1.先定义一个类对象vector
为了防止和库里面发生冲突,定义一个命名空间,将类对象放在命名空间 里面
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace zjw {class vector {public:private:};
}
2.定义变量,需要一个迭代器,为了便于修改,变成任意类型的迭代器,我们使用函数模版,三个迭代器变量 _start用于指向顺序表的头,_finish指向顺序表的结尾的下一位,_end_of_storage保存总容量,在初始化列表中先设置为空
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace zjw {template<class T>class vector {public:typedef T * iterator;//迭代器类型vector():_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){}private:iterator _start;iterator _finish;iterator _end_of_storage};
}
3.定义函数
1.返回指向顺序表开始的迭代器函数
2.返回指向顺序表结尾的迭代器函数
3.返回容量大小的函数
4.返回顺序表元素多少
5.判断顺序表为空地的函数
5.一个运算符重载的函数(返回给定下标下的值)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace zjw {template<class T>class vector {public:typedef T * iterator;//迭代器类型vector():_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){}iterator begin()//1{return _start;}iterator end()//2{return _finish;}size_t capacity()//3{return _end_of_storage - _start;}size_t size()//4{return _finish - _start;}bool empty()//5{return _finish == _start;}T& operator[](size_t pos)//6{assert(pos < size());return _start[pos];}private:iterator _start;iterator _finish;iterator _end_of_storage;};
}
4.reserve函数开空间
void reserve(size_t n){if (n > capacity){T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start){memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * size());delete[] _start;}_start = tmp;_finish = _start + size();_end_of_storage = _start + n;}}
5.push_back函数尾插,以及尾删函数
void push_back(const T& x){if (_finish == _end_of_storage){reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);}*_finish = x;_finish++;}void pop_back(){assert(!empty());--_finish;}
6.测试尾插,尾删,下标遍历,迭代器遍历,范围for遍历,以及运算符重载返回对应下标的元素
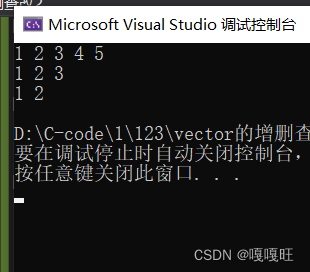
void test1(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);v1.push_back(5);for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++){cout << v1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;v1.pop_back();v1.pop_back();vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin();while (it != v1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;v1.pop_back();for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}
这里开空间的函数会发生问题
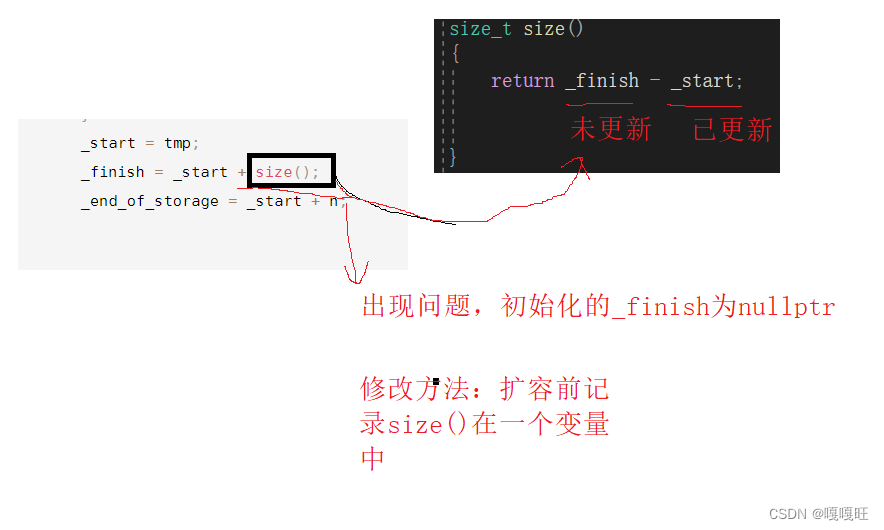
7.修改扩容函数
void reserve(size_t n){if (n > capacity){ int sz=size();T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start){memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * size());delete[] _start;}_start = tmp;_finish = _start + sz;_end_of_storage = _start + n;}}
8.resize函数
参数小于容量大小,相当于缩容,参数大于容量大小,相当于扩容,超过_finish的用值初始化
在讲resize之前看看模版会不会给匿名变量初始化,内置类型是否能初始化.
