目录
中缀表达式转后缀表达式
图解
代码实现过程:
完整代码:
利用后缀表达式求值:
完整代码:
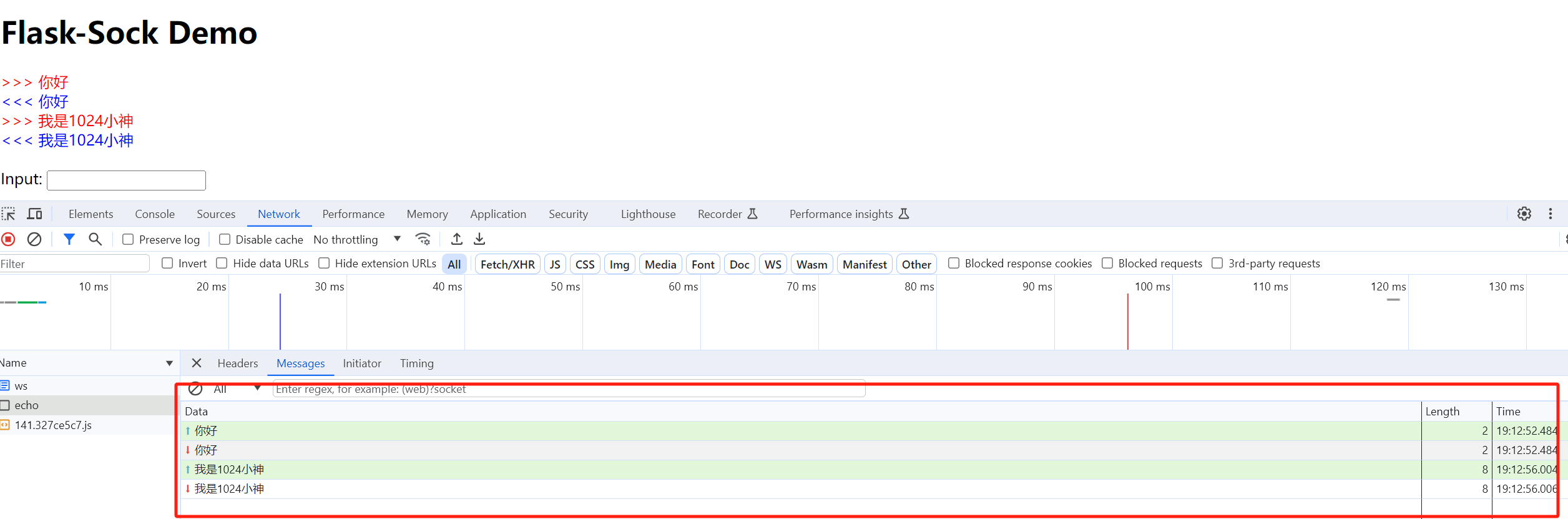
首先我们得先了解逆波兰表达式。
中缀表达式转后缀表达式
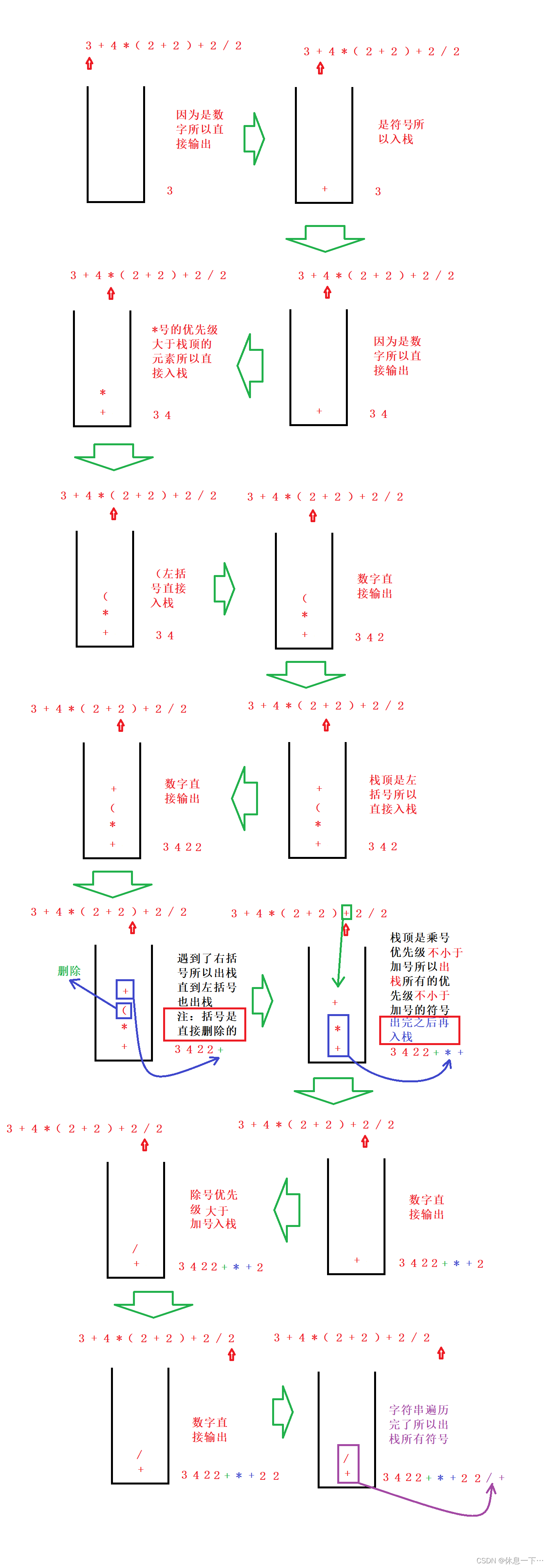
所谓的中缀表达式其实就是我们平时写的例如:;而它的后缀表达式(也成为逆波兰表达式)为
;
后缀表达式:指的是不包含括号,运算符放在两个运算对象的后面,所有的计算按运算符出现的顺序,严格从左向右进行(不再考虑运算符的优先规则)。
我们如果要利用程序来进行四则混合运算最重要的就是将输入的中缀表达式转后缀表达式。
首先我们假设运算符中只有 加 减 乘 除 和 括号不然的话程序太复杂了(其实是我不会写【哭】)。
图解
代码实现过程:
首先我们先写一个方法 返回值是动态字符串数组(为了后面好计算),形参为字符串类型(因为输入值不只有数字还有运算符)。这里会用到栈所以也定义一个栈。
public ArrayList<String> midChangeEng(String str) {//这里用动态数组就不用担心不够用ArrayList<String> ret = new ArrayList<String>();Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();}此时再创建一个新方法用来判断传入字符是不是运算符
public boolean isOperator(char s) {if (s == '+' || s == '-' || s == '*' || s == '/' || s == '(' || s == ')') {return true;}return false;}我们再利用运算符再ASCII码中的位置,创建一个数组用来表示它们的优先级


int[] able = {1,0,0,0,0,1};//分别代表 * + (null) - (null) / 的优先级 利用循环遍历字符串
//遍历字符串for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {char a = str.charAt(i);String tmp = "";//用来暂时存储出栈的数字if (isOperator(a)) {//是操作数}else{//如果是数字就放到ret中}}return ret;对操作数的操作 ,可是此段代码中重复代码过多,所以可以将其封装成一个方法。
if (isOperator(a)) {//是操作数switch (a) {case '+'://判断如果优先级不大于栈顶的元素那么就先出栈在入栈if(!stack.isEmpty()) {//出栈while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() != '(' && able[(int)stack.peek() - 42] >= able[(int)a-42]) {String b = "";b += stack.pop();ret.add(b);}}stack.push(a);break;case '-':if(!stack.isEmpty()) {//出栈while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() != '(' && able[(int)stack.peek() - 42] >= able[(int)a-42]) {String b = "";b += stack.pop();ret.add(b);}}stack.push(a);break;case '*':if(!stack.isEmpty()) {//出栈while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() != '(' && able[(int)stack.peek() - 42] >= able[(int)a-42]) {String b = "";b += stack.pop();ret.add(b);}}stack.push(a);break;case '/':if(!stack.isEmpty()) {//出栈while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() != '(' && able[(int)stack.peek() - 42] >= able[(int)a-42]) {String b = "";b += stack.pop();ret.add(b);}}stack.push(a);break;case '(':stack.push(a);break;case ')':while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() != '(') {String b = "";b += stack.pop();ret.add(b);}stack.pop();//删除‘(’break;}}如果是数字就进行以下操作
else{//如果是数字就放到ret中String tmp = "";while(i < str.length() && !isOperator(str.charAt(i))) {//数字有可能是多位的tmp += str.charAt(i);i++;}i--;ret.add(tmp);}再出函数之前要先将栈里面的全部导出来
//将栈里面剩余的全部出栈while(!stack.isEmpty()) {String b = "";b += stack.pop();ret.add(b);}return ret;完整代码:
public static ArrayList<String> midChangeEng(String str) {//这里用动态数组就不用担心不够用ArrayList<String> ret = new ArrayList<String>();Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();int[] able = {1,0,0,0,0,1};//分别代表 * + (null) - (null) / 