密度。
好久前用pdb2gmx生成的posre.itp文件现在派上用场了
posre.itp文件的作用是约束蛋白质的重原子(C、O、N),受能量约束的原子依然可以移动,但是要克服一个巨大的能量惩罚(penalty)。这方便我们整顿蛋白周围的溶剂分子,而蛋白本身的结构没有发生太大的变化。
约束需要一个原点(约束力就像弹簧力,原子在原点,跑越远,受到拉扯回的力越大,向外的阻力也越大),这个原点就是能力最小化后的结构坐标。
一个平衡模拟由两个时相组成
6.1、NVT系综(NVT ensemble)模拟
在恒定的粒子数、体积和温度下进行模拟。这种程序的时间范围取决于系统的内容,但在NVT中,系统的温度应该达到所需值的平台,如果温度尚未稳定,则需要额外的时间。一般地,50~100ps是足够的。这里,我们进行一个100ps的NVT模拟。
拷贝如下的nvt.mdp文件:
title = OPLS Lysozyme NVT equilibration define = -DPOSRES ; position restrain the protein ; Run parameters integrator = md ; leap-frog integrator nsteps = 50000 ; 2 * 50000 = 100 ps dt = 0.002 ; 2 fs ; Output control nstxout = 500 ; save coordinates every 1.0 ps nstvout = 500 ; save velocities every 1.0 ps nstenergy = 500 ; save energies every 1.0 ps nstlog = 500 ; update log file every 1.0 ps ; Bond parameters continuation = no ; first dynamics run constraint_algorithm = lincs ; holonomic constraints constraints = h-bonds ; bonds involving H are constrained lincs_iter = 1 ; accuracy of LINCS lincs_order = 4 ; also related to accuracy ; Nonbonded settings cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching ns_type = grid ; search neighboring grid cells nstlist = 10 ; 20 fs, largely irrelevant with Verlet rcoulomb = 1.0 ; short-range electrostatic cutoff (in nm) rvdw = 1.0 ; short-range van der Waals cutoff (in nm) DispCorr = EnerPres ; account for cut-off vdW scheme ; Electrostatics coulombtype = PME ; Particle Mesh Ewald for long-range electrostatics pme_order = 4 ; cubic interpolation fourierspacing = 0.16 ; grid spacing for FFT ; Temperature coupling is on tcoupl = V-rescale ; modified Berendsen thermostat tc-grps = Protein Non-Protein ; two coupling groups - more accurate tau_t = 0.1 0.1 ; time constant, in ps ref_t = 300 300 ; reference temperature, one for each group, in K ; Pressure coupling is off pcoupl = no ; no pressure coupling in NVT ; Periodic boundary conditions pbc = xyz ; 3-D PBC ; Velocity generation gen_vel = yes ; assign velocities from Maxwell distribution gen_temp = 300 ; temperature for Maxwell distribution gen_seed = -1 ; generate a random seed
上面的NVT参数以及EM后的结构和拓扑文件,利用grompp集合成一个二进制文件nvt.tpr:
gmx grompp -f nvt.mdp -c em.gro -r em.gro -p topol.top -o nvt.tpr用MD引擎mdrun进行模拟:
gmx mdrun -deffnm nvtCPU烧了6min,就好了。教程里说"如果在 16 个内核左右并行运行,则不到一个小时"
但我的机子没这么厉害......
