摘要
博文主要介绍二叉树的前/中/后/层遍历(递归与栈)方法
一、前/中/后/层遍历问题
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
二、二叉树遍历递归解析
// 前序遍历·递归·LC144_二叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();preorder(root, result);return result;}public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {if (root == null) {return;}result.add(root.val);preorder(root.left, result);preorder(root.right, result);}
}// 中序遍历·递归·LC94_二叉树的中序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();inorder(root, res);return res;}void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {if (root == null) {return;}inorder(root.left, list);list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句inorder(root.right, list);}
}// 后序遍历·递归·LC145_二叉树的后序遍历
class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();postorder(root, res);return res;}void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {if (root == null) {return;}postorder(root.left, list);postorder(root.right, list);list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句}
}
三、二叉树遍历栈解析

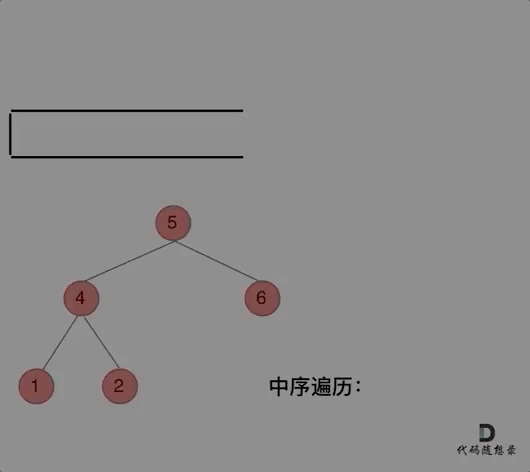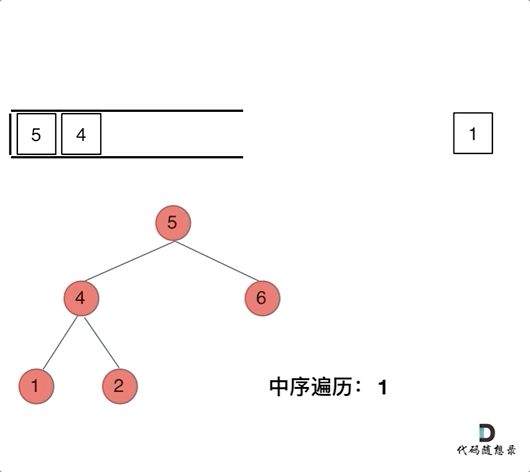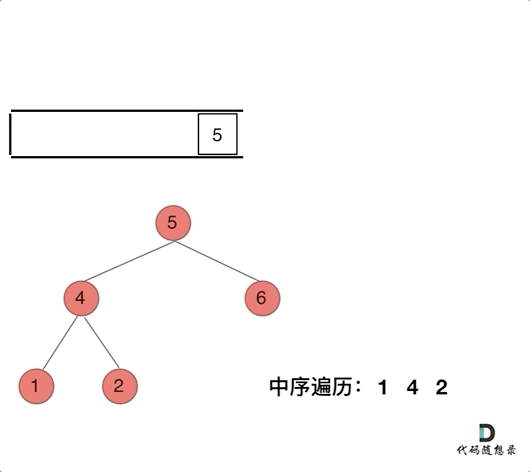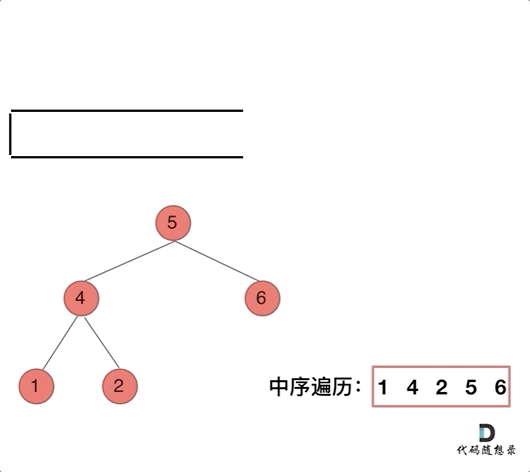

// 前序遍历顺序:中-左-右,入栈顺序:中-右-左
class Solution {public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null){return result;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.pop();result.add(node.val);if (node.right != null){stack.push(node.right);}if (node.left != null){stack.push(node.left);}}return result;}
}// 中序遍历顺序: 左-中-右 入栈顺序: 左-右
