文章目录
- 0 前言
- 1 课题背景
- 2 实现效果
- 3 相关技术
- 3.1 YOLOV4
- 3.2 基于 DeepSort 算法的行人跟踪
- 4 最后
0 前言
🔥 优质竞赛项目系列,今天要分享的是
🚩 **基于深度学习疫情社交安全距离检测算法 **
该项目较为新颖,适合作为竞赛课题方向,学长非常推荐!
🥇学长这里给一个题目综合评分(每项满分5分)
- 难度系数:3分
- 工作量:3分
- 创新点:5分
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate
1 课题背景
安全的社交距离是公共预防传染病毒的途径之一。所以,在人群密集的区域进行社交距离的安全评估是十分重要的。社交距离的测量旨在保持个体之间的物理距离和减少相互接触的人群来减缓或阻止病毒传播,在抗击病毒和预防大流感中发挥重要作用。但时刻保持安全距离具有一定的难度,特别是在校园,工厂等场所,在这种情况下,开发智能摄像头等技术尤为关键。将人工智能,深度学习集成至安全摄像头对行人进行社交距离评估。现阶段针对疫情防范的要求,主要采用人工干预和计算机处理技术。人工干预存在人力资源要求高,风险大,时间成本高等等缺点。计算机处理等人工智能技术的发展,对社交安全距离的安全评估具有良好的效果。
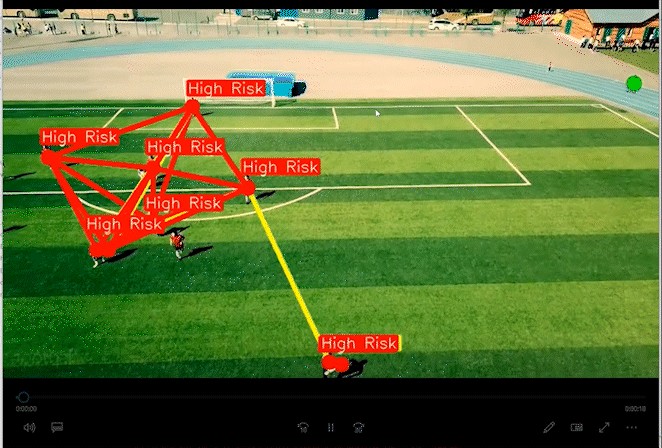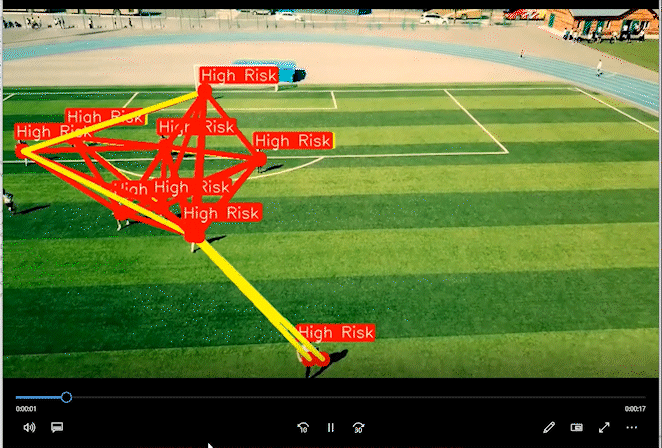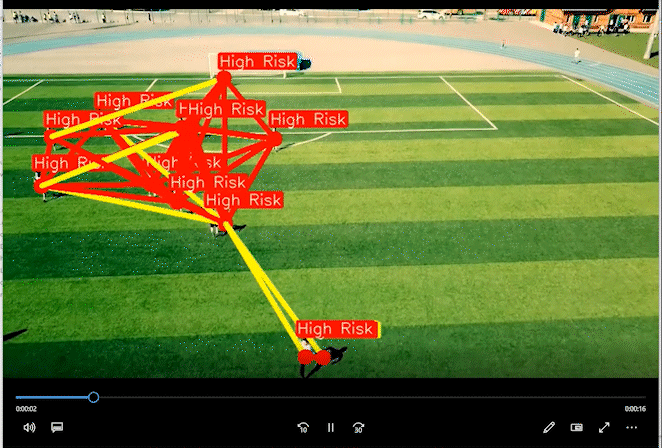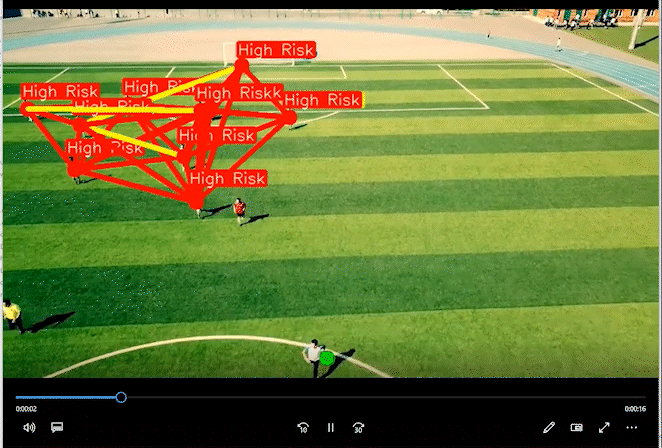
2 实现效果
通过距离分类人群的高危险和低危险距离。
相关代码
import argparse
from utils.datasets import *
from utils.utils import *def detect(save_img=False):out, source, weights, view_img, save_txt, imgsz = \opt.output, opt.source, opt.weights, opt.view_img, opt.save_txt, opt.img_sizewebcam = source == '0' or source.startswith('rtsp') or source.startswith('http') or source.endswith('.txt')# Initializedevice = torch_utils.select_device(opt.device)if os.path.exists(out):shutil.rmtree(out) # delete output folderos.makedirs(out) # make new output folderhalf = device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA# Load modelgoogle_utils.attempt_download(weights)model = torch.load(weights, map_location=device)['model'].float() # load to FP32# torch.save(torch.load(weights, map_location=device), weights) # update model if SourceChangeWarning# model.fuse()model.to(device).eval()if half:model.half() # to FP16# Second-stage classifierclassify = Falseif classify:modelc = torch_utils.load_classifier(name='resnet101', n=2) # initializemodelc.load_state_dict(torch.load('weights/resnet101.pt', map_location=device)['model']) # load weightsmodelc.to(device).eval()# Set Dataloadervid_path, vid_writer = None, Noneif webcam:view_img = Truetorch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inferencedataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz)else:save_img = Truedataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz)# Get names and colorsnames = model.names if hasattr(model, 'names') else model.modules.namescolors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(len(names))]# Run inferencet0 = time.time()img = torch.zeros((1, 3, imgsz, imgsz), device=device) # init img_ = model(img.half() if half else img) if device.type != 'cpu' else None # run oncefor