分析模拟后的温度变化:
gmx energy -f nvt.edr -o temperature.xvg终端里输入16 0
对*xvg绘图的结果应该是:
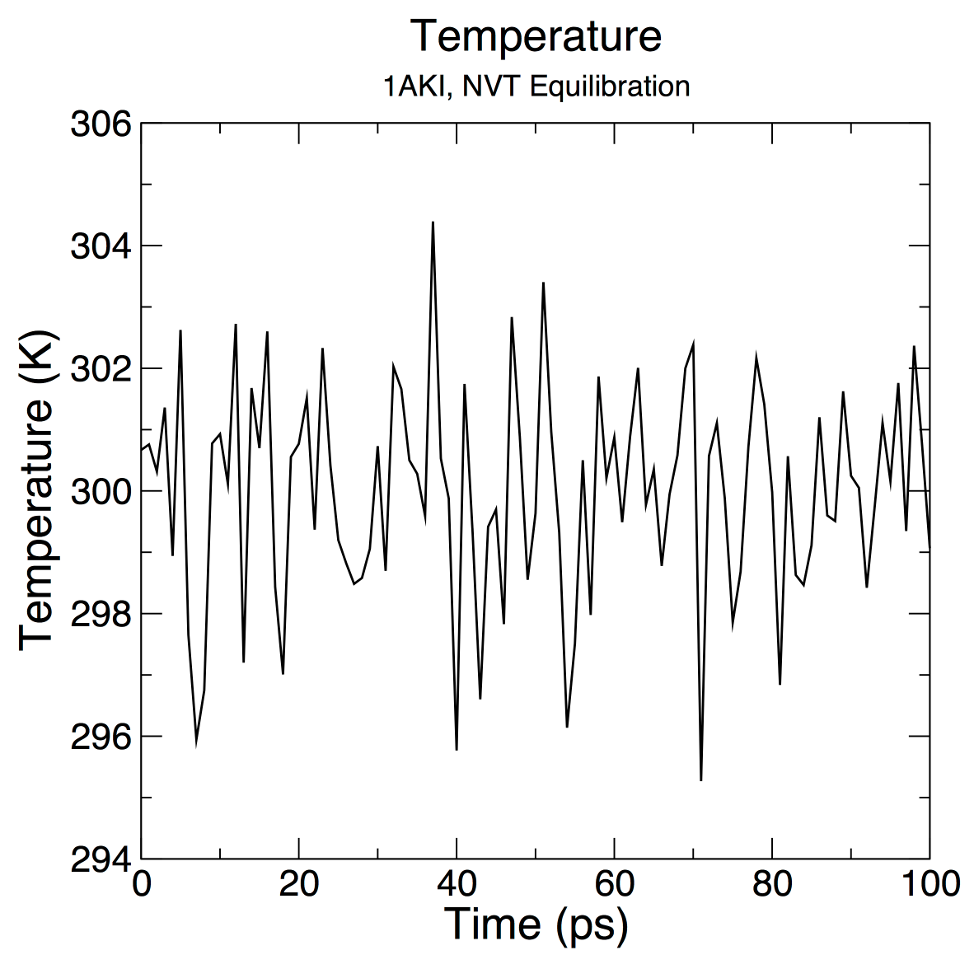
从图像中可见,体系的温度迅速达到目标温度(300K),然后在其附近稳定波动。
对于这样的体系,NVT只需要50ps的模拟就能达到
6.2、NPT系综(NPT ensemble)模拟:
稳定温度后,需要稳定体系的压力,让体系的密度达到稳定,更接近实验条件。
NPT模拟同样进行100ps
模拟的参数信息(文本格式)如下,拷贝成一个npt.mdp文件
title = OPLS Lysozyme NPT equilibration define = -DPOSRES ; position restrain the protein ; Run parameters integrator = md ; leap-frog integrator nsteps = 50000 ; 2 * 50000 = 100 ps dt = 0.002 ; 2 fs ; Output control nstxout = 500 ; save coordinates every 1.0 ps nstvout = 500 ; save velocities every 1.0 ps nstenergy = 500 ; save energies every 1.0 ps nstlog = 500 ; update log file every 1.0 ps ; Bond parameters continuation = yes ; Restarting after NVT constraint_algorithm = lincs ; holonomic constraints constraints = h-bonds ; bonds involving H are constrained lincs_iter = 1 ; accuracy of LINCS lincs_order = 4 ; also related to accuracy ; Nonbonded settings cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching ns_type = grid ; search neighboring grid cells nstlist = 10 ; 20 fs, largely irrelevant with Verlet scheme rcoulomb = 1.0 ; short-range electrostatic cutoff (in nm) rvdw = 1.0 ; short-range van der Waals cutoff (in nm) DispCorr = EnerPres ; account for cut-off vdW scheme ; Electrostatics coulombtype = PME ; Particle Mesh Ewald for long-range electrostatics pme_order = 4 ; cubic interpolation fourierspacing = 0.16 ; grid spacing for FFT ; Temperature coupling is on tcoupl = V-rescale ; modified Berendsen thermostat tc-grps = Protein Non-Protein ; two coupling groups - more accurate tau_t = 0.1 0.1 ; time constant, in ps ref_t = 300 300 ; reference temperature, one for each group, in K ; Pressure coupling is on pcoupl = Parrinello-Rahman ; Pressure coupling on in NPT pcoupltype = isotropic ; uniform scaling of box vectors tau_p = 2.0 ; time constant, in ps ref_p = 1.0 ; reference pressure, in bar compressibility = 4.5e-5 ; isothermal compressibility of water, bar^-1 refcoord_scaling = com ; Periodic boundary conditions pbc = xyz ; 3-D PBC ; Velocity generation gen_vel = no ; Velocity generation is off
用grompp对文件整合成二进制文件tpr:
gmx grompp -f npt.mdp -c nvt.gro -r nvt.gro -t nvt.cpt -p topol.top -o npt.tpr-t: #检查点文件,来自上一步的NVT模拟用md引擎开始跑:
gmx mdrun -deffnm npt同样也需要点时间
完成模拟后,用energy模块进行压力数据提取:
gmx energy -f npt.edr -o pressure.xvg命令回车后,输入18 0

压力的波动很大,图中红线是每10ps计算均值绘制出的曲线。
100ps模拟的压力均值是7.5 ± 160.5 bar,参考的压力设置为1bar,这在npt.mdp文件里可以找到
