数据代理+事件处理+计算属性与监视+绑定样式+条件渲染
- 1 数据代理
- 1.1 回顾Object.defineProperty方法
- 1.2 数据代理
- 2 事件处理
- 2.1 绑定监听
- 2.2 事件修饰符
- 2.3 键盘事件
- 3 计算属性与监视
- 3.1 计算属性
- 3.2 监视属性(侦视属性)
- 3.3 watch对比computed
- 4 绑定样式
- 4.1 绑定class样式
- 4.2 绑定style样式
- 4.3 总结
- 5 条件渲染
1 数据代理
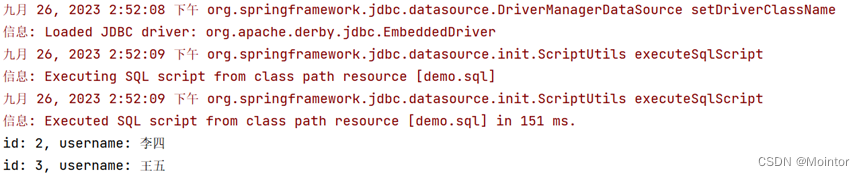
1.1 回顾Object.defineProperty方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>回顾Object.defineProperty方法</title>
</head>
<body><!-- 给对象添加属性 --><script>let number = 30let person = {name:'张三',sex:'男'}// 给person添加age属性Object.defineProperty(person,'age',{// 可传递四个基本配置项/* value: 18,enumerable:true, // 控制属性是否可以枚举,默认值是falsewritable:true, // 控制属性是否可以被修改,默认值是falseconfigurable:true, // 控制属性是否可以被删除,默认值是false */// 传递高级配置// 当有人读取person的age属性时,get函数(getter)就会被调用,且返回值就是age的值// get:function(){get(){console.log('有人读取了age属性');return number},// 当有人修改person的age属性时,set函数(setter)就会被调用,且会收到修改的具体值set(value){console.log('有人修改了age属性,且值是',value);number = value}})// console.log(Object.keys(person));// console.log(person);</script>
</body>
</html>
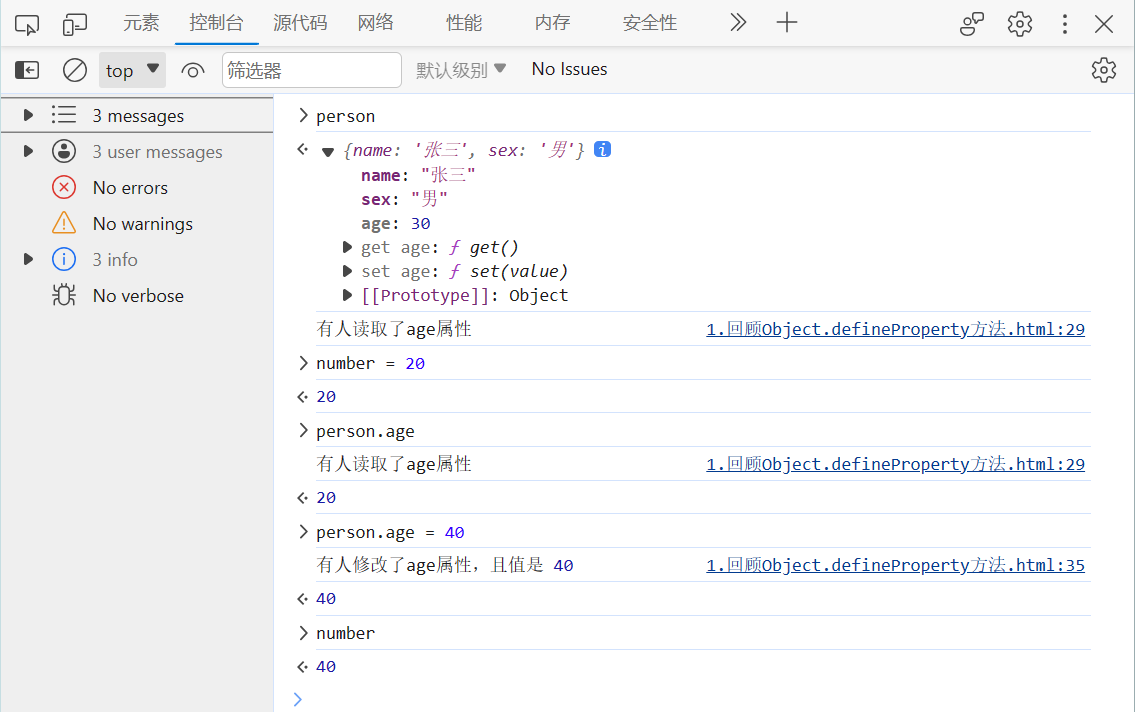
1.2 数据代理
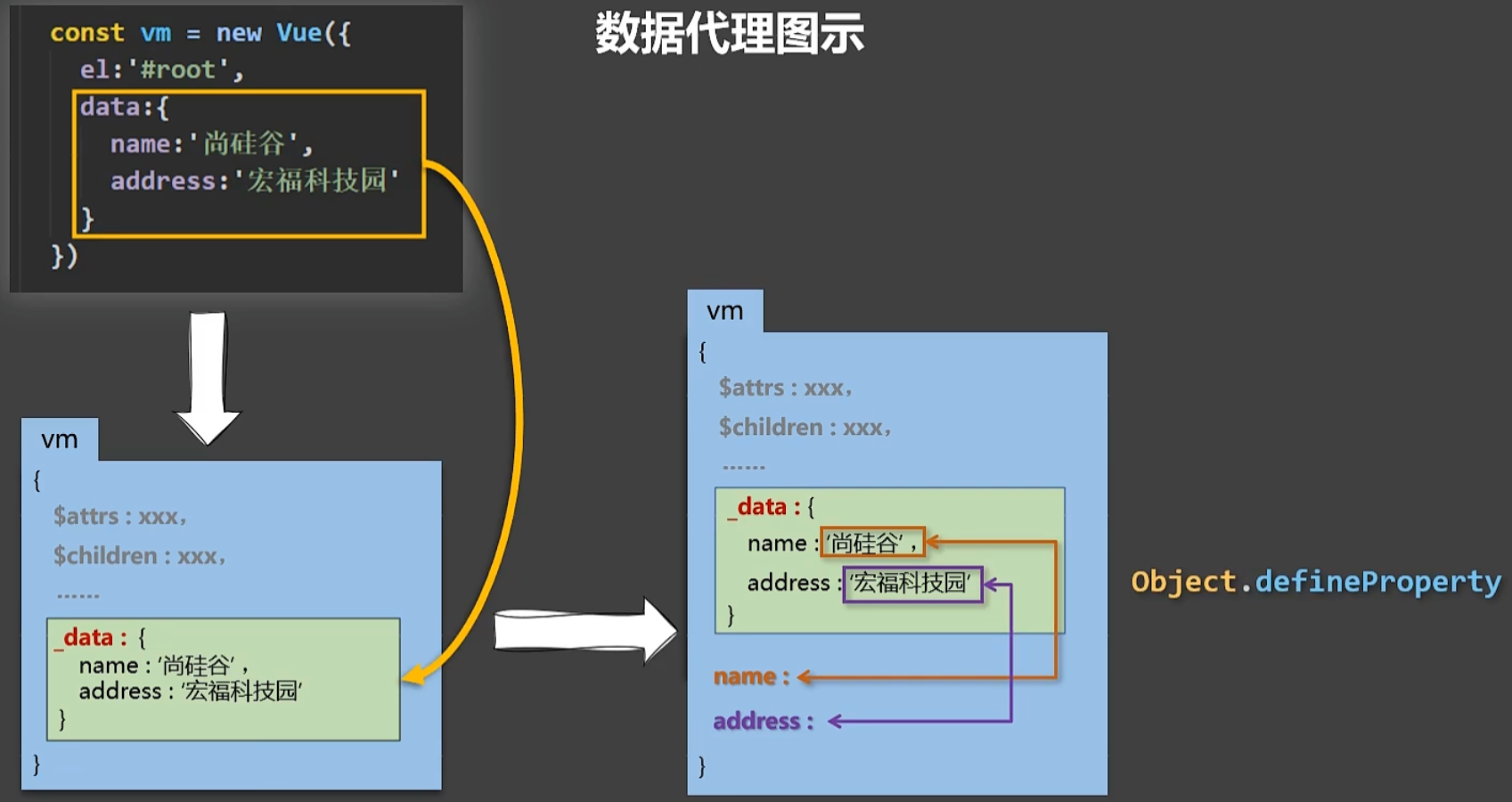
- 数据代理:通过一个对象代理对另一个对象中的属性的操作(读/写)。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>何为数据代理</title>
</head>
<body><!-- 数据代理:通过一个对象代理对另一个对象中的属性的操作(读/写) --><script>let obj = { x: 100 }let obj2 = { y: 200 }// 想通过obj2读取或修改xObject.defineProperty(obj2,'x',{get(){return obj.x},set(value){obj.x = value}})</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Vue中的数据代理</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
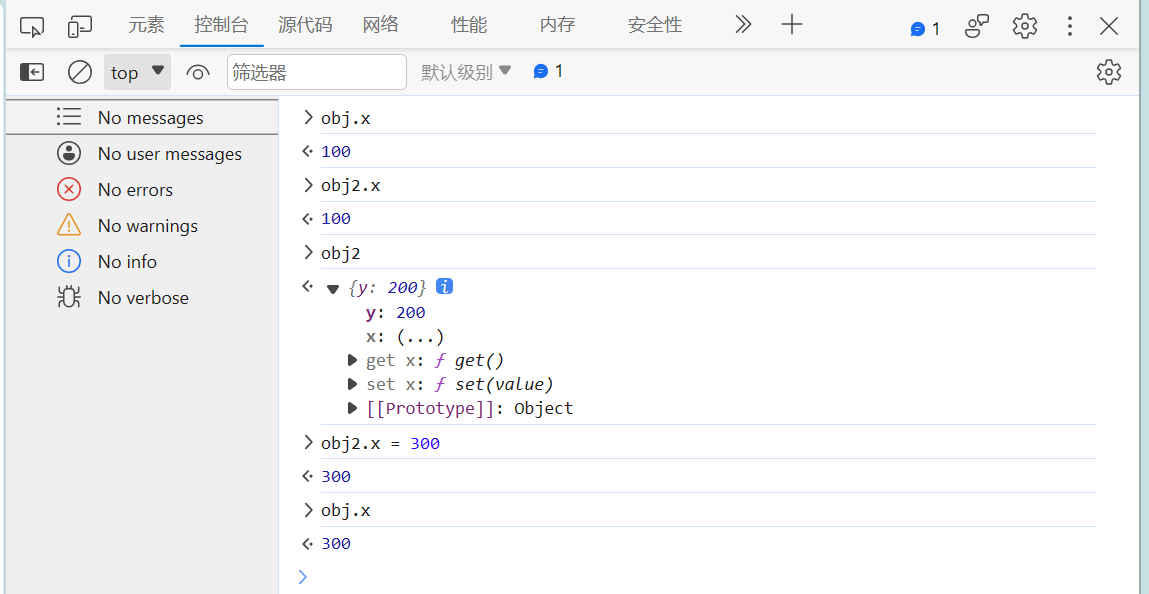
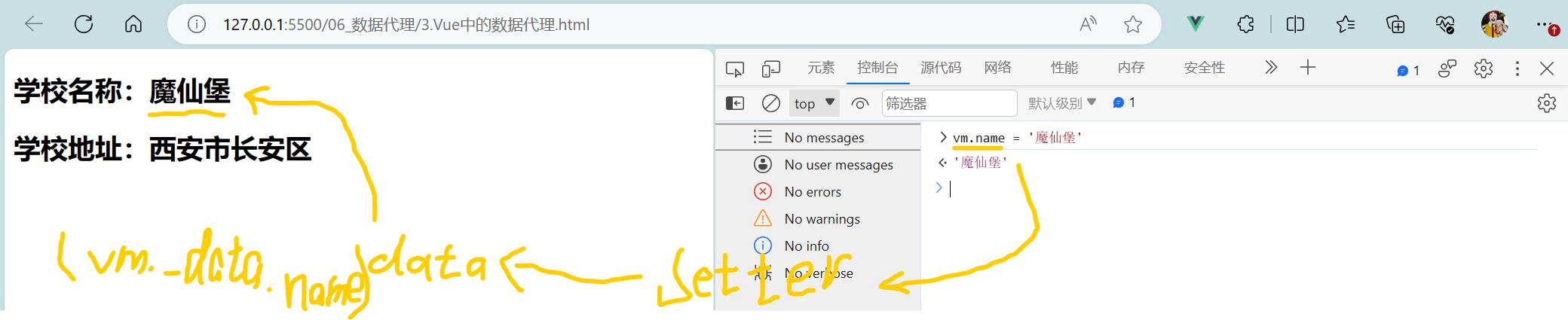
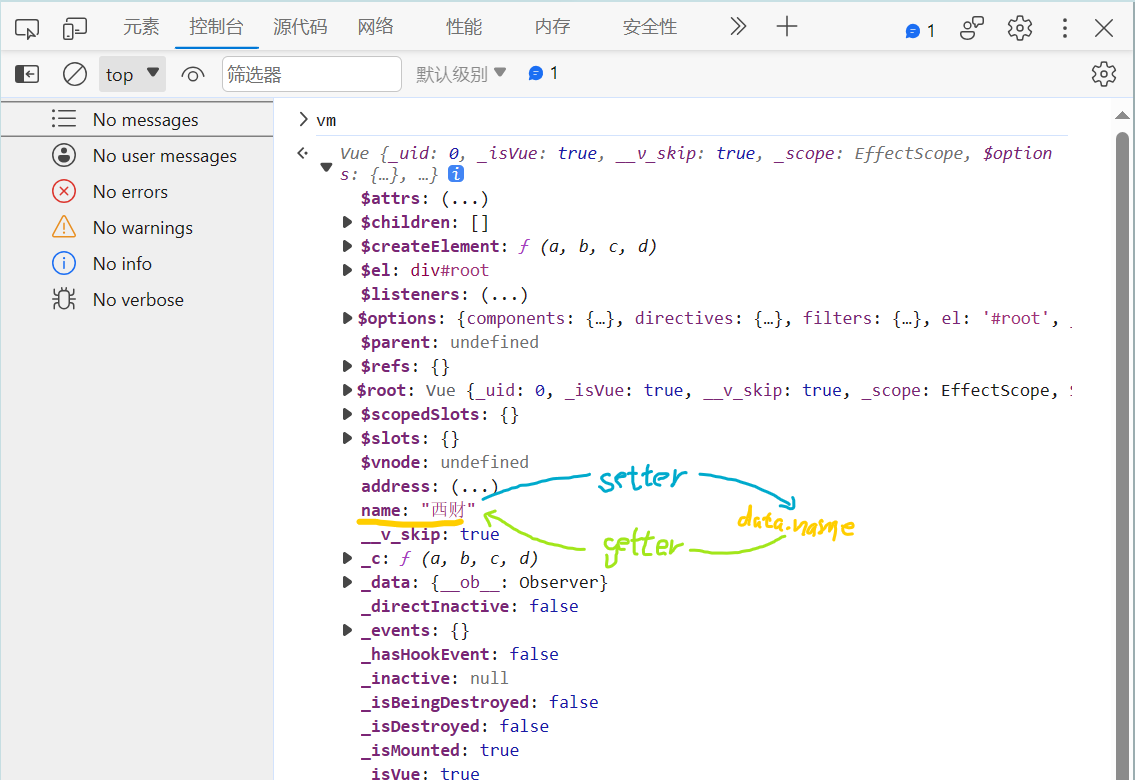
<body><!--总结1.Vue中的数据代理:通过vm对象来代理data对象中属性的操作(读/写)2.Vue中数据代理的好处:更加方便的操作data中的数据3.基本原理:通过Object.defineProperty()把data对象中所有属性添加到vm上。为每一个添加到vm上的属性,都指定一个getter/setter。在getter/setter内部去操作(读/写)data中对应的属性。--><!-- 准备一个容器 --><div id="root"><h2>学校名称:{{name}}</h2><h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el: '#root',data: {name:'西财',address:'西安市长安区'}})
</script>
</html>
2 事件处理
2.1 绑定监听

- 默认事件形参:event
- 隐含属性对象:$event
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>事件的基本使用</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
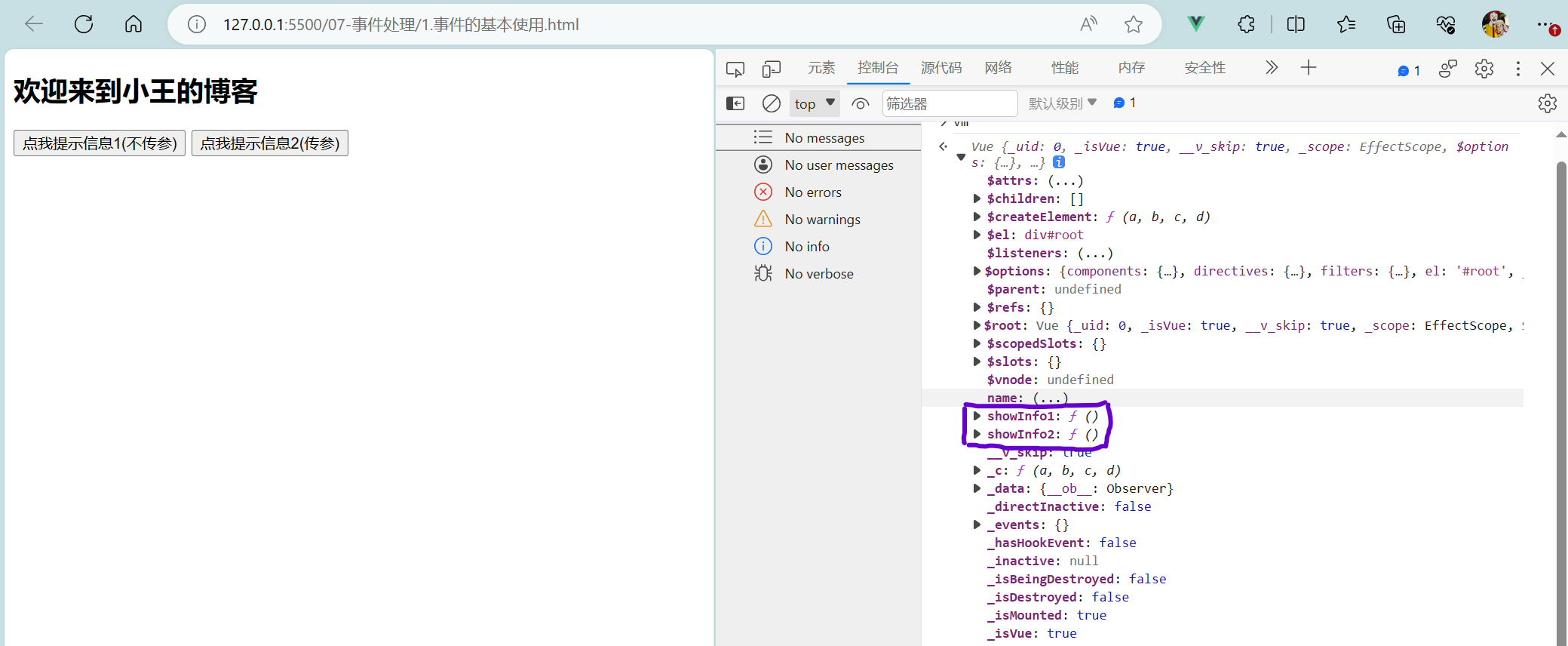
