目录
- 1. GraalVM
- 1.1 生成本地可执行应用
- 1.2 生成docker镜像
- 2. 支持虚拟线程
- 2.1 不开启虚拟线程时压测
- 2.2 开启虚拟线程时压测
- 3. HTTP Interface
1. GraalVM
- 使用GraalVM将SpringBoot应用程序编译成本地可执行的镜像文件,可以显著提升启动速度、峰值性能以及减少内存应用。
- 传统的应用都是编译成字节码,然后通过JVM解释并最终编译成机器码来运行,而Spring Native则是通过AOT提前编译为机器码,在运行时直接静态编译成可执行文件,比如windows上的.exe文件,不依赖JVM。GraalVM的即时编译器和AOT编译器可以显著提高应用程序的性能。
- AOT: Ahead-of-Time Compilation,预编译在Java9中作为实验性功能提出。将Java类编译为本机代码,减少Java应用的启动时间和内存占用。
1.1 生成本地可执行应用
- maven使用的插件
<plugin><groupId>org.graalvm.buildtools</groupId><artifactId>native-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
- 生成本地应用命令
mvn -Pnative native:compile
- gradle需要使用下面的插件
plugins {id 'java'id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.2.2'id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.4'id 'org.graalvm.buildtools.native' version '0.9.28'
}
- 生成本地应用命令
gradle nativeCompile
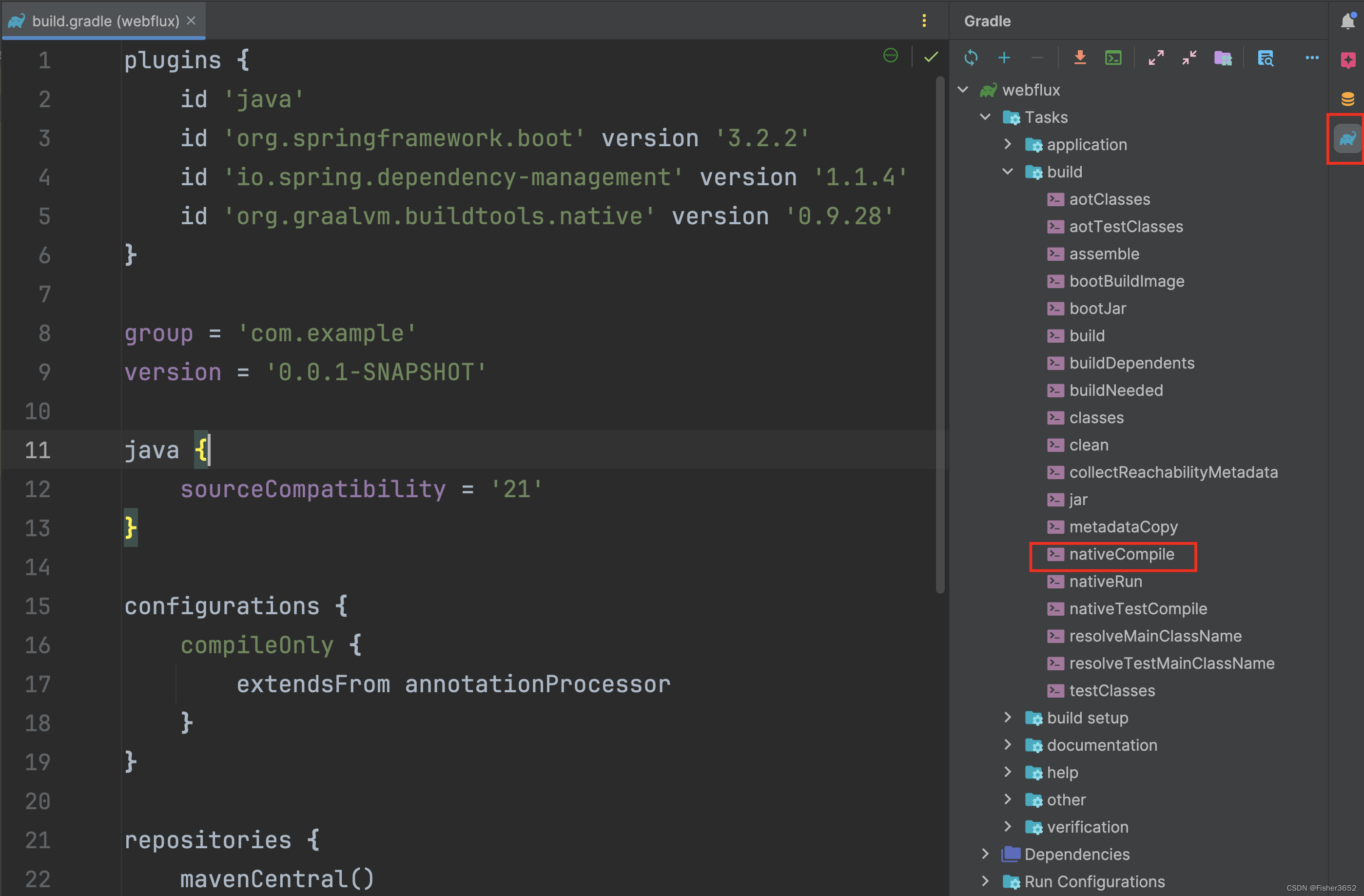
- 或者在IDEA中点击build下的
nativeCompile
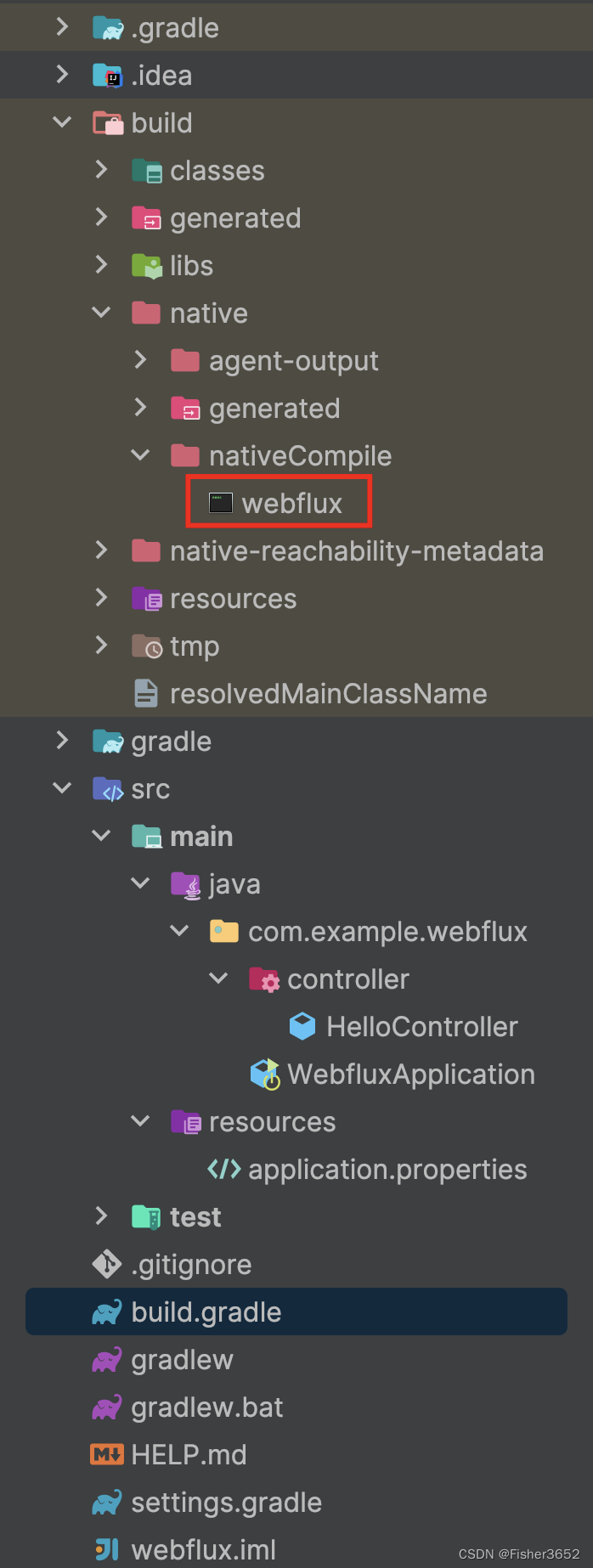
- 最后会在
build/native/nativeCompile下生成一个本地可执行文件,可以双击运行
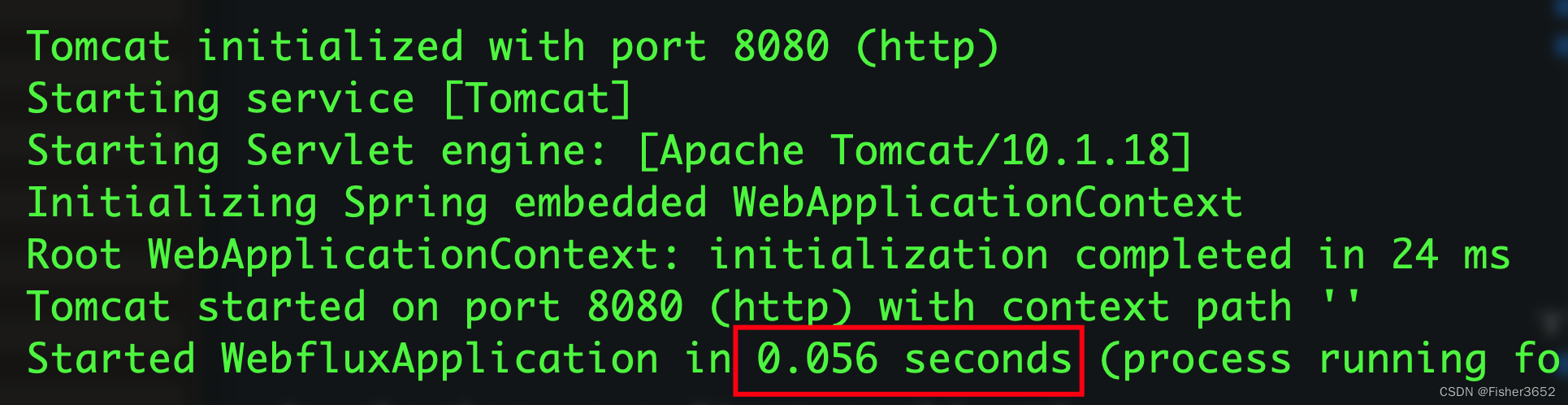
- 启动速度只有毫秒级
- 参考https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/native-image.html#native-image.developing-your-first-application.native-build-tools.maven
1.2 生成docker镜像
- maven使用的命令
mvn -Pnative spring-boot:build-image
- gradle使用的命令
gradle bootBuildImage
- 或者在IDEA中点击build下的
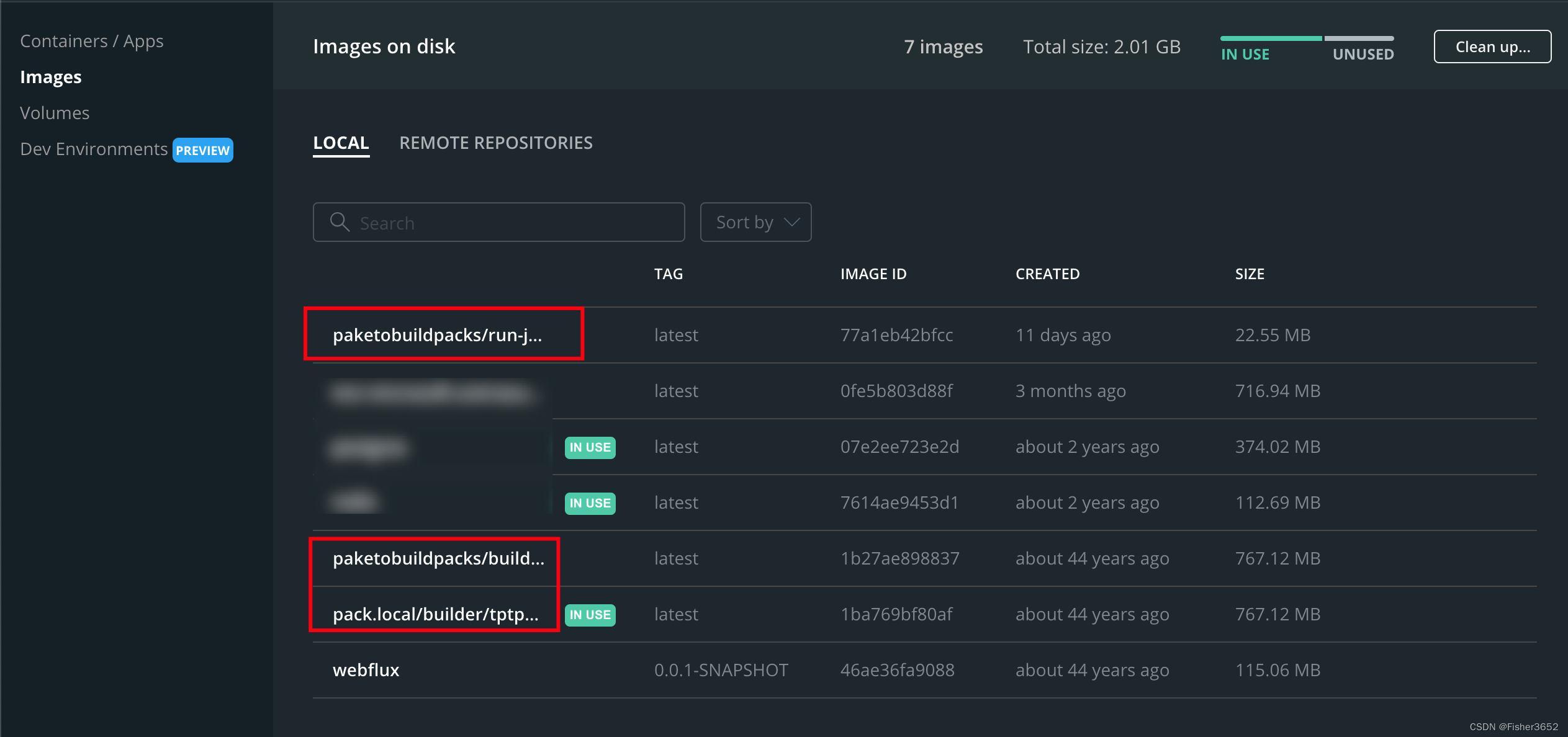