由于均值较大的RMSF(160.5 bar),尚不能从统计学上分析样本均值和参考均值有无差异。
用energy对密度进行提取:
gmx energy -f npt.edr -o density.xvg输入24 0在光标处

100ps内的平均密度是1019 ± 3 kg m-3,和实验值(1000 kg m-3)接近,使用的SPC/E model的预期密度是1008 kg m-3。
模拟过程中,密度、温度、压力达到稳定,体系达到平衡。
NPT模拟还需要延长点时间
7、成品模拟:
7.1、操作:
拷贝如下的模拟参数,命名为md.mdp
title = OPLS Lysozyme NPT equilibration ; Run parameters integrator = md ; leap-frog integrator nsteps = 500000 ; 2 * 500000 = 1000 ps (1 ns) dt = 0.002 ; 2 fs ; Output control nstxout = 0 ; suppress bulky .trr file by specifying nstvout = 0 ; 0 for output frequency of nstxout, nstfout = 0 ; nstvout, and nstfout nstenergy = 5000 ; save energies every 10.0 ps nstlog = 5000 ; update log file every 10.0 ps nstxout-compressed = 5000 ; save compressed coordinates every 10.0 ps compressed-x-grps = System ; save the whole system ; Bond parameters continuation = yes ; Restarting after NPT constraint_algorithm = lincs ; holonomic constraints constraints = h-bonds ; bonds involving H are constrained lincs_iter = 1 ; accuracy of LINCS lincs_order = 4 ; also related to accuracy ; Neighborsearching cutoff-scheme = Verlet ; Buffered neighbor searching ns_type = grid ; search neighboring grid cells nstlist = 10 ; 20 fs, largely irrelevant with Verlet scheme rcoulomb = 1.0 ; short-range electrostatic cutoff (in nm) rvdw = 1.0 ; short-range van der Waals cutoff (in nm) ; Electrostatics coulombtype = PME ; Particle Mesh Ewald for long-range electrostatics pme_order = 4 ; cubic interpolation fourierspacing = 0.16 ; grid spacing for FFT ; Temperature coupling is on tcoupl = V-rescale ; modified Berendsen thermostat tc-grps = Protein Non-Protein ; two coupling groups - more accurate tau_t = 0.1 0.1 ; time constant, in ps ref_t = 300 300 ; reference temperature, one for each group, in K ; Pressure coupling is on pcoupl = Parrinello-Rahman ; Pressure coupling on in NPT pcoupltype = isotropic ; uniform scaling of box vectors tau_p = 2.0 ; time constant, in ps ref_p = 1.0 ; reference pressure, in bar compressibility = 4.5e-5 ; isothermal compressibility of water, bar^-1 ; Periodic boundary conditions pbc = xyz ; 3-D PBC ; Dispersion correction DispCorr = EnerPres ; account for cut-off vdW scheme ; Velocity generation gen_vel = no ; Velocity generation is off
进行信息整合为一个二进制的tpr文件:
gmx grompp -f md.mdp -c npt.gro -t npt.cpt -p topol.top -o md_0_1.tprgrompp 将打印 PME 负载的估计值,这将指示应将多少处理器专用于 PME 计算,以及有多少处理器专用于 PP 计算。
开始成品模拟:
gmx mdrun -deffnm md_0_1 -nt 4-nt:#使用多少线程我机子能开8个线程,但这里占了我60~70%的CPU
Gabba Gabba Hey!
