今天我们来分析Spring中AOP的源码,主要是关于SpringAOP是如何发挥作用的。
前期准备
首先我们需要有一个Spring AOP项目,添加好了SpringAOP的依赖。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>6.0.2</version></dependency><!--spring aop依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId><version>6.0.2</version></dependency><!--spring aspects依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId><version>6.0.2</version></dependency>
开始分析
首先我们肯定是需要先定义一个我们启动类,这里我采用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext来进行测试,当然还需要一个AppConfig。
@ComponentScan("com.zly.aop.learn")
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {我这里主要是为了扫包而已,然后使用Aop还得开启EnableAspectJAutoProxy,这个就和我们在以往的xml开启aop:aspectj-autoproxy是一样的作用,这里也支持xml的所有配置。
切面的定义
关于切面的定义和对应的通知,我就不再解释了,实在不了解可以看我之前写的博客或者去网上进行了解。
@Component
@Aspect
public class AopAspect {/*** 设置切入点和通知类型* 切入点表达式 execution(访问修饰符 返回值类型 方法所在类的全路径 方法名 参数列表* 通知类型:* 前置@Before* 返回@AfterReturning* 异常@AfterThrowing* 后置@After* 环绕@Around()*/@Before(value = "pointCut()")public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();System.out.println("Logger-->前置通知,方法名称:" + methodName + "参数:" + Arrays.toString(args));}@After(value = "pointCut()")public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("Logger-->后置通知,方法名称:" + methodName);}@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()", returning = "result")public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("Logger-->返回前置通知,方法名称:" + methodName + "返回值:" + result.toString());}@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut())", throwing = "exception")public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable exception) {String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();System.out.println("Logger-->异常通知,方法名称:" + methodName + "异常:" + exception.toString());}@Around(value = "pointCut()")public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();String argsString = joinPoint.getArgs().toString();Object result = null;try {System.out.println("环绕通知");// 调用目标方法result = joinPoint.proceed();System.out.println("环绕通知==目标方法返回值之后");} catch (Throwable ex) {System.out.println("环绕通知==目标方法出现异常之后");} finally {System.out.println("环绕通知==目标方法执行完毕");}return result;}/*** 重用切入点表达式*/@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.zly.aop.learn.service.*.*(..))")public void pointCut() {}
}业务类
这里我们先以有实现接口为示例:
public interface UserService {void add(String name);
}@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {@Overridepublic void add(String name) {System.out.println("add ===>" + name);}
}关于Spring的动态代理,我们知道有JDK的动态代理和CgLib的动态代理,那么我们的对象是在Bean生命周期中的那个阶段被代理的呢?或者说,我们SpringAOP的运行时织入还是初始化时就已经织入了呢?
对于后面的这个问题很好回答,我们可以跟下源码getBean方法,最后你会发现它最后是从singletonObjects中获取出来的,也就是我们常说的三级缓存。所以后面的这个问题就很好解答了,代理在ApplicationContext初始化时就已经创建完成了,然后再通过代码定位,我们就可以容易知道,这个对象是在下面的这个方法就已经添加入三级缓存了。
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);}}
源碼技巧:看堆栈,然后我们通过条件判断和堆栈定位到是在Bean生命周期中哪个方法
这里我已经找到了,是在org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean中
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {try {return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);}catch (BeansException ex) {// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.destroySingleton(beanName);throw ex;}});