<body><!-- 事件的基本使用:1.使用v-on:xxx 或 @xxx 绑定事件,其中xxx是事件名;2.事件的回调需要配置在methods对象中,最终会在vm上;3.methods中配置的函数,不要用箭头函数!否则this就不是vm了;4.methods中配置的函数,都是被Vue所管理的函数,this的指向是vm 或 组件实例对象;5.@click="demo" 和 @click="demo($event)" 效果一致,但后者可以传参;--><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><h2>欢迎来到{{name}}的博客</h2><!-- <button v-on:click="showInfo1">点我提示信息1</button> --><!-- 可简写为 --><button @click="showInfo1">点我提示信息1(不传参)</button><button @click="showInfo2($event,66)">点我提示信息2(传参)</button></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{name:'小王'},methods:{showInfo1(event) {// console.log(event.target.innerText); // 点我提示信息1// console.log(this); // 此处的this是vmalert('同学你好!')},// showInfo2(event) {showInfo2(event,number) {// console.log(event.target.innerText); // 点我提示信息1// console.log(this); // 此处的this是vm// alert('同学你好!!')console.log(event,number);}}})
</script>
</html>
2.2 事件修饰符
- prevent:阻止默认事件(常用)
- stop:阻止事件冒泡(常用)
- once:事件只触发一次(常用)
- capture:使用事件的捕获模式
- self:只有event.target是当前操作的元素时才触发事件
- passive:事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>事件修饰符</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script><style>*{margin-top: 13px;}.demo1{height: 50px;background-color: skyblue;}.box1{padding: 5px;background-color: pink;}.box2{padding: 5px;background-color: orange;}.list{width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: peru;overflow: auto; /* 形成滚动条 */}li{height: 100px;}</style>
</head>
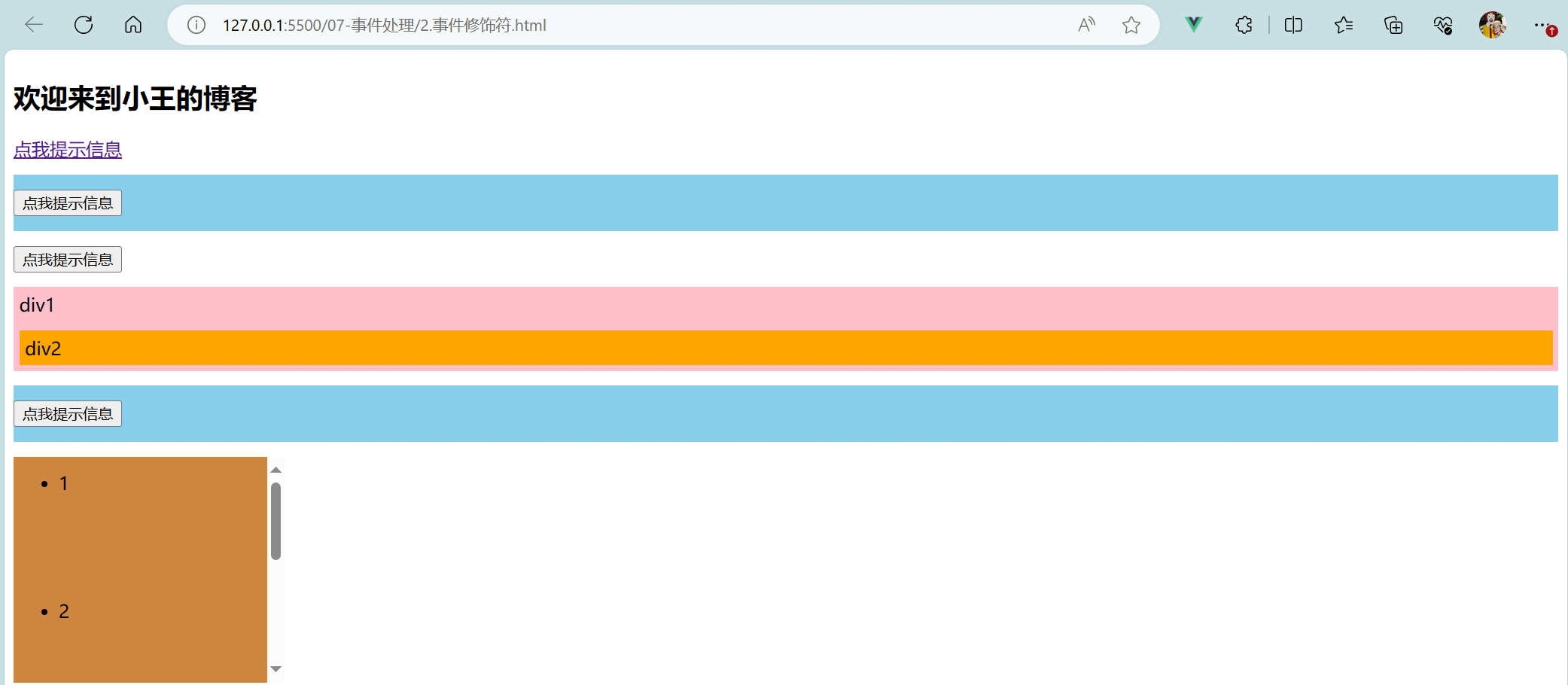
<body><!--总结Vue中的事件修饰符:1.prevent:阻止默认事件(常用);2.stop:阻止事件冒泡(常用);3.once:事件只触发一次(常用);4.capture:使用事件的捕获模式;5.self:只有event.target是当前操作的元素时才触发事件;6.passive:事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕;--><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><h2>欢迎来到{{name}}的博客</h2><!-- 阻止默认事件 --><a href="https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_64875217?type=blog" @click.prevent="showInfo">点我提示信息</a> <!-- 方式二 --><!-- 阻止事件冒泡 --><div class="demo1" @click="showInfo"><button @click.stop="showInfo">点我提示信息</button> <!-- 方式二 --><!-- 修饰符可以连续写 --><!-- <a href="https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_64875217?type=blog" @click.stop.prevent="showInfo">点我提示信息</a> --></div><!-- 事件只触发一次 --><button @click.once="showInfo">点我提示信息</button><!-- 使用事件的捕获模式 --><div class="box1" @click.capture="showMsg(1)"> <!-- 点击div2,先输出1再输出2 -->div1<div class="box2" @click="showMsg(2)">div2</div></div><!-- 只有event.target是当前操作的元素时才触发事件 --><div class="demo1" @click.self="showInfo"><button @click="showInfo">点我提示信息</button> <!-- 方式二 --></div><!-- 事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕 --><!-- 滚动:scroll(滚动条滚动) wheel(滚动轮滚动) --><!-- <ul @scroll="demo" class="list"> --><ul @wheel.passive="demo" class="list"><li>1</li><li>2</li><li>3</li><li>4</li></ul></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({el: '#root',data: {name:'小王',},methods: {showInfo(e) {// e.preventDefault() // 阻止默认行为:阻止跳转链接 (方式一)// e.stopPropagation() // 阻止事件冒泡:阻止弹出两次弹窗(方式一)alert('同学你好!')// console.log(e.target);},showMsg(msg) {console.log(msg);},demo() {// console.log('@');for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {console.log('#');}console.log('累坏了');}}})