7.2、RMSD分析:
现在我们已经模拟了我们的蛋白质,我们应该对系统进行一些分析。哪些类型的数据很重要?这是运行模拟之前要问的一个重要问题,因此您应该对要在自己的系统中收集的数据类型有一些想法。在本教程中,将介绍一些基本工具。
第一个是trjconv,它被用作后处理工具,用于剥离坐标,校正周期性或手动更改轨迹(时间单位,帧频率等)。在本练习中,我们将使用 trjconv 来解释系统中的任何周期性。蛋白质将通过晶胞扩散,可能看起来“破碎”或可能“跳”到盒子的另一侧。要解释此类行为,请发出以下问题:
gmx trjconv -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1.xtc -o md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -pbc mol -center
选择 1(“蛋白质”)作为要居中的组,选择 0(“系统”)作为输出。我们将对这种“修正”的轨迹进行所有分析。让我们先看一下结构稳定性。GROMACS有一个内置的RMSD计算实用程序,称为rms。要使用 rms,请发出以下命令:
gmx rms -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -o rmsd.xvg -tu ns
选择 4(“主干”)作为最小二乘拟合和用于 RMSD 计算的组。-tu 标志将以 ns 为单位输出结果,即使轨迹是用 ps 写的。这样做是为了输出的清晰度(特别是如果你有一个长时间的模拟 - 1e + 05 ps看起来不如100 ns)。输出图将显示相对于最小化平衡系统中存在的结构的RMSD:
