为什么会有线程?
————————>>>> 进程实现多任务的缺点:
- 进程间切换的计算机资源开销很大,切换效率非常低
- 进程间数据共享的开销也很大
线程和进程的关系
- 线程是进程的一个执行单元,是进程内的调度实体。比进程更小的独立运行的基本单位。线程也被称为轻量级进程
- 同一进程的线程共享本进程的地址空间,而进程之间则是独立的地址空间。
- 进程退出,进程中所有线程全部退出;
- 一个进程崩溃后,不会对其他进程产生影响,但是一个线程崩溃整个进程都死掉。所以多进程要比多线程健壮。
- 线程不可能完全替代进程;
- 线程拥有独立的属性;
线程是任务调度和执行的基本单位
线程的特点
线程不安全,不稳定,不健壮————(一个线程的释放可能会影响其他线程)
线程切换的开销很低————(实质就是函数的切换)
线程通信机制简单(但不安全)————(访问全局变量)
线程操作
线程函数(不是OS提供,不是系统调用API,而是线程库libpthread.a/.so,库函数则可以跨平台)
线程库和函数手册的安装
sudo apt-get install glibc-doc :安装线程库
sudo apt-get install manpages-posix-dev:安装线程库的函数手册
线程创建
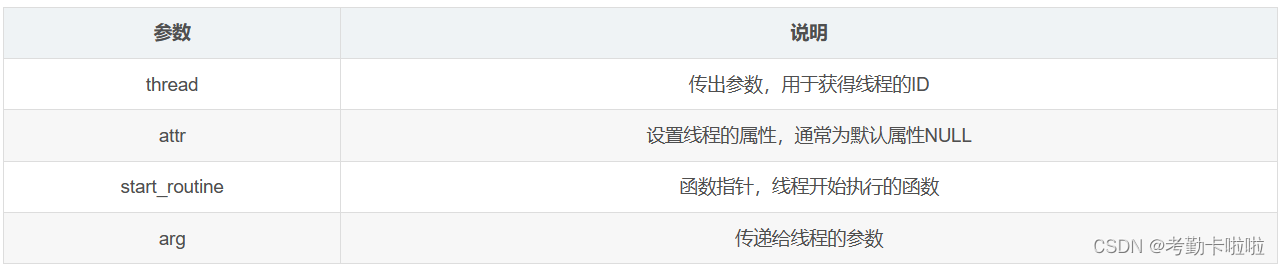
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
执行顺序:先创建的先执行
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
void *read_mouse(void *ptr)
{int mouse;while (1){read(*((int *)ptr), &mouse, sizeof(int));printf("mouse = %d\n", mouse);}
}
void *read_keyboard(void *ptr)
{char buffer[1024] = "0";while (1){read(0, buffer, sizeof(buffer));printf("%s\n", buffer);memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));}
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t id1;pthread_t id2;int fd = open("/dev/input/mouse0", O_RDONLY);if (fd < 0){perror("fd mouse is error");exit(-1);}if (pthread_create(&id1, NULL, read_mouse, (void *)(&fd)) < 0) // 传递给线程的参数{perror("pthread_creat 1 error");exit(-1);}if (pthread_create(&id2, NULL, read_keyboard, NULL) < 0){perror("pthread_creat 2 error");exit(-1);}pause(); // 若无pause,则主进程执行完,所有的线程会结束;所以需要return 0;
}封装:
void *read_mouse(void *ptr)
{int mouse;while (1){int fd = open("/dev/input/mouse0", O_RDONLY);if (fd < 0){perror("fd mouse is error");exit(-1);}read(fd, &mouse, sizeof(int));printf("mouse = %d\n", mouse);}
}
void *read_keyboard(void *ptr)
{char buffer[1024] = "0";while (1){read(0, buffer, sizeof(buffer));printf("%s\n", buffer);memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));}
