关于作者:CSDN内容合伙人、技术专家, 从零开始做日活千万级APP。
专注于分享各领域原创系列文章 ,擅长java后端、移动开发、人工智能等,希望大家多多支持。
目录
- 一、导读
- 二、概览
- 三、使用
- 3.1 Preferences DataStore
- 添加依赖
- 数据读写
- 3.2 ProtoDataStore
- 添加依赖
- 数据读写
- 3.3、在同步代码中使用 DataStore
- 3.4、在多进程代码中使用 DataStore
- 四、DataStore & MMKV
- 五、 推荐阅读

一、导读
我们继续总结学习Java基础知识,温故知新。
二、概览
DataStore 是一种用于 Android 应用程序数据存储的新的推荐方式。
它是在 Android Jetpack 组件中引入的,旨在替代 SharedPreferences,并提供更强大、易于使用的 API。
DataStore 基于 Kotlin 协程和 Flow 构建而成, 提供了一种类型安全且异步的数据存储解决方案。
相比于 SharedPreferences,DataStore 具有以下优点:
-
异步操作:DataStore 提供了异步的读写操作,避免了阻塞主线程的问题。这使得在读取和写入数据时,应用程序可以更好地保持响应性能。
-
类型安全:DataStore 支持使用协议缓冲区(Protocol Buffers)来定义数据模型,这样可以确保在编译时进行类型检查。数据模型的更改不会导致运行时错误,而是在编译时进行检测。
-
支持多种数据类型:DataStore 支持存储不同类型的数据,包括原始类型、对象或自定义类。
-
数据一致性:DataStore 提供了一致性和安全性保证,保证在多个写入操作中的数据一致性。
-
流式数据访问:DataStore 支持使用流(Flow)来访问数据,使得可以轻松地观察数据的变化并进行相应的更新。
DataStore 提供了两个主要的实现方式:PreferencesDataStore 和 ProtoDataStore。
PreferencesDataStore 适用于存储简单的数据类型,使用键值对来存储数据。
ProtoDataStore 则使用 Protocol Buffers 定义数据模型,并支持存储更复杂的数据结构(类型化对象)。
三、使用
3.1 Preferences DataStore
适用于存储简单的数据类型,使用键值对来存储数据
添加依赖
// Preferences DataStore (SharedPreferences like APIs)dependencies {implementation "androidx.datastore:datastore-preferences:1.0.0"// optional - RxJava2 supportimplementation "androidx.datastore:datastore-preferences-rxjava2:1.0.0"// optional - RxJava3 supportimplementation "androidx.datastore:datastore-preferences-rxjava3:1.0.0"}// Alternatively - use the following artifact without an Android dependency.dependencies {implementation "androidx.datastore:datastore-preferences-core:1.0.0"}数据读写
RxDataStore<Preferences> dataStore =new RxPreferenceDataStoreBuilder(context, /*name=*/ "settings").build();Preferences.Key<Integer> EXAMPLE_COUNTER = PreferencesKeys.int("example_counter");Flowable<Integer> exampleCounterFlow = dataStore.data().map(prefs -> prefs.get(EXAMPLE_COUNTER));Single<Preferences> updateResult = dataStore.updateDataAsync(prefsIn -> {MutablePreferences mutablePreferences = prefsIn.toMutablePreferences();Integer currentInt = prefsIn.get(INTEGER_KEY);mutablePreferences.set(INTEGER_KEY, currentInt != null ? currentInt + 1 : 1);return Single.just(mutablePreferences);
});
// The update is completed once updateResult is completed.
