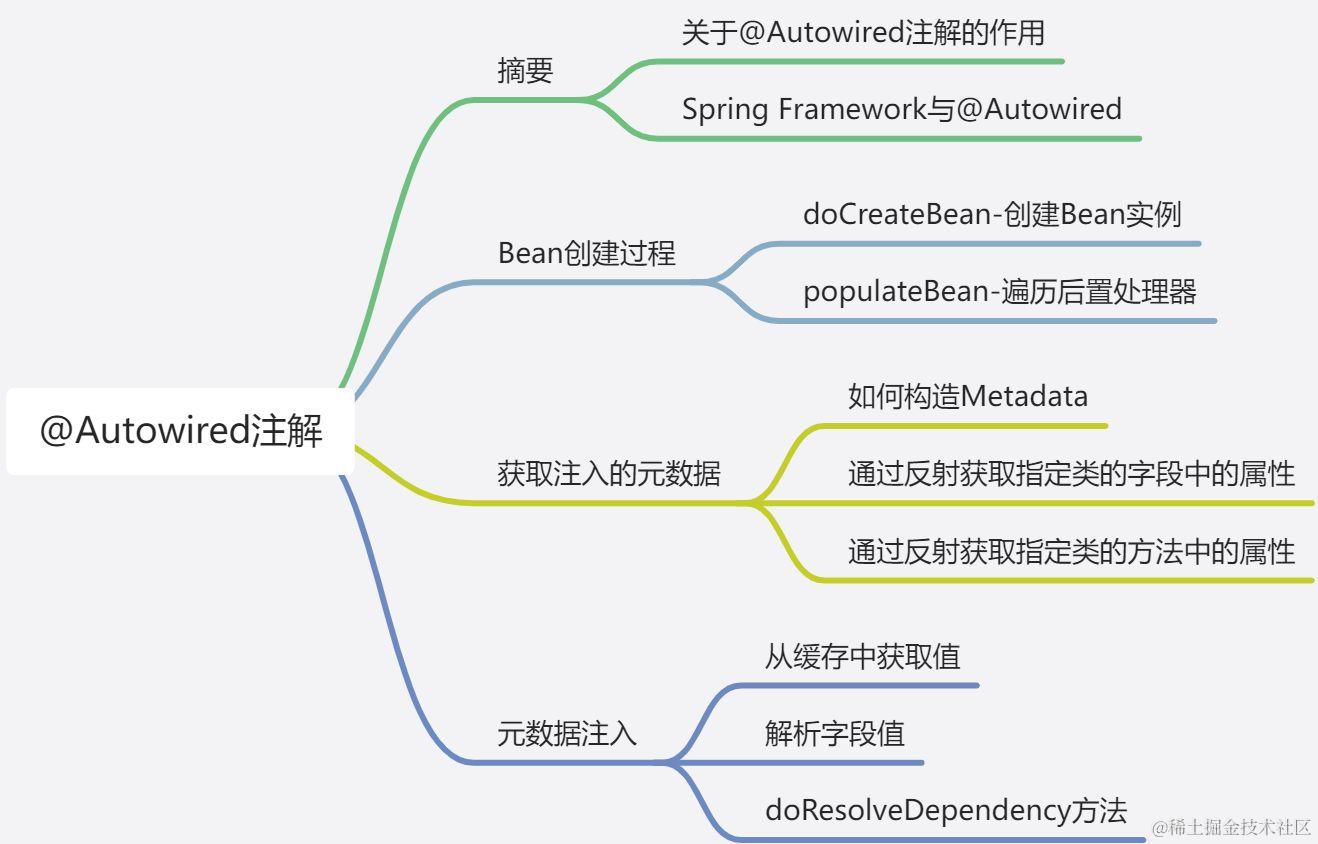
摘要
关于@Autowired注解的作用
@Autowired 注解在Spring中的作用是实现依赖注入(Dependency Injection),它用于自动装配(autowiring)Spring Bean 的依赖关系。具体来说, @Autowired 注解有以下作用:
- 自动装配依赖:通过在类的字段、构造函数、方法参数等地方使用 @Autowired 注解,Spring 容器会自动识别需要注入的依赖,并将适当的 Bean 实例注入到目标组件中。
- 减少手动配置:使用 @Autowired 注解可以减少手动配置依赖关系的工作,因为它会自动发现并管理组件之间的依赖关系,从而降低了配置的复杂性。
- 提高可维护性: @Autowired 注解明确地标识了类的依赖关系,使代码更易于理解和维护,因为它清晰地表达了组件之间的关联。
- 解耦:通过将依赖项的注入交给 Spring 容器处理,实现了松散耦合,使组件更容易替换、扩展和测试,同时降低了组件之间的耦合度。
- 支持多种装配模式: @Autowired 提供了多种装配模式,包括按类型、按名称、按限定符(qualifier)等方式,以满足不同的装配需求。
Spring Framework与@Autowired
在Spring Framework框架中最重要的概念是IoC和DI,通过这两个特性可以实现对象间的依赖关系由框架管理,构造对象间的依赖关系,将依赖对象自动注入到需要它们的类中,在使用时无需手动创建或查找依赖对象,注入依赖关系主要有以下方法:
- 通过xml配置注入
- 通过@Autowired等注解注入
- 当前Spring Framework推荐的通过构造方法注入
无论何种注入方法,Spring都会获取该Bean配置的元数据(Bean定义和依赖关系),那么接下来我将从源码层面分析@Autowired注入依赖的过程。

Bean创建过程
doCreateBean-创建Bean实例
/*** Central method of this class: creates a bean instance,* populates the bean instance, applies post-processors, etc.* @see #doCreateBean*/@Overrideprotected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)throws BeanCreationException {//省略其他代码,展示主要流程try {Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Finished creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");}return beanInstance;}catch (BeanCreationException | ImplicitlyAppearedSingletonException ex) {// A previously detected exception with proper bean creation context already,// or illegal singleton state to be communicated up to DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.throw ex;}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Unexpected exception during bean creation", ex);}}
创建Bean方法的主要逻辑在doCreateBean中,Spring Framework通过doCreateBean创建指定Bean,在该方法中,其中通过populateBean()遍历对应后置处理器,即:一个被注解标注的类被注入到Spring容器时,首先会创建Bean对象,创建后调用populateBean方法以遍历后置处理器通过后置处理器获取到需要的value,将@Autowired注解中的属性(元数据)赋值到Bean中。
populateBean-遍历后置处理器

// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the//InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors可以为@Autowired注解提供后置处理,// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,// to support styles of field injection.if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {//遍历所有相关后置处理器,获取需要的valuefor (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {return;}}}}