bootBuildImage - 因为这里会通过docker拉取其他的依赖,所以这时候需要启动docker,通过docker客户端会发现多了3个image,后面显示的created时间是错的,不需要在意
paketobuildpacks/run-jammy-tiny
paketobuildpacks/builder-jammy-tiny
# tptpbfysrt会每次不一样
pack.local/builder/tptpbfysrt
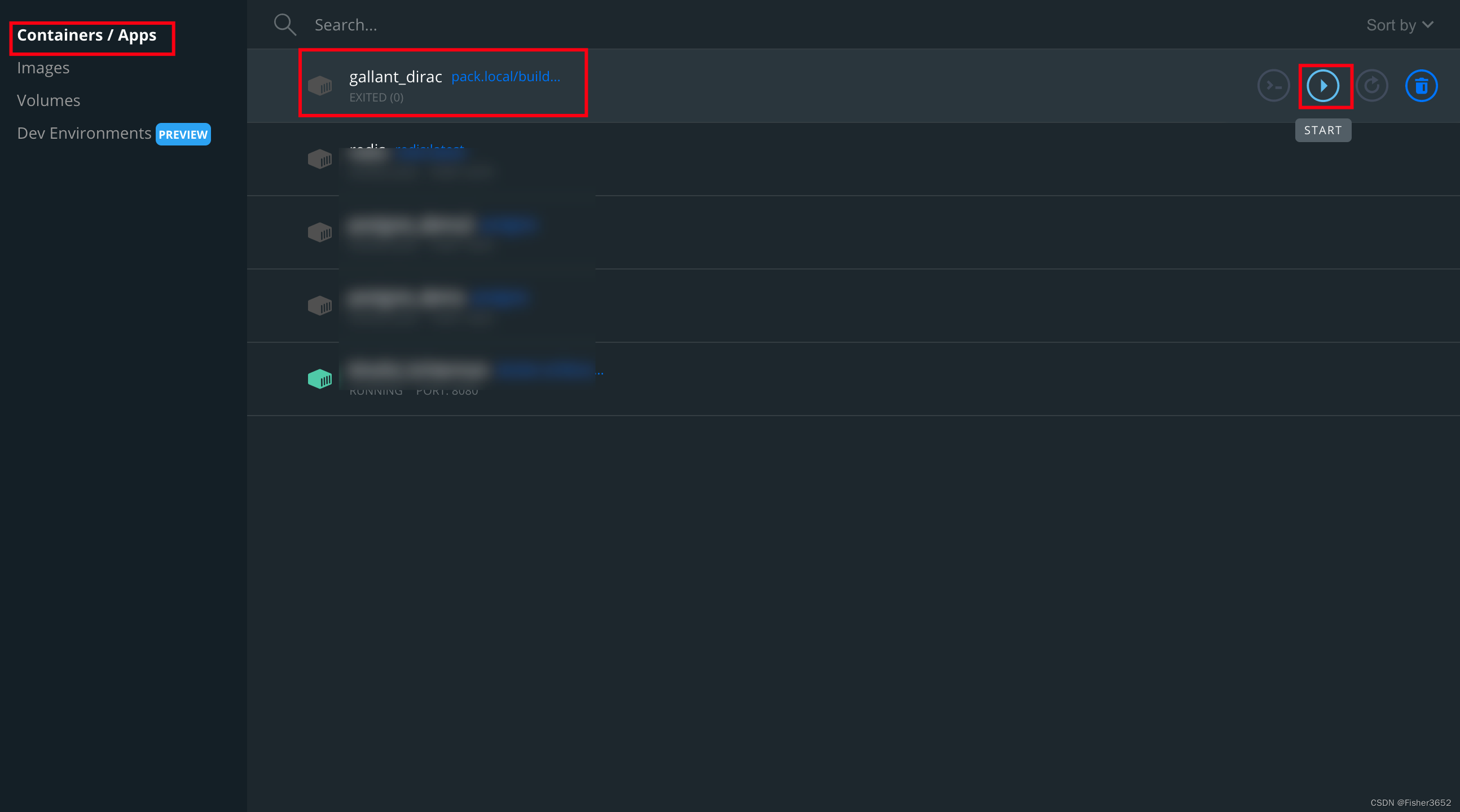
- 然后会自动使用
pack.local/builder/...启动一个container用来创建镜像,会下载很多东西,如果执行失败,再次点击start运行即可,不会重新下载已经下载过的文件,不要重新执行gradle bootBuildImage命令,不然会全部从头开始执行一遍下载依赖的过程,非常耗费时间。
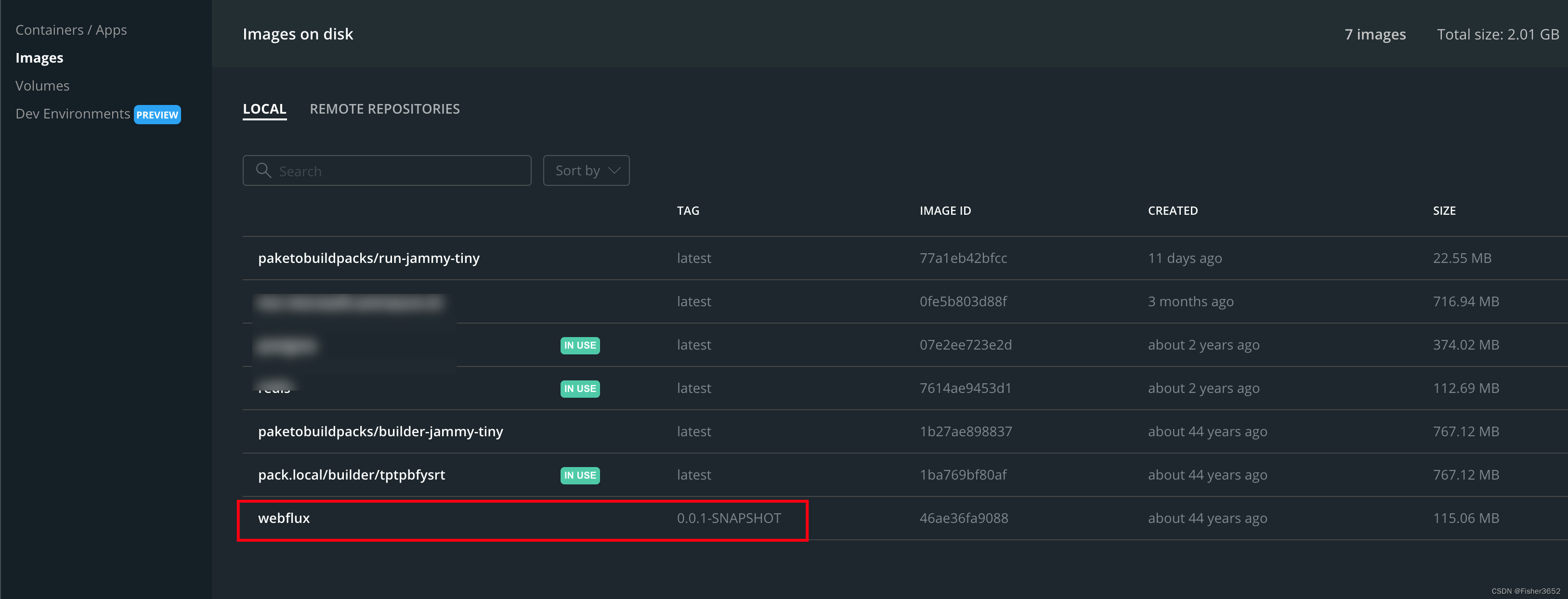
- 执行成功后,会在images中出现一个新生成的镜像文件
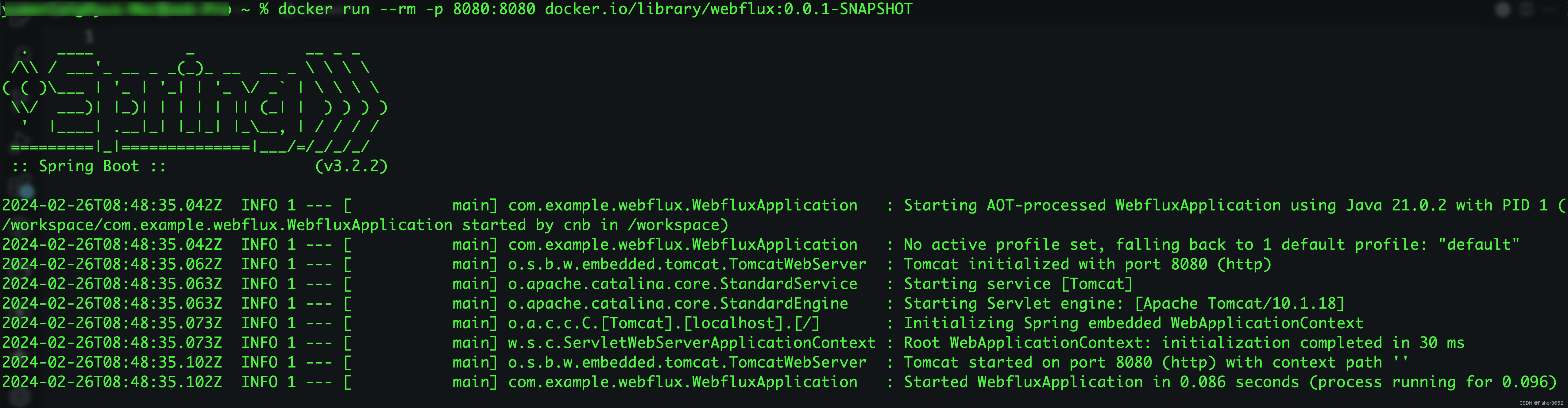
- 使用下面命令启动
# myproject:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT换成你自己的项目名称和版本
docker run --rm -p 8080:8080 docker.io/library/myproject:0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
- 参考https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/native-image.html#native-image.developing-your-first-application.buildpacks.maven
2. 支持虚拟线程
- Spring Boot3.2开始虚拟线程,需要使用JDK21,并设置以下属性
spring.threads.virtual.enabled=true
- 启用虚拟线程后,Tomcat 和 Jetty 将使用虚拟线程处理请求。这意味着处理网络请求的应用代码(如Controller中的方法)将在虚拟线程上运行。下面是Tomcat开启虚拟线程的代码,在
tomcat-embed-core-10.1.19.jar!\org\apache\tomcat\util\net\AbstractEndpoint.class中
public void createExecutor() {internalExecutor = true;if (getUseVirtualThreads()) {executor = new VirtualThreadExecutor(getName() + "-virt-");} else {TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue();TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-", daemon, getThreadPriority());executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,taskqueue, tf);taskqueue.setParent( (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor);}}
- 创建一个controller

- 启动程序,调用hello接口,查看日志打印
2024-02-24T16:41:15.778+08:00 INFO 14252 --- [omcat-handler-0] com.example.demo.Controller : [Controller][hello] VirtualThread[#46,tomcat-handler-0]/runnable@ForkJoinPool-1-worker-1
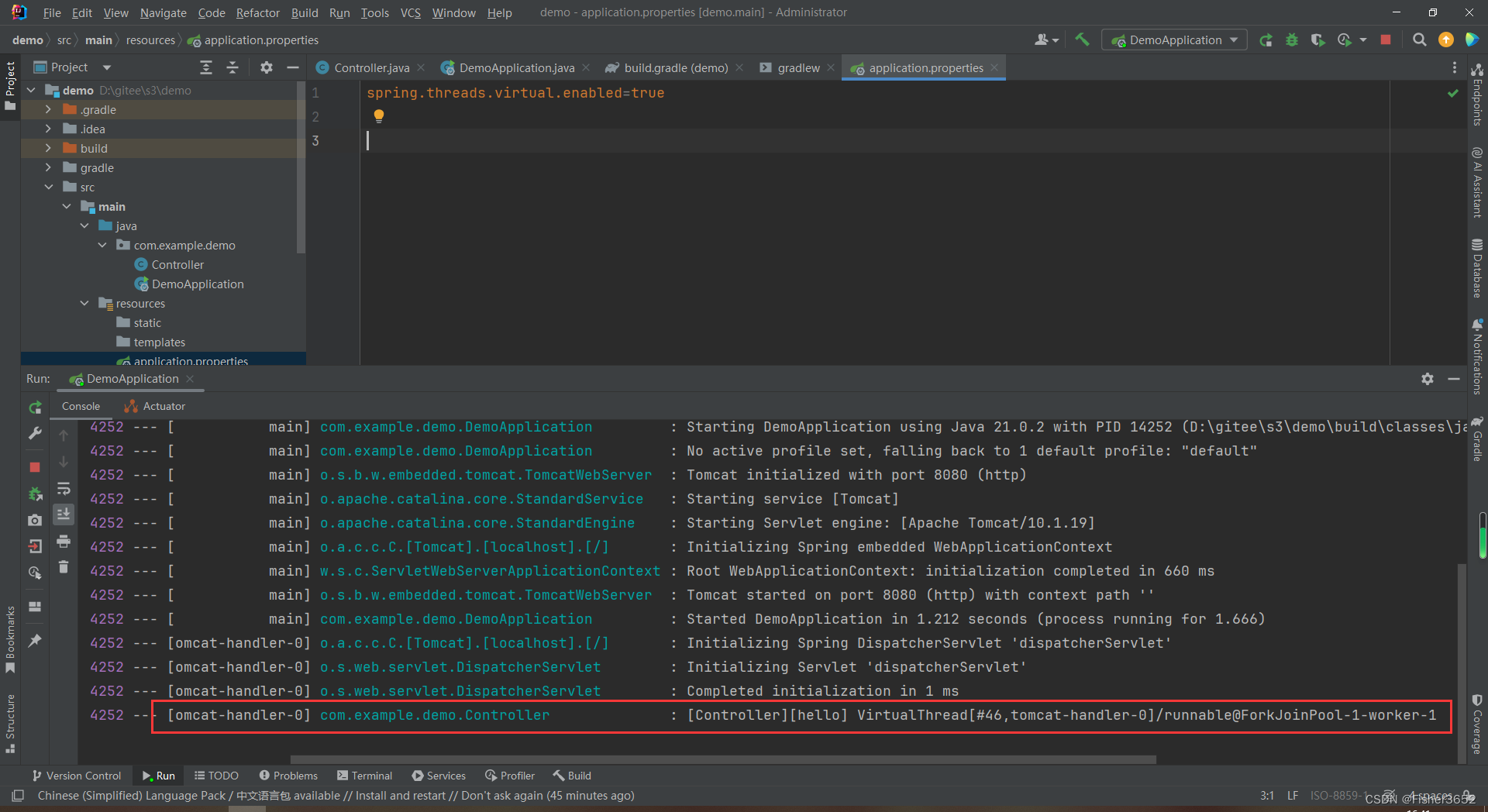
- 通过
VirtualThread[#46,tomcat-handler-0]可以看出使用的是虚拟线程 - 关闭虚拟线程,再次调用接口,查看日志打印
2024-02-24T16:43:14.715+08:00 INFO 15844 --- [nio-8080-exec-1] com.example.demo.Controller : [Controller][hello] Thread[#39,http-nio-8080-exec-1,5,main]