</script>
</html>
2.3 键盘事件
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>键盘事件</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!--总结1.Vue中常用的按键别名:回车 => enter删除 => delete (捕获“删除”和“退格”键)退出 => esc空格 => space换行 => tab (特殊,必须配合keydown去使用)上 => up下 => down左 => left右 => right2.Vue未提供别名的按键,可以使用按键原始的key值去绑定,但注意要转为kebab-case(短横线命名)3.系统修饰键(用法特殊):ctrl、alt、shift、meta(1).配合keyup使用:按下修饰键的同时,再按下其他键,随后释放其他键,事件才被触发。(2).配合keydown使用:正常触发事件。4.也可以使用keyCode去指定具体的按键(不推荐)5.Vue.config.keyCodes.自定义键名 = 键码,可以去定制按键别名--><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><h2>欢迎来到{{name}}的博客</h2><!-- <input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.enter = "showInfo"> 方式二 --><!-- <input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.13 = "showInfo"> --><!-- <input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keydown.tab = "showInfo"> --><!-- <input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.caps-lock = "showInfo"> --><!-- <input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.ctrl = "showInfo"> --><input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.ctrl.y = "showInfo"> // 只有按ctrl+y时才会输出<!-- <input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.huiche = "showInfo"> --></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseVue.config.keyCodes.huiche = 13 // 相当于定义了一个别名按键new Vue({el:'#root',data:{name:'小王'},methods:{showInfo(e){// if(e.keyCode !== 13) return // 方式一// console.log(e.target.value);console.log(e.key,e.keyCode);}}})
</script>
</html>
3 计算属性与监视
3.1 计算属性
- 姓名案例_插值语法实现:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>姓名案例_插值语法实现</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><!-- 姓:<input type="text" v-model:value="firstName"><br/><br/> -->姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/><!-- 名:<input type="text" v-model:value="lastName"><br/><br/> -->名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/><!-- 全名:<span>{{firstName + '-' + lastName}}</span> -->全名:<span>{{firstName.slice(0,3)}}-{{lastName}}</span></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({el:'#root',data:{firstName:'张',lastName:'三'}})
</script>
</html>
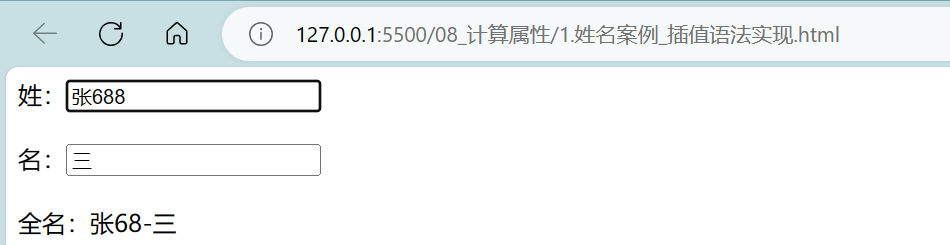