@Autowired注解所需的后置处理器是:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。接下来Spring容器开始使用该注解的后置处理器去获取对应的属性value,假设我们不知道@Autowired注解对应后置处理器的逻辑,那么根据这个需求来猜测后置处理器中的相关逻辑的方法名:需要带有处理、属性,那么对应的单词就是:Process、Properties,对应找一下,postProcessProperties()便是目标方法。
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {//根据BeanName获取注入的元数据InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);try {//元数据Value注入目标Bean中metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);}catch (BeanCreationException ex) {throw ex;}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);}return pvs;
}
获取注入的元数据
//用于缓存Spring解析过的Bean元数据
private final Map<String, InjectionMetadata> injectionMetadataCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());// 查询缓存中是否存在对应元数据-Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {if (metadata != null) {metadata.clear(pvs);}//当缓存中不存在指定Bean的MetaData时,构建MetaDatametadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);}}}return metadata;}
如何构造Metadata
Spring Framework通过buildAutowiringMetadata()方法解析注解中的数据。
//需要解析的注解结合
private final Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> autowiredAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
/*** Create a new {@code AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor} for Spring's* standard {@link Autowired @Autowired} and {@link Value @Value} annotations.* <p>Also supports JSR-330's {@link javax.inject.Inject @Inject} annotation,* if available.* 为 Spring 的标准@Autowired和@Value注释创建一个新的AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);try {this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));logger.trace("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");}catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.}}
这段代码首先会调用 isCandidateClass 方法判断当前类是否为一个候选类,判断的依据就是 类、属性、方法上是否包含autowiredAnnotationTypes 集合中初始化的值(@Autowired、@Value、@Inject),当Bean的定义中包含集合中对应类型的注解时,被判定为候选类,再去获取该类对应注解中的元数据。
如果Bean中没有没有指定类型的注解时,返回一个空的元数据注入对象。如果有指定注解,则开始获取注解中的元数据。
获取元数据的方式,是通过反射实现的。以下是通过反射获取类、属性、方法中对应注解的逻辑。
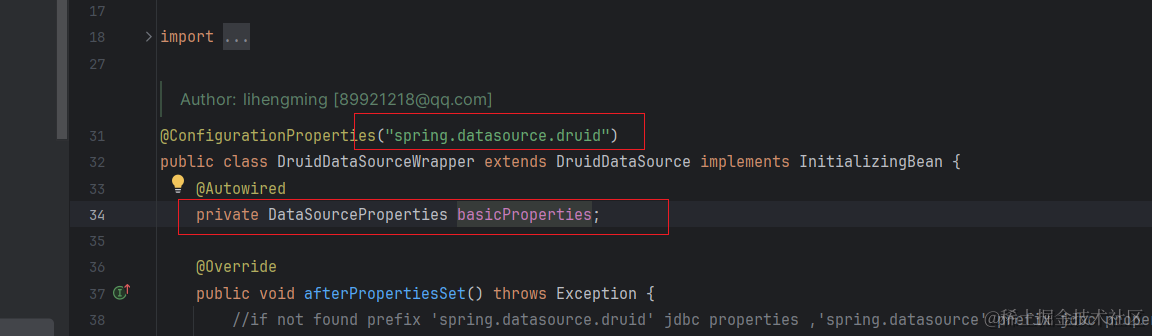
以DruidDataSourceWrapper为例:
通过反射获取指定类的字段中的属性