template <class T>void f(){T x = T();cout << x << endl;}void test3(){f<int>();f<int*>();f<double>();}
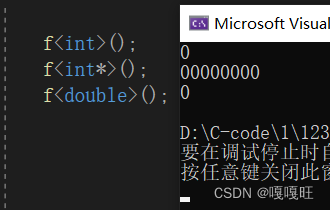
发现可以,所以我们在resize里面当n>capacity(),我们可以把顺序表外的用来初始化,自定义类型相当于调用自己的构造函数,内置函数我们在这假装理解为调用自己的构造函数.
void resize(size_t n, T val = T()){if (n < size()){_finish = _start + n;}else{if (n > capacity())reserve(n);while (_finish != _start + n){*_finish = val;++_finish;}}}
9.测试resize
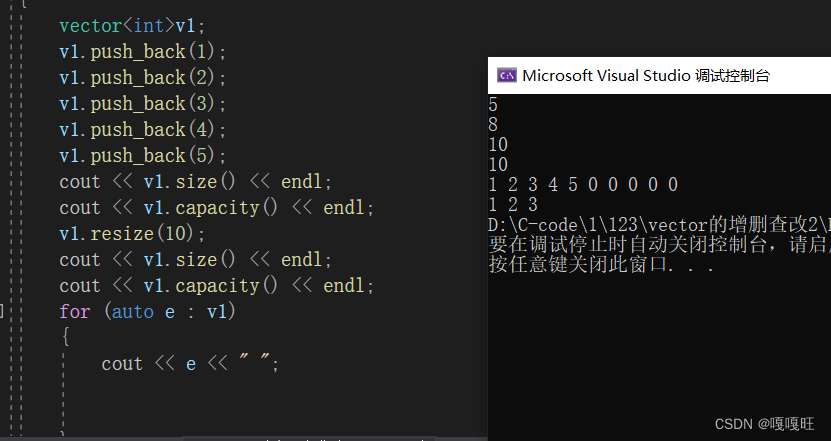
void test2(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);v1.push_back(5);cout << v1.size() << endl;cout << v1.capacity() << endl;v1.resize(10);cout << v1.size() << endl;cout << v1.capacity() << endl;for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;v1.resize(3);for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}}}
10.封装一个打印函数用于任何vector对象
void func(const vector<int>& v){for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)//下标{cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();//迭代器while (it != v.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : v)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}
因为打印不同对象的元素,为了区分是有一个this指针的,但是参数是const 无法产生this指针
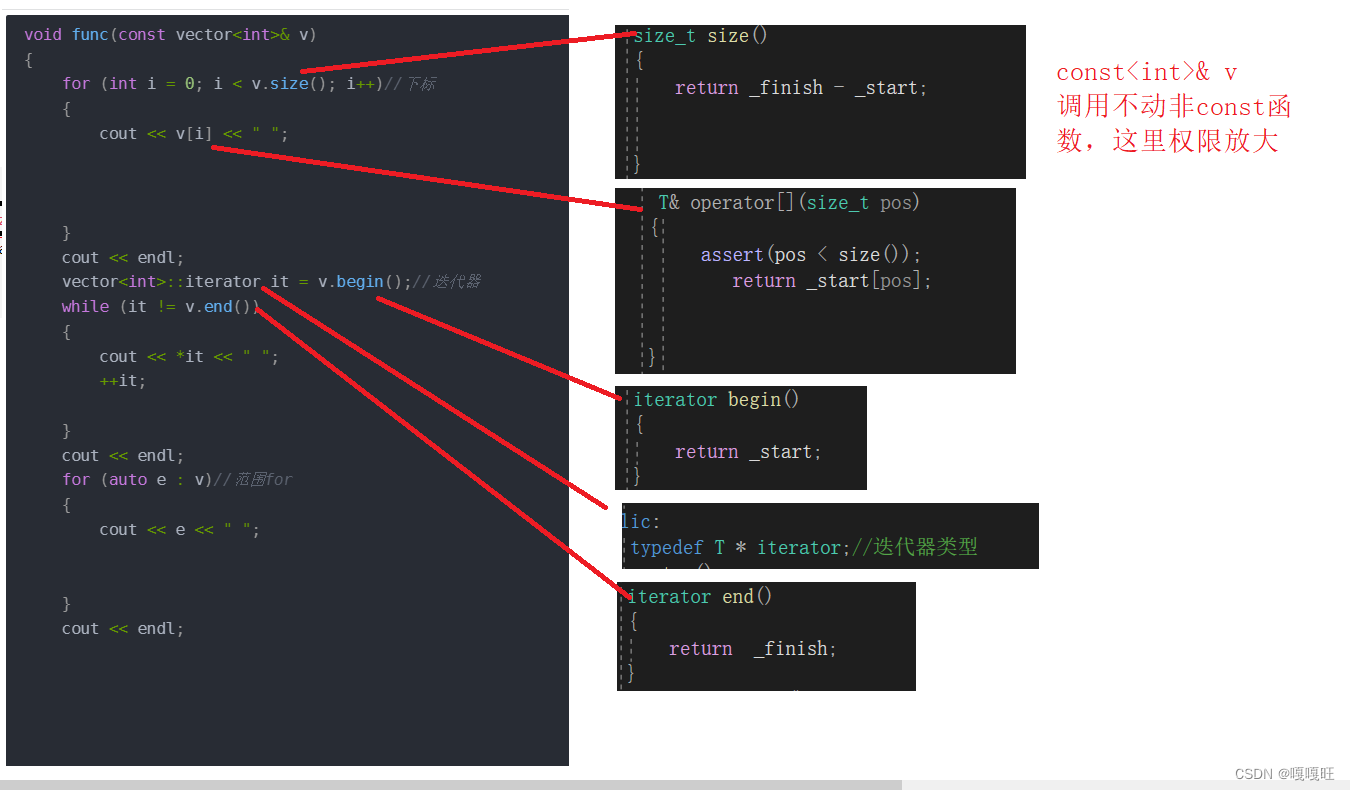
解决方法,在这些函数后面加 const ,如果是const对象调用的话,就是权限平移,如果是非const的话,是权限缩小,都可以调用了,如果要限制别人去修改这个*it,我们可以定义一个const的迭代器
void func(const vector<int>& v){for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)//下标{cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();//迭代器while (it != v.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : v)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}
