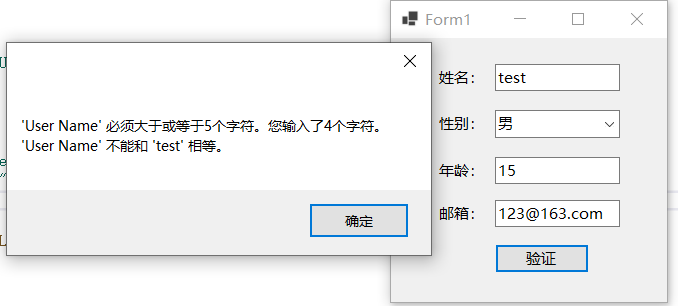
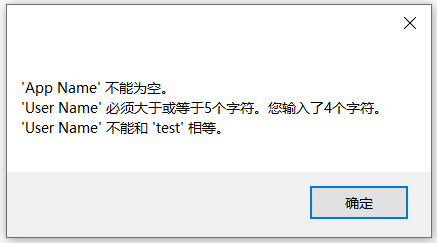
FluentValidation模块支持链式验证方法调用,也就是说,除了 RuleFor(r => r.UserName).NotEmpty()调用方式之外,还可以将对单个属性的多种验证函数以链式调用方式串接起来,比如UserName属性不能为空,长度在5~10之间,且不能是test,使用FluentValidation模块的链式验证方式及运行效果如下所示:
RuleFor(r => .UserName).NotEmpty().MinimumLength(5).MaximumLength(10).NotEqual("test");
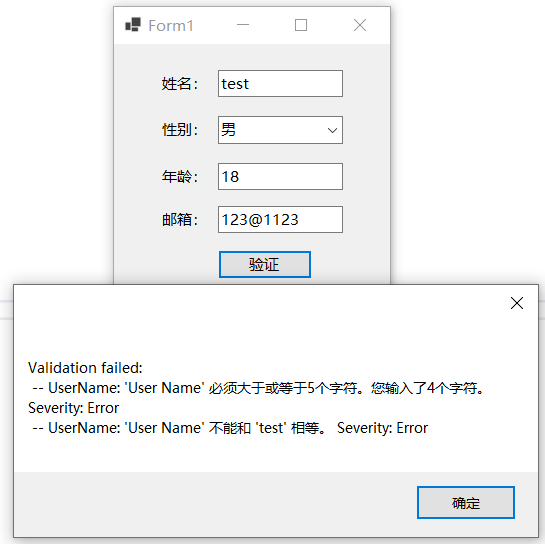
调用继承自AbstractValidator类的自定义验证类验证时,一般调用Validate函数获取验证结果及验证错误信息,除此之外,还可以调用ValidateAndThrow函数,当验证失败时直接抛ValidationException异常,后者包含类型为IEnumerable<ValidationFailure>的验证错误信息集合,供程序捕获及处理。
AppUserValidator validationRules = new AppUserValidator();
try
{validationRules.ValidateAndThrow(user);
}
catch (FluentValidation.ValidationException ex)
{MessageBox.Show(ex.Message);
}
FluentValidation模块支持两种方式验证复杂类型的属性,方式1是为每种类型定义相应的验证类,并在上一级类型的验证类构造函数中调用SetValidator函数指定类型属性的验证,方式2是在上一级类型的验证类构造函数中按属性层级设置需要验证的规则(官网说明中提到第2种方式要手动增加属性的非null条件验证,否则就不会对下一级属性进行自动验证,但是测试时并没有出现这种情况,可以正常运行AppUser实例对象的验证),这两种方式的使用示例和效果如下所示:
public class AppUser
{public string UserName { get; set; }public string Sex { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }public string Email { get; set; }
}public class AppInfo
{public string AppName { get; set; }public AppUser User { get; set; }
}public class AppInfoalidator : AbstractValidator<AppInfo>
{//方式1public AppInfoalidator() {RuleFor(x=>x.AppName).NotEmpty();RuleFor(x=>x.User).SetValidator(new AppUserValidator());}//方式2public AppInfoalidator() {RuleFor(x=>x.AppName).NotEmpty();RuleFor(x=>x.User.UserName).NotEmpty().MinimumLength(5).MaximumLength(10).NotEqual("test"); }
}
public class AppUserValidator:AbstractValidator<AppUser>
{public AppUserValidator(){RuleFor(r => r.UserName).NotEmpty().MinimumLength(5).MaximumLength(10).NotEqual("test");}
}
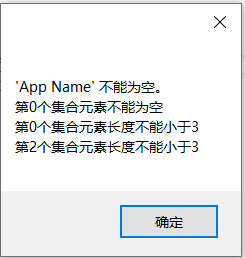
针对集合类型的属性,FluentValidation模块提供了RuleForEach函数验证集合属性,针对简单类型的集合属性,可以直接调用RuleForEach对每个元素进行验证,如下所示。
public class AppInfo
{public string AppName { get; set; }public List<string> Roles { get; set; }
}public class AppInfoalidator : AbstractValidator<AppInfo>
{public AppInfoalidator() {RuleFor(x=>x.AppName).NotEmpty();RuleForEach(x => x.Roles).NotEmpty().WithMessage("第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素不能为空").MinimumLength(3).WithMessage("第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素长度不能小于3");}
}AppInfo app = new AppInfo();
app.Roles = new List<string>();
app.Roles.Add(string.Empty);
app.Roles.Add("办公室主任");
app.Roles.Add("职员");AppInfoalidator appValidator=new AppInfoalidator();
FluentValidation.Results.ValidationResult result =appValidator.Validate(app);
if(!result.IsValid)
{MessageBox.Show(result.ToString());
}
针对复杂类型的集合属性,类似于上面复杂类型的属性验证方式,既可以调用RuleForEach和SetValidator函数设置每个元素的验证类,也可以调用 RuleForEach和ChildRules函数直接设置每个元素的验证方式,这两种方式的使用示例和效果如下所示:
public class AppUser
{public string UserName { get; set; }public string Sex { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }public string Email { get; set; }
}public class AppInfo
{public string AppName { get; set; }public List<string> Roles { get; set; }public List<AppUser> Users { get; set; }
}public class AppInfoalidator : AbstractValidator<AppInfo>
{//方式1public AppInfoalidator() {RuleFor(x=>x.AppName).NotEmpty();RuleForEach(x => x.Roles).NotEmpty().WithMessage("角色属性第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素不能为空").MinimumLength(3).WithMessage("角色属性第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素长度不能小于3");RuleForEach(x => x.Users).SetValidator(new AppUserValidator());}//方式2public AppInfoalidator() {RuleFor(x=>x.AppName).NotEmpty();RuleForEach(x => x.Roles).NotEmpty().WithMessage("角色属性第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素不能为空").MinimumLength(3).WithMessage("角色属性第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素长度不能小于3");RuleForEach(x => x.Users).ChildRules(r =>{r.RuleFor(r => r.UserName).NotEmpty().MinimumLength(5).WithMessage("用户属性第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素长度不能小于5").MaximumLength(10).NotEqual("test").WithMessage("用户属性第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素值不能等于test");});}
}
public class AppUserValidator:AbstractValidator<AppUser>
{public AppUserValidator(){RuleFor(r => r.UserName).NotEmpty().MinimumLength(5).WithMessage("用户属性第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素长度不能小于5").MaximumLength(10).NotEqual("test").WithMessage("用户属性第{CollectionIndex}个集合元素值不能等于test");}
}

参考文献:
[1]https://docs.fluentvalidation.net/en/latest/start.html