函数式接口
java.util.function :
Consumer :消费型函数接口 void accept(T t)
Function :函数型接口 R apply(T t)
Predicate :判断型接口 boolean test(T t)
Supplier :供给型接口 T get()
Consumer - 消费型函数接口
该接口代表了一个接受一个参数并且不返回结果的操作。
方法签名:void accept(T t)
Function<T, R> - 函数型接口
T代表参数的类型 R是返回值的类型
该接口代表了一个接受一个参数并返回结果的操作。
方法签名:R apply(T t)
Predicate - 判断型接口
该接口代表了一个接受一个参数并返回布尔值的判断操作。
方法签名:boolean test(T t)
Supplier - 供给型接口
该接口代表了一个不接受参数但返回结果的操作,用于提供数据
方法签名:T get()
代码示例:
/**** @author sunyuan* @date 2023/9/25 21:06*/
@Slf4j
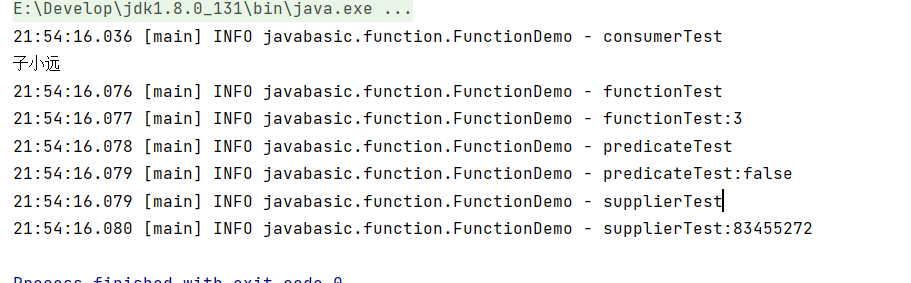
public class FunctionDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {consumerTest();functionTest();predicateTest();supplierTest();}/*** Consumer<T> - 消费型函数接口* 该接口代表了一个接受一个参数并且不返回结果的操作。* 方法签名:void accept(T t)*/public static void consumerTest() {log.info("consumerTest");Consumer<String> consumer = str -> System.out.println(str);consumer.accept("子小远");}/*** Function<T, R> - 函数型接口* T代表参数的类型 R是返回值的类型* 该接口代表了一个接受一个参数并返回结果的操作。* 方法签名:R apply(T t)*/public static void functionTest() {log.info("functionTest");Function<String, Integer> function = str -> str.length();Integer apply = function.apply("子小远");log.info("functionTest:{}", apply);}/*** Predicate<T> - 判断型接口* 该接口代表了一个接受一个参数并返回布尔值的判断操作。* 方法签名:boolean test(T t)*/public static void predicateTest() {log.info("predicateTest");Predicate<String> predicate = str -> str.isEmpty();boolean test = predicate.test("子小远");log.info("predicateTest:{}", test);}/*** Supplier<T> - 供给型接口* 该接口代表了一个不接受参数但返回结果的操作,用于提供数据。* 方法签名:T get()*/public static void supplierTest() {log.info("supplierTest");Supplier<Integer> supplier = () -> new Random().nextInt();Integer s = supplier.get();log.info("supplierTest:{}", s);}}
运行结果