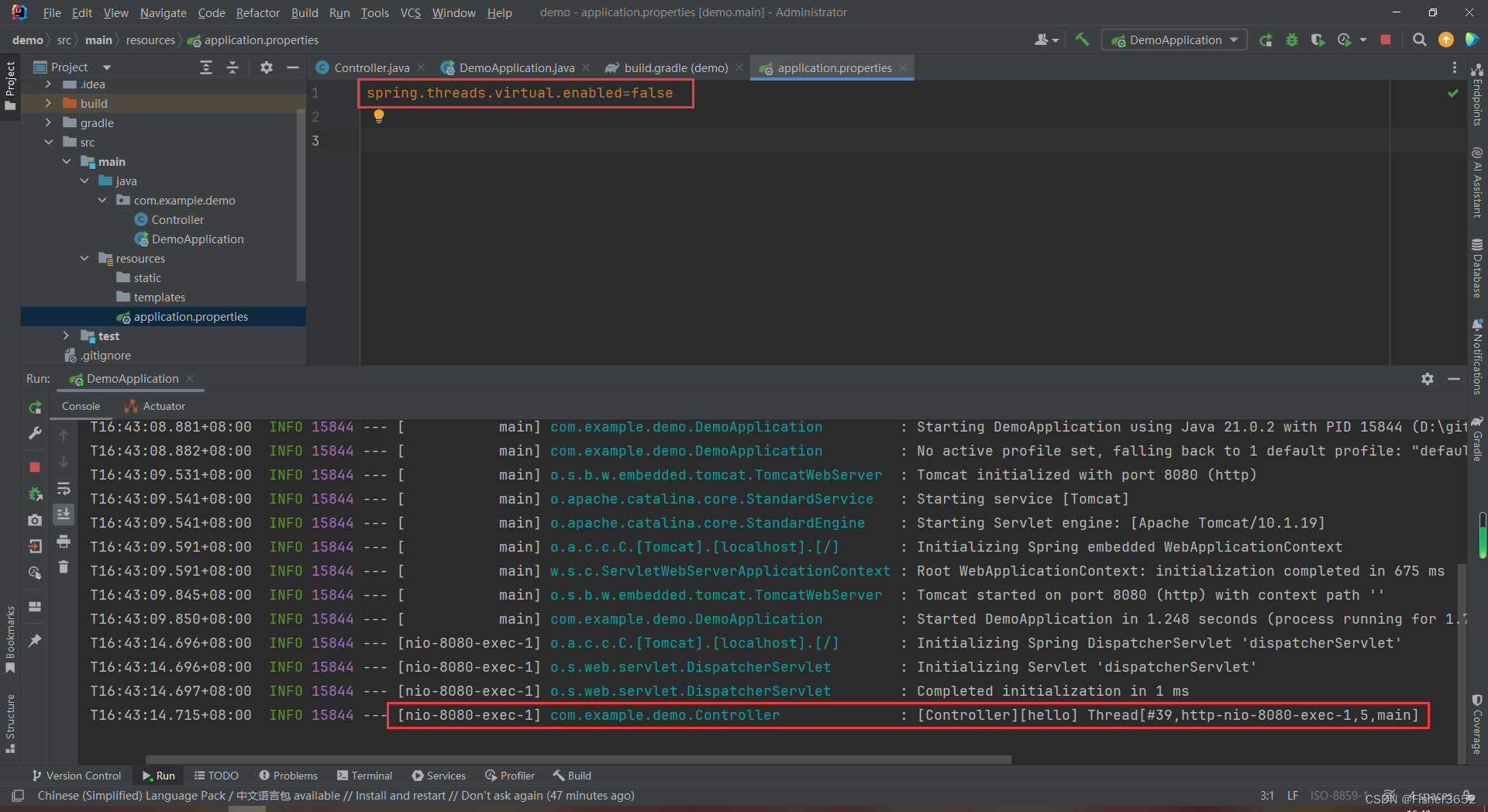
- 通过
Thread[#39,http-nio-8080-exec-1,5,main]可以看出使用的是平台线程
2.1 不开启虚拟线程时压测
- 需要提前安装压测工具plow
# 100000个请求,500个并发
plow http://localhost:8080/hello -c 500 -n 100000
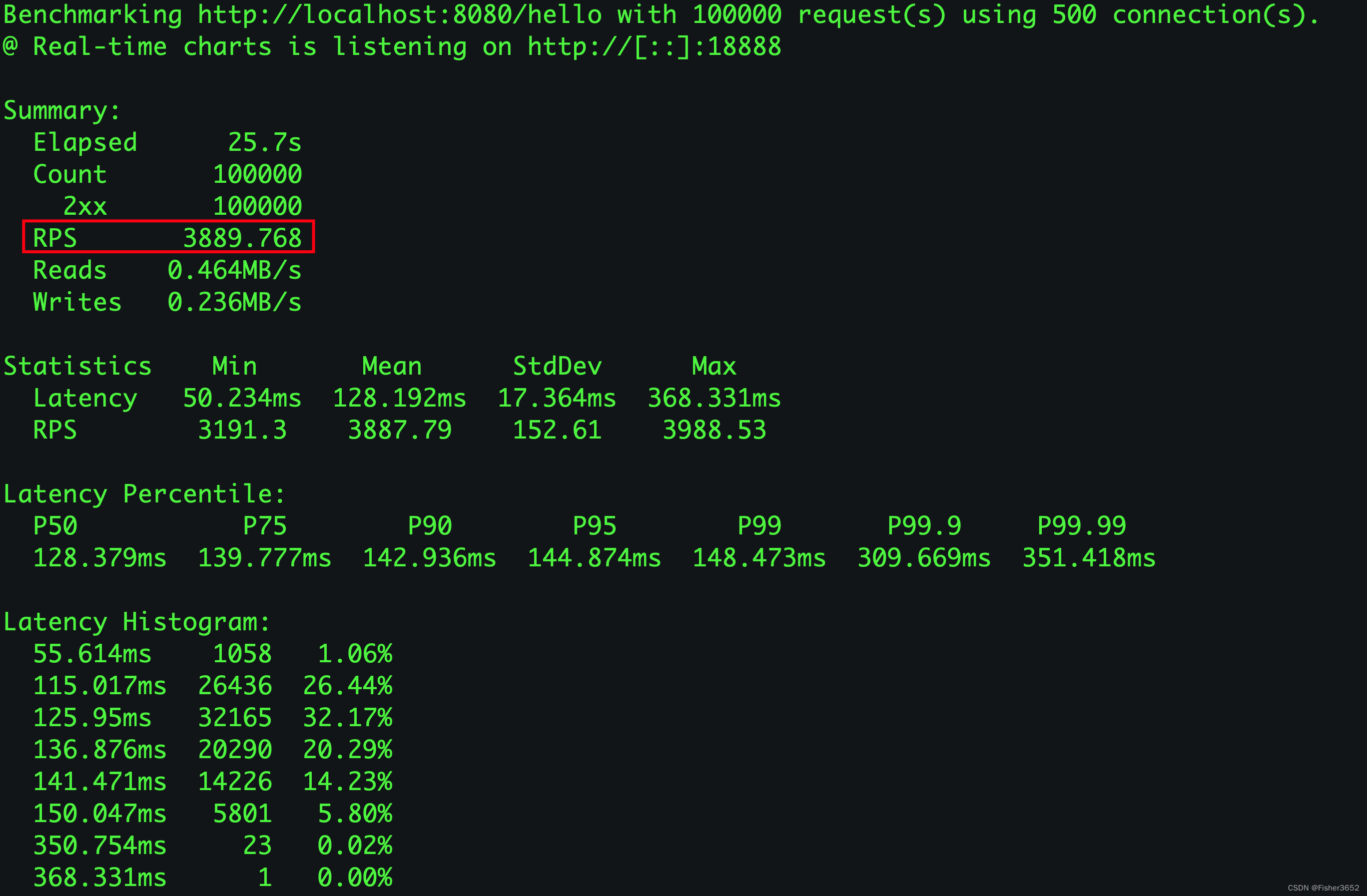
- 平均每秒处理3889.768个请求,延迟主要集中在115到140ms左右
2.2 开启虚拟线程时压测
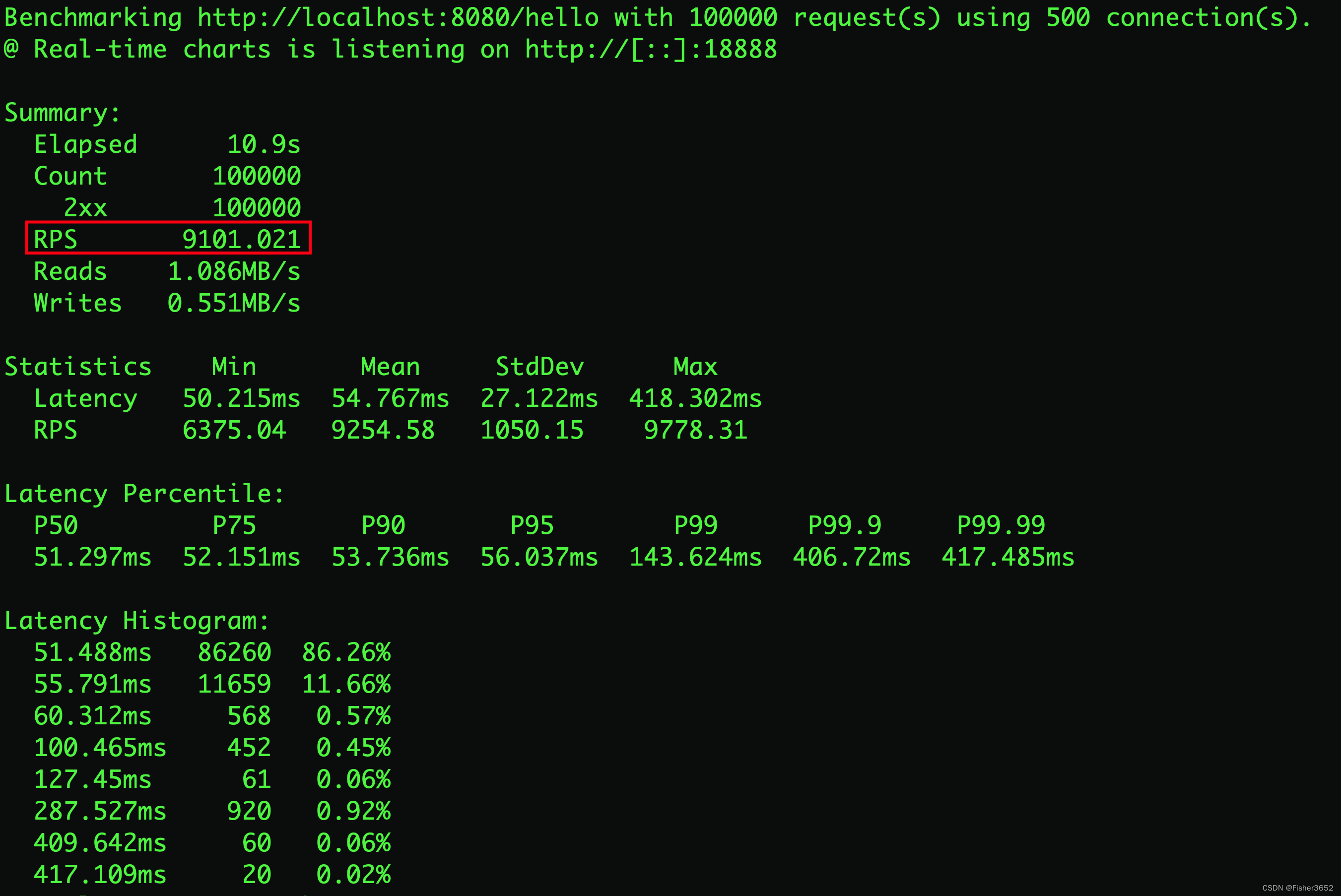
- 平均每秒处理9101.021个请求,延迟主要集中在51.488ms
3. HTTP Interface
-
将 HTTP 服务定义为带有 @HttpExchange 方法的接口,并将这样的接口传递给 HttpServiceProxyFactory,创建一个代理,通过 HTTP 客户端(如 RestClient 或 WebClient)执行请求。类似于Feign使用声明式的方式访问Http服务。可以参考https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/integration/rest-clients.html#rest-http-interface
-
创建一个http interface
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.service.annotation.GetExchange;
import org.springframework.web.service.annotation.HttpExchange;@HttpExchange("/api")
public interface HelloClient {@GetExchange("/hello")String hello(@RequestParam String msg);}- 注入声明式客户端,通过给HttpServiceProxyFactory注入带目标接口baseUrl的client,可以RestClient、WebClient、RestTemplate,这里使用RestClient
import com.example.springboot3.client.HelloClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestClient;
import org.springframework.web.client.support.RestClientAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.service.invoker.HttpServiceProxyFactory;@Configuration
public class AppConfig {@Beanpublic HelloClient toClient() {RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder().baseUrl("http://localhost:80/").build();HttpServiceProxyFactory httpServiceProxyFactory = HttpServiceProxyFactory.builderFor(RestClientAdapter.create(restClient)).build();return httpServiceProxyFactory.createClient(HelloClient.class);}}- Controller
import com.example.springboot3.client.HelloClient;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController
public class HelloController {@Resourceprivate HelloClient client;@GetMapping("hello")public String hello(@RequestParam String msg) {return client.hello(msg);}}- 更具体的修改内容可以查看https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-3.2-Release-Notes