path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset:img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0if img.ndimension() == 3:img = img.unsqueeze(0)# Inferencet1 = torch_utils.time_synchronized()pred = model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0]# Apply NMSpred = non_max_suppression(pred, opt.conf_thres, opt.iou_thres,fast=True, classes=opt.classes, agnostic=opt.agnostic_nms)t2 = torch_utils.time_synchronized()# Apply Classifierif classify:pred = apply_classifier(pred, modelc, img, im0s)# List to store bounding coordinates of peoplepeople_coords = []# Process detectionsfor i, det in enumerate(pred): # detections per imageif webcam: # batch_size >= 1p, s, im0 = path[i], '%g: ' % i, im0s[i].copy()else:p, s, im0 = path, '', im0ssave_path = str(Path(out) / Path(p).name)s += '%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:] # print stringgn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwhif det is not None and len(det):# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 sizedet[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()# Print resultsfor c in det[:, -1].unique():n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per classs += '%g %ss, ' % (n, names[int(c)]) # add to string# Write resultsfor *xyxy, conf, cls in det:if save_txt: # Write to filexywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywhwith open(save_path[:save_path.rfind('.')] + '.txt', 'a') as file:file.write(('%g ' * 5 + '\n') % (cls, *xywh)) # label formatif save_img or view_img: # Add bbox to imagelabel = '%s %.2f' % (names[int(cls)], conf)if label is not None:if (label.split())[0] == 'person':people_coords.append(xyxy)# plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, line_thickness=3)plot_dots_on_people(xyxy, im0)# Plot lines connecting peopledistancing(people_coords, im0, dist_thres_lim=(200,250))# Print time (inference + NMS)print('%sDone. (%.3fs)' % (s, t2 - t1))# Stream resultsif view_img:cv2.imshow(p, im0)if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quitraise StopIteration# Save results (image with detections)if save_img:if dataset.mode == 'images':cv2.imwrite(save_path, im0)else:if vid_path != save_path: # new videovid_path = save_pathif isinstance(vid_writer, cv2.VideoWriter):vid_writer.release() # release previous video writerfps = vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)w = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))h = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*opt.fourcc), fps, (w, h))vid_writer.write(im0)if save_txt or save_img:print('Results saved to %s' % os.getcwd() + os.sep + out)if platform == 'darwin': # MacOSos.system('open ' + save_path)print('Done. (%.3fs)' % (time.time() - t0))
