今天这篇文章,我想梳理一下Spring事务用到的几个核心组件。这些核心组件是我们理解Spring事务原理的基础。通过它们我们可以体会学习一下Spring设计者设计Spring事务时的基本思路。这些组件是:TransactionInfo、TransactionStatus、TransactionManager、TransactionAttribute、TransactionAttributeSource、ReactiveTransactionSupport等等。
首先让我们一起看一下TransactionInfo类。它是一个位于TransactionAspectSupport类中的内部类(这个类是上一节介绍的TransactionInterceptor的父类,TransactionInterceptor是一个增强类,用于对那些需要事务的方法进行增强)。TransactionInfo类的源码如下:
protected static final class TransactionInfo {@Nullableprivate final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;@Nullableprivate final TransactionAttribute transactionAttribute;private final String joinpointIdentification;@Nullableprivate TransactionStatus transactionStatus;@Nullableprivate TransactionInfo oldTransactionInfo;public TransactionInfo(@Nullable PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager,@Nullable TransactionAttribute transactionAttribute, String joinpointIdentification) {this.transactionManager = transactionManager;this.transactionAttribute = transactionAttribute;this.joinpointIdentification = joinpointIdentification;}public PlatformTransactionManager getTransactionManager() {Assert.state(this.transactionManager != null, "No PlatformTransactionManager set");return this.transactionManager;}@Nullablepublic TransactionAttribute getTransactionAttribute() {return this.transactionAttribute;}/*** Return a String representation of this joinpoint (usually a Method call)* for use in logging.*/public String getJoinpointIdentification() {return this.joinpointIdentification;}public void newTransactionStatus(@Nullable TransactionStatus status) {this.transactionStatus = status;}@Nullablepublic TransactionStatus getTransactionStatus() {return this.transactionStatus;}/*** Return whether a transaction was created by this aspect,* or whether we just have a placeholder to keep ThreadLocal stack integrity.*/public boolean hasTransaction() {return (this.transactionStatus != null);}private void bindToThread() {// Expose current TransactionStatus, preserving any existing TransactionStatus// for restoration after this transaction is complete.this.oldTransactionInfo = transactionInfoHolder.get();transactionInfoHolder.set(this);}private void restoreThreadLocalStatus() {// Use stack to restore old transaction TransactionInfo.// Will be null if none was set.transactionInfoHolder.set(this.oldTransactionInfo);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return (this.transactionAttribute != null ? this.transactionAttribute.toString() : "No transaction");}
}
通过源码不难看出TransactionInfo是一个最终类,也没有继承或实现其他接口或类,其中的属性有PlatformTransactionManager、TransactionAttribute、TransactionStatus、TransactionInfo(通过其变量名可以知道其代表的是老事务。还记得《Spring事务原理总结一》这篇文章中提到的事务传播属性吗?其中提到的REQUIRES_NEW可能就是通过这个属性来实现的)等。
然后让我们再一起看一下TransactionStatus接口,其又继承了SavepointManager、Flushable、TransactionExecution等接口。下面是该接口的源码:
public interface TransactionStatus extends TransactionExecution, SavepointManager, Flushable {/*** Return whether this transaction internally carries a savepoint,* that is, has been created as nested transaction based on a savepoint.* <p>This method is mainly here for diagnostic purposes, alongside* {@link #isNewTransaction()}. For programmatic handling of custom* savepoints, use the operations provided by {@link SavepointManager}.* <p>The default implementation returns {@code false}.* @see #isNewTransaction()* @see #createSavepoint()* @see #rollbackToSavepoint(Object)* @see #releaseSavepoint(Object)*/default boolean hasSavepoint() {return false;}/*** Flush the underlying session to the datastore, if applicable:* for example, all affected Hibernate/JPA sessions.* <p>This is effectively just a hint and may be a no-op if the underlying* transaction manager does not have a flush concept. A flush signal may* get applied to the primary resource or to transaction synchronizations,* depending on the underlying resource.* <p>The default implementation is empty, considering flush as a no-op.*/@Overridedefault void flush() {}}
下图则是TransactionStatus接口的继承体系:

接着来让我们来看一下TransactionAttribute接口,该位于org.springframework.transaction.interceptor包中,先来看一下其源码:
public interface TransactionAttribute extends TransactionDefinition {/*** Return a qualifier value associated with this transaction attribute.* <p>This may be used for choosing a corresponding transaction manager* to process this specific transaction.* @since 3.0*/@NullableString getQualifier();/*** Return labels associated with this transaction attribute.* <p>This may be used for applying specific transactional behavior* or follow a purely descriptive nature.* @since 5.3*/Collection<String> getLabels();/*** Should we roll back on the given exception?* @param ex the exception to evaluate* @return whether to perform a rollback or not*/boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex);}
下图是TransactionAttribute这个接口的继承体系(这里面我们中断关注RuleBasedTransactionAttribute这个类,第一次跟踪事务的执行代码时实际类型为RuleBasedTransactionAttribute):

最后再来看一下PlatformTransactionManager这个接口,该接口继承了TransactionManager接口,其有4个实现类,分别为AbstractPlatformTransactionManager、DataSourceTransactionManager、JdbcTransactionManager、JtaTransactionManager。个人理解它是一个管理接口。先看一下它的继承体系:
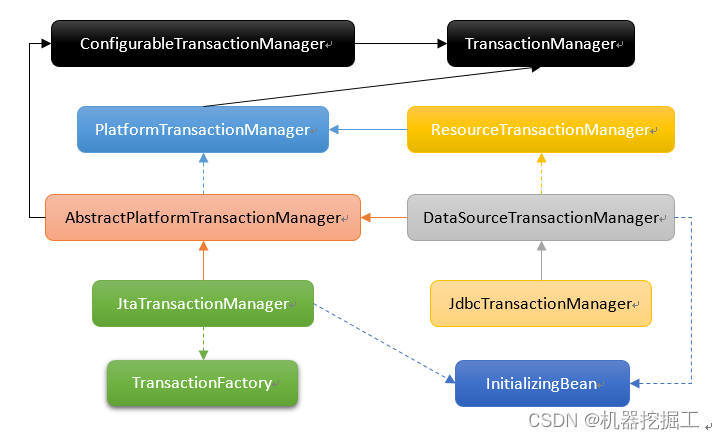
至此我们梳理了Spring事务涉及到的一些基本组件及其体系结构(这只是个人粗浅的认知,如果不全,还望各位大佬指正)。至于这些组件的作用,我们将在下一篇博客中逐一梳理。