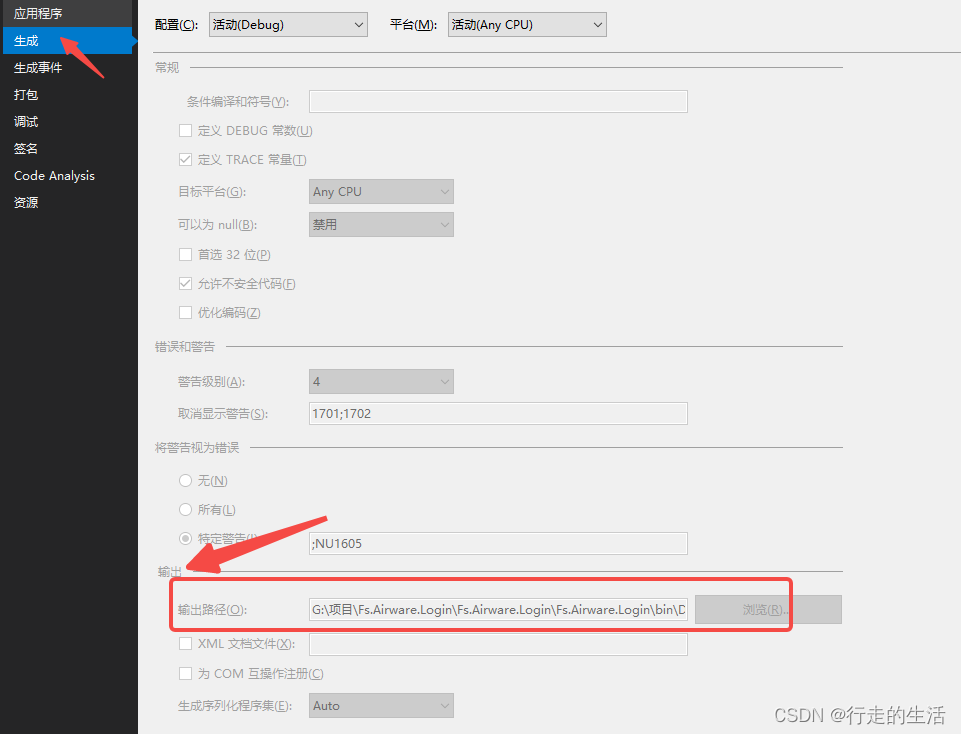
前言
官网地址:Pinia | The intuitive store for Vue.js (vuejs.org)
看以下内容,需要有
vuex的基础,下面很多概念会直接省略,比如state、actions、getters用处含义等
1、什么是Pinina
Pinia 是 Vue 的存储库,它允许您跨组件/页面共享状态。 如果您熟悉 Composition API,您可能会认为您已经可以通过一个简单的
export const state = reactive({}). 这对于单页应用程序来说是正确的,但如果它是服务器端呈现的,会使您的应用程序暴露于安全漏洞。 但即使在小型单页应用程序中,您也可以从使用 Pinia 中获得很多好处:
- dev-tools 支持
- 跟踪动作、突变的时间线
- Store 出现在使用它们的组件中
- time travel 和 更容易的调试
- 热模块更换
- 在不重新加载页面的情况下修改您的 Store
- 在开发时保持任何现有状态
- 插件:使用插件扩展 Pinia 功能
- 为 JS 用户提供适当的 TypeScript 支持或 autocompletion
- 服务器端渲染支持
2、与vuex比较
Pinia 最初是为了探索 Vuex 的下一次迭代会是什么样子,结合了 Vuex 5 核心团队讨论中的许多想法。最终,我们意识到 Pinia 已经实现了我们在 Vuex 5 中想要的大部分内容,并决定实现它 取而代之的是新的建议。
与 Vuex 相比,Pinia 提供了一个更简单的 API,具有更少的规范,提供了 Composition-API 风格的 API,最重要的是,在与 TypeScript 一起使用时具有可靠的类型推断支持。
与 Vuex 3.x/4.x 的比较
Vuex 3.x是 Vuex 的Vue 2而Vuex 4.x是Vue 3Pinia API 与 Vuex ≤4 有很大不同,即:
- mutations 不再存在。他们经常被认为是 非常 冗长。他们最初带来了 devtools 集成,但这不再是问题。
- 无需创建自定义复杂包装器来支持 TypeScript,所有内容都是类型化的,并且 API 的设计方式尽可能利用 TS 类型推断。
- 不再需要注入、导入函数、调用函数、享受自动完成功能!
- 无需动态添加 Store,默认情况下它们都是动态的,您甚至都不会注意到。请注意,您仍然可以随时手动使用 Store 进行注册,但因为它是自动的,您无需担心。
- 不再有 modules 的嵌套结构。您仍然可以通过在另一个 Store 中导入和 使用 来隐式嵌套 Store,但 Pinia 通过设计提供平面结构,同时仍然支持 Store 之间的交叉组合方式。 您甚至可以拥有 Store 的循环依赖关系。
- 没有 命名空间模块==。鉴于 Store 的扁平架构,“命名空间” Store 是其定义方式所固有的,您可以说所有 Store 都是命名空间的==。
安装
- 以下方式基于
vue3,如果想在vue2中使用,则自行查看官网使用方法安装 | Pinia 中文文档 (web3doc.top),下面就省略了…
1、npm安装
yarn add pinia
# 或者使用 npm
npm install pinia
2、main.js导入
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'createApp(App)
.use(createPinia())
.mount('#app')
核心概念
1、Store
1.1、定义Store
- Store 是使用
defineStore()定义的,并且它需要一个唯一名称,作为第一个参数传递:- 这个 name,也称为 id,是必要的,Pinia 使用它来将 store 连接到 devtools。 将返回的函数命名为 use… 是跨可组合项的约定,以使其符合你的使用习惯。
- 您可以根据需要定义任意数量的 store ,并且**您应该在不同的文件中定义每个 store **以充分利用 pinia
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'// useStore 可以是 useUser、useCart 之类的任何东西
// 第一个参数是应用程序中 store 的唯一 id
export const useStore = defineStore('main', {// other options...
})
1.2、使用Store
- 一旦 store 被实例化,你就可以直接在 store 上访问