3 相关技术
3.1 YOLOV4
YOLOv4使用卷积网络 CSPDarknet-53 特征提取,网络结构模型如图 2 所示。在每个 Darknet-53的残块行加上 CSP(Cross
Stage Partial)结构13,将基础层划分为两部分,再通过跨层次结构的特征融合进行合并。并采用 FPN( feature pyramid
networks)结构加强特征金字塔,最后用不同层的特征的高分辨率来提取不同尺度特征图进行对象检测。最终网络输出 3
个不同尺度的特征图,在三个不同尺度特征图上分别使用 3 个不同的先验框(anchors)进行预测识别,使得远近大小目标均能得到较好的检测。
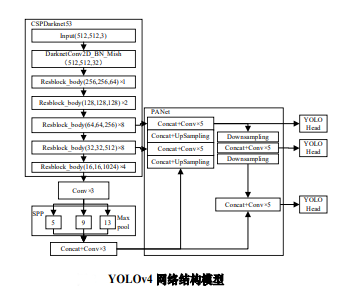
YOLOv4 的先验框尺寸是经PASCALL_VOC,COCO
数据集包含的种类复杂而生成的,并不一定完全适合行人。本研究旨在研究行人之间的社交距离,针对行人目标检测,利用聚类算法对 YOLOv4
的先验框微调,首先将行人数据集 F 依据相似性分为i个对象,即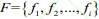 ,其中每个对象都具有 m
,其中每个对象都具有 m
个维度的属性。聚类算法的目的是 i 个对象依据相似性聚集到指定的 j 个类簇,每个对象属于且仅属于一个其到类簇中心距离最小的类簇中心。初始化 j 个 聚 类
中 心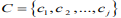 ,计算每一个对象到每一个聚类中心的欧式距离,见公式
,计算每一个对象到每一个聚类中心的欧式距离,见公式
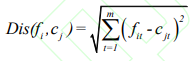
之后,依次比较每个对象到每个聚类中心的距离,将对象分配至距离最近的簇类中心的类簇中,
得到 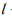 个类簇
个类簇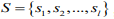 ,聚类算法中定义了类簇的原型,类簇中心就是类簇内所有对象在各个维度的均值,其公式见
,聚类算法中定义了类簇的原型,类簇中心就是类簇内所有对象在各个维度的均值,其公式见
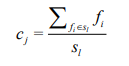
相关代码
def check_anchors(dataset, model, thr=4.0, imgsz=640):# Check anchor fit to data, recompute if necessaryprint('\nAnalyzing anchors... ', end='')m = model.module.model[-1] if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.model[-1] # Detect()shapes = imgsz * dataset.shapes / dataset.shapes.max(1, keepdims=True)wh = torch.tensor(np.concatenate([l[:, 3:5] * s for s, l in zip(shapes, dataset.labels)])).float() # whdef metric(k): # compute metricr = wh[:, None] / k[None]x = torch.min(r, 1. / r).min(2)[0] # ratio metricbest = x.max(1)[0] # best_xreturn (best > 1. / thr).float().mean() # best possible recallbpr = metric(m.anchor_grid.clone().cpu().view(-1, 2))print('Best Possible Recall (BPR) = %.4f' % bpr, end='')if bpr < 0.99: # threshold to recomputeprint('. Attempting to generate improved anchors, please wait...' % bpr)na = m.anchor_grid.numel() // 2 # number of anchorsnew_anchors = kmean_anchors(dataset, n=na, img_size=imgsz, thr=thr, gen=1000, verbose=False)new_bpr = metric(new_anchors.reshape(-1, 2))if new_bpr > bpr: # replace anchorsnew_anchors = torch.tensor(new_anchors, device=m.anchors.device).type_as(m.anchors)m.anchor_grid[:] = new_anchors.clone().view_as(m.anchor_grid) # for inferencem.anchors[:] = new_anchors.clone().view_as(m.anchors) / m.stride.to(m.anchors.device).view(-1, 1, 1) # lossprint('New anchors saved to model. Update model *.yaml to use these anchors in the future.')else:print('Original anchors better than new anchors. Proceeding with original anchors.')print('') # newline