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t id[2];void *(*ptr[2])(void *);ptr[0] = read_keyboard;ptr[1] = read_mouse;for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){pthread_create(id + i, NULL, *(ptr+i), NULL);}pause(); // 若无pause,则主进程执行完,所有的线程会结束;所以需要return 0;
}线程可以访问全局数据区
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>char buffer[1024];void *write_data(void *)
{while (1){scanf("%s", buffer);}
}
void *read_data(void *)
{while (1){if (strlen(buffer) != 0){printf("%s\n", buffer);memset(buffer,0,sizeof(buffer));}sleep(3);}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t id[2];void *(*func[2])(void *);func[0] = write_data;func[1] = read_data;for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){pthread_create(id + i, NULL, *(func + i), NULL);}pause();return 0;
}线程退出
1.被动退出:
主线程关闭子线程:
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
1)功能
当次线程是死循环时,可以调动这个函数主动取消该线程
2)返回值
成功返回0,失败返回非零错误号。
2〉参数
thread:要取消线程的ID号
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t id[2];void *(*func[2])(void *);func[0] = write_data;func[1] = read_data;for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){pthread_create(id + i, NULL, *(func + i), NULL);}sleep(5);pthread_cancel(id[1]);//五秒钟后,次线程被主线程取消了,则不再能读取到buffer内数据pause();return 0;
}2.主动退出
2.1 void pthread_exit(void *retval);函数用于退出当前线程,并可选择返回一个指定的值(用的多)
2.2 return ; 也是直接退出(用得少)
void *read_data(void *)
{while (1){if (strlen(buffer) != 0){if (strcmp(buffer,"exit")==0)//如果读到了exit就退出{pthread_exit(NULL); // 读取到exit,就会主动的退出线程}printf("%s\n", buffer);memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));}}
}void *read_data(void *)
{while (1){if (strlen(buffer) != 0){if (strcmp(buffer,"exit")==0)//如果读到了exit就退出{return NULL; // 读取到exit,就会主动的退出线程}printf("%s\n", buffer);memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));}}
}3.注册线程退出处理函数
pthread_cleanup_push
pthread_cleanup_pop
必须成对出现,且不能在{ }的语句中间,(因为他们是宏定义,各包含一个括号

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>char buffer[1024];
void *read_exit_handler(void *arg)
{printf("%s\n", (char *)arg);
}
void *write_data(void *)