state、getters和actions中定义的任何属性。 我们将在接下来的页面中详细介绍这些内容,但自动补全会对您有所帮助。- 请注意,
store是一个用reactive包裹的对象,这意味着不需要在getter 之后写.value,但是,就像setup中的props一样,我们不能对其进行解构- 为了从 Store 中提取属性同时保持其响应式,您需要使用
storeToRefs()。 它将为任何响应式属性创建 refs。
<template><h2>用户名称:{{ userStore.userRealName }}</h2><h2>用户账号:{{ userStore.userName }}</h2><h2>用户密码:{{ userStore.passward }}</h2>
</template><script setup>import { ref } from 'vue'import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'import { storeToRefs} from 'pinia';// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();console.log(userStore);// 解构将使下面三个变量将失去响应式 userStore里面的数据是一个被reactive包裹的对象const { userRealName, userName, passward } = userStore;// 下面三个变量拥有响应式,因为被storeToRefs包裹了,它将为任何响应式属性创建 refsconst { userRealName: userRealName2, userName: userName2, passward: passward2 } = storeToRefs(userStore);</script>
2、State
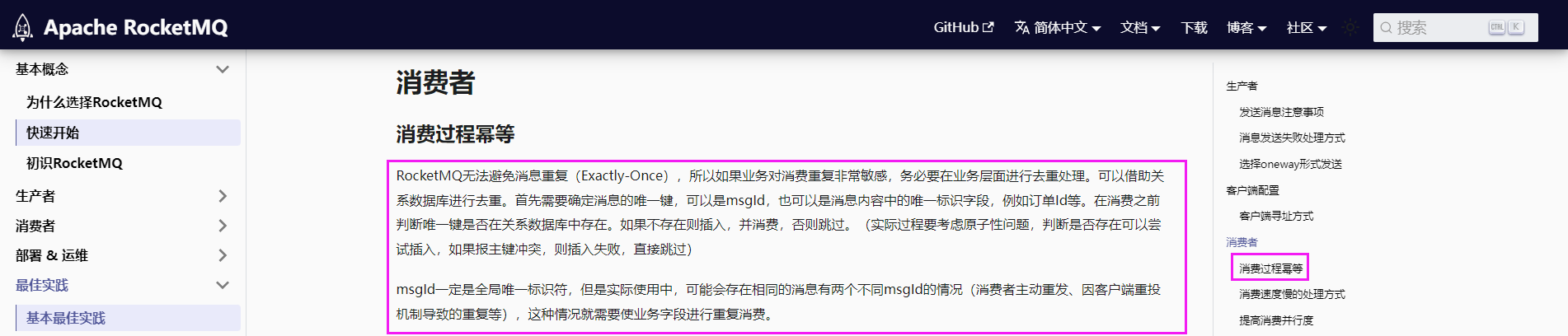
- 大多数时候,state 是 store 的核心部分。 我们通常从定义应用程序的状态开始。 在 Pinia 中,状态被定义为返回初始状态的函数。 Pinia 在服务器端和客户端都可以工作。
2.1、定义state
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {/** 相当于 state: () => {return {//xxxx}}*/state: () => ({userRealName: '张三',userName: 'admin',passward: '123456',})
})
2.2、访问state
<template><h2>用户名称:{{ userStore.userRealName }}</h2><h2>用户账号:{{ userStore.userName }}</h2><h2>用户密码:{{ userStore.passward }}</h2>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// userStore是一个被ractive包裹的对象 state里面定义的属性,将在userStore对象上const userStore = useUserStore();// 将返回整个storeconsole.log(userStore);</script>
2.3、重置状态
可以通过调用 store 上的
$reset()方法将状态 重置 到其初始值:
代码
<template><h2>用户名称:{{ userStore.userRealName }}</h2><h2>用户账号:{{ userStore.userName }}</h2><h2>用户密码:{{ userStore.passward }}</h2><button @click="changeUser">修改用户信息</button><button @click="resetStore">重置store数据</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();// 修改store中的用户信息function changeUser() {userStore.userRealName = '李四';userStore.userName = 'lisi';userStore.passward = '654321';}// 重置store数据function resetStore() {userStore.$reset();}</script>
效果