如果想要将能量最小化后的结构(晶体结构)作为RMSD计算的参考结构,可以用如下的命令:
gmx rms -s em.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -o rmsd_xtal.xvg -tu ns
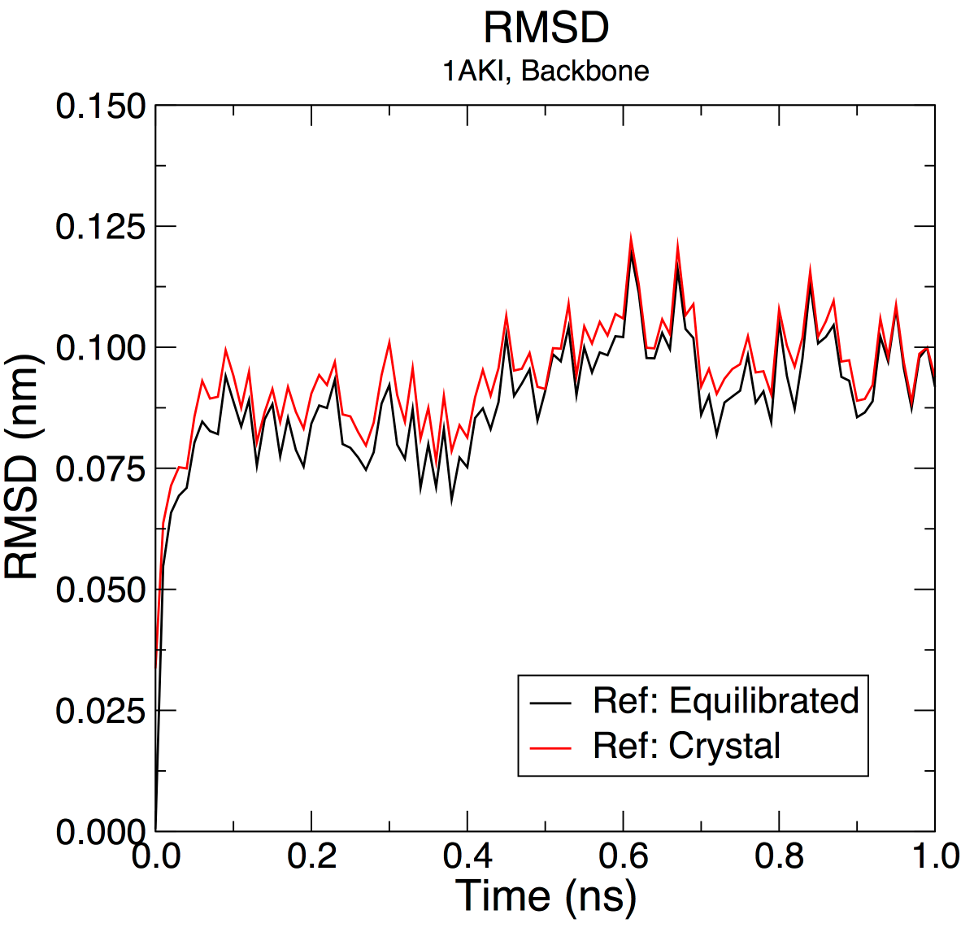
两个时间序列都显示RMSD水平降至~0.1 nm(1 Å),表明结构非常稳定。
图之间的细微差异表明t = 0 ns时的结构与该晶体结构略有不同。这是意料之中的,因为它已被能量最小化,并且因为位置约束不是 100% 完美的,如前所述。
7.3、Rg分析:
蛋白质的回转半径(Rg)是一种衡量它的紧凑性的参数。 如果一个蛋白质是稳定的折叠,它将有可能保持相对稳定的Rg。 如果一个蛋白质的在模拟过程中展开,其Rg将随着时间而改变。
gmx gyrate -s md_0_1.tpr -f md_0_1_noPBC.xtc -o gyrate.xvg
选择 1(“蛋白质”)作为分析的组
图形绘制如下:
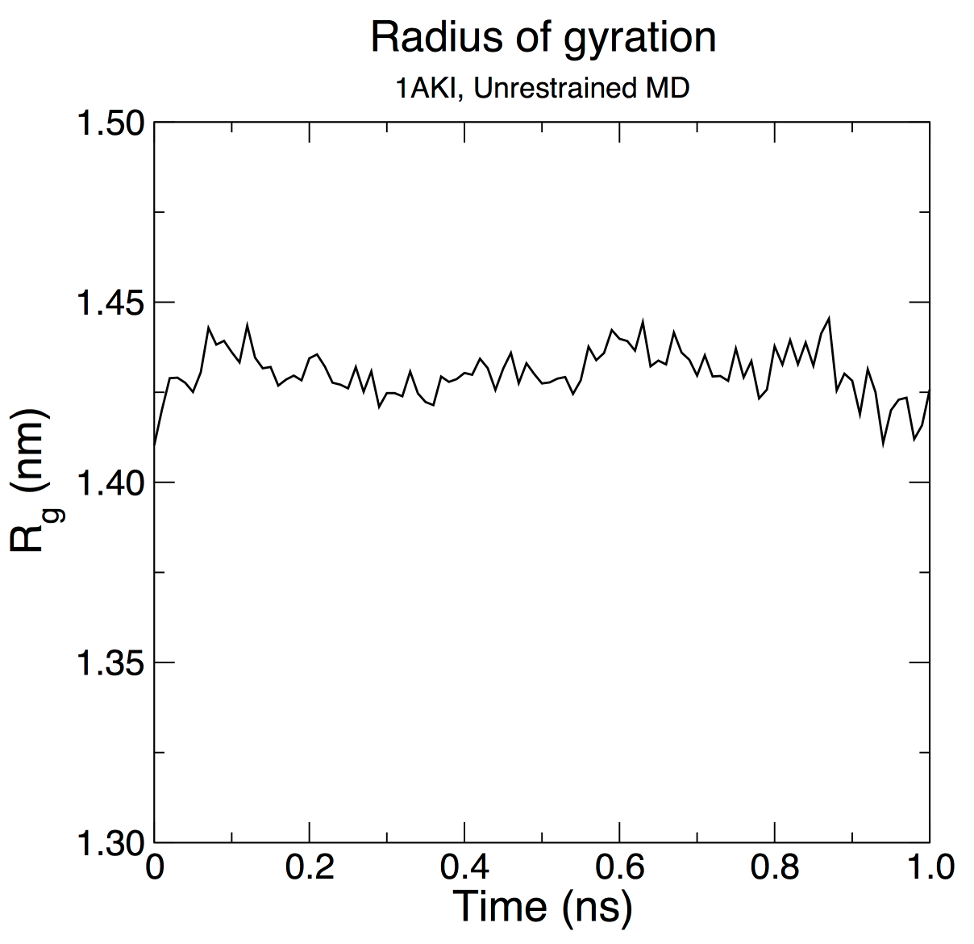
我们可以看到从合理的不变Rg值的蛋白质仍然非常稳定,在其紧凑(折叠)的形式过程中1ns在300K.这种结果并不意外,但说明了一个先进的能力GROMACS分析,来建立