引言
我们的产品主打金融服务领域,以B端客户为我们的核心合作伙伴,然而,我们的服务最终将惠及C端消费者。在技术实现上,我们采用了公司自主研发的微服务框架,该框架基于SpringBoot,旨在提供高效、可靠的服务支持。
本文继《生产问题排查系列——未知404状态接口请求》之后,深入探讨并扩展了对我们公司自主研发框架的理解。在上一篇文章中,我们通过应用性能管理工具定位并解决了持续出现的404请求问题。
代码实例
下面给出一个简单的示例,方面读者在后续源码阅读中能着我们的排查思路一起来看上述问题。
pom.xml中引入Spring Boot以及Spring MVC
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"><modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><parent><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId><version>2.7.14</version><relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --></parent><groupId>org.example</groupId><artifactId>springmvc</artifactId><version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version><properties><maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source><maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target></properties><dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><scope>test</scope></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId></dependency></dependencies><build><plugins><plugin><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId></plugin></plugins></build></project>
TestController:定义一个请求接口
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;@Controller
public class TestController {@RequestMapping("/test")@ResponseBodypublic String test(){return "ok";}
}源码阅读
下面我们将从一个Spring提供的Health监控请求,一步一步分析Spring MVC是如何转发请求的。
Spring MVC所有的接口请求都将由doDispatch方法负责转发。源码如下:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);try {ModelAndView mv = null;Exception dispatchException = null;try {processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);// 确定当前请求处理的实际处理类mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null) {noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);return;}// 确定当前请求的处理程序适配器。HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());// 如果处理程序支持,则处理上次修改的标头。String method = request.getMethod();boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {return;}}if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {return;}// 调用处理程序mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {return;}applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);}catch (Exception ex) {dispatchException = ex;}catch (Throwable err) {// 从4.3开始,我们也在处理处理程序方法抛出的错误,//使它们可用于@ExceptionHandler方法和其他场景。dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);}processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);}catch (Exception ex) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);}catch (Throwable err) {triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));}finally {if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {// 而不是postHandle和afterCompletionif (mappedHandler != null) {mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);}}else {// 清理由多部分请求使用的所有资源。if (multipartRequestParsed) {cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);}}}}
监控接口请求会转发给AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.handle方法处理,源码如下:
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)throws Exception {return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);}然后请求会转发到AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.handleInternal方法中,源码如下:
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {ModelAndView mav;checkRequest(request);// 如果需要,在同步块中执行invokeHandlerMethod。if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);if (session != null) {Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);synchronized (mutex) {mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);}}else {// 没有可用的HttpSession->不需要互斥mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);}}else {// 根本不需要对会话进行同步。。。mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);}if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);}else {prepareResponse(response);}}return mav;}
然后接口请求会转发到RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.invokeHandlerMethod,进行一系列参数填充后调用invokeAndHandle方法,源码如下:
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);try {WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);}if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);}invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";});invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);}invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {return null;}return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);}finally {webRequest.requestCompleted();}}
此时请求会转发到ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle,之后调用InvocableHandlerMethod.invokeForRequest执行方法,源码如下:
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);setResponseStatus(webRequest);if (returnValue == null) {if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);return;}}else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);return;}mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");try {this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);}catch (Exception ex) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);}throw ex;}}
InvocableHandlerMethod.invokeForRequest会调用InvocableHandlerMethod.doInvoke执行实际方法
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));}return doInvoke(args);}
InvocableHandlerMethod.doInvoke会调用实际的bean执行方法。从这一步的getBean()方法我们就能知道执行spring bean是什么类。
protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception {Method method = getBridgedMethod();try {if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) {return CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args);}return method.invoke(getBean(), args);}catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {assertTargetBean(method, getBean(), args);String text = (ex.getMessage() != null ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument");throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError(text, args), ex);}catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {// Unwrap for HandlerExceptionResolvers ...Throwable targetException = ex.getTargetException();if (targetException instanceof RuntimeException) {throw (RuntimeException) targetException;}else if (targetException instanceof Error) {throw (Error) targetException;}else if (targetException instanceof Exception) {throw (Exception) targetException;}else {throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError("Invocation failure", args), targetException);}}}
总结
上述源码调用流程如下:
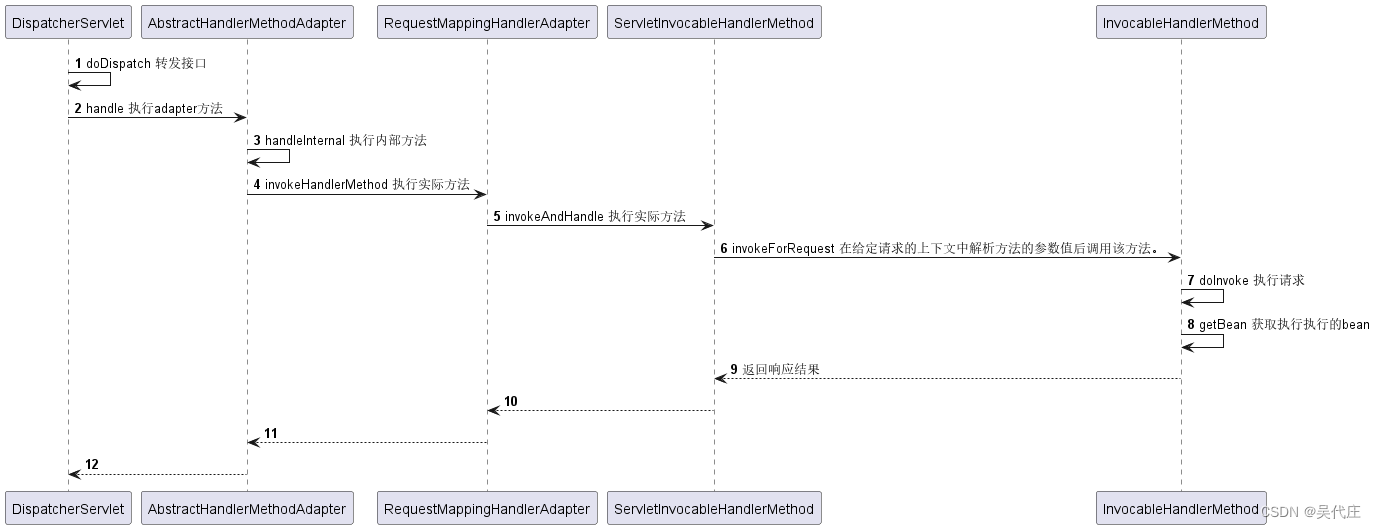
在深入研究Spring MVC的源码调用链路后,有了以下体会:
代码之间的调用关系错综复杂,构成了一个深广交织的网络。通过阅读源码,我们可以发现,从请求的接收到处理再到响应的返回,涉及了众多组件和层次的交互。这种深度的耦合使得没有全景图的情况下,仅凭对各个类功能的碎片化认识,难以形成对框架整体工作机制的实际理解。
为了真正掌握Spring MVC的内在逻辑,后续工作需要着手细致地梳理这些类之间的组织结构,明确它们如何协同工作以及各自的职责边界。这对于后续的框架使用、问题排查乃至自定义扩展都至关重要。