2.4、改变状态
- 除了直接用
store.counter++修改 store,你还可以调用$patch方法。 它允许您使用部分“state”对象同时应用多个更改- 主要区别是
$patch()允许您将批量更改的日志写入开发工具中的一个条目中。 注意两者,state和$patch()的直接更改都出现在 devtools 中,并且可以进行 time travelled(在 Vue 3 中还没有)。
<template><h2>用户名称:{{ userStore.userRealName }}</h2><h2>用户账号:{{ userStore.userName }}</h2><h2>用户密码:{{ userStore.passward }}</h2><button @click="changeUser">修改用户信息</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();// 修改store中的用户信息function changeUser() {// 只会修改userRealName和userName的值userStore.$patch({userRealName: '李四',userName: 'lisi',});}
</script>
但是,使用这种语法应用某些突变非常困难或代价高昂:任何集合修改(例如,从数组中推送、删除、拼接元素)都需要您创建一个新集合。 正因为如此,
$patch方法也接受一个函数来批量修改集合内部分对象的情况:给
userSore的state中添加用户爱好
store
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({userRealName: '张三',userName: 'zhangsan',passward: '123456',hobby: ['吃饭', '睡觉', '打豆豆'],})
})
页面
<template><h2>用户名称:{{ userStore.userRealName }}</h2><h2>用户账号:{{ userStore.userName }}</h2><h2>用户密码:{{ userStore.passward }}</h2><h2>用户爱好:{{ userStore.hobby }}</h2><button @click="changeUserHobby">修改用户爱好</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();// 修改store中的用户信息function changeUserHobby() {// 这样修改很麻烦/* userStore.$patch({hobby: ['吃饭', '睡觉', '打豆豆', '篮球', '台球', '乒乓球']}); */// 直接往后追加userStore.$patch((store) => {store.hobby.push('篮球', '台球', '乒乓球');})}
</script>
2.5、替换state
可以通过将其
$state属性设置为新对象来替换 Store 的整个状态:
<template><h2>用户名称:{{ userStore.userRealName }}</h2><h2>用户账号:{{ userStore.userName }}</h2><h2>用户密码:{{ userStore.passward }}</h2><h2>用户爱好:{{ userStore.hobby }}</h2><button @click="changeUser">替换用户对象</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();// 修改整个store对象function changeUser() {userStore.$state = {userRealName: '李四',userName: 'lisi',passward: '654321',hobby: ['打篮球']}}
</script>
2.6、订阅状态
- 可以通过 store 的
$subscribe()方法查看状态及其变化,类似于 Vuex 的 subscribe 方法。 与常规的watch()相比,使用$subscribe()的优点是 subscriptions 只会在 patches 之后触发一次(例如,当使用上面的函数版本时)。- 本人试了下用
wathch监听userStore,结果和使用$subscribe()一致,都只会触发一次。- 可能与
watch的唯一区别是:$subscribe函数里面可以传入第二个参数{detached: true},当组件销毁时,这个监听函数依旧会被保留,而没有第二个参数的$subscribe和watch将会跟着组件一起被销毁
代码
<template><h2>用户名称:{{ userStore.userRealName }}</h2><h2>用户账号:{{ userStore.userName }}</h2><h2>用户密码:{{ userStore.passward }}</h2><h2>用户爱好:{{ userStore.hobby }}</h2><button @click="changeUser">替换用户对象</button><button @click="changeUser2">替换用户对象2</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'import { watch } from 'vue'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();userStore.$subscribe((mutation, state) => {console.log("subscribe", mutation, state)// 每次修改state,都会刷新localStorage里面的数据localStorage.setItem('userStore', JSON.stringify(state))})// 修改整个store对象function changeUser() {userStore.$patch({userRealName: '李四',userName: 'lisi',passward: '654321',hobby: ['打篮球']})}// 与上面写法一致,也只会触发一次watch 和 subscribe方法function changeUser2() {userStore.hobby.push('打篮球');}// 使用传统watchwatch(userStore, (val) => {console.log('watch:', val)})
</script>
效果