3.2 基于 DeepSort 算法的行人跟踪
YOLOv4中完成行人目标检测后生成边界框(Bounding box,Bbox),Bbox 含有包含最小化行人边框矩形的坐标信息,本研究引入
DeepSort 算法[18]完成对行人的质点进行跟踪,目的是为了在运动矢量分析时算行人安全社交距离中。首先,对行人进行质点化计算。其质点计算公式如
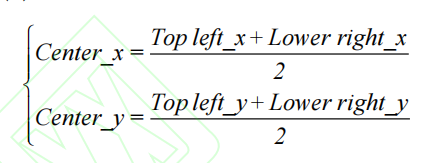
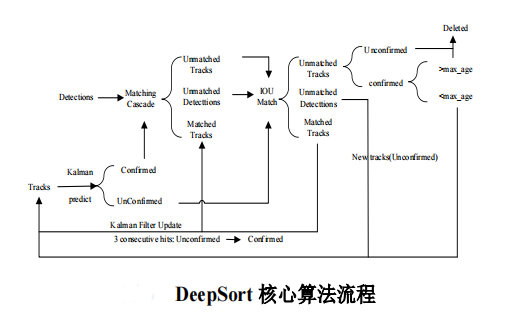
确定行人质点后,利用 DeepSort 算法实现对多个目标的精确定位与跟踪,其核心算法流程如图所示:
相关代码
class TrackState:'''单个轨迹的三种状态'''Tentative = 1 #不确定态Confirmed = 2 #确定态Deleted = 3 #删除态class Track:def __init__(self, mean, covariance, track_id, class_id, conf, n_init, max_age,feature=None):'''mean:位置、速度状态分布均值向量,维度(8×1)convariance:位置、速度状态分布方差矩阵,维度(8×8)track_id:轨迹IDclass_id:轨迹所属类别hits:轨迹更新次数(初始化为1),即轨迹与目标连续匹配成功次数age:轨迹连续存在的帧数(初始化为1),即轨迹出现到被删除的连续总帧数time_since_update:轨迹距离上次更新后的连续帧数(初始化为0),即轨迹与目标连续匹配失败次数state:轨迹状态features:轨迹所属目标的外观语义特征,轨迹匹配成功时添加当前帧的新外观语义特征conf:轨迹所属目标的置信度得分_n_init:轨迹状态由不确定态到确定态所需连续匹配成功的次数_max_age:轨迹状态由不确定态到删除态所需连续匹配失败的次数''' self.mean = meanself.covariance = covarianceself.track_id = track_idself.class_id = int(class_id)self.hits = 1self.age = 1self.time_since_update = 0self.state = TrackState.Tentativeself.features = []if feature is not None:self.features.append(feature) #若不为None,初始化外观语义特征self.conf = confself._n_init = n_initself._max_age = max_agedef increment_age(self):'''预测下一帧轨迹时调用'''self.age += 1 #轨迹连续存在帧数+1self.time_since_update += 1 #轨迹连续匹配失败次数+1def predict(self, kf):'''预测下一帧轨迹信息'''self.mean, self.covariance = kf.predict(self.mean, self.covariance) #卡尔曼滤波预测下一帧轨迹的状态均值和方差self.increment_age() #调用函数,age+1,time_since_update+1def update(self, kf, detection, class_id, conf):'''更新匹配成功的轨迹信息'''self.conf = conf #更新置信度得分self.mean, self.covariance = kf.update(self.mean, self.covariance, detection.to_xyah()) #卡尔曼滤波更新轨迹的状态均值和方差self.features.append(detection.feature) #添加轨迹对应目标框的外观语义特征self.class_id = class_id.int() #更新轨迹所属类别self.hits += 1 #轨迹匹配成功次数+1self.time_since_update = 0 #匹配成功时,轨迹连续匹配失败次数归0if self.state == TrackState.Tentative and self.hits >= self._n_init:self.state = TrackState.Confirmed #当连续匹配成功次数达标时轨迹由不确定态转为确定态def mark_missed(self):'''将轨迹状态转为删除态'''if self.state == TrackState.Tentative:self.state = TrackState.Deleted #当级联匹配和IOU匹配后仍为不确定态elif self.time_since_update > self._max_age:self.state = TrackState.Deleted #当连续匹配失败次数超标'''该部分还存在一些轨迹坐标转化及状态判定函数,具体可参考代码来源'''
4 最后
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate