一、包装类
概述
Java提供了两个类型系统,基本类型与引用类型,使用基本类型在于效率,然而很多情况,会创建对象使用,因为对象可以做更多的功能,如果想要我们的基本类型像对象一样操作,就可以使用基本类型对应的包装类,如下:
byte—>Byte
short—>Short
int—>Integer
long–>Long
char–>Character
float–>Float
double–>Double
boolean—>Boolean
装箱与拆箱
基本类型与对应的包装类对象之间,来回转换的过程称为”装箱“与”拆箱“:
装箱:从基本类型转换为对应的包装类对象。
拆箱:从包装类对象转换为对应的基本类型。
用Integer与 int为例:
基本数值---->包装对象
Integer i = new Integer(4);//使用构造函数函数
Integer iii = Integer.valueOf(4);//使用包装类中的valueOf方法
包装对象---->基本数值
int num = i.intValue();
自动装箱与自动拆箱
由于我们经常要做基本类型与包装类之间的转换,从Java 5(JDK 1.5)开始,基本类型与包装类的装箱、拆箱动作可以自动完成。例如:
Integer i = 4;//自动装箱。相当于Integer i = Integer.valueOf(4);
i = i + 5;//等号右边:将i对象转成基本数值(自动拆箱) i.intValue() + 5;
//加法运算完成后,再次装箱,把基本数值转成对象。
基本类型与字符串之间的转换
基本类型直接与””相连接即可;如:34+“”
String转换成对应的基本类型
除了Character类之外,其他所有包装类都具有parseXxx静态方法可以将字符串参数转换为对应的基本类型:
public static byte parseByte(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的byte基本类型。
public static short parseShort(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的short基本类型。
public static int parseInt(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的int基本类型。
public static long parseLong(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的long基本类型。
public static float parseFloat(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的float基本类型。
public static double parseDouble(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的double基本类型。
public static boolean parseBoolean(String s):将字符串参数转换为对应的boolean基本类型。
以Integer类的静态方法parseXxx为例
public class Demo18WrapperParse {public static void main(String[] args) {int num = Integer.parseInt("100");}
}
注意:如果字符串参数的内容无法正确转换为对应的基本类型,则会抛出java.lang.NumberFormatException异常。
示例:
System.out.println("int 的最大值:"+Integer.MAX_VALUE);System.out.println("int 的最小值:"+Integer.MIN_VALUE);int i = 100;//基本数据类型System.out.println(i);Integer i1 = new Integer(10);//包装数据类型Integer i2 = new Integer("100");Integer i3 = new Integer("10a");//报错System.out.println(i1.toString());System.out.println("i2:"+i2);//自动化完成//装箱Integer i4 = 5;//拆箱int i5 = i4;int i6 = Integer.parseInt("12");System.out.println("i6:"+i6);Integer.valueOf(1);//转为包装类型Double d1 = 3.14;System.out.println(d1.isNaN());//is not a number;
二、字符串String类
String构造函数
//构造函数String str = new String();System.out.println(str);/*字符数组构建字符串*/char data[] = {'a', 'b', 'c'};String str2 = new String(data);System.out.println("str2"+str2);/*字节数组构建字符创*/byte[] bs = {97,98,99,100,101,102,103};String str3 = new String(bs);System.out.println("str3:"+str3);//从1开始,长度为3String str4 = new String(bs,1,3);System.out.println("str4--->"+str4);String str5 = new String("abc");System.out.println("str5:"+str5);String str6 = "abc";//创建字符串System.out.println("str6:"+str6);
String常用方法
| public char charAt(int index) | 根据下标获取字符 |
|---|---|
| public boolean contains(String str) | 判断当前字符串中是否包含str |
| public char[] toCharArray() | 将字符串转换成数组。 |
| public int indexOf(String str) | 查找str首次出现的下标,存在,则返回该下标;不存在,则返回-1 |
| public int length() | 返回字符串的长度 |
| public String trim() | 去掉字符串前后的空格 |
| public String toUpperCase() | 将小写转成大写 |
| public boolean endsWith(String str) | 判断字符串是否以str结尾 |
| public String replace(char oldChar,char newChar) | 将旧字符串替换成新字符串 |
| public String[] split(String str) | 根据str做拆分 |
| public String subString(int beginIndex,int endIndex) | 在字符串中截取出一个子字符串 |
示例:
/*charAt(int index)返回 char指定索引处的值。注意越界问题:java.lang.StringIndexOutOfBoundsException: String index out of range: 100index:0---->length()-1*/String str = "helloworld";System.out.println(str.charAt(3));//System.out.println(str.charAt(100));/*concat(String str)将指定的字符串连接到该字符串的末尾。同+连接符一样*/String str2 = str.concat("***");System.out.println();/*boolean contains(CharSequence s)当且仅当此字符串包含指定的char值序列时才返回true。*/boolean flag = str.contains("hello");System.out.println("flag:"+flag);/*boolean endsWith(String suffix)测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结尾。*/String s3 = "aa.jpg";System.out.println(s3.endsWith(".jpg"));/*boolean startsWith(String prefix)测试此字符串是否以指定的前缀开头。*/String s4 = "20190831.txt";System.out.println(s4.startsWith("201908"));/*boolean equals(Object anObject)将此字符串与指定对象进行比较。boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)将此 String与其他 String比较,忽略大小写*/System.out.println("abc".equals("abc"));System.out.println("Abc".equals("abc"));/*byte[] ---->StringString ---->byte[]getBytes()使用平台的默认字符集将此 String编码为字节序列,将结果存储到新的字节数组中。char[] toCharArray()将此字符串转换为新的字符数组。*/byte[] bs = str.getBytes();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bs));char[] cs = str.toCharArray();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(cs));/*搜索int indexOf(int ch)返回指定字符第一次出现的字符串内的索引。int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex)返回指定字符第一次出现的字符串内的索引,以指定的索引开始搜索。int lastIndexOf(String str)返回指定子字符串最后一次出现的字符串中的索引。int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)返回指定子字符串的最后一次出现的字符串中的索引,从指定索引开始向后搜索*/System.out.println(str.indexOf('c'));//helloworldSystem.out.println(str.indexOf('e',0));System.out.println(str.indexOf("w"));System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("o"));/*boolean isEmpty()返回 true如果,且仅当 length()为 0 。*/System.out.println(str.isEmpty());/*String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)返回从替换所有出现的导致一个字符串 oldChar在此字符串 newChar 。*/String s7 = str.replace("o","uu");System.out.println("s7:---->"+s7);/*String[] split(String regex)按照切符,将此字符串分割为数组注意点:分隔符放在首位,中间起作用。放在末尾不起作用*/String s8 = "abc,123,wowo,33,";String[] strArr = s8.split(",");System.out.println("strArr.length---->"+strArr.length);for(int i=0;i<strArr.length;i++){System.out.println("---->"+strArr[i]);}/*String substring(int beginIndex)返回一个字符串,该字符串是此字符串的子字符串。String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)返回一个字符串,该字符串是此字符串的子字符串。 包含前面的下标,不包含后面的下标*/System.out.println("str.substring(5)"+str.substring(5));//helloworldSystem.out.println("str.substring(5,7)"+str.substring(5,7));/*String toLowerCase()将所有在此字符 String使用默认语言环境的规则,以小写。String toUpperCase()将所有在此字符 String使用默认语言环境的规则大写。*/String s9 = "abcDDaaADCD123**";System.out.println("s9--->"+s9);System.out.println("---->"+s9.toLowerCase());System.out.println("---->"+s9.toUpperCase());/*String trim()返回一个字符串,其值为此字符串,并删除任何前导和尾随空格。不会删除中间的空格*/String s10 = " he llo ";System.out.println("s10:"+s10.length());System.out.println("s10.trim()-->:"+s10.trim());System.out.println("s10.trim().length()--->"+s10.trim().length());/*static String valueOf(int i)返回 int参数的字符串 int形式。*/int i =10;String iStr = i+"";String iStr2 = String.valueOf(i);System.out.println(iStr);System.out.println(iStr2);
String类的内存分析
示例:
String s1 = "abc";String s2 = "abc";String s3 = new String("abc");String s4 = new String ("abc");System.out.println(s1==s2);//trueSystem.out.println("s1==s3:"+s1==s3);//falseSystem.out.println("s3==s4:"+s3==s4);//false//使用字符串常量池,每当我们使用字面量(String s=”1”;)创建字符串常量时,JVM会首先检查字符串常量池,
//如果该字符串已经存在常量池中,那么就将此字符串对象的地址赋值给引用s(引用s在Java栈中)。
//如果字符串不存在常量池中,就会实例化该字符串并且将其放到常量池中,并将此字符串对象的地址赋值给引用s(引用s在Java栈中)。// String str2 = "ab"; //1个对象
// String str3 = "cd"; //1个对象
// String str4 = str2+str3; //new StringBuilder().append(str).append(str3).toString()
// String str5 = "abcd";
// System.out.println("str4 = str5 : " + (str4==str5)); // false /*String str6 = "b"; String str7 = "a" + str6; String str67 = "ab"; System.out.println("str7 = str67 : "+ (str7 == str67)); //↑str6为变量,在运行期才会被解析。 final String str8 = "b"; String str9 = "a" + str8; String str89 = "ab"; System.out.println("str9 = str89 : "+ (str9 == str89)); //↑str8为常量变量,编译期会被优化 */

三、可变字符串
概念:可在内存中创建可变的缓冲空间,存储频繁改变的字符串。
Java中提供了两个可变字符串类:
StringBuilder:可变长字符串,JDK5.0提供,运行效率快、线程不安全。
StringBuffer:可变长字符串,JDK1.0提供,运行效率慢、线程安全。
这两个类中方法和属性完全一致
验证StringBuilder效率高于String。
public class TestStringBuilder {public static void main(String[] args) {//开始时间long start=System.currentTimeMillis();String string="";for(int i=0;i<99999;i++) {string+=i;}System.out.println(string);
// StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
// for(int i=0;i<99999;i++) {
// sb.append(i);
// }
// System.out.println(sb.toString());long end=System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("用时:"+(end-start)); }
}
常用的方法:
| 方法名 | 属性 |
|---|---|
| public StringBuilder append(String str) | 追加内容。 |
| public StringBuilder insert(int dstOffset, CharSequence s) | 将指定 字符串插入此序列中。 |
| public StringBuilder delete(int start, int end) | 移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
| public StringBuilder replace(int start, int end, String str) | 使用给定字符串替换此序列的子字符串中的字符。start开始位置、end结束位置。 |
| public int length() | 返回长度(字符数)。 |
示例:
//step1:创建StringBufferStringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();//step2:sb.append("abc");sb.append(true);sb.append(1);sb.append("3.14").append("wowo");//方法的链式调用System.out.println(sb);// System.out.println(sb.capacity());//在指定的位置添加了新的字符串sb.insert(3,"hello");System.out.println(sb);sb.insert(0,"**");System.out.println(sb);sb.insert(sb.length(),"@@");System.out.println("删除前:"+sb);sb.deleteCharAt(0);System.out.println("删除后:"+sb);sb.delete(0,4);System.out.println("删除后2:"+sb);sb.setCharAt(1,'u');//设置指定位置的字符为'u'System.out.println(sb);// sb.setLength(6);
// System.out.println(sb);sb.reverse();System.out.println(sb);
四、日期
Date
- Date表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒。
- Date类中的大部分方法都已经被Calendar类中的方法所取代。
- 时间单位
- 1秒=1000毫秒
- 1毫秒=1000微秒
- 1微秒=1000纳秒
Calendar
- Calendar提供了获取或设置各种日历字段的方法。
- protected Calendar() 构造方法为protected修饰,无法直接创建该对象。
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static Calendar getInstance() | 使用默认时区和区域获取日历 |
| void set(int year,int month,int date,int hourofday,int minute,int second) | 设置日历的年、月、日、时、分、秒。 |
| int get(int field) | 返回给定日历字段的值。字段比如年、月、日等 |
| void setTime(Date date) | 用给定的Date设置此日历的时间。Date-Calendar |
| Date getTime() | 返回一个Date表示此日历的时间。Calendar-Date |
| void add(int field,int amount) | 按照日历的规则,给指定字段添加或减少时间量 |
| long getTimeInMillis() | 毫秒为单位返回该日历的时间值 |
SimpleDateFormat
SimpleDateFormat是以与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的类。
进行格式化(日期 -> 文本)、解析(文本 -> 日期)。
yyyy:年
MM:月
dd:日
hh:1~12小时制(1-12)
HH:24小时制(0-23)
mm:分
ss:秒
S:毫秒
E:星期几
D:一年中的第几天
F:一月中的第几个星期(会把这个月总共过的天数除以7)
w:一年中的第几个星期
W:一月中的第几星期(会根据实际情况来算)
a:上下午标识
k:和HH差不多,表示一天24小时制(1-24)。
K:和hh差不多,表示一天12小时制(0-11)。
z:表示时区
示例:
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();System.out.println(cal);System.out.println(cal.getTime());SimpleDateFormat sdf =new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");/*SimpleDateFormat: 格式化Date---->StringString ------->Date*/
// Date date = cal.getTime();
// //SimpleDateFormat sdf =new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
// String str = sdf.format(date);
// System.out.println("str:"+str);
//
// System.out.println(sdf.format(date));
//
// String dateStr = "2019-12-02";
// try {
// Date dateFromStr = sdf.parse(dateStr);
// System.out.println("dateFromStr:"+dateFromStr);
// } catch (ParseException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }/*获取日期时间常用的6个值:*/System.out.println("年:"+cal.get(Calendar.YEAR));System.out.println("月:"+cal.get(Calendar.MONTH));//System.out.println("日:"+cal.get(Calendar.DATE));System.out.println("日:"+cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));System.out.println("时:"+cal.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY));System.out.println("时:"+cal.get(Calendar.HOUR));//12小时制的System.out.println("分:"+cal.get(Calendar.MINUTE));System.out.println("秒:"+cal.get(Calendar.SECOND));/*设置日期*/cal.set(2019,12,2,12,12,10);System.out.println(cal.getTime());//单独每个字段设置 或者6个字段分别进行设置,由于月份下标从0开始赋值月份要-1cal.set(Calendar.YEAR,2018);//年cal.set(Calendar.MONTH,Calendar.NOVEMBER);//月cal.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,12);//日cal.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY,23);//时,24小时cal.set(Calendar.MINUTE,23);//分cal.set(Calendar.SECOND,23);//秒System.out.println("设置日期后输出:"+sdf.format(cal.getTime()));//把月份+1;,或者-1cal.add(Calendar.MONTH,-1);System.out.println("设置日期后输出:"+sdf.format(cal.getTime()));
五、BigDecimal
为什么使用BigDecimal?
很多实际应用中需要精确计算,而double是近似值存储,不再符合要求,需要借助BigDecimal。
double d1 = 1.0;
double d2 = 0.9;
System.out.println(d1-d2);
BigDeicmal基本用法
位置:java.math包中。
作用:精确计算浮点数。
创建方式:BigDecimal bd=new BigDecimal(“1.0”)。
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BigDecimal add(BigDecimal bd) | 加 |
| BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal bd) | 减 |
| BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal bd) | 乘 |
| BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal bd) | 除 |
除法:divide(BigDecimal bd,int scal,RoundingMode mode)。
参数scale :指定精确到小数点后几位。
参数mode :
指定小数部分的取舍模式,通常采用四舍五入的模式。
取值为BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP。
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {double d1=1.0;double d2=0.9;System.out.println(d1-d2);//面试题double result=(1.4-0.5)/0.9;System.out.println(result);//BigDecimal,大的浮点数精确计算BigDecimal bd1=new BigDecimal("1.0");BigDecimal bd2=new BigDecimal("0.9");//减法BigDecimal r1=bd1.subtract(bd2);System.out.println(r1);//加法BigDecimal r2=bd1.add(bd2);System.out.println(r2);//乘法BigDecimal r3=bd1.multiply(bd2);System.out.println(r3);//除法BigDecimal r4=new BigDecimal("1.4").subtract(new BigDecimal("0.5")).divide(new BigDecimal("0.9"));System.out.println(r4);BigDecimal r5=new BigDecimal("20").divide(new BigDecimal("3"),2,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);System.out.println(r5);}
}
六、System
System系统类,主要用于获取系统的属性数据和其他操作。
常用方法:
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static void arraycopy(…) | 复制数组 |
| static long currentTimeMillis() | 获取当前系统时间,返回的是毫秒值 |
| static void gc(); | 建议JVM赶快启动垃圾回收器回收垃圾 |
| static void exit(int status) | 退出jvm,如果参数是0表示正常退出jvm,非0表示异常退出jvm。 |
示例:
public class TestSystem {public static void main(String[] args) {//1 arraycopy:数组的复制//src:源数组//srcPos:从那个位置开始复制 0//dest:目标数组//destPos:目标数组的位置//length:复制的长度int[] arr= {20,18,15,8,35,26,45,90};int[] dest=new int[8];System.arraycopy(arr, 4, dest, 4, 4);for(int i=0;i<dest.length;i++) {System.out.println(dest[i]);}//Arrays.copyOf(original, newLength)System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());long start=System.currentTimeMillis();for(int i=-9999999;i<99999999;i++) {for(int j=-999999;j<9999999;j++) {int result=i+j;}}//2 获取毫秒数long end=System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("用时:"+(end-start));new Student("aaa", 19);new Student("bbb", 19);new Student("ccc", 19);//3回收垃圾System.gc();//告诉垃圾回收期回收//4推出jvmSystem.exit(0);System.out.println("程序结束了....");}
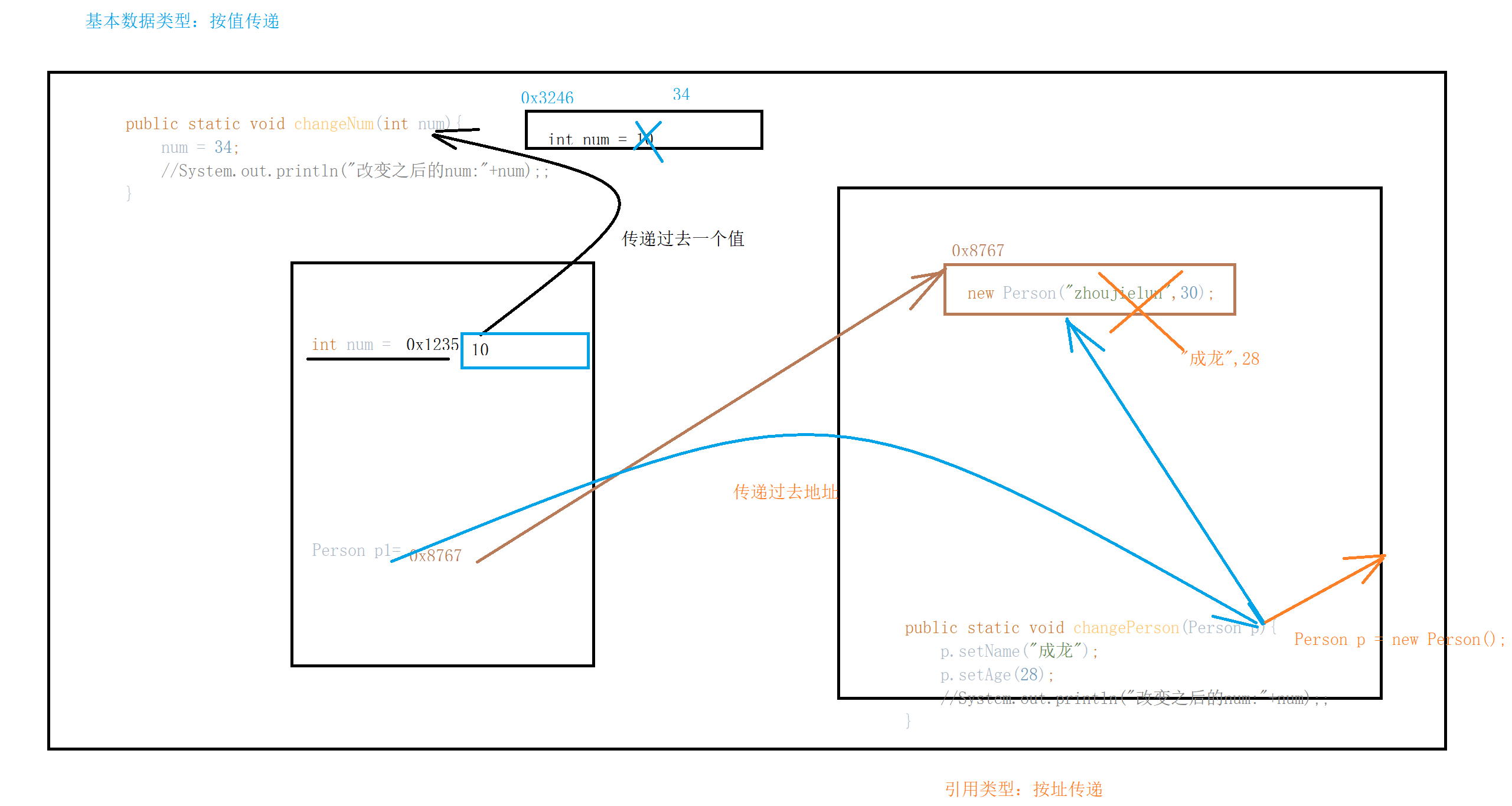
}七、对象内存分析
按值传递
按址传递
class Person{int age;String name;public Person(String name,int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}public void eat(){System.out.println("吃东西。。");}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"age=" + age +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}
}public class Demo {public static void test(int i){System.out.println(i);i = 100;System.out.println(i);}public static void test2(Person person){person.setName("wowo");}public static void main(String[] args) {Person p1 = new Person("王二狗",5);Person p2 = new Person("李晓华",12);Person p3 = p1;System.out.println(p1);System.out.println(p2);System.out.println(p3);test2(p3);System.out.println(p3);System.out.println(p1);int a = 5;test(a);System.out.println(a);}
}

![P1017 [NOIP2000 提高组] 进制转换](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5492d6e2a39d48e0b73e8fdfa246f0ad.png)





![[NISACTF 2022]popchains - 反序列化+伪协议](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/bdc25a942cea4657b389febe43930bcc.png#pic_center)