3.2 ProtoDataStore
使用 Protocol Buffers 定义数据模型,并支持存储更复杂的数据结构
添加依赖
// Typed DataStore (Typed API surface, such as Proto)dependencies {implementation "androidx.datastore:datastore:1.0.0"// optional - RxJava2 supportimplementation "androidx.datastore:datastore-rxjava2:1.0.0"// optional - RxJava3 supportimplementation "androidx.datastore:datastore-rxjava3:1.0.0"}// Alternatively - use the following artifact without an Android dependency.dependencies {implementation "androidx.datastore:datastore-core:1.0.0"}数据读写
Proto DataStore 要求在 app/src/main/proto/ 目录的 proto 文件中保存预定义的架构。
此架构用于定义在 Proto DataStore 中保存的对象的类型。
syntax = "proto3";option java_package = "com.example.application";
option java_multiple_files = true;message Settings {int32 example_counter = 1;
}
private static class SettingsSerializer implements Serializer<Settings> {@Overridepublic Settings getDefaultValue() {Settings.getDefaultInstance();}@Overridepublic Settings readFrom(@NotNull InputStream input) {try {return Settings.parseFrom(input);} catch (exception: InvalidProtocolBufferException) {throw CorruptionException(“Cannot read proto.”, exception);}}@Overridepublic void writeTo(Settings t, @NotNull OutputStream output) {t.writeTo(output);}
