背景
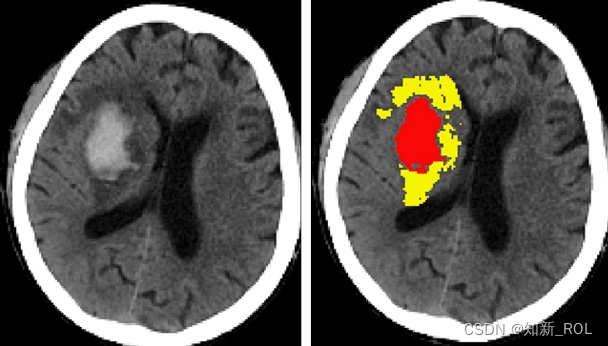
由于需要经常分析浮点型的图像,而浮点型图像经常不能突出显示感兴趣的区域的,如下图所示:

而使用imagej软件,选中一个较小的感兴趣区域,调出其直方图,然后点击设置就可以增强整个图像对比度,突出显示感兴趣的区域,如下图所示。

我一直很好奇,他这个的实现原理什么。
实现
通过观察imagej的直方图可知,在那个局部区域内有明显的两个波峰,分别对应图像深度的下限和上限,我们只要找到这两个波峰,然后只保留在此波峰限定的范围内的值即可,小于波峰下限的值赋值一个更小的值,大于波峰上限的值赋值一个更大的值,最后基于OpenCV把深度图转换为灰度图即可。
找到直方图的第二个峰值,第二个峰值不一定是直方图的第二大值,因为它很有可能出现在第一个峰值的附近。可以通过以下公式进行计算
s e c o n d P e a k = a r g k m a x ( k − f i r s t P e a k ) 2 ∗ h i s t o g r a m I ( k ) , 0 ≤ k ≤ 255 secondPeak = arg_k max { ( k − firstPeak )^2 ∗ histogram I ( k ) } , 0 ≤ k ≤ 255 secondPeak=argkmax(k−firstPeak)2∗histogramI(k),0≤k≤255
cv::Mat depth2Gray(cv::Mat depth)
{cv::Mat d = depth.clone();const int width = d.cols;const int height = d.rows;const size_t allNum = size_t(width) * size_t(height);// 需要显示的深度上下限const float minValue = -5.f;const float maxValue = 2.f;float* data = (float*)d.data;// 直方图统计int channels[] = { 0 };cv::Mat_<float> hist;const int dims = 1;const float step = 1.0;const float low = -4.f;const float high = 1.0;const int hBins = std::floor((high - low) / step) + 1;int histSize[] = { hBins };//每一个维度取值范围float pranges[] = { low, high };//取值区间const float* ranges[] = { pranges };cv::calcHist(&d, 1, channels, cv::Mat(), hist, dims,histSize, ranges, true, false);// 取第一个最大波峰double minvv, maxvv;int minIndx, maxIndx;cv::minMaxIdx(hist, &minvv, &maxvv, &minIndx, &maxIndx);// 取第二大波峰const int num = hist.rows * hist.cols;std::vector<float> peaks(num);for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i){peaks[i] = std::abs(i - maxIndx) * ((float*)hist.data)[i];}int secondMaxIndx;cv::minMaxIdx(peaks, &minvv, &maxvv, &minIndx, &secondMaxIndx);float lowv, highv;float edge_step = (high - low) / hBins;if (0 == maxIndx){lowv = low;highv = low + edge_step;}else if (hBins - 1 == maxIndx){lowv = high - edge_step;highv = high;}else{lowv = low + maxIndx * edge_step;highv = lowv + edge_step;}float lowv1, highv1;if (0 == secondMaxIndx){lowv1 = low;highv1 = low + edge_step;}else if (hBins - 1 == secondMaxIndx){lowv1 = high - edge_step;highv1 = high;}else{lowv1 = low + maxIndx * edge_step;highv1 = lowv + edge_step;}// 两个波峰对应的值float lowPeak, highPeak;if (lowv < lowv1) { lowPeak= lowv; }else { lowPeak= lowv1; }if (highv1 > highv) { highPeak= highv1; }else { highPeak= highv; }for (size_t i = 0; i < allNum; ++i){float& z = ((float*)data)[i];if (z < v1) { z = minValue; }if (z > v2) { z = maxValue; }}cv::Mat gray;cv::normalize(d, gray, 0, 255, cv::NORM_MINMAX, CV_8UC1);return gray;}
实现2
写完第一版代码才发现,搞那么复杂干嘛,又是直方图统计,又是找波峰的。深度图转灰度图突出显示感兴趣的特征,本质上不就是只把感兴趣的特征对应的深度信息保留下来,而其他干扰信息全部赋值无效数据吗。
第二版就补贴代码了。