- 姓名案例_methods实现:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>姓名案例_methods实现</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><!-- 姓:<input type="text" v-model:value="firstName"><br/><br/> -->姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/><!-- 名:<input type="text" v-model:value="lastName"><br/><br/> -->名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/><!-- 全名:<span>{{firstName + '-' + lastName}}</span> -->全名:<span>{{fullName()}}</span></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({el:'#root',data:{firstName:'张',lastName:'三'},methods:{fullName(){return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName}}})
</script>
</html>
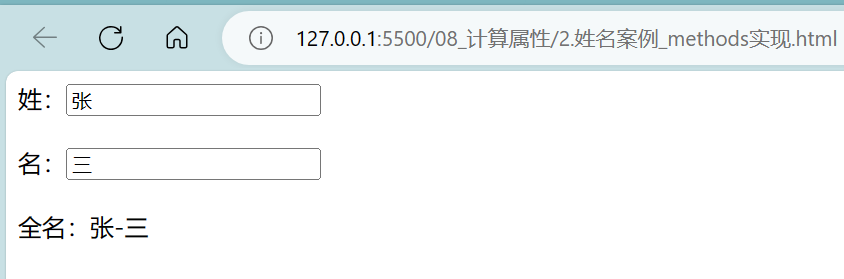
- 姓名案例_计算属性实现:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>姓名案例_计算属性实现</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!--总结计算属性:1.定义:要用的属性不存在,要通过已有属性计算得来。2.原理:底层借助了Objcet.defineproperty方法提供的getter和setter。3.get函数什么时候执行?(1).初次读取时会执行一次。(2).当依赖的数据发生改变时会被再次调用。4.优势:与methods实现相比,内部有缓存机制(复用),效率更高,调试方便。5.备注:1.计算属性最终会出现在vm上,直接读取使用即可。2.如果计算属性要被修改,那必须写set函数去响应修改,且set中要引起计算时依赖的数据发生改变。--><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><!-- 姓:<input type="text" v-model:value="firstName"><br/><br/> -->姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/><!-- 名:<input type="text" v-model:value="lastName"><br/><br/> -->名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/><!-- 全名:<span>{{firstName + '-' + lastName}}</span> -->全名:<span>{{fullName}}</span></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{firstName:'张',lastName:'三'},computed:{fullName:{// 当有人读取fullName时,get就会被调用,且返回值就作为fullName的值// get什么时候调用:1.初次读取fullName时 2.所依赖的数据发生变化时get(){console.log('get被调用了');// console.log(this); // 此处的this是vmreturn this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName},// set什么时候调用:当fullName被修改时set(value){console.log('set',value);const arr = value.split('-')this.firstName = arr[0]this.lastName = arr[1]}}}})
</script>
</html>
- 姓名案例_计算属性简写实现(确定只读不改,就用简写):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>姓名案例_计算属性简写实现</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><!-- 姓:<input type="text" v-model:value="firstName"><br/><br/> -->姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/><!-- 名:<input type="text" v-model:value="lastName"><br/><br/> -->名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/><!-- 全名:<span>{{firstName + '-' + lastName}}</span> -->全名:<span>{{fullName}}</span> <!-- fullName看似是函数 实则是vm的属性值 因此此处不能写为{{fullName()}} --></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{firstName:'张',lastName:'三'},computed:{// 此时function及后面函数可看作get()/* fullName:function() {console.log('get被调用了');return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName} */// 再精简:fullName() {console.log('get被调用了');return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName}}})
