文章目录
- 前言
- 实例
- 导入库
- application.yaml
- Runner
- SpringBootCommandLineRunnerApplication
- 执行结果
- 先后顺序示例
- OrderRunner1
- OrderRunner2
- 执行结果
- 通常用法
- 加载初始化数据
- 示例
- 启动后打印应用信息
- 示例
- 启动异步任务
- 示例
- 接口健康检查
- 示例
- 外部服务调用
- 示例
- 参数校验
- 示例
- 动态设置配置
- 示例
- application.yaml
- MyConfig
- ConfigRunner
- 启动阻塞
- 总结
- 源码获取
- 写在最后

前言
Spring Boot的CommandLineRunner接口是一个函数式接口,用于在Spring Boot应用程序启动后执行一些初始化操作。它提供了一个run方法,该方法在应用程序启动后被调用。
使用CommandLineRunner接口,可以在应用程序启动后执行一些必要的初始化操作,例如加载配置文件、初始化数据库连接、创建默认数据等。可以通过实现CommandLineRunner接口,并重写run方法来定义自己的初始化逻辑。
实例
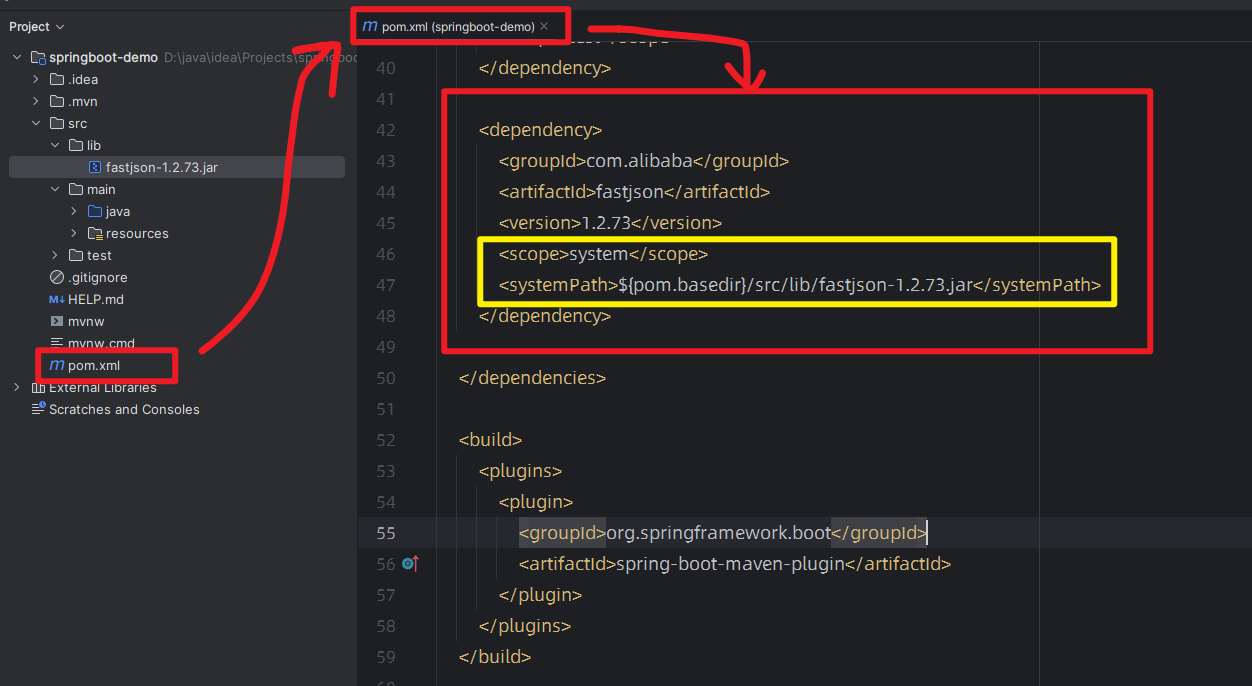
导入库
<parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>3.1.0</version>
</parent><groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-CommandLineRunner</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><name>Spring Boot banner</name>
<description>Spring Boot and commandLineRunner</description><properties><maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target><project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId><artifactId>lombok</artifactId></dependency>
</dependencies>
application.yaml
server:port: 8080spring:profiles:active: dev
Runner
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Slf4j
public class Runner implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {log.info("The Runner start to initialize ...");}
}
SpringBootCommandLineRunnerApplication
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
public class SpringBootCommandLineRunnerApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(SpringBootCommandLineRunnerApplication.class, args);log.info("The service to end");}
}
执行结果
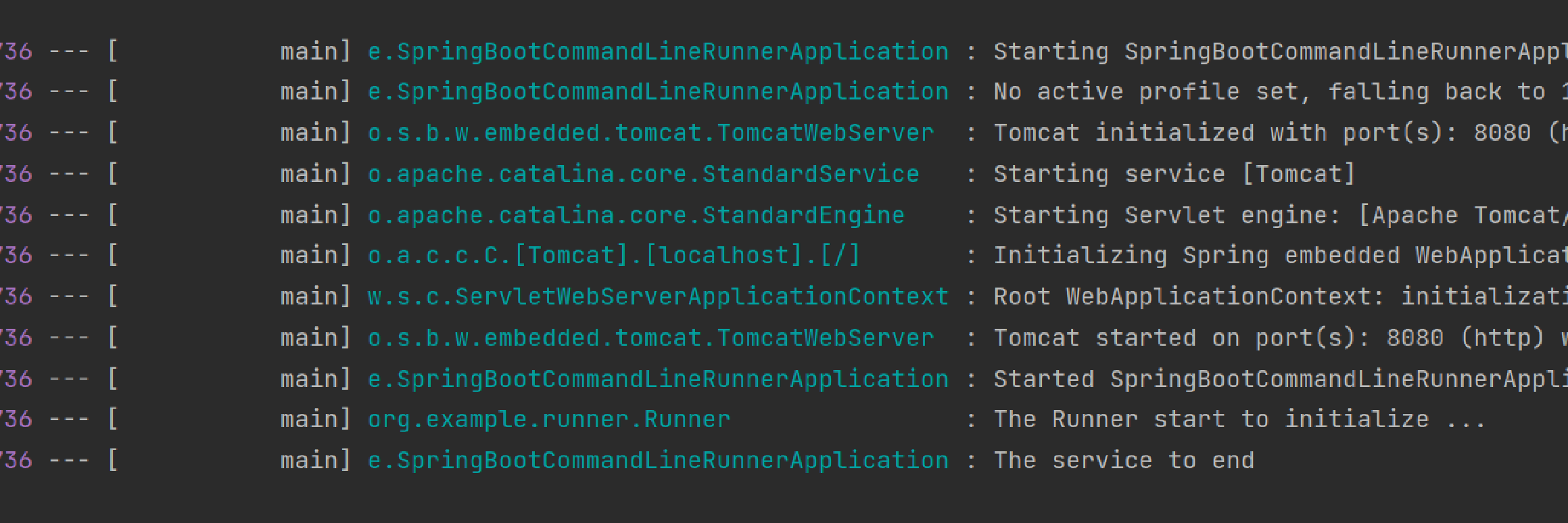
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个名为MyCommandLineRunner的类,并实现了CommandLineRunner接口。在run方法中,我们可以编写需要在应用程序启动后执行的初始化逻辑。
需要注意的是,实现CommandLineRunner接口的类需要被Spring容器扫描到,可以使用@Component注解或其他方式将其注册为Spring Bean。
先后顺序示例
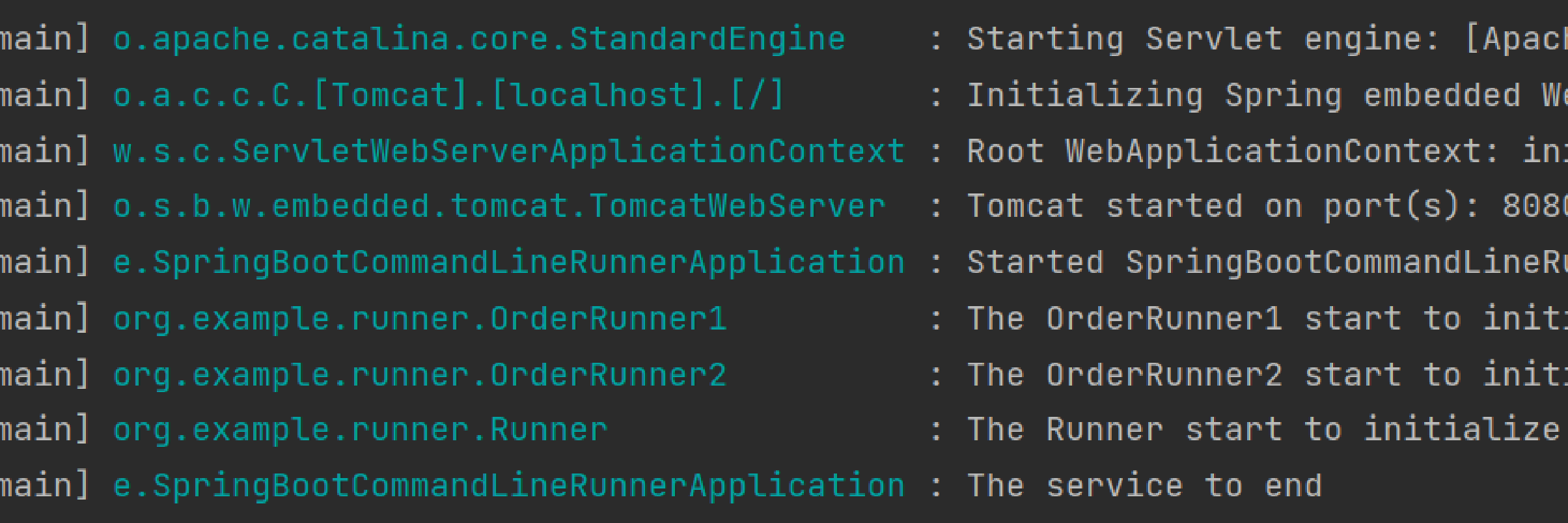
可以通过@Order()来设置Runner的先后顺序,在上面例子的基础上增加
OrderRunner1
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Order(1)
@Slf4j
