朝菌不知晦朔
蟪蛄不知春秋
眼界决定境界
CSDN 请求进入专栏
是否进入《51单片机专栏》?
确定
目录
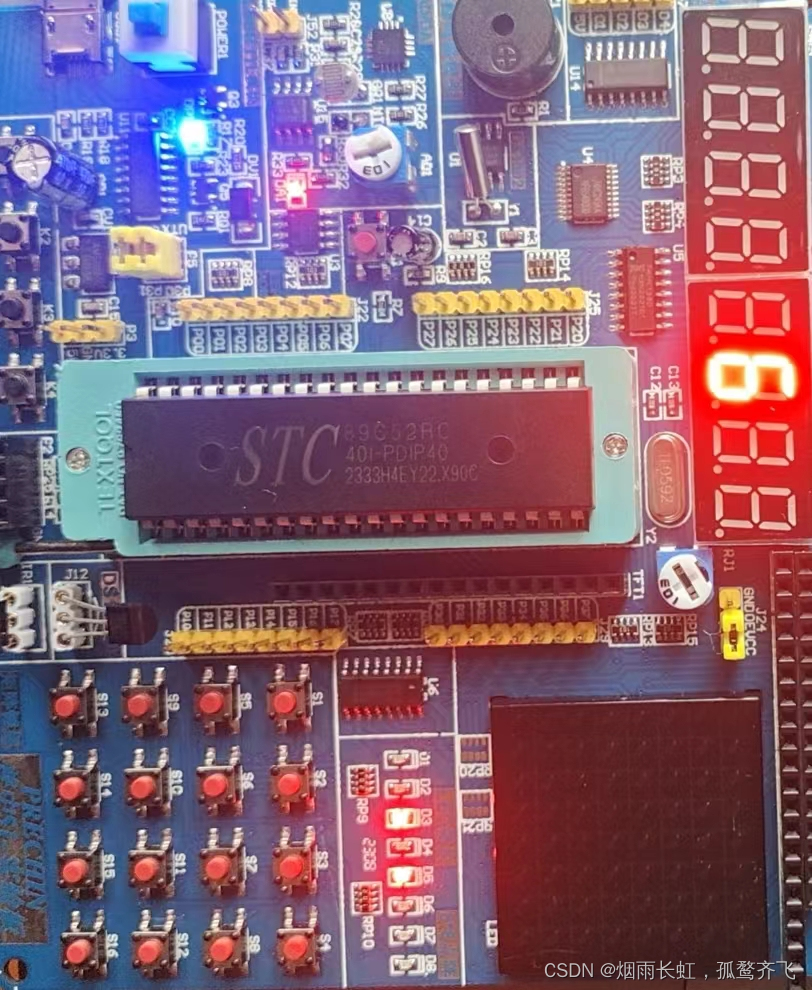
数码管的简介
数码管引脚定义
数码管的原理图
74HC245
代码实现
静态数码管的显示
动态数码管的显示
数码管实现表白画面
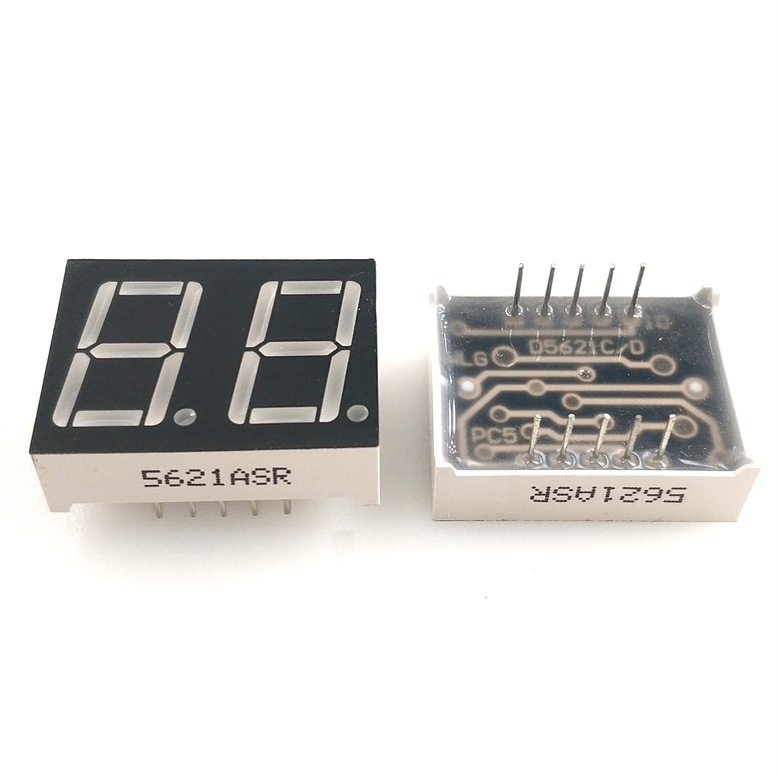

数码管的简介
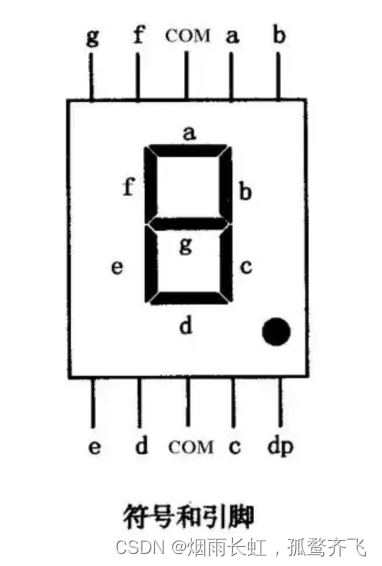
LED数码管(LED Segment Displays):由多个 发光二极管 封装在一起组成 8 字型的器件,引线已在内部连接完成,只需引出它们的各个笔划,公共电极。数码管实际上是由七个发光管组成 8 字形构成的,加上小数点就是 8 个。这些段分别由字母 a b c d e f g dp 来表示
数码管引脚定义
使数码管显示数字的方法就是控制不同的发光体来发光,达到显示不同数字的目的
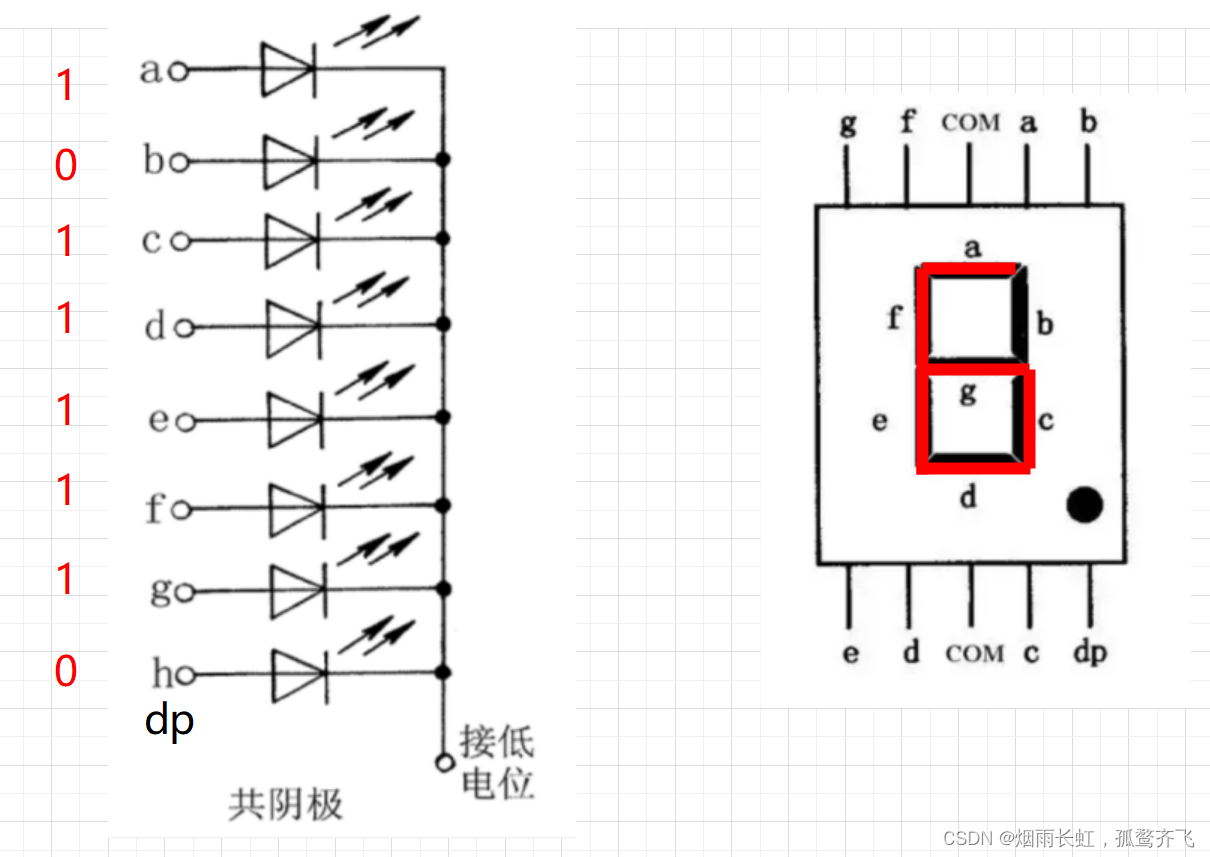
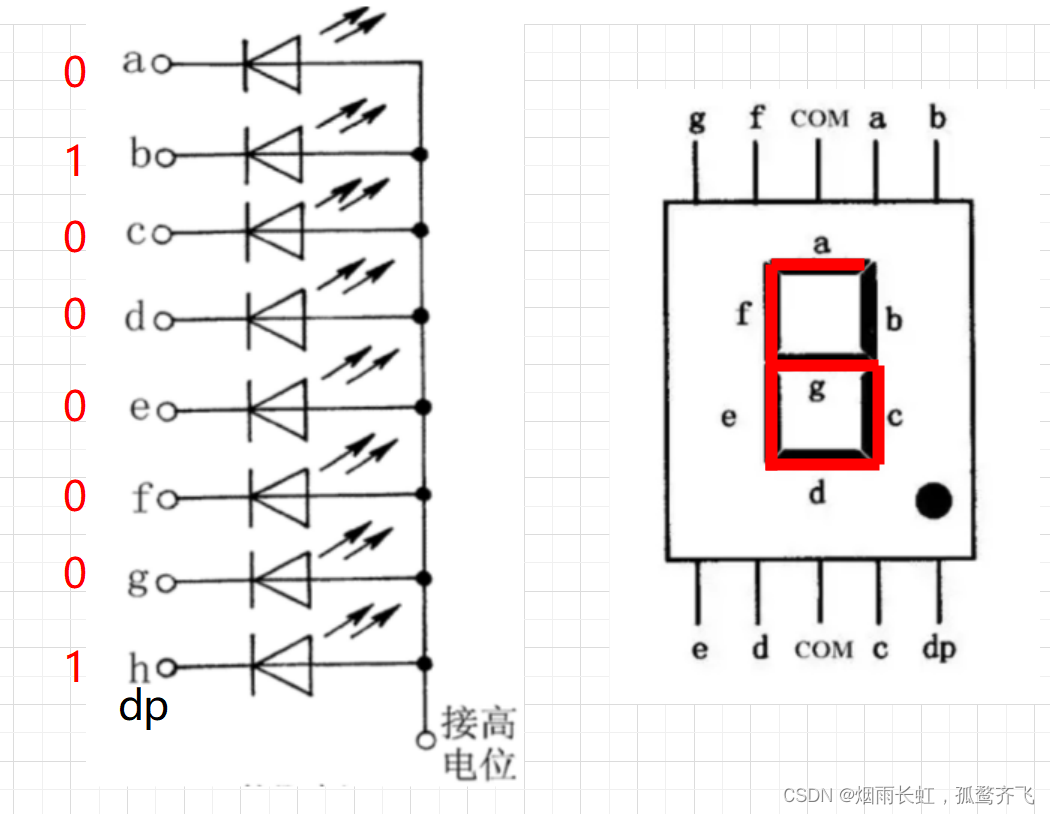
八段数码管中八个LED发光体有两种接法:共阴极 和 共阳极
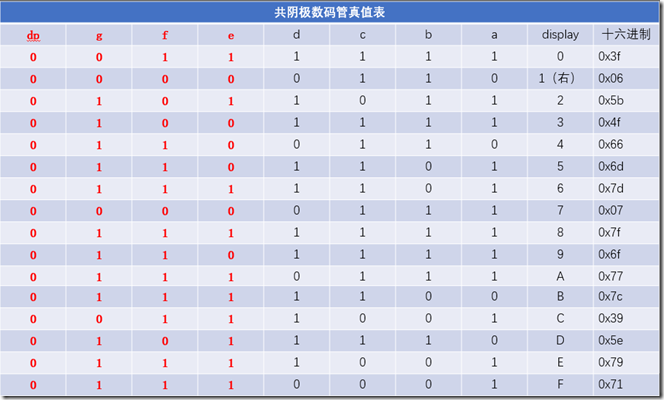
共阴极:公共端为阴极,加阳极数码管点亮
即当真值为 1 时,数码管点亮;真值为 0 时,数码管不亮
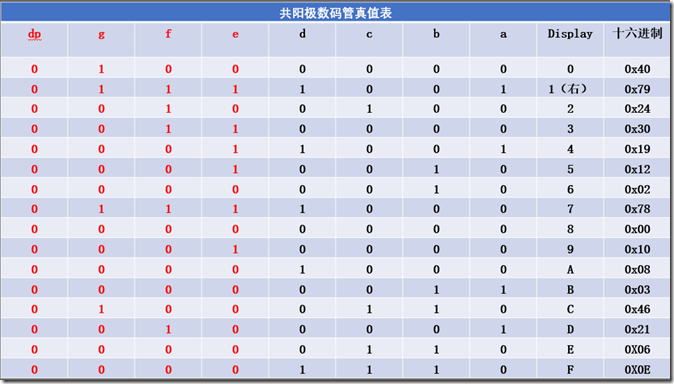
共阳极:公共端为阳极,加阴极数码管点亮
即当真值为 0 时,数码管点亮;真值为 1 时,数码管不亮
注意:
我们的单片机数码管上端是共阴极的,所以发光的条件是上端赋予低电平,下端赋予高电平
为了下面的方便这里总结出单片机的段码
/*0~9*/0x3f,0x06,0x5b,0x4f,0x66,0x6d,0x7d,0x07,0x7f,0x6f /*A~F*/0x77,0x7c,0x39,0x5e,0x79,0x71
位选:在使用时,需要程序选定使用哪几个数码管
段选:选定数码管后再对选定的数码管进行操作,其操作与单个数码管的操作一致
如果我们想在数码管显示我们的数字 6
共阴极:
<1>共阴极的公共端要接地(低电平)
<2>阳极(位选端)根据LED的亮灭需求给数据 0 或 1(1亮、0灭) ,这串数据称为 段码
<3>共阴极的环境下我们应该位选 a b c d e f 个数码管
<4>再对数码管进行电频的输入:1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 (段码)也就是 0x7d
共阳极:
<1>共阳极端的公共端要接到 VCC(高电平),阴极给数据 0 或 1 (1灭,0亮)
<2>共阳极的环境下我们应该位选 a b c d e f 个数码管
<3>再对数码管进行电频的输入:0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1
通过以上我们可以知道:共阴极与共阳极的段选是 互补 的
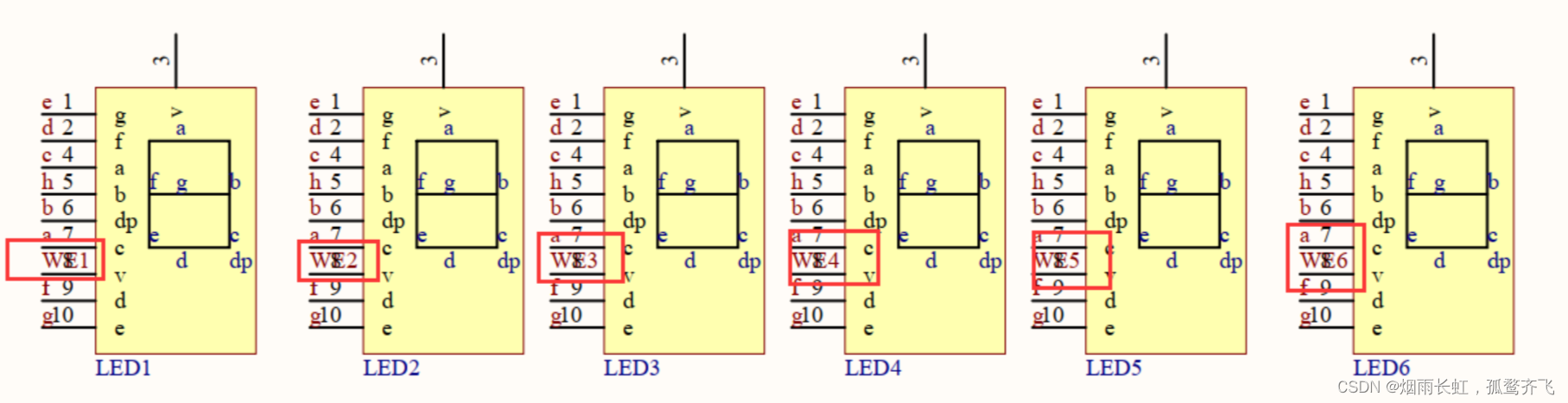
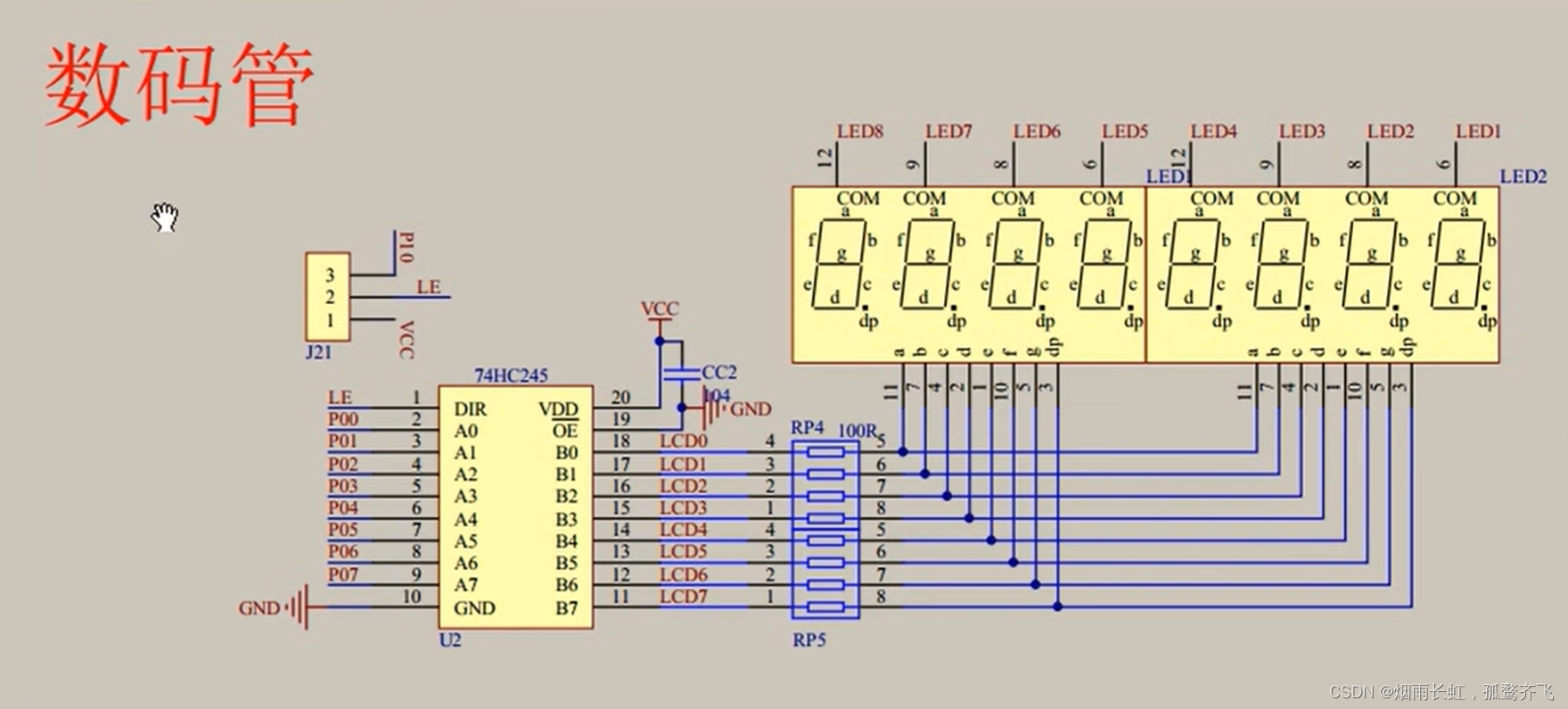
数码管的原理图
<1>数码管连接方式为共阴极连接
<2>而上面的 LED1 ~ 8,其实接在了138译码器的输出端138译码器正好可以实现让LED1 ~ 8输出 0 或 1
<3>138译码器可将LED 1 ~ 8的八个端口转化为由3个端口 (P22、P23、P24)控制,而G1、G2A、G2B端口被称为 使能端
<4>38译码器也叫 38线译码器 ,是由3个线到8个线,其中C是高位、A是低位,CBA组成的数符合 8 进制,控制着Y0 ~ Y7 这 8 个端口
<5>138译码器的作用就是用来选中某一位数码管的
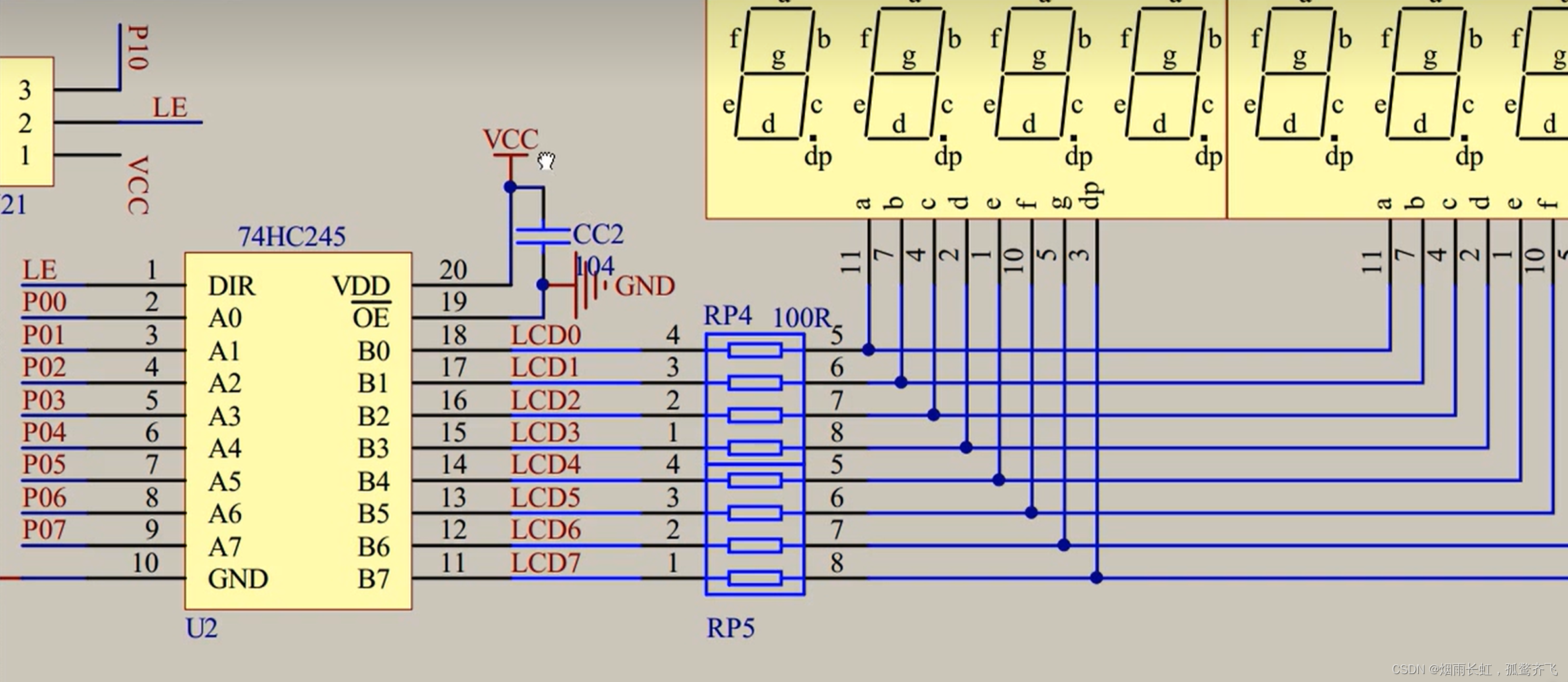
74HC245
<1>74HC245是一种 双向数据缓冲器,
输出使能(OE),方向控制(DIR),电源(VDD)和地(GND)<2>
方向控制(DIR):它接到了VCC(高电平)上,将数据从左边输出到右边,从右边将数据读取回左边<3>单片机的高电频驱动能力弱,低电频驱动能力强
<4>CC2电容是用来 稳定 电源的,叫电源滤波
<5>上图的中间位置有一排电阻(100R),作用为限流电阻 ,防止数码管的电流过大
代码实现
静态数码管的显示
#include <REGX52.H>unsigned char NixieTable[] = {0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F,0x77,0x7F,0x39,0x3F,0x79,0x71};void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number) {switch(Location){case 1:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 2:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 3:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 4:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;case 5:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 6:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 7:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 8:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;}P0 = NixieTable[Number]; }void main() {Nixie(6,6);while(1){} }
动态数码管的显示
#include <REGX52.H>unsigned char NixieTable[] = {0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F,0x77,0x7F,0x39,0x3F,0x79,0x71};void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz {unsigned char data i, j;while(xms){i = 2;j = 239;do{while (--j);} while (--i);xms--;} }void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number) {switch(Location){case 1:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 2:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 3:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 4:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;case 5:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 6:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 7:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 8:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;}P0 = NixieTable[Number];Delay(1);P0 = 0x00; }void main() {while(1){Nixie(1,1);Nixie(2,2);Nixie(3,3);} }
数码管实现表白画面
#include <REGX52.H>unsigned int sum = 3; unsigned char NixieTable[] = {0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F,0x77,0x7F,0x39,0x3F,0x79,0x71,0x40};void Delay(unsigned int xms) {unsigned char data i, j;while(xms){i = 2;j = 239;do{while (--j);} while (--i);xms--;} }void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number) {switch(Location){case 1:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 2:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 3:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 4:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;case 5:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 6:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 7:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 8:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;}P0 = NixieTable[Number];Delay(500); P0 = 0x00; }void Nixie1(unsigned char Location,Number) {switch(Location){case 1:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 2:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 3:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 4:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;case 5:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 6:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 7:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 8:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;}P0 = NixieTable[Number];Delay(100); P0 = 0x00; }void Nixie2(unsigned char Location,Number) {switch(Location){case 1:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 2:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 3:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 4:P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;case 5:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;case 6:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;case 7:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;case 8:P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;}P0 = NixieTable[Number];Delay(1); P0 = 0x00; }void main() {Nixie(1,5);Nixie(2,2);Nixie(3,0);Nixie(4,16);Nixie(5,1);Nixie(6,3);Nixie(7,1);Nixie(8,4);while(sum--){Nixie1(1,5);Nixie1(2,2);Nixie1(3,0);Nixie1(4,16);Nixie1(5,1);Nixie1(6,3);Nixie1(7,1);Nixie1(8,4);}while(1){Nixie2(1,5);Nixie2(2,2);Nixie2(3,0);Nixie2(4,16);Nixie2(5,1);Nixie2(6,3);Nixie2(7,1);Nixie2(8,4);} }