最近在阅读一些AI项目,写入markdown,持续更新,算是之后也能回想起做法
项目 https://github.com/calssion/Fun_AI
Kaggle--House Prices: Advanced Regression Techniques
Kaggle address(网址):https://www.kaggle.com/c/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques
tutorial(教程):kernal notebook https://www.kaggle.com/serigne/stacked-regressions-top-4-on-leaderboard
Data preprocessing(数据预处理)
Documentation for the Ames Housing Data indicates that there are outliers present in the training data(数据文档表明训练集中有离群点)
We can see at the bottom right two with extremely large GrLivArea that are of a low price. These values are huge oultliers. Therefore, we can safely delete them.(我们可以发现右下有两个离群点,因此我们可以安全地将其删除)
train = train.drop(train[(train['GrLivArea']>4000) & (train['SalePrice']<300000)].index)
There are probably others outliers in the training data. However, removing all them may affect badly our models if ever there were also outliers in the test data. That's why , instead of removing them all, we will just manage to make some of our models robust on them.(训练数据中可能存在其他异常值。然而,如果测试数据中存在异常值,则删除它们可能会严重影响我们的模型。这就是为什么我们不将它们全部删除,我们将设法使我们的一些模型对它们具有鲁棒性。)
sns.distplot(train['SalePrice'] , fit=norm);
(mu, sigma) = norm.fit(train['SalePrice'])
print( '\n mu = {:.2f} and sigma = {:.2f}\n'.format(mu, sigma))
plt.legend(['Normal dist. ($\mu=$ {:.2f} and $\sigma=$ {:.2f} )'.format(mu, sigma)],loc='best')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.title('SalePrice distribution')
fig = plt.figure()
res = stats.probplot(train['SalePrice'], plot=plt)
plt.show()
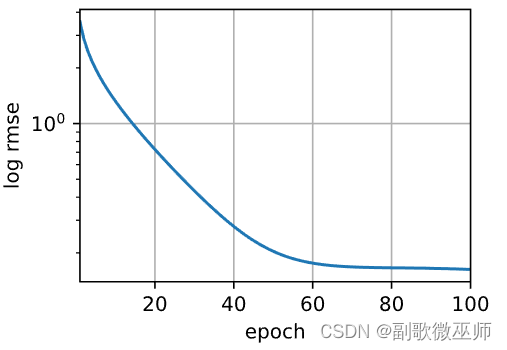
The target variable is right skewed. As (linear) models love normally distributed data , we need to transform this variable and make it more normally distributed. (目标变量是右偏的。由于(线性)模型喜欢正态分布的数据,所以我们需要变换这个变量并使其更加正常分布。)
Log-transformation of the target variable(用log函数转换变量)
train["SalePrice"] = np.log1p(train["SalePrice"])
The skew seems now corrected and the data appears more normally distributed.(现在斜线正确了而且也呈现正太分布了)
Missing Data(缺失值)
all_data_na = (all_data.isnull().sum() / len(all_data)) * 100
all_data_na = all_data_na.drop(all_data_na[all_data_na == 0].index).sort_values(ascending=False)[:30]
missing_data = pd.DataFrame({'Missing Ratio' :all_data_na})
missing_data.head(20)
corrmat = train.corr()
plt.subplots(figsize=(12,9))
sns.heatmap(corrmat, vmax=0.9, square=True)
Imputing missing values(填充缺失值)
Stacking averaged Models Class(Stacking平均模型)
stacked_averaged_models = StackingAveragedModels(base_models = (ENet, GBoost, KRR),meta_model = lasso)
score = rmsle_cv(stacked_averaged_models)
print("Stacking Averaged models score: {:.4f} ({:.4f})".format(score.mean(), score.std()))
we just average Elastic Net Regression、 Kernel Ridge Regression、Gradient Boosting Regression, then we add LASSO Regression as meta-model. this is the Ensembling StackedRegressor
(stacking模型以Elastic Net Regression、Kernel Ridge Regression、Gradient Boosting Regression集成为初级学习器,然后以LASSO Regression作为二级学习器,这是Ensembling StackedRegressor)
and then Ensembling StackedRegressor, XGBoost and LightGBM
(然后我们集成刚训练完的stacking模型和XGBoost和LightGBM)
the submission will be ensemble = stacked_pred * 0.70 + xgb_pred * 0.15 + lgb_pred * 0.15
(以stacked_train_pred0.70 + xgb_train_pred0.15 + lgb_train_pred*0.15 集成为最终结果)
Submissions are evaluated on Root-Mean-Squared-Error (RMSE) between the logarithm of the predicted value and the logarithm of the observed sales price. (提交结果用RMSE来评价预测值和真实值)
get the score of 0.11549 (获得评分0.11549)