public class OrderRunner1 implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {log.info("The OrderRunner1 start to initialize ...");}
}
OrderRunner2
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component
@Order(2)
@Slf4j
public class OrderRunner2 implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {log.info("The OrderRunner2 start to initialize ...");}
}
执行结果
通常用法
加载初始化数据
可以实现CommandLineRunner接口,在run方法中加载一些初始化数据到数据库等。适合做一些数据预加载工作。
示例
@Component
public class DataInitializer implements CommandLineRunner {@Autowiredprivate UserRepository userRepository;@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {// 创建初始用户User admin = new User("admin", "123456");userRepository.save(admin);User normalUser = new User("user", "123456");userRepository.save(normalUser);System.out.println("数据加载完毕!");}
}
这里创建了一个 DataInitializer 类,实现 CommandLineRunner 接口。在 run() 方法中,我们注入了 UserRepository,然后创建了两个用户对象保存到数据库中。这个类会在 Spring Boot 应用启动完成后执行,从而实现了数据预加载的效果。通过 CommandLineRunner,我们可以灵活地在 Spring Boot 启动时进行一些初始化操作,如预先加载测试数据、插入管理员账户等,很好地增强了应用的功能。
假设我们有一个User模型和用户Repository,需要在Spring Boot启动时预加载几个用户数据,可以这样使用CommandLineRunner:
@Component
public class DataInitializer implements CommandLineRunner {@Autowiredprivate UserRepository userRepository;@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {// 清除所有数据userRepository.deleteAll(); // 创建几个用户User user1 = new User("John", "john@example.com");User user2 = new User("Mary", "mary@example.com");userRepository.save(user1);userRepository.save(user2);// 打印已保存用户数System.out.println("Number of users saved: " + userRepository.count());}}
这里我们实现了CommandLineRunner接口,然后注入UserRepository bean。在run方法中,首先清空所有数据,然后创建两个用户对象并保存,最后打印已保存的用户数。这样在Spring Boot应用启动完成后,就会自动执行run方法,预加载指定的用户数据。
启动后打印应用信息
可以打印出一些应用启动信息,如启动端口、运行环境信息等,用于确认应用配置。
示例
@Component
@Slf4j
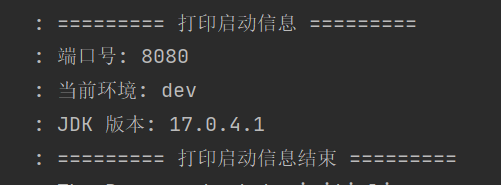
public class AppInfoPrinter implements CommandLineRunner {@Autowiredprivate Environment environment;@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {log.info("========= 打印启动信息 =========");// 打印应用端口log.info(("端口号: " + environment.getProperty("server.port")));// 打印当前环境log.info("当前环境: " + environment.getProperty("spring.profiles.active"));// 打印JDK版本log.info("JDK 版本: " + System.getProperty("java.version"));log.info("========= 打印启动信息结束 =========");}}
执行打印结果
启动异步任务
可以使用多线程启动一些异步任务,进行后台数据处理等复杂业务逻辑。
示例
@Component
@Slf4j
public class AsyncTaskRunner implements CommandLineRunner {@Autowiredprivate AsyncTaskService asyncTaskService;@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {log.info("========= 执行任务 =========");// 在新线程中执行任务new Thread(() -> {asyncTaskService.doTaskOne();asyncTaskService.doTaskTwo();asyncTaskService.doTaskThree();}).start();}}@Service
@Slf4j
class AsyncTaskService {public void doTaskOne() {log.info("执行任务1");}public void doTaskTwo() {log.info("执行任务2");}public void doTaskThree() {log.info("执行任务3");}
}
执行结果
[ main] org.example.runner.AsyncTaskRunner : ========= 执行任务 =========
[ Thread-1] org.example.runner.AsyncTaskService : 执行任务1
[ Thread-1] org.example.runner.AsyncTaskService : 执行任务2
[ Thread-1] org.example.runner.AsyncTaskService : 执行任务3
接口健康检查
可以调用并验证依赖服务的健康状态,如果不正常可以终止Spring Boot启动。
示例
@Component
@Slf4j
public class HealthCheckRunner implements CommandLineRunner {@Autowiredprivate DatabaseService databaseService;@Autowiredprivate MessageQueueService messageQueueService;@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {if(!databaseService.isConnected()) {log.error("数据库服务不可用,退出应用!");System.exit(1);}if(!messageQueueService.isConnected()) {log.error("消息队列服务不可用,退出应用!");System.exit(1);}log.info("所有服务正常,应用启动。");}
}
这里我们注入两个依赖服务 DatabaseService 和 MessageQueueService。在run方法中,调用它们的健康检查方法,如果任何一个服务不可用,则直接调用System.exit(1)退出Spring Boot应用启动。
外部服务调用
可以在启动时调用外部服务,进行验证、数据同步等操作。
示例
@Component
public class OtherServiceCheckRunner implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {// 健康检查的URLString healthCheckUrl = "http://localhost:8080/actuator/health";RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();// 发送GET请求进行健康检查String response = restTemplate.getForObject(healthCheckUrl, String.class);// 根据响应判断健康状态if (response.contains("\"status\":\"UP\"")) {System.out.println("Application is healthy");} else {System.out.println("Application is not healthy");}}