{while (1){scanf("%s", buffer);}
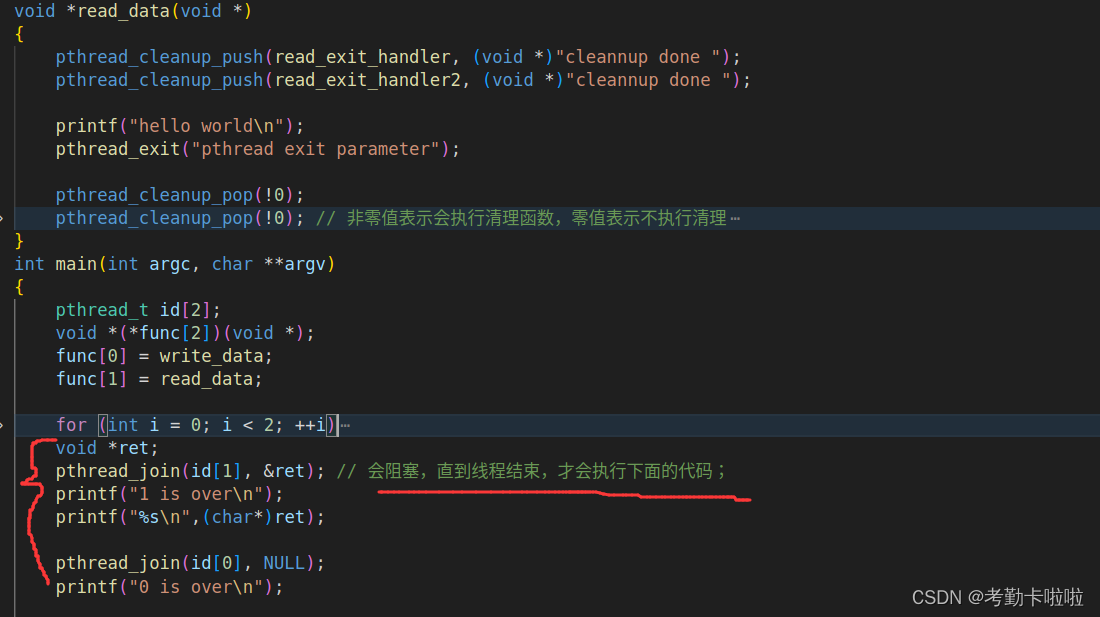
}void *read_data(void *)
{pthread_cleanup_push(read_exit_handler, (void *)"cleannup done ");while (1){if (strlen(buffer) != 0){if (strcmp(buffer, "exit") == 0) // 如果读到了exit就退出{pthread_exit(NULL); // 可以调用退出清理函数(出栈)// return NULL; // 不可以调用退出清理函数(出栈)}printf("%s\n", buffer);memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));}sleep(1); // 无限的循环,会导致无法调用pthread_cancel(id[1]);来调用退出处理函数!!!!!所以给每次循环睡眠一秒}pthread_cleanup_pop(0); // 非零值表示会执行清理函数,零值表示不执行清理
//------------------------即使pthread_cleanup_pop(0),但如果还是遇到了 pthread_exit(NULL)和pthread_cancel 还是会执行清理函数-------------------------------------
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t id[2];void *(*func[2])(void *);func[0] = write_data;func[1] = read_data;for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){pthread_create(id + i, NULL, *(func + i), NULL);}sleep(3);pthread_cancel(id[1]); // 五秒钟后,次线程被主线程取消了,则不再能读取到buffer内数据pause();return 0;
}多个线程的退出清理函数执行顺序:
char buffer[1024];
void *read_exit_handler(void *arg)
{printf("%s\n", (char *)arg);
}
void *read_exit_handler2(void *arg)
{printf("%s 2\n", (char *)arg);
}
void *write_data(void *)
{while (1){scanf("%s", buffer);}
}void *read_data(void *)
{pthread_cleanup_push(read_exit_handler, (void *)"cleannup done ");pthread_cleanup_push(read_exit_handler2, (void *)"cleannup done ");printf("hello world\n");pthread_cleanup_pop(!0);pthread_cleanup_pop(!0); // 非零值表示会执行清理函数,零值表示不执行清理}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t id[2];void *(*func[2])(void *);func[0] = write_data;func[1] = read_data;for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){pthread_create(id + i, NULL, *(func + i), NULL);}pause();return 0;
}线程等待
1.等待的目的:
1.1保证线程的退出顺序:保证一个线程退出并且回收资源后允许下一个线程退出
1.2回收线程退出时的资源情况:保证当前线程退出后,创建的新线程不会复用刚才退出线程的地址空间
1.3获得新线程退出时的结果是否正确的退出返回值,这个有点类似回收僵尸进程的wait,保证不会发生内存泄露等问题
2.pthread_join(id[1], &ret); // 会阻塞,直到线程结束,才会执行下面的代码;)
线程状态
1.线程资源为什么不采用进程退出后一起回收?