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;}List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();Class<?> targetClass = clazz;do {final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();//通过反射获取指定类的字段中的属性ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);if (ann != null) {if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);}return;}boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));}});}
以DruidDataSource为例
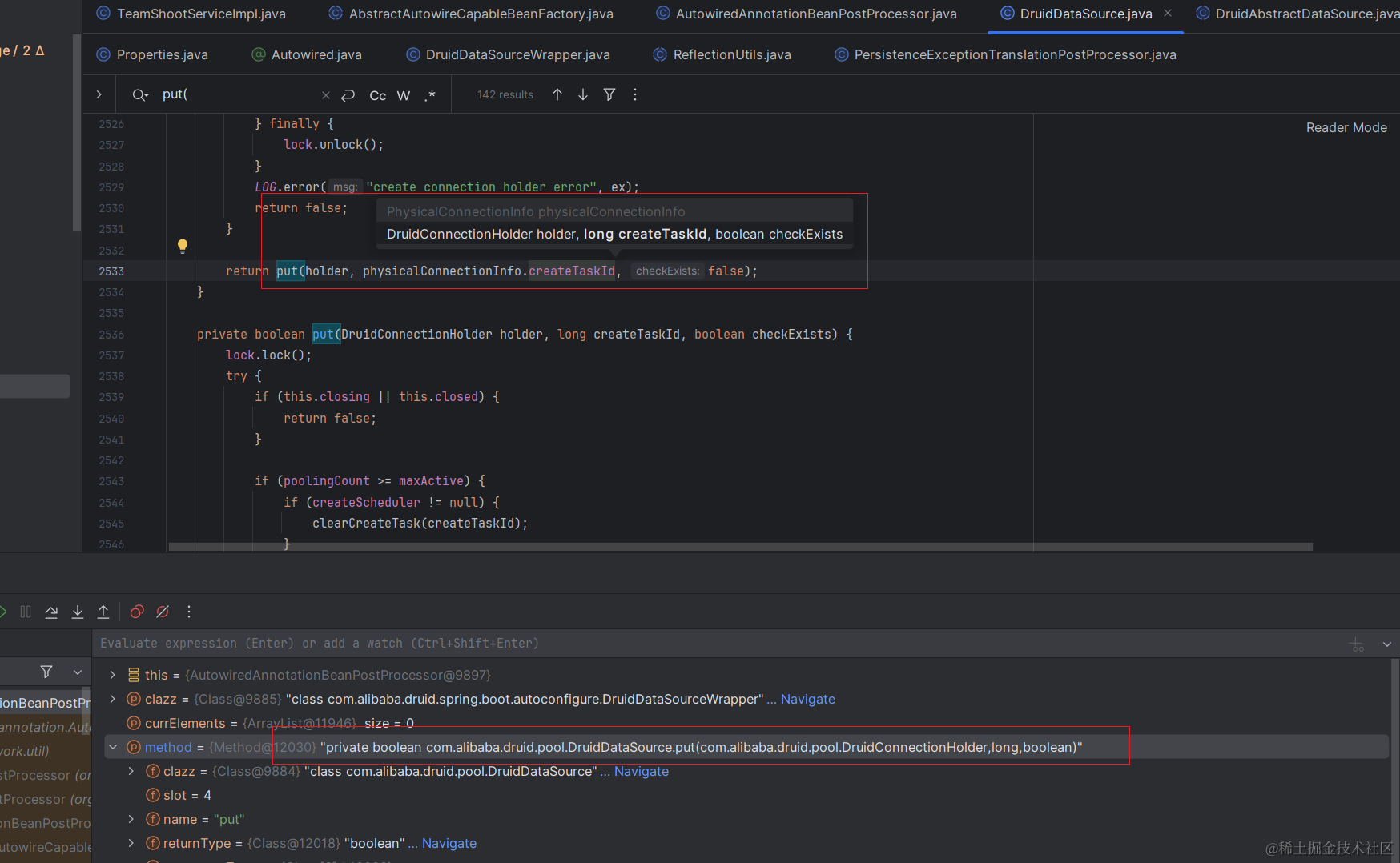
通过反射获取指定类的方法中的属性
//通过反射获取指定类的方法中的属性ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {return;}MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);}return;}if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +method);}}boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));}});

元数据注入
从缓存中获取值
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类中的inject方法用来注入元数据。
该方法会首先从缓存中获取元数据,如果缓存中没有,则执行resolvedCachedArgument解析字段值。
@Overrideprotected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {Field field = (Field) this.member;Object value;if (this.cached) {try {value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);}catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {// Unexpected removal of target bean for cached argument -> re-resolvevalue = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);}}else {value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);}if (value != null) {ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);field.set(bean, value);}}
解析字段值
@Nullable
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;@Nullableprivate Object resolveFieldValue(Field field, Object bean, @Nullable String beanName) {DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();Object value;try {//解析核心方法value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);}catch (BeansException ex) {throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);}synchronized (this) {if (!this.cached) {Object cachedFieldValue = null;if (value != null || this.required) {cachedFieldValue = desc;registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());}}}this.cachedFieldValue = cachedFieldValue;this.cached = true;}}return value;}
DependencyDescriptor:表示和处理Bean之间的依赖关系。
resolveDependency方法是接口BeanFactory接口提供的,DefaultListableBeanFactory是BeanFactory的一个实现类。
resolveDependency方法用于解析和解决依赖关系,该方法的作用是根据给定的 DependencyDescriptor 对象,解析并返回不同类型的依赖对象,当前方法最终会走doResolveDependency。
@Override
@Nullable