}
参数校验
可以对输入的运行参数做校验,如果不满足条件可以终止Spring Boot启动。
示例
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ParameterValidator implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {// 校验参数1if(args.length < 2) {log.error("参数不正确,请传入至少2个参数!");System.exit(1);}// 校验参数2是否为数字if(!args[1].matches("\\d+")) {log.error("第二个参数必须是数字!");System.exit(1);}// 校验通过,应用继续启动log.info("参数校验通过,应用启动中...");}
}
在run方法中,我们可以对main方法输入的参数args进行自定义校验:
- 检查参数数量
- 校验参数类型
如果参数不满足需求,可以直接调用System.exit(1)来终止Spring Boot的启动。这样就可以在应用启动前验证参数的正确性,避免应用启动后发生未知错误。
动态设置配置
可以根据运行参数等条件动态设置Spring Boot的配置,实现不同环境的适配。
示例
application.yaml
myconfig:foo: 十五bar: 1
MyConfig
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "myconfig")
public class MyConfig {private String foo;private int bar;// getter和setter方法省略@Overridepublic String toString() {return "MyConfig{" +"foo='" + foo + '\'' +", bar=" + bar +'}';}
}
ConfigRunner
@Component
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MyConfig.class)
public class ConfigRunner implements CommandLineRunner {@Autowiredprivate MyConfig myConfig;@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// 打印当前配置System.out.println("Current config: " + myConfig);// 动态设置配置myConfig.setFoo("new value");myConfig.setBar(100);// 打印更新后的配置System.out.println("Updated config: " + myConfig);}
}
启动阻塞
可以使应用启动后阻塞住主线程,防止main方法直接退出,从而保持Spring Boot应用运行。
示例
@Component
@Slf4j
public class StartBlocker implements CommandLineRunner {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {// 加载提示信息log.info("正在等待管理员授权...");// 等待授权,阻塞启动流程waitAuth();// 授权完成后继续启动log.info("管理员已授权,应用启动中...");}private void waitAuth() {// 死循环模拟等待管理员操作授权while(true) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {break;}}}}
总结
通过 CommandLineRunner,我们可以深度控制 Spring Boot 应用的启动流程,在应用启动阶段增强各种自定义逻辑。是 Spring Boot 提供的一个很实用的扩展点。
源码获取
如果需要完整源码请关注公众号"架构殿堂" ,回复 "SpringBoot+CommandLineRunner"即可获得
写在最后
感谢您的支持和鼓励! 😊🙏
如果大家对相关文章感兴趣,可以关注公众号"架构殿堂",会持续更新AIGC,java基础面试题, netty, spring boot, spring cloud等系列文章,一系列干货随时送达!