</script>
</html>
3.2 监视属性(侦视属性)
- 天气案例:点击一次按钮切换一次天气
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>天气案例</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2><!-- <button @click = 'changeWeather'>切换天气</button> --><!-- 32-36行简化后变为: --><button @click = 'isHot = !isHot'>切换天气</button></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falsenew Vue({el:'#root',data:{isHot:true},computed:{info(){return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}},/* methods:{changeWeather(){this.isHot = !this.isHot}} */// 简化后:methods:{}})
</script>
</html>

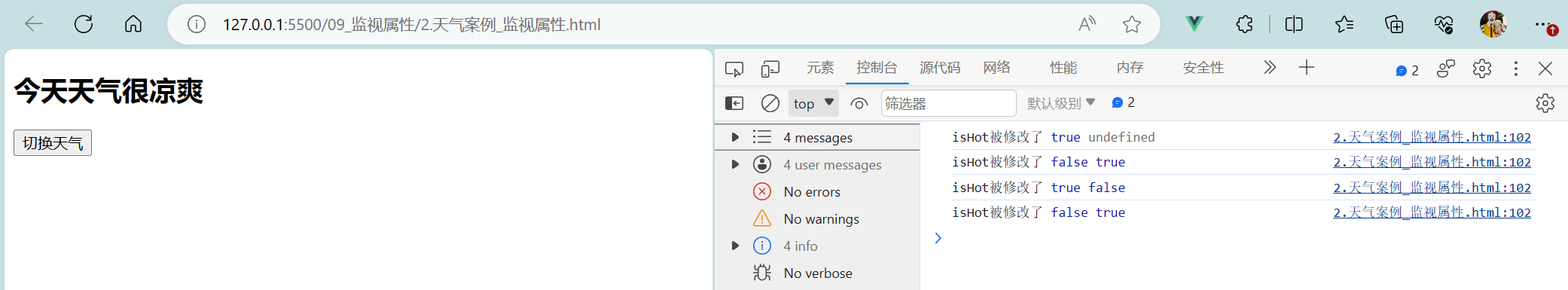
- 天气案例_监视属性:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>天气案例_监视属性</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!--总结监视属性watch:1.当被监视的属性变化时, 回调函数自动调用, 进行相关操作2.监视的属性必须存在,才能进行监视!!3.监视的两种写法:(1).new Vue时传入watch配置(2).通过vm.$watch监视--><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2><button @click = 'changeWeather'>切换天气</button></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{isHot:true},computed:{info(){return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}},methods:{changeWeather(){this.isHot = !this.isHot}},// 监视写法一:/* watch:{// 此时监视的是isHotisHot:{immediate:true, // immediate默认值为false,初始化时让handler调用一下// handler()函数 什么时候调用:当isHot发生改变时就调用handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue);}}} */})// 监视写法二:vm.$watch('isHot',{immediate:true, // immediate默认值为false,初始化时让handler调用一下// handler()函数 什么时候调用:当isHot发生改变时就调用handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue);}})
</script>
</html>
- 天气案例_深度监视:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>天气案例_深度监视</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
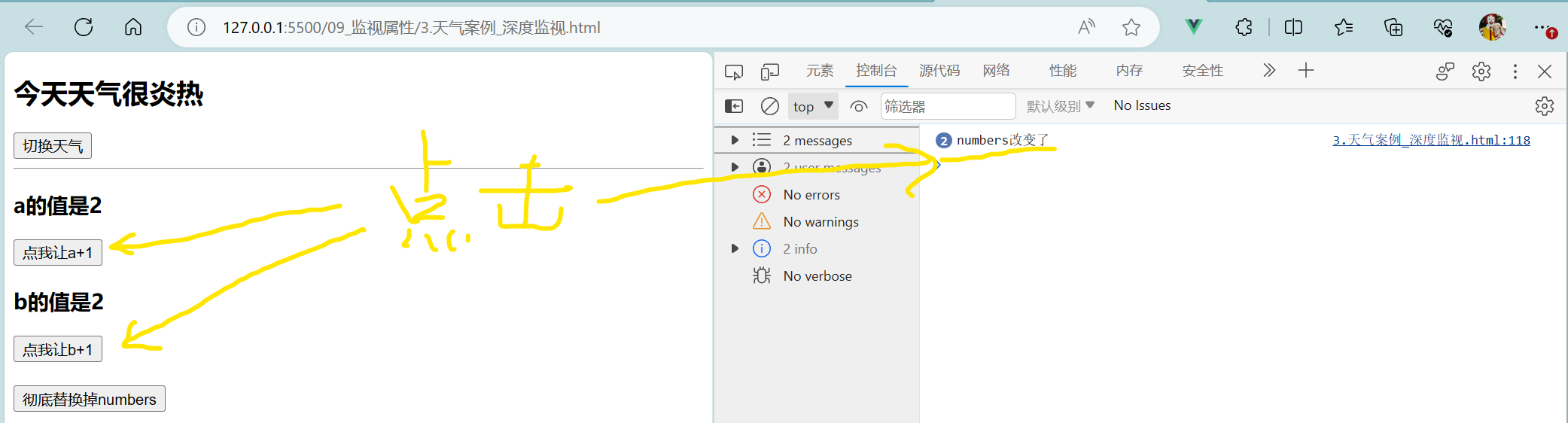
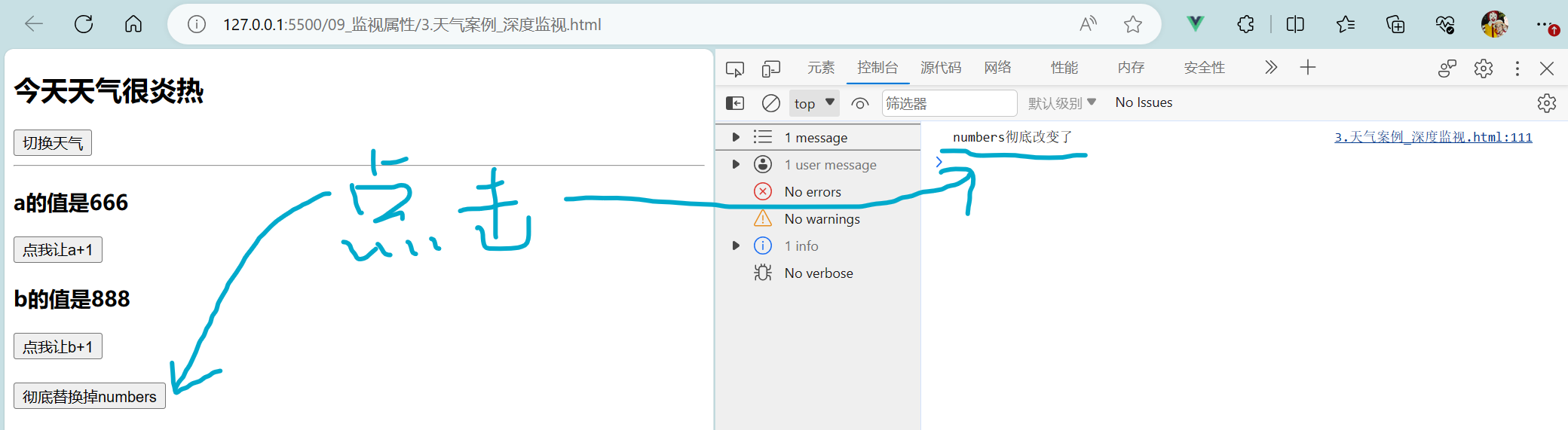
<body><!--总结深度监视:(1).Vue中的watch默认不监测对象内部值的改变(一层)。(2).配置deep:true可以监测对象内部值改变(多层)。备注:(1).Vue自身可以监测对象内部值的改变,但Vue提供的watch默认不可以!(2).使用watch时根据数据的具体结构,决定是否采用深度监视。--><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2><button @click = 'changeWeather'>切换天气</button><hr/><h3>a的值是{{numbers.a}}</h3><button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a+1</button><h3>b的值是{{numbers.b}}</h3><button @click="numbers.b++">点我让b+1</button><br/><br/><button @click="numbers = {a:666,b:888}">彻底替换掉numbers</button></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{isHot:true,numbers:{a:1,b:1}},computed:{info(){return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}},methods:{changeWeather(){this.isHot = !this.isHot}},watch:{// 此时监视的是isHotisHot:{// immediate:true, // immediate默认值为false,初始化时让handler调用一下// handler()函数 什么时候调用:当isHot发生改变时就调用handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue);}},// 监视多级结构中某个属性的变化(只监测a)/* 'numbers.a':{handler(){console.log('a被改变了');}}, */// 监视整个numbers的改变(numbers整体改变)/* numbers:{handler(){console.log('numbers彻底改变了');}}, */// 监视多级结构中所有属性的变化(既监测a也监测b)numbers:{deep:true, // deep配置项 默认值是false 深入的、有深度的handler(){console.log('numbers改变了');}}}})
</script>
</html>
- 天气案例_深度监视简写:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>天气案例_深度监视简写</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2><button @click = 'changeWeather'>切换天气</button></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{isHot:true,numbers:{a:1,b:1}},computed:{info(){return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'}},methods:{changeWeather(){this.isHot = !this.isHot}},watch:{// 此时监视的是isHot// 正常写法:/* isHot:{// immediate:true, // immediate默认值为false,初始化时让handler调用一下// deep:true, // deep默认值为false,深度监视// 当配置项只有handler()时,可采用简写形式// handler()函数 什么时候调用:当isHot发生改变时就调用handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue);}} */// 简写:/* isHot(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue);} */}})// 正常写法:/* vm.$watch('isHot',{// immediate:true, // immediate默认值为false,初始化时让handler调用一下// deep:true, // deep默认值为false,深度监视handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue);}}) */// 简写:vm.$watch('isHot',function(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue);})
</script>
</html>
3.3 watch对比computed
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>姓名案例_watch实现</title><!-- 引入Vue --><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><!--总结computed和watch之间的区别:1.computed能完成的功能,watch都可以完成。2.watch能完成的功能,computed不一定能完成,例如:watch可以进行异步操作(如:定时器)。两个重要的小原则:1.所被Vue管理的函数,最好写成普通函数,这样this的指向才是vm 或 组件实例对象。2.所有不被Vue所管理的函数(定时器的回调函数、ajax的回调函数等、Promise的回调函数),最好写成箭头函数,这样this的指向才是vm 或 组件实例对象。--><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><!-- 姓:<input type="text" v-model:value="firstName"><br/><br/> -->姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/><!-- 名:<input type="text" v-model:value="lastName"><br/><br/> -->名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/><!-- 全名:<span>{{firstName + '-' + lastName}}</span> -->全名:<span>{{fullName}}</span></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{firstName:'张',lastName:'三',fullName:'张-三'},computed:{// 此时function及后面函数可看作get()/* fullName:function() {console.log('get被调用了');return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName} */// 再精简:/* fullName() {console.log('get被调用了');return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName} */},watch:{firstName(newValue){// console.log(this); // this指向vmthis.fullName = newValue + '-' + this.lastName// 若要延时:/* setTimeout(()=>{console.log(this)this.fullName = val + '-' + this.lastName},1000); */},lastName(newValue){// console.log(this); // this指向vmthis.fullName = this.firstName + '-' + newValue}}})
</script>
</html>
4 绑定样式
4.1 绑定class样式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>绑定样式</title><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script><style>.basic{width: 400px;height: 100px;border: 1px solid black;}.happy{border: 4px solid red;;background-color: rgba(255, 255, 0, 0.644);background: linear-gradient(30deg,yellow,pink,orange,yellow);}.sad{border: 4px dashed rgb(2, 197, 2);background-color: gray;}.normal{background-color: skyblue;}.atguigu1{background-color: yellowgreen;}.atguigu2{font-size: 30px;text-shadow:2px 2px 10px red;}.atguigu3{border-radius: 20px;}</style></head>
<body><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><!-- 绑定class样式——字符串写法,适用于:样式的类名不确定,需要动态指定 --><!-- class正常的样式正常写 变化的样式用绑定的方法:class写 --><div class="basic" :class="mood" id="demo" @click="changeMood">{{name}}</div><br/><br/><!-- 绑定class样式——数组写法,适用于:要绑定的样式个数不确定、名字也不确定 --><div class="basic" :class="classArr">{{name}}</div><br/><br/><!-- 绑定class样式——对象写法,适用于:要绑定的样式个数确定、名字也确定,但要动态决定用不用 --><div class="basic" :class="classObj">{{name}}</div></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{name:'小王',mood:'normal',classArr:['atguigu1','atguigu2','atguigu3'],classObj:{atguigu1:false,atguigu2:false}},methods:{changeMood(){// this.mood = 'happy' // 点击后 心情变为happy// 点击后 心情随机变const arr = ['happy','sad','normal']// 随机生成0、1、2三个数字中的任一个// Math.random() 生成的是0-1的数 无限接近于1 但得不到1// Math.random()*3 生成的是0-3的数 无限接近于3 但得不到3// Math.floor() 向下取整const index = Math.floor(Math.random()*3)this.mood = arr[index]}}})
</script>
</html>

4.2 绑定style样式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>绑定样式</title><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script><style>.basic{width: 400px;height: 100px;border: 1px solid black;}.happy{border: 4px solid red;;background-color: rgba(255, 255, 0, 0.644);background: linear-gradient(30deg,yellow,pink,orange,yellow);}.sad{border: 4px dashed rgb(2, 197, 2);background-color: gray;}.normal{background-color: skyblue;}.atguigu1{background-color: yellowgreen;}.atguigu2{font-size: 30px;text-shadow:2px 2px 10px red;}.atguigu3{border-radius: 20px;}</style></head>
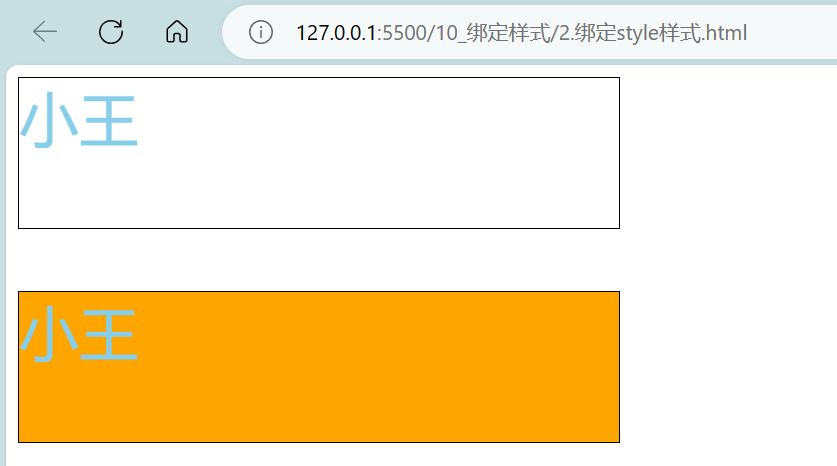
<body><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><!-- 绑定style样式——对象写法 --><!-- <div class="basic" :style="{fontSize: fsize+'px'}">{{name}}</div> --><div class="basic" :style="styleObj">{{name}}</div><br/><br/><!-- 绑定style样式——数组写法 --><!-- <div class="basic" :style="[styleObj,styleObj2]">{{name}}</div> --><div class="basic" :style="styleArr">{{name}}</div></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{name:'小王',// fsize:40styleObj:{fontSize: '40px',color:'skyblue',// backgroundColor:'orange'},/* styleObj2:{backgroundColor:'orange'}, */styleArr:[{fontSize: '40px',color:'skyblue',},{backgroundColor:'orange'}]}})
</script>
</html>
4.3 总结
<!--总结绑定样式:1. class样式写法:class="xxx" xxx可以是字符串、对象、数组。字符串写法适用于:类名不确定,要动态获取。对象写法适用于:要绑定多个样式,个数不确定,名字也不确定。数组写法适用于:要绑定多个样式,个数确定,名字也确定,但不确定用不用。2. style样式:style="{fontSize: xxx}"其中xxx是动态值。:style="[a,b]"其中a、b是样式对象。
-->
5 条件渲染
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>条件渲染</title><script src="../JS/vue.js"></script>
</head>
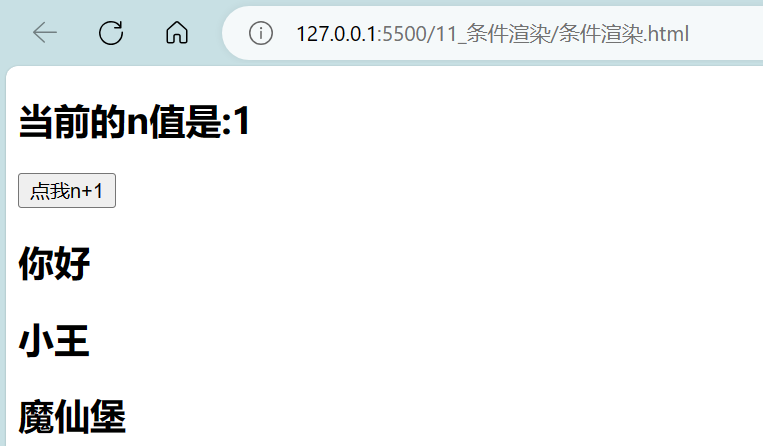
<body><!--总结条件渲染:1.v-if写法:(1).v-if="表达式" (2).v-else-if="表达式"(3).v-else="表达式"适用于:切换频率较低的场景。特点:不展示的DOM元素直接被移除。注意:v-if可以和:v-else-if、v-else一起使用,但要求结构不能被“打断”。2.v-show写法:v-show="表达式"适用于:切换频率较高的场景。特点:不展示的DOM元素未被移除,仅仅是使用样式隐藏掉3.备注:使用v-if的时,元素可能无法获取到,而使用v-show一定可以获取到。--><!-- 准备好一个容器 --><div id="root"><!-- 使用v-show做条件渲染 --><!-- <h2 v-show="false">欢迎来到{{name}}</h2> --><!-- <h2 v-show="1 === 3">欢迎来到{{name}}</h2> --><!-- <h2 v-show="a">欢迎来到{{name}}</h2> --><!-- 使用v-if做条件渲染 --><!-- <h2 v-if="false">欢迎来到{{name}}</h2> --><!-- <h2 v-if="1 === 3">欢迎来到{{name}}</h2> --><h2>当前的n值是:{{n}}</h2><button @click="n++">点我n+1</button><!-- <div v-show="n === 1">Angular</div><div v-show="n === 2">React</div><div v-show="n === 3">vue</div> --><!-- <div v-if="n === 1">Angular</div><div v-if="n === 2">React</div><div v-if="n === 3">vue</div> --><!-- v-else和v-else-if --><!-- <div v-if="n === 1">Angular</div><div v-else-if="n === 2">React</div><div v-else-if="n === 3">vue</div><div v-else>哈哈</div> --><!-- <h2 v-show="n === 1">你好</h2><h2 v-show="n === 1">小王</h2><h2 v-show="n === 1">魔仙堡</h2> --><!-- 上三行可写为如下,但会破坏结构 --><!-- <div v-show="n === 1"><h2>你好</h2><h2>小王</h2><h2>魔仙堡</h2></div> --><!-- 再进行改写,改为: --><!-- 注意:template只能和v-if搭配使用 --><template v-if="n === 1"><h2>你好</h2><h2>小王</h2><h2>魔仙堡</h2></template></div>
</body>
<script>Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{name:'魔仙堡',// a:falsen:0}})
</script>
</html>
![[尚硅谷React笔记]——第2章 React面向组件编程](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/872662c853d44b0d9a2568b1fbecbbb7.png)