文章目录
- 一、目标检测
- 1.1 TXT
- 1.2 COCO
- 1.3 XML
- 二、图像分割
- 2.1 json
- 2.1 TXT
- 2.1.1 json转txt
- 三、行为分析
- 3.1 TXT
- 3.2 JSON
一、目标检测
1.1 TXT
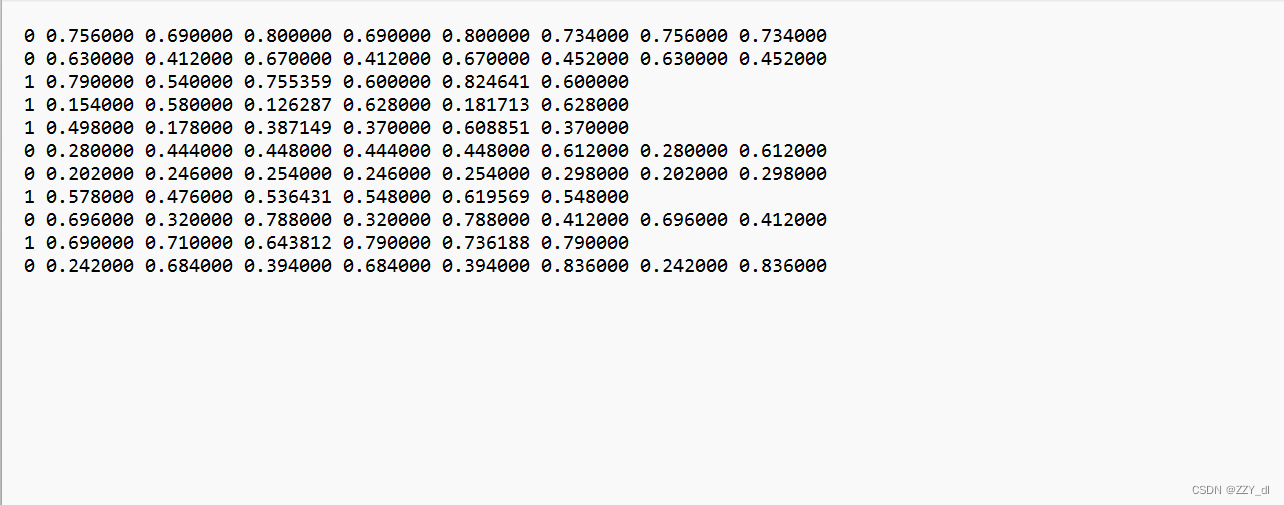
每行表示(类别,中心x相对坐标,中心y相对坐标,相对宽度、相对高度)
1.2 COCO
里面存放了五个信息
info licenses images annotations categories
其中
- info中存放标注文件标注时间、版本等信息。
- licenses中存放数据许可信息。
- images中存放一个list,存放所有图像的图像名,下载地址,图像宽度,图像高度,图像在数据集中的id等信息。
- annotations中存放一个list,存放所有图像的所有物体区域的标注信息,每个目标物体标注以下信息:
{'area': 899, 'iscrowd': 0, 'image_id': 839, 'bbox': [114, 126, 31, 29], 'category_id': 0, 'id': 1, 'ignore': 0, 'segmentation': []}1.3 XML
<annotation><folder>17</folder> # 图片所处文件夹<filename>77258.bmp</filename> # 图片名<path>~/frcnn-image/61/ADAS/image/frcnn-image/17/77258.bmp</path><source> #图片来源相关信息<database>Unknown</database> </source><size> #图片尺寸<width>640</width><height>480</height><depth>3</depth></size><segmented>0</segmented> #是否有分割label<object> 包含的物体<name>car</name> #物体类别<pose>Unspecified</pose> #物体的姿态<truncated>0</truncated> #物体是否被部分遮挡(>15%)<difficult>0</difficult> #是否为难以辨识的物体, 主要指要结体背景才能判断出类别的物体。虽有标注, 但一般忽略这类物体<bndbox> #物体的bound box<xmin>2</xmin> #左<ymin>156</ymin> #上<xmax>111</xmax> #右<ymax>259</ymax> #下</bndbox></object>
</annotation>
二、图像分割
2.1 json
"version": "4.6.0","flags": {},"shapes": [{"label": "break","points": [[988.936170212766,297.0],[1053.8297872340424,368.27659574468083]],"group_id": null,"shape_type": "rectangle","flags": {}}],"imagePath": "20220617_blue_h_24.jpg",points是指矩形框的两个对角点
2.1 TXT

class x y w h ptx pty
其中:
- class 表示目标类别序号(从0开始)。
- x、y 是中心点的坐标,经过归一化处理,即相对于图片宽度和高度的比例。
- w、h 是框的宽度和高度,经过归一化处理,即相对于图片宽度和高度的比例。
- ptx、pty 是关键点的坐标,经过归一化处理,即相对于图片宽度和高度的比例。
归一化怎么实现??中心点x坐标/图片宽,y坐标/图片高,矩形框的宽/图片宽,高/图片高,关键点横/除以图片宽,关键点纵坐标/图片高
2.1.1 json转txt
代码:
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import json
import os
import cv2img_folder_path = 'datasets/500' # 图片存放文件夹
folder_path = 'datasets/picbiaozhu' # 标注数据的文件地址
txt_folder_path = 'datasets/txtresults' # 转换后的txt标签文件存放的文件夹# 保存为相对坐标形式 :label x_center y_center w h
def relative_coordinate_txt(img_name, json_d, img_path):src_img = cv2.imread(img_path)# h, w = src_img.shape[:2]h, w, c = src_img.shapetxt_name = img_name.split(".")[0] + ".txt"txt_path = os.path.join(txt_folder_path, txt_name)print(txt_path)with open(txt_path, 'w') as f:for item in json_d["shapes"]:if item['shape_type'] == 'rectangle' and item['label'] == 'nameplate':point = item['points']x_center = (point[0][0] + point[1][0]) / 2y_center = (point[0][1] + point[1][1]) / 2width = point[1][0] - point[0][0]height = point[1][1] - point[0][1]# print(x_center)f.write(" {} ".format(0))f.write(" {} ".format(x_center / w))f.write(" {} ".format(y_center / h))f.write(" {} ".format(width / w))f.write(" {} ".format(height / h))continuekeypoint = item['points']x = keypoint[0][0]y = keypoint[0][1]f.write(" {} ".format(x / w))f.write(" {} ".format(y / h))f.write(" \n")print('finish!')for jsonfile in os.listdir(folder_path):# os.listdir用来返回指定文件夹包含的文件或文件夹的名字的列表temp_path = os.path.join(folder_path, jsonfile)print("json_path:\t", temp_path)jsonfile_path = temp_pathwith open(jsonfile_path, "r", encoding='utf-8') as fff:json_d = json.load(fff, strict=False)img_name = json_d['imagePath'].split("\\")[-1].split(".")[0] + ".jpg"img_path = os.path.join(img_folder_path, img_name)print("img_path:\t", img_path)retname = img_name.replace(".jpg", ".txt")retpath = os.path.join(txt_folder_path, retname)if os.path.exists(retpath):continueelse:relative_coordinate_txt(img_name, json_d, img_path)
三、行为分析
3.1 TXT
如果是行为检测,这里和目标检测的txt参数情况是一样的。
3.2 JSON
OpenPose行为识别的数据集格式是一个json文件,其中包含了人体关键点的信息。json文件中的参数代表的含义如下:
- people:人体关键点的数量。
- poses:每个人体关键点的名称和位置。
- keypoints:每个人体关键点的名称、类型和坐标。
- images:图像的路径。