默认情况下,state subscriptions 绑定到添加它们的组件(如果 store 位于组件的
setup()中)。 意思是,当组件被卸载时,它们将被自动删除。 如果要在卸载组件后保留它们,请将{ detached: true }作为第二个参数传递给 detach 当前组件的 state subscription:
// 这个函数当组件被挂载后,将会一直存在!!!
userStore.$subscribe((mutation, state) => {console.log("subscribe", mutation, state)// 每次修改state,都会刷新localStorage里面的数据localStorage.setItem('userStore', JSON.stringify(state))
}, { detached: true })
3、Getters
3.1、定义getter
Getter 完全等同于 Store 状态的 计算值。 它们可以用
defineStore()中的getters属性定义。 他们接收“状态”作为第一个参数以鼓励箭头函数的使用
代码
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,},
})
3.2、使用getter
和state属性一样,直接使用
userStore.xxx即可
<template><h2>count:{{ userStore.count }}</h2><h2>doubleCount:{{ userStore.doubleCount }}</h2><button @click="userStore.count++">修改count</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();</script>
效果

4.2、访问其他getter
- 大多数时候,getter 只会依赖状态,但是,他们可能需要使用其他 getter。
- 正因为如此,我们可以在定义常规函数时通过
this访问到 整个 store 的实例*- 但是需要定义返回类型(在 TypeScript 中)。 这是由于 TypeScript 中的一个已知限制,并且不会影响使用箭头函数定义的 getter,也不会影响不使用
this的 getter:- 案例没有用到TS,所以没有定义返回类型
userStore中
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,doublePlusOne() {return this.doubleCount * 2 + 1},},
})
homeView中
<template><h2>count:{{ userStore.count }}</h2><h2>doubleCount:{{ userStore.doubleCount }}</h2><h2>doublePlusOne: {{ userStore.doublePlusOne }}</h2><button @click="userStore.count++">修改count</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();</script>
效果

4.3、访问其他store里的getter
- 与计算属性一样,您可以组合多个 getter。 通过
this访问任何其他 getter。- 即使不使用 TypeScript,您也可以使用 JSDoc 提示您的 IDE 类型:
userStore中
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,// count是否小于10doublePlusOne() {return this.doubleCount * 2 + 1},otherGetter(state) {const useU2Store = useUserStore2();// 2 + (state.count * 2) + (state.count * 2 + 1) + state.countreturn useU2Store.doubleCount + this.doublePlusOne + state.count}},
})export const useUserStore2 = defineStore('user2', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,},
})
homeView中
<template><h2>count:{{ userStore.count }}</h2><h2>doubleCount:{{ userStore.doubleCount }}</h2><h2>doublePlusOne: {{ userStore.doublePlusOne }}</h2><h2>otherGetter: {{ userStore.otherGetter }}</h2><button @click="userStore.count++">修改count</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();</script>
效果