2.Linux下把线程分为可结合态和分离态
可结合态:(默认的状态) 这种状态下的线程是能被其它进程回收其资源或杀死,资源只能通过pthread_join来回收(不能自己释放,进程主动回收)
分离态:这种状态下的线程是不能够被其它进程回收其资源或杀死;存储资源在它终止时由系统自动释放
3.如何避免多线程退出导致的内存泄漏
3.1 可结合线程都显示调用pthread_join回收
3.2 将其变成分离态的线程:
【
3.2.1:int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread); (不阻塞)
功能: 如果次线程的资源不希望别人调用pthread_join函数来回收的话,而是希望自己在结束时自动回收资源的话,就可以调用这个函教
这个函数的功能就是分离次线程,让次线程在结束时自动回收资源
返回值: 成功返回0,失败返回错误号
参数: thread:你要分离的那个次线程的TID
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t id[2];void *(*func[2])(void *);func[0] = write_data;func[1] = read_data;for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){if (pthread_create(id + i, NULL, *(func + i), NULL) < 0){perror("pthread creat error");exit(-1);}pthread_detach(id[i]); // 设置为分离态, 资助回收资源,减少内存泄漏//此时也不需要pthread_join来回收资源了
}pause();return 0;
}3.2.2 修改属性
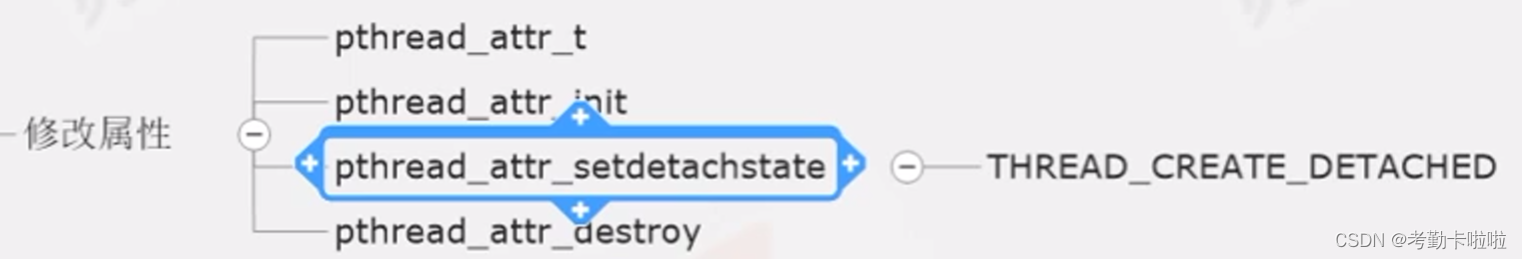
】
线程实现,向毅个文件里分别写如“hhhhhwwwww”和“helloworld”
线程同步(难点)
1.进程vs线程
进程:进程空间天然是独立的,因此进程间资源的保护是天然的(现成的),需要重点关心的进程间的通信
线程:多线程天然的共享进程空间,因此线程数据共享是天然的(现成的),需要重点关心的是资源的保护
2.线程的资源保护机制
2.1互斥锁
定义一个互斥锁(变量)
初始化互斥锁:预设互斥锁的初始值
【
1.直接赋值
2.初始化互斥锁的函数:int pthread_mutex_init ( pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,const pthread mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
功能:初始化定义的互斥锁
什么是初始化:就是设置互斥锁所需要的值。
返回值:总是返回0,所以这个函数不需要进行出错处理。
参数:~~~
【在C语言中,初始化静态全局变量时,只能使用常量表达式。PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER`是一个宏,它并不是常量表达式,因此不能直接用于初始化静态全局变量。
如果你想在主函数内初始化互斥锁变量`mutex1`,可以使用`pthread_mutex_init`函数来实现。你可以将以下代码添加到主函数的开头,用于初始化互斥锁:
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1, NULL);
这样,你就可以在主函数中正确地初始化互斥锁,并在其他线程中使用它。
对于你的代码,你可以这样修改:
pthread_mutex_t mutex1 = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
或者使用`pthread_mutex_init`函数进行初始化:
pthread_mutex_t mutex1;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1, NULL);
这样修改后,`mutex1`将在主函数内正确地进行初始化。】
】
加锁、解锁
【pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);————pthread_mutex_trylock( &mutex)(非阻塞加锁)
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);】
进程退出时销毁互斥锁
void handler(int sig)
{pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex1);
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>pthread_mutex_t mutex1= PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//定义一个互斥锁变量
//*****不能在主函数内调用这句话来初始化静态全局变量
int fd;
void handler(int sig)
{pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex1);
}
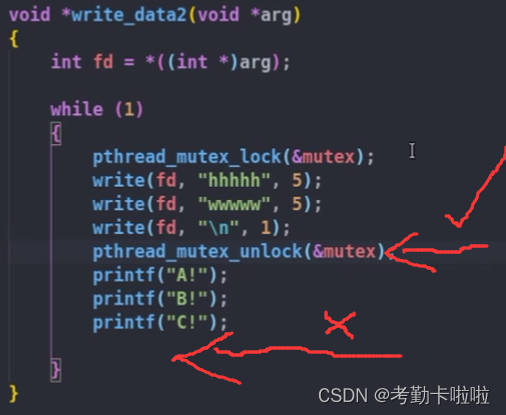
void *write1(void *arg)
{while (1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);write(fd, "hhhhh", 5);write(fd, "wwwww", 5);write(fd, "\n", 1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);}
}
void *write2(void *arg)
{while (1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);write(fd, "hello", 5);write(fd, "world", 5);write(fd, "\n", 1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{// pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1, NULL);pthread_t id[2];void *(*pfunc[2])(void *);pfunc[0] = write1;pfunc[1] = write2;fd = open("a.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0655);if (fd < 0){perror("fd error");exit(-1);}for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){if (pthread_create(&id[i], NULL, pfunc[i], NULL) < 0){perror("pthread error");exit(-1);}pthread_detach(id[i]);}pause();signal(SIGINT, handler);return 0;
}/-------------------------- -----------------------------/
void *write1(void *arg)
{while (1){if (pthread_mutex_trylock(&mutex1) == 0)//非阻塞的上锁,如果已经上锁,则返回0;{write(fd, "hhhhh", 5);write(fd, "wwwww", 5);write(fd, "\n", 1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);}else{printf("trylock is busy\n");}}
}注意事项:
1.凡是访问进程的全局变量,都要加锁;
2.涉及到共享资源的访问,必须上锁
【对于一个功能实现中,并不涉及访问共享资源的代码段,尽量不要放在上锁和解锁中间】
2.2线程信号量
2.2.1.定义信号量集合

2.2.2.初始化集合中的每个信号量


2.2.3.p、v操作


2.2.4.进程结束时,删除线程信号量集

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <semaphore.h>sem_t sem1; // 1.定义信号量 (数组)
int fd;
pthread_t id[2];
void handler(int sig) // 4.注册的信号处理函数:用以删除信号量
{sem_destroy(&sem1);
}
void *write1(void *arg)
{while (1){sem_wait(&sem1); // 3.p操作write(fd, "hhhhh", 5);write(fd, "wwwww", 5);write(fd, "\n", 1);sem_post(&sem1); // 3.v操作}
}
void *write2(void *arg)
{while (1){sem_wait(&sem1);write(fd, "hello", 5);write(fd, "world", 5);write(fd, "\n", 1);sem_post(&sem1);}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{sem_init(&sem1, 0, 1); // 2.初始化信号量void *(*pfunc[2])(void *);pfunc[0] = write1;pfunc[1] = write2;fd = open("c.txt", O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0655);if (fd < 0){perror("fd error");exit(-1);}for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){if (pthread_create(&id[i], NULL, pfunc[i], NULL) < 0){perror("pthread error");exit(-1);}pthread_detach(id[i]);}pause();signal(SIGINT, handler);return 0;
}实现google面试题
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>int fd[4]; // 四个文件描述符
sem_t sem_abcd[4]; // 含有四个信号量的数组
pthread_t id[4]; // 四个线程id的数组
void *write1(void *arg)
{int flag = 0;while (1){sem_wait(&sem_abcd[0]);for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){if (flag != 0 || i <= 0){write(fd[i], "A", 1);}}flag = 1;sleep(1);sem_post(&sem_abcd[1]);}
}
void *write2(void *arg)
{int flag = 0;while (1){sem_wait(&sem_abcd[1]);for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){if (flag != 0 || i <= 1){write(fd[i], "B", 1);}}flag = 1;sleep(1);sem_post(&sem_abcd[2]);}
}
void *write3(void *arg)
{int flag = 0;while (1){sem_wait(&sem_abcd[2]);for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){if (flag != 0 || i <= 2){write(fd[i], "C", 1);}}flag = 1;sleep(1);sem_post(&sem_abcd[3]);}
}
void *write4(void *arg)
{int flag = 0;while (1){sem_wait(&sem_abcd[3]);for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){if (flag != 0 || i <= 3){write(fd[i], "D", 1);}}flag = 1;sleep(1);sem_post(&sem_abcd[0]);}
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{char temp[1] = "A";for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){temp[0] = temp[0] + i;if ((fd[i] = open(temp, O_CREAT | O_RDWR | O_TRUNC, 0655)) < 0) // 打开四个文件{perror("open error");exit(-1);}temp[0] = 'A';}void *(*pfunc[4])(void *) = {// 函数指针数组write1,write2,write3,write4,};for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){if (i == 0){sem_init(&sem_abcd[i], 0, 1); // 先初始化第一个线程的信号量————置为1}else{sem_init(&sem_abcd[i], 0, 0); // 其他线程的信号量全关闭————置为0}if (pthread_create(&id[i], NULL, pfunc[i], NULL) < 0) // 线程创建{perror("pthread creat error");exit(-1);}pthread_detach(id[i]); // 分离态}pause();return 0;
}功能封装:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>int fd[4]; // 四个文件描述符
sem_t sem_abcd[4]; // 含有四个信号量的数组
pthread_t id[4]; // 四个线程id的数组
int flag = 0;void *write_demo(void *arg)
{char c[1] = "A";int num = *(int *)arg;c[0] = 'A' + num;while (1){sem_wait(&sem_abcd[num]);for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){if (flag >= 4 || i <= num){write(fd[i], c, 1);}}flag++;sleep(1);sem_post(&sem_abcd[(num + 1) % 4]);}
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{char temp[1] = "A";int demo[4] = {0, 1, 2, 3};for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){temp[0] = temp[0] + i;if ((fd[i] = open(temp, O_CREAT | O_RDWR | O_TRUNC, 0655)) < 0) // 打开四个文件{perror("open error");exit(-1);}temp[0] = 'A';}for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){if (i == 0){sem_init(&sem_abcd[i], 0, 1); // 先初始化第一个线程的信号量————置为1}else{sem_init(&sem_abcd[i], 0, 0); // 其他线程的信号量全关闭————置为0}if (pthread_create(&id[i], NULL, write_demo, (void *)(demo + i)) < 0) // 线程创建{perror("pthread creat error");exit(-1);}pthread_detach(id[i]); // 分离态}pause();return 0;
}2.3条件变量
作用:多线程配合工作时,当线程检测到某条件不满足时就休眠,直到别的线程将条件准备好然后通过条件变量将其唤醒。
【需要和互斥锁配合】
1.定义条件变量:pthread_cond_t;
2.初始化:
1.pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,const thread_condattr_t * restrict attr)
2.赋值初始化:pthread_cond_t cond=PTHREAD_COND_INITLIALIZER
3.等待条件的函数
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); // 不满足条件则阻塞等待,并释放互斥锁
4.满足条件,通知阻塞的线程
pthread_cond_signal(&cond); // 满足条件,则通知因cond这一条件变量而阻塞等待的线程,
或者: pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);唤醒所有睡眠的进程
5.销毁条件变量和互斥锁
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>pthread_t id[2];
int val = 0;
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;pthread_cond_t cond; // 1.定义条件变量
// 条件变量的初始化可以 1.在主函数内调用pthread_cond——init初始化; 2.也可以用PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER赋值;void handler_exit(int sig)
{pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&cond); // 5.注册退出处理函数,删除条件变量printf(" pthread_cond is cancel\n");
}
void *fun1(void *arg)
{while (1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);val++;if (val == 2){ // 通知线程2打印pthread_cond_signal(&cond); // 4.满足条件,则通知因cond这一条件变量而阻塞等待的线程,// pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);唤醒所有睡眠的进程}pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);sleep(1);}
}
void *fun2(void *arg)
{while (1){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);if (val != 2){pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); // 3.不满足条件则阻塞等待,并释放互斥锁}printf("val == 2\n");val = 0;pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{signal(SIGINT, handler_exit);pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL); // 2.初始化条件变量void *(*pfun[2])(void *arg) = {fun1, fun2};for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i){if (pthread_create(&id[i], NULL, pfun[i], NULL) < 0){perror("pthread_creat error");exit(-1);}pthread_detach(id[i]);}pause();return 0;
}