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer());if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {return createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);}else if (ObjectFactory.class == descriptor.getDependencyType() ||ObjectProvider.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {return new DependencyObjectProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);}else if (javaxInjectProviderClass == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {return new Jsr330Factory().createDependencyProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);}else {Object result = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(descriptor, requestingBeanName);if (result == null) {result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);}return result;}
}
doResolveDependency方法
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);if (multipleBeans != null) {return multipleBeans;}Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {if (isRequired(descriptor)) {raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);}return null;}String autowiredBeanName;Object instanceCandidate;if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);if (autowiredBeanName == null) {if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);}else {// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).return null;}}instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);}else {// We have exactly one match.Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();}if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);}if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);}Object result = instanceCandidate;if (result instanceof NullBean) {if (isRequired(descriptor)) {raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);}result = null;}if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());}return result;}finally {ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);}
- resolveMultipleBean:见名知意, 解析多个Bean,在注入时,当前类中能有不同类型的Bean,如Bean、数组、集合、Map等,该方法针对不同类型的Bean查找返回。
- findAutowireCandidates:查找满足条件的Bean,该方法查找出来的Bean可能有一个或多个。
以上,完成了满足条件的候选对象列表并注入。
关于我
👋🏻你好,我是Debug.c。微信公众号:种颗代码技术树 的维护者,一个跨专业自学Java,对技术保持热爱的bug猿,同样也是在某二线城市打拼四年余的Java Coder。
🏆在掘金、CSDN、公众号我将分享我最近学习的内容、踩过的坑以及自己对技术的理解。
📞如果您对我感兴趣,请联系我。