4.4、将参数传递给 getter
- Getters 只是幕后的 computed 属性,因此无法向它们传递任何参数。 但是,您可以从 getter 返回一个函数以接受任何参数
- 在执行此操作时,getter 不再缓存,它们只是您调用的函数。
userStore中
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,doublePlusOne(state) {return (addSum) => state.count + addSum;},},
})
homeView中
<template><h2>count:{{ userStore.count }}</h2><h2>doubleCount:{{ userStore.doubleCount }}</h2><h2>doublePlusOne: {{ userStore.doublePlusOne(10) }}</h2><button @click="userStore.count++">修改count</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();</script>
效果

4、Actions
4.1、定义action
- Actions 相当于组件中的 methods。 它们可以使用
defineStore()中的actions属性定义,并且它们非常适合定义业务逻辑- 相比于
vuex,省去了mutation
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {},actions: {increment() {// 通过this,获取state里面属性this.count++},decrement() {this.count--},// 异步方法async asyncChangeCount() {// 模仿异步请求const data = await new Promise(resolve => {setTimeout(() => {resolve(1233333333333)}, 1000)})this.count = data;}}
})
4.2、使用action
直接调用
userState.xxx()方法即可
代码
<template><h2>count:{{ userStore.count }}</h2><button @click="addCount">count+1</button><button @click="deCount">count-1</button><button @click="asyncChangeCount">异步修改count</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();function addCount() {userStore.increment()}function deCount() {userStore.decrement();}function asyncChangeCount() {userStore.asyncChangeCount()}</script>
效果

4.3、访问其他action
和
getters一样,直接使用this.xxxx()调用其他函数即可
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {},actions: {// 无用,测试testFun(sum) {return this.count + sum;},increment() {// 直接使用this.xxx()调用其他action 相当于 +2this.count = this.testFun(1) + 1;},decrement() {// +2 -1,相当于+1this.count = this.testFun(2) - 1;},}
})
4.4、访问其他store的action
和
getters里面一致,导入另一个store,在actions中调用xxxStore.xxx(xx)方法即可
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {},actions: {increment() {const u2Store = useUserStore2();// 相当于 this.count + 2;this.count = this.count + u2Store.testFun(1) + 1;},decrement() {this.count--;},}
})export const useUserStore2 = defineStore('user2', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),getters: {},actions: {// 无用,测试testFun(sum) {return sum;},}
})
4.5、订阅action
- 可以使用
store.$onAction()订阅 action 及其结果。- 传递给它的回调在 action 之前执行。
after处理 Promise 并允许您在 action 完成后执行函数。- 以类似的方式,
onError允许您在处理中抛出错误。 这些对于在运行时跟踪错误很有用,类似于 Vue 文档中的这个提示。$onAction()会返回一个函数,调用函数即可停止订阅
userStore代码
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {state: () => ({count: 1,}),actions: {increment() {return this.count--;},decrement() {return --this.count;},// 异步方法async asyncChangeCount(val = 520) {// 模仿异步请求const data = await new Promise(resolve => {setTimeout(() => {resolve(val)}, 1000)})this.count = data;}}
})
homeView代码
<template><h2>count:{{ userStore.count }}</h2><button @click="addCount">count+1</button><button @click="deCount">count-1</button><button @click="asyncChangeCount">异步修改count</button><button @click="unOnAction()">关闭onAction</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();// 每次调用完action后,都会执行const unOnAction = userStore.$onAction(({name, // action 的名字store, // store 实例args, // 调用这个 action 的参数after, // 在这个 action 执行完毕之后,执行这个函数onError, // 在这个 action 抛出异常的时候,执行这个函数}) => {console.log("action函数名:" + name + ",store实例:" + JSON.stringify(store) + ",参数" + args.toString());// 执行开始事件const now = Date.now();// action执行完成后回调,异步会等待最终执行完成after((result) => {console.log("action共执行了:" + (Date.now() - now) + "ms" + ",返回结果:" + result);})onError((error) => {console.log("action执行失败:" + error);})})function addCount() {userStore.increment()}function deCount() {userStore.decrement();}function asyncChangeCount() {userStore.asyncChangeCount(1314);}</script>
效果

Plugins
- 由于有了底层 API 的支持,Pinia store 现在完全支持扩展。以下是你可以扩展的内容:
- 为 store 添加新的属性
- 定义 store 时增加新的选项
- 为 store 增加新的方法
- 包装现有的方法
- 改变甚至取消 action
- 实现副作用,如本地存储
- 仅应用插件于特定 store
- 插件是通过
pinia.use()添加到 pinia 实例的。最简单的例子是通过返回一个对象将一个静态属性添加到所有 store。- Pinia 插件是一个函数,可以选择性地返回要添加到 store 的属性。它接收一个可选参数,即 context。
- 插件只会应用于在
pinia传递给应用后创建的 store,否则它们不会生效。
1、基本演示
1.1、userStore
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref } from 'vue';export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => {const count = ref(0);return { count };
})export const useUserStore2 = defineStore('user2', () => {const count2 = ref(0);return { count2 };
})
1.2、main
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'import { createPinia } from 'pinia'const pinina = createPinia();function myPiniaPlugin() {// 创建的每个 store 中都会添加一个名为 `myPlugin` 的属性。// 在安装此插件后,插件可以保存在不同的文件中return {myPlugin: 'test'}
}
// 将该插件交给 Pinia
pinina.use(myPiniaPlugin);createApp(App)
.use(pinina)
.mount('#app')1.3、效果
通过
vue-devtools即可看出效果


2、参数介绍
Pinia 插件是一个函数,可以选择性地返回要添加到 store 的属性。它接收一个可选参数,即 context。
export function myPiniaPlugin(context) {context.pinia // 用 `createPinia()` 创建的 pinia。 context.app // 用 `createApp()` 创建的当前应用(仅 Vue 3)。context.store // 该插件想扩展的 storecontext.options // 定义传给 `defineStore()` 的 store 的可选对象。// ...
}
从下图可以看出,每个store执行,都会调用一次插件函数(需要页面调用
usexxxStore()后,才会执行)

3、扩展Store
可以直接通过在一个插件中返回包含特定属性的对象来为每个 store 都添加上特定属性
pinina.use(() => ({myPlugin: 'test'}));
也可以直接在
store上设置该属性,但可以的话,请使用返回对象的方法,这样它们就能被 devtools 自动追踪到
pinina.use(({ store }) => store.myPlugin = 'test');

任何由插件返回的属性都会被 devtools 自动追踪,所以如果你想在 devtools 中调试
hello属性,为了使 devtools 能追踪到hello,请确保在 dev 模式下将其添加到store._customProperties中:
pinina.use(({ store }) => {store.myPlugin = 'test'// 确保你的构建工具能处理这个问题,webpack 和 vite 在默认情况下应该能处理。if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {// 添加你在 store 中设置的键值store._customProperties.add('myPlugin')}
});

- 值得注意的是,每个 store 都被
reactive包装过,所以可以自动解包任何它所包含的 Ref(ref()、computed()…)。- 在没有
.value的情况下你依旧可以访问所有计算属性的原因,也是它们为什么是响应式的原因。
const str = ref('test2');
pinina.use(({ store }) => {// 每个 store 都有单独的 `test` 属性store.myPlugin = 'test'store.hello = ref('test')// 它会被自动解包console.log(store.hello); // 'test'// 确保你的构建工具能处理这个问题,webpack 和 vite 在默认情况下应该能处理。if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {// 添加你在 store 中设置的键值store._customProperties.add('myPlugin')}// 所有的 store 都在共享 `str` 属性的值store.myPlugin2 = strconsole.log(store.myPlugin2); // 'test2'
});

4、添加新的 state
- 如果你想给 store 添加新的 state 属性或者在服务端渲染的激活过程中使用的属性,你必须同时在两个地方添加它。。
- 在
store上,然后你才可以用store.myState访问它。- 在
store.$state上,然后你才可以在 devtools 中使用它,并且,在 SSR 时被正确序列化(serialized)。- 需要注意的是,在一个插件中, state 变更或添加(包括调用
store.$patch())都是发生在 store 被激活之前,因此不会触发任何订阅函数。
pinia.use(({ store }) => {// 为了正确地处理 SSR,我们需要确保我们没有重写任何一个 // 现有的值if (!Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty(store.$state, 'hasError')) {// 在插件中定义 hasError,因此每个 store 都有各自的// hasError 状态const hasError = ref(false)// 在 `$state` 上设置变量,允许它在 SSR 期间被序列化。store.$state.hasError = hasError}// 我们需要将 ref 从 state 转移到 store// 这样的话,两种方式:store.hasError 和 store.$state.hasError 都可以访问// 并且共享的是同一个变量// 查看 https://cn.vuejs.org/api/reactivity-utilities.html#torefstore.hasError = toRef(store.$state, 'hasError')// 在这种情况下,最好不要返回 `hasError`// 因为它将被显示在 devtools 的 `state` 部分// 如果我们返回它,devtools 将显示两次。
})
5、添加新的外部属性
当添加外部属性、第三方库的类实例或非响应式的简单值时,你应该先用
markRaw()来包装一下它,再将它传给 pinia。下面是一个在每个 store 中添加路由器的例子:
import { markRaw } from 'vue'
// 根据你的路由器的位置来调整
import { router } from './router'pinia.use(({ store }) => {store.router = markRaw(router)
})
6、在插件中调用 $subscribe
你也可以在插件中使用 store.KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '#' at position 63: …epts/state.html#̲subscribing-to-…onAction 。
这样每个
store都会执行相同的订阅
pinia.use(({ store }) => {store.$subscribe(() => {// 响应 store 变化})store.$onAction(() => {// 响应 store actions})
})
7、添加新的选项
在定义 store 时,可以创建新的选项,以便在插件中使用它们。例如,你可以创建一个
debounce选项,允许你让任何 action 实现防抖。
defineStore('user', {actions: {increment() {count.value++;}},// 这将在后面被一个插件读取debounce: {// 让 action searchContacts 防抖 300msincrement: 1000,},
})
然后,该插件可以读取该选项来包装 action,并替换原始 action:
// 使用任意防抖库
import debounce from 'lodash/debounce'pinia.use(({ options, store }) => {if (options.debounce) {// 我们正在用新的 action 来覆盖这些 actionreturn Object.keys(options.debounce).reduce((debouncedActions, action) => {// {}.increment = debounce(originAction, 1000)debouncedActions[action] = debounce(store[action],options.debounce[action])return debouncedActions}, {})}
})
注意,在使用 setup 语法时,自定义选项作为第 3 个参数传递:
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => {const count = ref(0);function increment() {count.value++;}return { count, increment };
}, {debounce: {increment: 1000}
})

Setup Store
defineStore()的第二个参数可接受两类值:Setup 函数或 Option 对象。option Store
- 与 Vue 的选项式 API 类似,我们也可以传入一个带有
state、actions与getters属性的 Option 对象- 你可以认为
state是 store 的数据 (data),getters是 store 的计算属性 (computed),而actions则是方法 (methods)。- 为方便上手使用,Option Store 应尽可能直观简单。
setup Store
- 与 Vue 组合式 API 的 setup 函数 相似,我们可以传入一个函数,该函数定义了一些响应式属性和方法,并且返回一个带有我们想暴露出去的属性和方法的对象。
- 在 Setup Store 中:
ref()就是state属性computed()就是gettersfunction()就是actionsSetup store比 Option Store 带来了更多的灵活性,因为你可以在一个 store 内创建侦听器,并自由地使用任何组合式函数。不过,请记住,使用组合式函数会让 SSR 变得更加复杂。
userStore
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { computed, ref } from 'vue';export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => {const count = ref(0);const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2);function increment() {count.value++;}return { count, doubleCount, increment };
})
homeView
<template><h2>count:{{ userStore.count }}</h2><h2>doubleCount:{{ userStore.doubleCount }}</h2><button @click="addCount">count+1</button>
</template><script setup>import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'// 定义 storeconst userStore = useUserStore();function addCount() {userStore.increment()}
</script>
效果