然后跟进doCreateBean方法,我们可以看到下面这段代码,然后它是在initializeBean方法做的,我们也知道BeanPostProcessor的扩展
// Initialize the bean instance.Object exposedObject = bean;try {populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);}
其实它是通过AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator这个处理器来实现的,主要看applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法,然后会通过遍历BeanPostProcessor找到AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization方法,最后进入wrapIfNecessary方法。
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);Object wrappedBean = bean;if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);}try {invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException((mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);}if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);}return wrappedBean;}
跟进这个方法,我们可以看到通知最后都会被解析放到specificInterceptors中,其中主要逻辑在createProxy中。
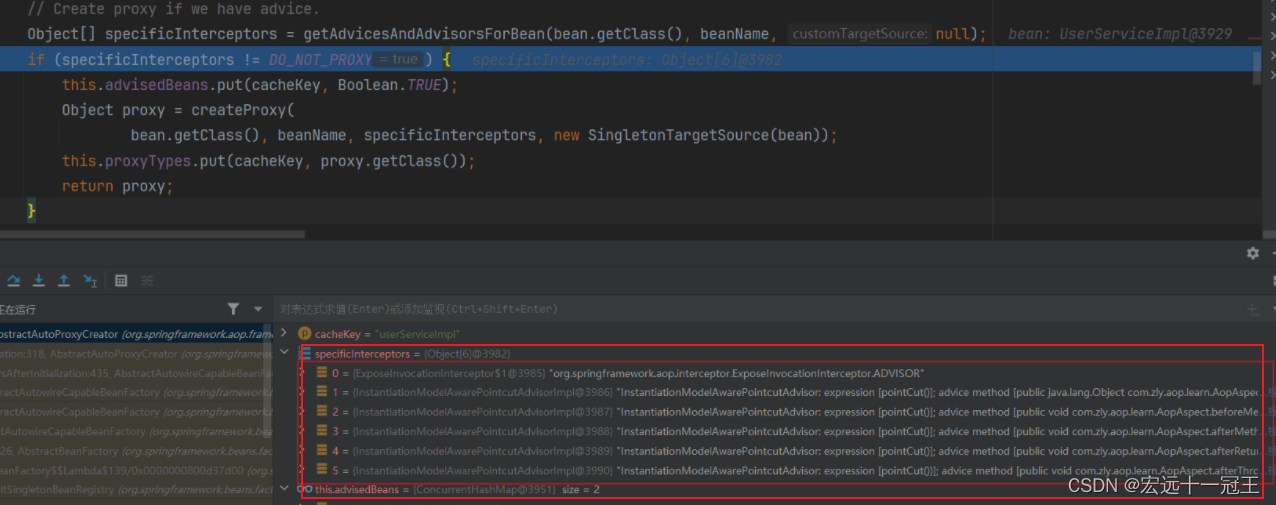
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {return bean;}if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {return bean;}if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return bean;}// Create proxy if we have advice.Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());return proxy;}this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return bean;}
然后跟进到AopFactory的创建时,主要是看这段代码,看到这里,相信就能理解为什么说提供了JDK代理和Cglib动态代理了。
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);}
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");}if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass) || ClassUtils.isLambdaClass(targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);}else {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}}再看getProxy方法,这里JDK动态代理和Cglib动态代理分别是自己实现的形式。
JDK 可以看到是通过Proxy来实现的。
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, this.proxiedInterfaces, this);}
Cglib
private Object buildProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader, boolean classOnly) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}try {Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);}}// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();if (classLoader != null) {enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {enhancer.setUseCache(false);}}enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);enhancer.setAttemptLoad(true);enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();}// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call aboveenhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.return (classOnly ? createProxyClass(enhancer) : createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks));}catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",ex);}catch (Throwable ex) {// TargetSource.getTarget() failedthrow new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);}}
当然在Spring中,我们是可以指定使用Cglib动态代理的(通过设置proxyTargetClass),但是JDK动态代理要求代理类是一定要实现接口的,但是为什么呢?我想应该和Java不支持多继承有关,具体还是留给大家自己思考吧。
总结
今天主要分享了Spring中AOP机制的作用原理和具体作用位置,提供了哪些动态代理方式,上面主要是我学习时留下的笔记,如果有哪些流程和写的不清楚,欢迎大致指正。




![[Leetcode] 0108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9c970c6c3847ede3a76b5d6faa682f47.png)