}RxDataStore<Byte> dataStore =new RxDataStoreBuilder<Byte>(context, /* fileName= */ "settings.pb", new SettingsSerializer()).build();Flowable<Integer> exampleCounterFlow =dataStore.data().map(settings -> settings.getExampleCounter());Single<Settings> updateResult = dataStore.updateDataAsync(currentSettings ->Single.just(currentSettings.toBuilder().setExampleCounter(currentSettings.getExampleCounter() + 1).build()));
3.3、在同步代码中使用 DataStore
DataStore 的主要优势之一是异步 API,但可能不一定始终能将周围的代码更改为异步代码。如果您使用的现有代码库采用同步磁盘 I/O,或者您的依赖项不提供异步 API,就可能出现这种情况。
Kotlin 协程提供 runBlocking() 协程构建器,以帮助消除同步与异步代码之间的差异。您可以使用 runBlocking() 从 DataStore 同步读取数据。RxJava 在 Flowable 上提供阻塞方法。以下代码会阻塞发起调用的线程,直到 DataStore 返回数据:
Settings settings = dataStore.data().blockingFirst();dataStore.data().first().subscribe();
这样,DataStore 可以异步读取数据并将其缓存在内存中。以后使用 runBlocking() 进行同步读取的速度可能会更快,或者如果初始读取已经完成,可能也可以完全避免磁盘 I/O 操作。
- 请尽可能避免在 DataStore 数据读取时阻塞线程。阻塞界面线程可能会导致 ANR 或界面卡顿,而阻塞其他线程可能会导致死锁。
3.4、在多进程代码中使用 DataStore
- DataStore 多进程功能目前仅在 1.1.0 Alpha 版中提供
为了能够在不同进程中使用 DataStore,需要使用 MultiProcessDataStoreFactory 构造 DataStore 对象。
val dataStore: DataStore<Settings> = MultiProcessDataStoreFactory.create(serializer = SettingsSerializer(),produceFile = {File("${context.cacheDir.path}/myapp.preferences_pb")}
)
四、DataStore & MMKV
看一组数据对比,图片来源于MMKV 开源网站
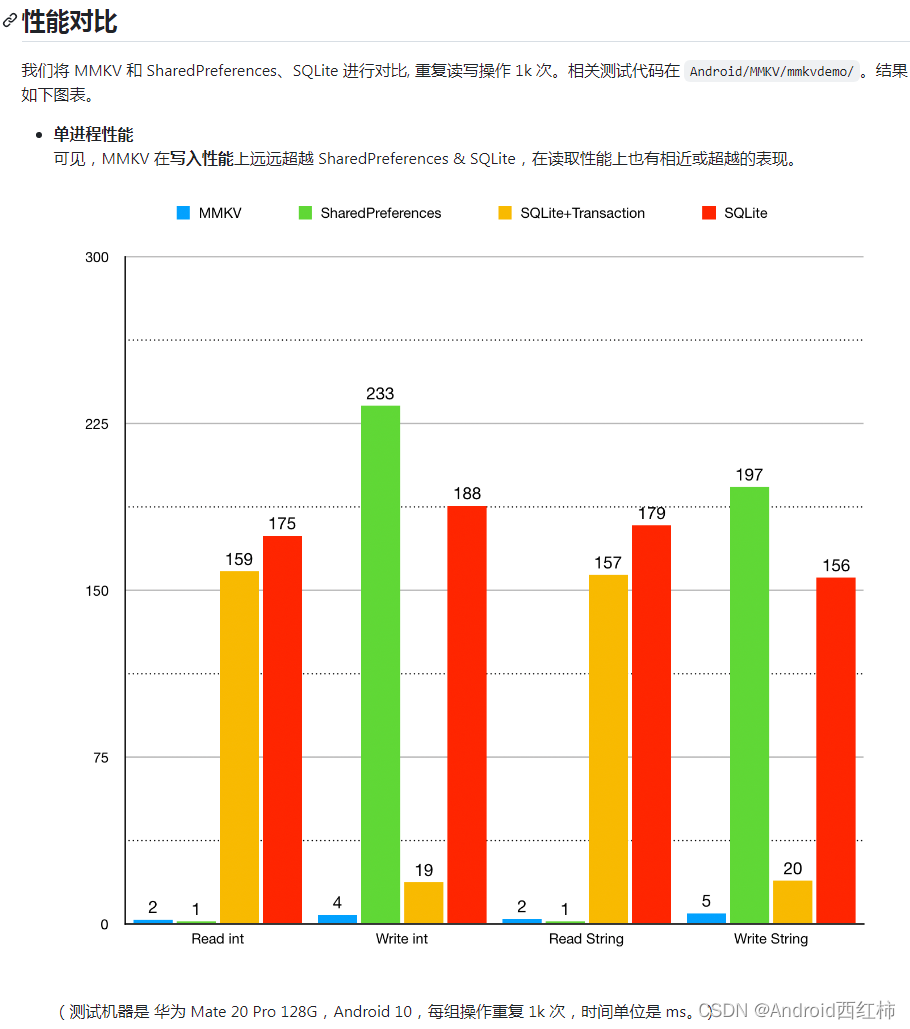
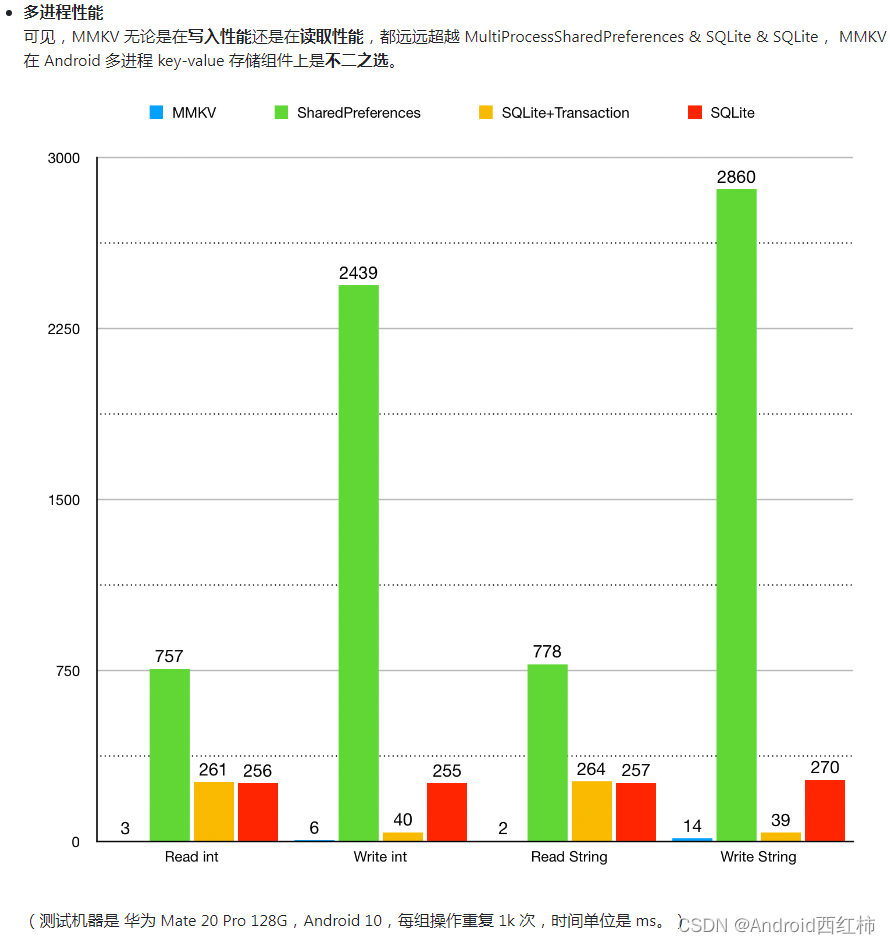
至于如何使用就不描述了,非常简单。
个人感觉 DataStore 没有 MMKV 好用,推荐使用 MMKV,但是各有优劣吧。
jetpack 官网
datastore
五、 推荐阅读
Java 专栏
SQL 专栏
数据结构与算法
Android学习专栏