class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null){return result;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();TreeNode cur = root;while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){if (cur != null){stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}else{cur = stack.pop();result.add(cur.val);cur = cur.right;}}return result;}
}// 后序遍历顺序 左-右-中 入栈顺序:中-左-右 出栈顺序:中-右-左, 最后翻转结果
class Solution {public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null){return result;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()){TreeNode node = stack.pop();result.add(node.val);if (node.left != null){stack.push(node.left);}if (node.right != null){stack.push(node.right);}}Collections.reverse(result);return result;}
}
四、二叉树层序遍历解析
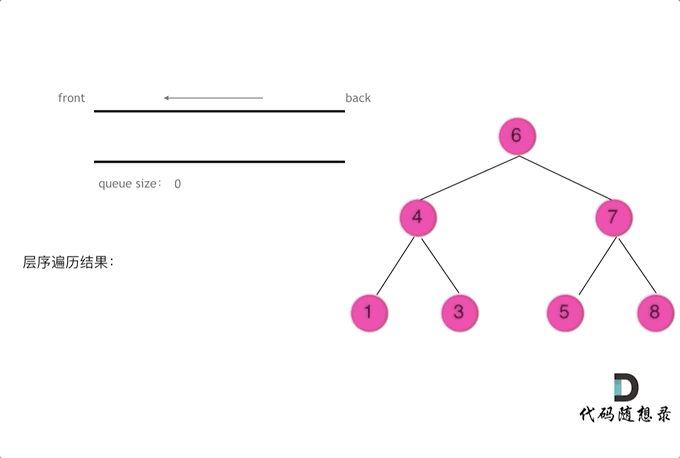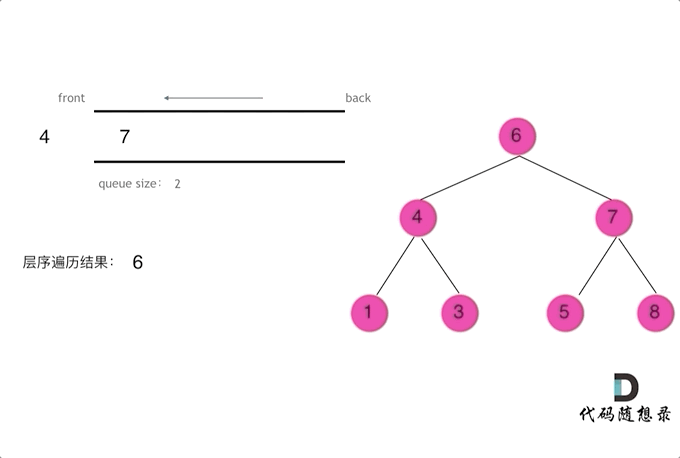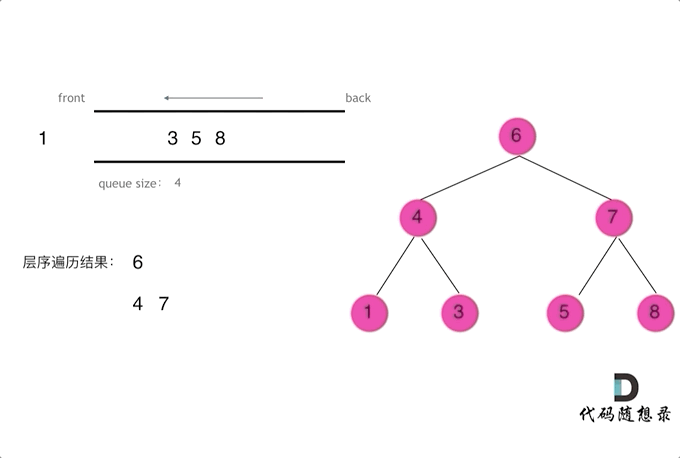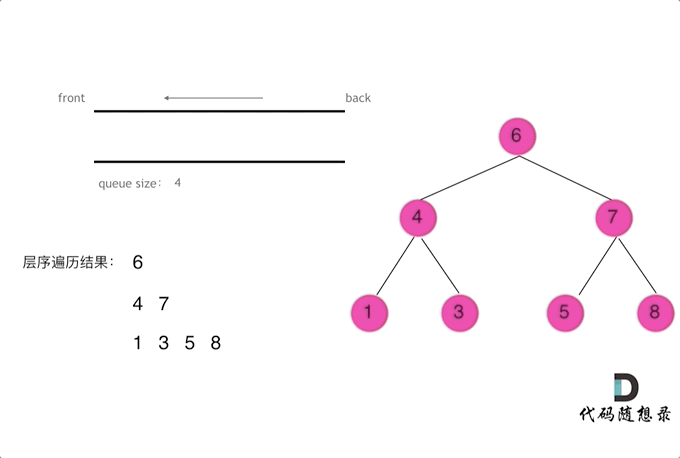
// 102.二叉树的层序遍历
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {//checkFun01(root,0);checkFun02(root);return resList;}public void checkFun02(TreeNode node) {if (node == null) return;Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();que.offer(node);while (!que.isEmpty()) {List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList<Integer>();int len = que.size();while (len > 0) {TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll();itemList.add(tmpNode.val);if (tmpNode.left != null) que.offer(tmpNode.left);if (tmpNode.right != null) que.offer(tmpNode.right);len--;}resList.add(itemList);}}
}
博文参考
《leetcode》