的优先级//遍历字符串for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {char a = str.charAt(i);if (isOperator(a)) {//是操作数switch (a) {case '+'://判断如果优先级不大于栈顶的元素那么就先出栈在入栈abcd(ret, stack, able, a);break;case '-':abcd(ret, stack, able, a);break;case '*':abcd(ret, stack, able, a);break;case '/':abcd(ret, stack, able, a);break;case '(':stack.push(a);break;case ')':while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() != '(') {String b = "";b += stack.pop();ret.add(b);}stack.pop();//删除‘(’break;}}else{//如果是数字就放到ret中String tmp = "";while(i < str.length() && !isOperator(str.charAt(i))) {//数字有可能是多位的tmp += str.charAt(i);i++;}i--;ret.add(tmp);}}//将栈里面剩余的全部出栈while(!stack.isEmpty()) {String b = "";b += stack.pop();ret.add(b);}return ret;}

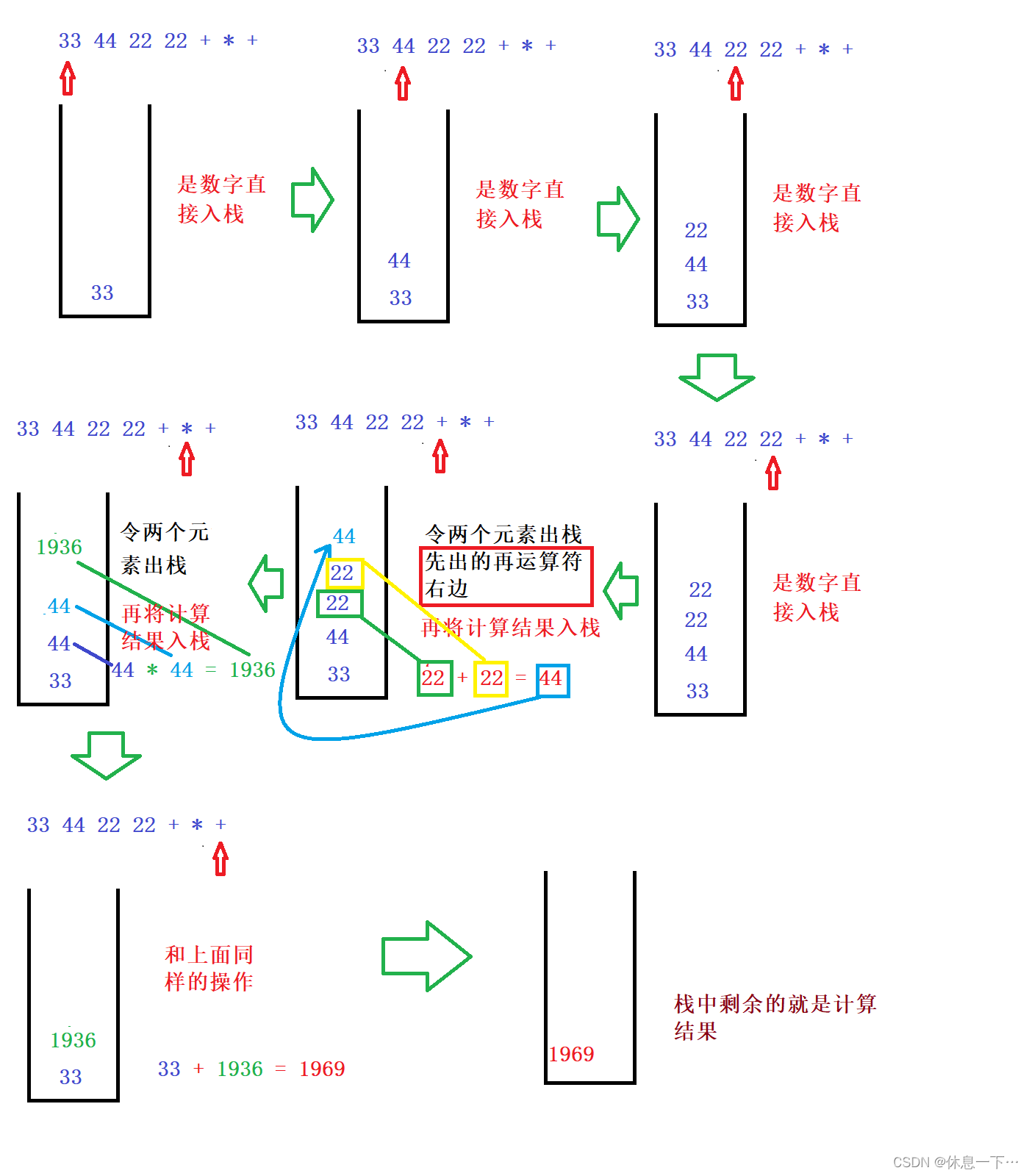
利用后缀表达式求值:
这部分比较简单所以就直接展示了
完整代码:
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++) {if (isOperator(tokens[i])) {int num2 = stack.pop();int num1 = stack.pop();switch(tokens[i].charAt(0)) {case '+':stack.push(num1 + num2);break;case '-':stack.push(num1 - num2);break;case '*':stack.push(num1 * num2);break;case '/':stack.push(num1 / num2);break;}}else {stack.push(Integer.parseInt(tokens[i]));}}return stack.pop();}public boolean isOperator(String str) {if (str.length() != 1) {return false;}if (str.charAt(0) == '+' || str.charAt(0) == '-' || str.charAt(0) == '*' || str.charAt(0) == '/') {return true;}return false;}