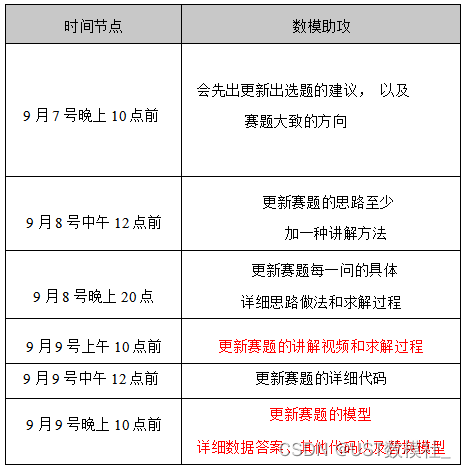
拦截器详细解析可以看大佬简书 "https://www.jianshu.com/p/6fac73f7570f"和 “https://www.jianshu.com/p/3c740829475c”

okhttp请求流程
1:OkHttpClient okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
构建一个okhttpClient对象,传入你想传入的对象,不传就是默认的;
2:构建request对象
Request request = new Request.Builder()
3:okHttpClient.newCall 实际上返回的realCall类 继续调用RealCall.newRealCall
4:调用enqueue方法,传入我们需要的回调接口,而且会判断,
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException(“Already Executed”);
executed = true;
}
如果当前这个call对象已经被运行的话,则抛出异常;
5:继续调用dispatcher的enqueue方法,如果当前运行队列<64并且正在运行,访问同一个服务器地址的请求<5
就直接添加到运行队列,并且开始运行;
不然就添加到等待队列;
6:运行AsyncCall,调用它的execute方法
7:在execute方法中处理完response之后,会在finally中调用dispathcer的finished方法;
8:当当前已经处理完毕的call从运行队列中移除掉;并且调用promoteCalls方法
9:promoteCalls方法中进行判断,
如果运行队列数目大于等于64,如果等待队列里啥都没有,也直接return?
循环等待队列,
将等待队列中的数据进行移除,移除是根据运行队列中还能存放多少来决定;
移到了运行队列中,并且开始运行;
OkHttpClient okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder().build();Request request = new Request.Builder().build();//newCall方法是调用RealCall的newRealCall返回一个RealCallCall call = okHttpClient.newCall(request);//执行请求call.enqueue(new Callback() {@Overridepublic void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {}@Overridepublic void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {}});//这里第二次执行会直接报IllegalStateException错误并提示Already Executedcall.enqueue(new Callback() {@Overridepublic void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {}@Overridepublic void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {}});
进入call.enqueue方法
@Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {//这个锁是为了防止重复请求 如果你同一个call enqueue多次就会直接返回Already Executedsynchronized (this) {if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");executed = true;}captureCallStackTrace();eventListener.callStart(this);//这里的enqueue是传入任务线程AsyncCall并分配到运行队列或等待队列client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));}
进入enqueue方法
//okhttp里执行任务分为两个队列 运行队列和等待队列
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {//当运行的队列中的数值小于64, //并且同时访问同一个机器目标HOST请求书小于5直接加入到运行队列不然的话就加入到等待队列if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {runningAsyncCalls.add(call);//这里维护着请求用的线程池executorService().execute(call);} else {readyAsyncCalls.add(call);}}
public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() {if (executorService == null) {//1:核心线程数 保持在线程池中的线程数量//2:线程池最大可容纳的线程数 //3参数:当线程池中的线程数量大于核心线程数,空闲线程就会等待60s才会被终止,如果小于就会立刻停止;executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false));}return executorService;}
//这个就是队列中传入的线程NameRunnable继承自Runnable
final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable {private final Callback responseCallback;AsyncCall(Callback responseCallback) {super("OkHttp %s", redactedUrl());this.responseCallback = responseCallback;}String host() {return originalRequest.url().host();}Request request() {return originalRequest;}RealCall get() {return RealCall.this;}//这个就是Async的run方法@Override protected void execute() {boolean signalledCallback = false;try {//getResponseWithInterceptorChain() 添加拦截器 okhttp的责任链设计也在这里//response就是请求结果Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();//判断重试/重定向拦截器是否被关闭if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {signalledCallback = true;responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));} else {signalledCallback = true;//返回结果responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);}} catch (IOException e) {if (signalledCallback) {// Do not signal the callback twice!Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);} else {eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e);responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);}} finally {//将执行完成的任务从队列中移除client.dispatcher().finished(this);}}}
添加拦截器
//添加拦截器 责任链设计
//拦截器详细解析可以看大佬简书 "https://www.jianshu.com/p/6fac73f7570f"和 "https://www.jianshu.com/p/3c740829475c"
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {// Build a full stack of interceptors.List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());//重试/重定向拦截器 连接失败后进行重试、对请求结果跟进后进行重定向interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);//桥拦截器:连接应用程序和服务器的桥梁,我们发出的请求会经过它的处理才能发给服务器,//比如设置请求内容的长度 封装header属性 host keep-live gzip header 进行基本设置,interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));//缓存拦截器 在发出请求前,先判断是否命中缓存,//如果命中则可以不请求,直接使用缓存的响应(默认只会对Get请求进行缓存);//如果未命中则进行网络请求,并将结果缓存,等待下次请求被命中。interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));//连接拦截器 与服务器建立连接。interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));if (!forWebSocket) {interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());}//与服务器通信;封装请求数据与解析响应数据(如:HTTP报文)。interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());//执行拦截器return chain.proceed(originalRequest);}
在execute方法中处理完response之后,会在finally中调用dispathcer的finished方法;
//将当前已经处理完毕的call从运行队列中移除掉;并且调用promoteCalls方法
private <T> void finished(Deque<T> calls, T call, boolean promoteCalls) {int runningCallsCount;Runnable idleCallback;synchronized (this) {if (!calls.remove(call)) throw new AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!");if (promoteCalls) promoteCalls();runningCallsCount = runningCallsCount();idleCallback = this.idleCallback;}if (runningCallsCount == 0 && idleCallback != null) {idleCallback.run();}}
promoteCalls方法中进行判断
//如果运行队列数目大于等于64,如果等待队列里啥都没有,也直接return
//循环等待队列,
//将等待队列中的数据进行移除,移除是根据运行队列中还能存放多少来决定;
//移到了运行队列中,并且开始运行;private void promoteCalls() {if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) return; // Already running max capacity.if (readyAsyncCalls.isEmpty()) return; // No ready calls to promote.for (Iterator<AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {AsyncCall call = i.next();if (runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {i.remove();runningAsyncCalls.add(call);executorService().execute(call);}if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) return; // Reached max capacity.}}