void test4(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);v1.push_back(5);func(v1);}
11.insert函数实现
void insert(iterator pos, const T& val){assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos <= _finish);if (_finish == _end_of_storage){reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);}iterator end = _finish - 1;while (end >= pos){*(end + 1) = *end;--end;}*pos = val;++_finish;}
测试insert
void test5(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);v1.push_back(5);for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;auto pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3);//找到3的位置if (pos != v1.end()){v1.insert(pos, 30);//3前插入30}for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;(*pos)++;//让3+1for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}}
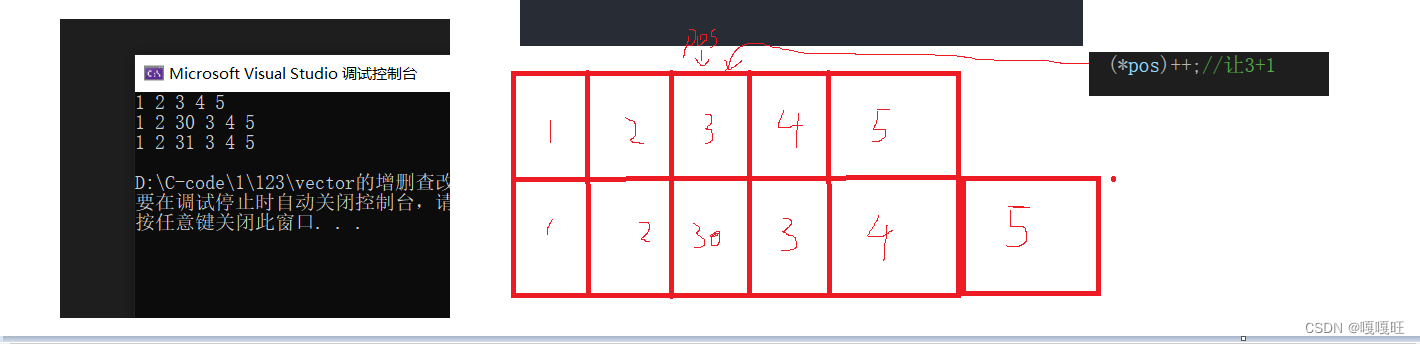
pos保存的之前是3的地址,如果在3前插入一个30,pos所指向的位置就变成了30,*pos++,就变成了31;
如果我们不使用push_back(5)的话
void test5(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);//v1.push_back(5);for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;auto pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3);//找到3的位置if (pos != v1.end()){v1.insert(pos, 30);//3前插入30}for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;(*pos)++;//让3+1for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}}
会出现报错,到底是怎么一回事??
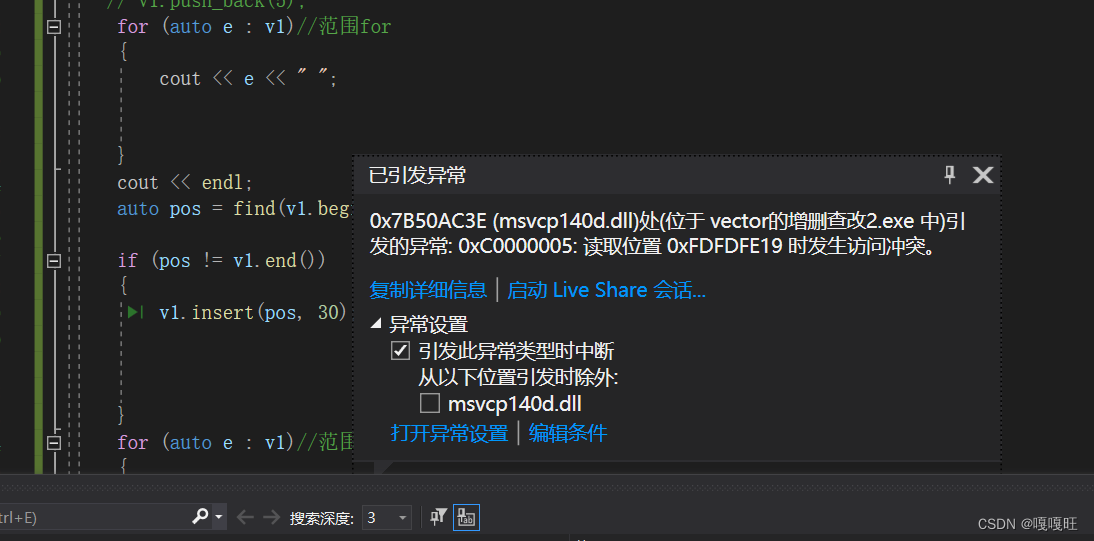
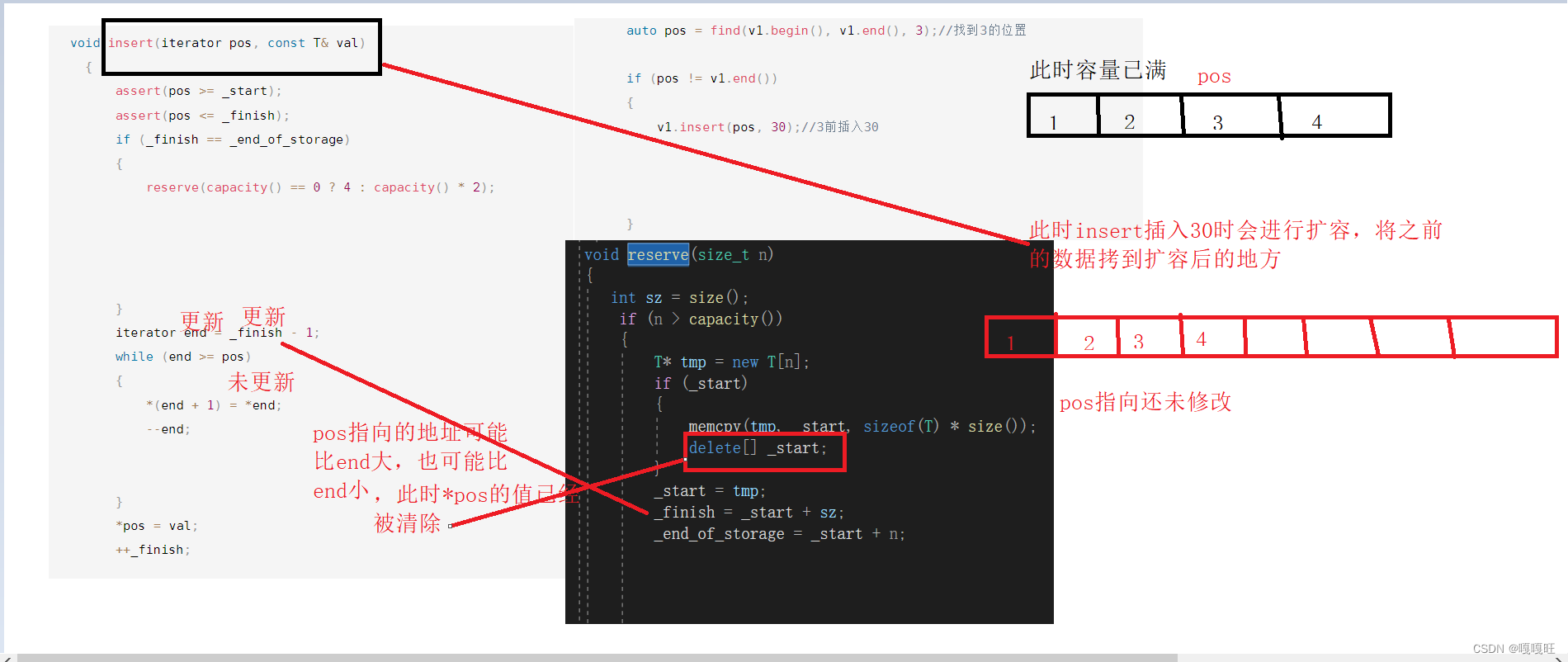
如何修改??
我们需要在未扩容前记录好pos距离_start的位置,拷到新空间,他与新_start也保持这个距离,更新pos
void insert(iterator pos, const T& val){assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos <= _finish);if (_finish == _end_of_storage){int len=pos - _start;reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);pos = _start + len;}iterator end = _finish - 1;while (end >= pos){*(end + 1) = *end;--end;}*pos = val;++_finish;}
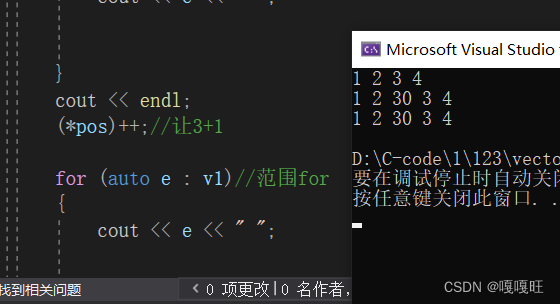
这里的*pos里面的数据被清理,如果不清理应该是3++,应该是4,我们可以注释掉reserve中的delete看看
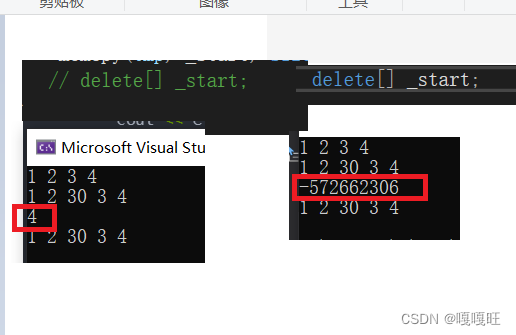
这里的问题被叫做迭代器失效
12.earse函数
void eraase(iterator pos){assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos < _finish);iterator start = pos + 1;while (start != _finish){*(start - 1) = *start;++start;}--_finish;}
earse函数测试
void test6(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;auto pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 2);if (pos != v1.end()){v1.erase(pos);//删除2}(*pos)++;2位置上的元素++for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}}
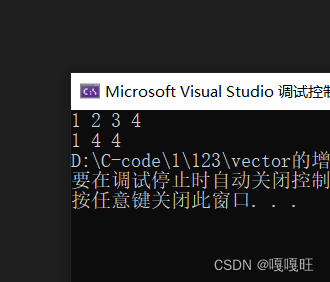
这里2删除后2的地址上存的就是3,然后给3++;在std中这个也算迭代器失效,由于这里是自己写的,所以没报错.
void test6(){std::vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;auto pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 2);if (pos != v1.end()){v1.erase(pos);}(*pos)++;for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}}}
上面会调用vector里面的函数
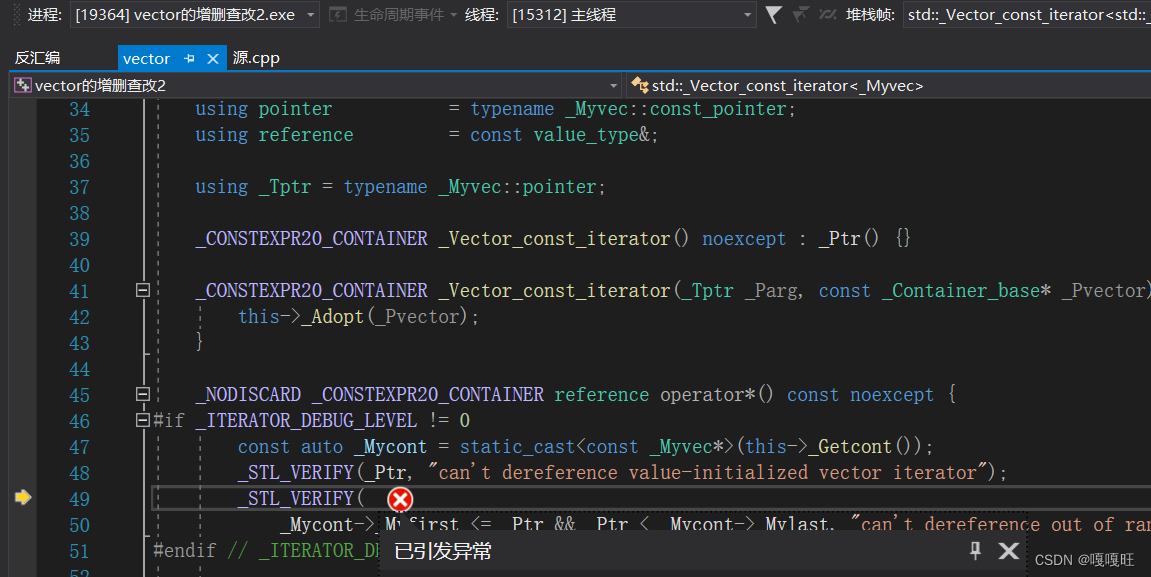
在不同编译器下有不同的处理情况。在vs中std我们认为迭代器失效,如果删除的是4的话,以我们实现的earse后,–_finish ;4那里的值没有被清理,所以后面的(*pos)++也不会出错,但在vs中我们使用vector里面的实现认为迭代器失效.
我们可以将代码拷过去在linux下试一下g++是怎么回事??
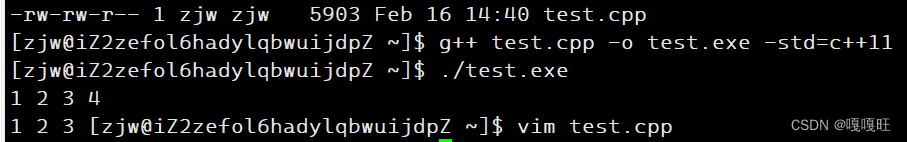
在g++中使用库中的vector函数删除数据4没有报错,对于迭代器失效,不同编译器也有不同处理.
13.整体代码
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
namespace zjw {template<class T>class vector {public:typedef T * iterator;//迭代器类型typedef T* const_iterator;//迭代器类型vector():_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){}iterator begin()const {return _start;}iterator end() const{return _finish;}size_t capacity(){return _end_of_storage - _start;}size_t size() const{return _finish - _start;}bool empty(){return _finish == _start;}T& operator[](size_t pos) const{assert(pos < size());return _start[pos];}void reserve(size_t n){int sz = size();if (n > capacity()){T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start){memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * size());delete[] _start;}_start = tmp;_finish = _start + sz;_end_of_storage = _start + n;}}void push_back(const T& x){if (_finish == _end_of_storage){reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);}*_finish = x;_finish++;}void pop_back(){assert(!empty());--_finish;}void resize(size_t n, T val = T()){if (n < size()){_finish = _start + n;}else{if (n > capacity())reserve(n);while (_finish != _start + n){*_finish = val;++_finish;}}}void insert(iterator pos, const T& val){assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos <= _finish);if (_finish == _end_of_storage){int len=pos - _start;reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);pos = _start + len;}iterator end = _finish - 1;while (end >= pos){*(end + 1) = *end;--end;}*pos = val;++_finish;}void erase(iterator pos){assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos < _finish);iterator start = pos + 1;while (start != _finish){*(start - 1) = *start;++start;}--_finish;}private:iterator _start;iterator _finish;iterator _end_of_storage;};void test1(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);v1.push_back(5);for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++){cout << v1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;v1.pop_back();v1.pop_back();vector<int>::const_iterator it = v1.begin();while (it != v1.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;v1.pop_back();for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}void test2(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);v1.push_back(5);cout << v1.size() << endl;cout << v1.capacity() << endl;v1.resize(10);cout << v1.size() << endl;cout << v1.capacity() << endl;for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;v1.resize(3);for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}}void func(const vector<int>& v){for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)//下标{cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();//迭代器while (it != v.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;for (auto e : v)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}void test4(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);v1.push_back(5);func(v1);}void test5(){vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);// v1.push_back(5);for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;auto pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3);//找到3的位置if (pos != v1.end()){v1.insert(pos, 30);//3前插入30}for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;(*pos)++;//让3+1cout << *pos << endl;for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}void test6(){std:: vector<int>v1;v1.push_back(1);v1.push_back(2);v1.push_back(3);v1.push_back(4);for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;auto pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 4);if (pos != v1.end()){v1.erase(pos);}(*pos)++;for (auto e : v1)//范围for{cout << e << " ";}}}int main()
{// zjw::test1();zjw::test6();// zjw::test3();
}