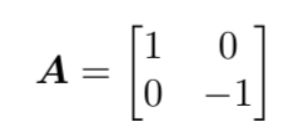SkipList,跳表,是一种有序的数据结构,可以作为平衡树的一种替代。本质上是一种利用稀疏索引加速链表查询的一组数据+索引的结构。
平衡树一般指BST和 红黑树等数据结构,这种数据结构解决了 排序树的不平衡问题,但带来了旋转,变色等问题,在并发场景下锁的粒度很大,会一定程度上影响性能,并且实现比较复杂。相对而言,SkipList避免了这些问题。
实现
跳表一般基于有序链表实现。首先是链表的排序问题,对于链表的来说,排序的问题其实等价于怎么找到新增节点的在有序链表中插入位置。
对于数组而言,只需要利用二分法查找到对应的位置,然后插入,并移动之后的元素,主要的开销在于拓展内存以及移动元素。
链表没法这么处理。链表的优势在于插入后无需移动后续元素,但无法跳跃查询,主要开销在于定位插入位置。
结合两者实际上就是跳表的基本思想:底层数据用有序链表维护,方便数据插入;在底层数据节点之上构建多层不同的稀疏索引(比如从上往下不断变密集),加速节点的查询,快速定位。

比如底层索引6节点,第一层索引在中点处[ (0 + 6) / 2]添加索引,第一层索引将底层分成两个分区,第二层索引再在两个分区的中点添加索引,以此类推。
索引节点+数据节点就是跳表的核心,但这又有了另一个问题:怎么样便利的维护索引节点?
显然,将每层的分区的中点作为索引节点是不合适的,因为节点的增减是一种常见需求,每次数据节点的增减都会导致索引节点的变化,带来不少额外的开销。我们需要一种与数据节点数量无关的、确定索引节点位置的方法。
基本的思路就是使用随机化。在每次增加节点时确定是否需要此节点上建立索引节点。
比如对于一个最高XX层的跳表,设底层NN个数据节点。每次添加节点时,以1/(2n)1/(2^n)判断是否要在前nn层添加索引节点(只有本层有索引节点才能往上层添加索引节点)。
对于第KK层,将有N/2kN / 2^k个节点,与取分区中点作为索引节点等价。
数据结构
type SkipListNode struct {data *codec.EntrynextPtrs []*SkipListNode
}type SkipList struct {header, tail *SkipListNodelevel intsize intrwmtx *sync.RWMutexmaxSize int
}
操作
值得关注的只有查询和插入节点两个操作。
查询
最核心的步骤是由上至下,利用每层的稀疏索引二分查找定位到需要的节点,或者位置。
// findPreNode find the node before node.key
func (sl *SkipList) findPreNode(key []byte) (*SkipListNode, bool) {// from top to bottomh := sl.headerfor i := sl.level - 1; i >= 0; i-- {for h.nextPtrs[i] != nil && bytes.Compare(h.nextPtrs[i].data.Key, key) != 1 {if bytes.Equal(h.nextPtrs[i].data.Key, key) {return h, true}h = h.nextPtrs[i]}}return nil, false
}
插入
首先要定位到插入的位置,插入,再随机化创建索引。
func (sl *SkipList) randomLevel() int {ans := 1rand.Seed(time.Now().Unix())for rand.Intn(2) == 0 && ans <= defaultMaxLevel {ans++}return ans
}func (sl *SkipList) Insert(data *codec.Entry) *SkipListNode {sl.rwmtx.Lock()defer sl.rwmtx.Unlock()h := sl.headerupdateNode := make([]*SkipListNode, defaultMaxLevel) // stores the node before newNode// search form the top levelfor i := sl.level - 1; i >= 0; i-- {// loop: 1. current nextPtrs is not empty && data is small than inserted one, curData < insertedDatafor h.nextPtrs[i] != nil && h.nextPtrs[i].data.Less(data) {h = h.nextPtrs[i]}updateNode[i] = h}// choose level to insertlvl := sl.randomLevel()if lvl > sl.level {// Insert into higher level, we need to create header -> tailfor i := sl.level; i < lvl; i++ {updateNode[i] = sl.header}sl.level = lvl}// insert after updatedNoten := NewSkipListNode(lvl, data)for i := 0; i < lvl; i++ {n.nextPtrs[i] = updateNode[i].nextPtrs[i]updateNode[i].nextPtrs[i] = n}sl.size++return n
}