问题现象:
最近在项目中,有一些逻辑想用List集合的Stream流式操作来快速实现,但由于之前没做好学习笔记和总结,导致一时间想不起来,只能用本方法来解决,如下:
可以看出来代码量是比较冗长的,于是就回顾了一下List集合的Stream流式操作的相关知识点;打算打一个代码优化!
问题分析:
由上图可以知道,我是想将集合list(List<Map<String, Object>> list )根据元素(Map<String, Object> map)中的key为"infoType"的字段值来作相关的业务逻辑,形成指定的集合(如:List<Map<String, Object>> baseInfoList等),然后再存到map集合(Map<String, Object> exportParams)中去。
根据这个思路其实就可以使用集合list中的Stream流式操作中的Collectors.groupingBy方法来解决了:
1、首先对集合list中使用Stream流式操作中的Collectors.groupingBy进行分组(分组依据是元素中的key:"infoType"),形成infoTypeListMap集合(Map<String, List<Map<String, Object>>> infoTypeListMap)。
2、遍历infoTypeListMap集合,然后将元素存入exportParams集合。
解决方法:
将上图的代码做如下修改即可:
exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.BASE_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.EDUCATION_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.TRAIN_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.WORK_EXPERIENCE_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.SALARY_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.FAMILY_CONTACT_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(StaffInfoTypeEnum.LANGUAGE_INFO.getCode() + "_LIST"), new ArrayList<>());Map<String, List<Map<String, Object>>> infoTypeListMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(map -> (String)map.get("infoType")));infoTypeListMap.entrySet().stream().forEach(entry->{String key = entry.getKey();List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = entry.getValue();exportParams.put(StrUtil.toCamelCase(key+"_LIST"), mapList);});拓展:
文末有我写的测试代码,有助于理解,可直接搬运使用!
相信小伙伴们都见识到List集合的Stream流式操作的强大了吧,接下来,我就把List集合的Stream流式操作实现数据类型转换的常用方法记录并分享在此,以供自己和大家学习记忆。
1、Collectors.toList()
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());作用:可用于克隆/拷贝原list集合。作用相当于以下代码:
new ArrayList<>(list);
2、Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));作用:List<Object> 转为 ArrayList<Object> 。作用相当于以下代码:
new ArrayList<>(list);
3、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));作用:List<Object> 转为 LinkedList<Object> 。作用相当于以下代码:
new LinkedList<>(list);
4、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));作用:List<Object> 转为 LinkedHashSet<Object>。作用相当于以下代码:
new LinkedHashSet<>(list);
5、Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
作用:List<Object> 转为 HashSet<Object> 。作用相当于以下代码:
new HashSet<>(list);
6、Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));作用:List<Object> 转为 TreeSet<Object>。
7、Collectors.partitioningBy
list.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.length() > 2));作用:List<Object> 转为 Map<Boolean, List<Object>>。
8、【重点】Collectors.groupingBy
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s));作用:List<Object> 转为 Map<Object, List<Object>>。
9、Collectors.collectingAndThen
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s));作用:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素形成的指定类型的结果集合后,再将结果集合做指定的结果集。如:List<Object> 转为 Map<Object, List<Object>> 再转为 Set<String>返回,如下:
list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s), Map::keySet));10、map
list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s));作用:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性/字段,形成新的类型(指定属性/字段的数据类型)集合。如:List<Object> 转为 List<Integer>。
list.stream().map(String::length).collect(Collectors.toList());11、【重点】Collectors.toMap
作用:List<Object> 转为 Map<Object, Object>。
具有3个重载方法:
11.1、Collectors.toMap(key, value)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str, String::length));作用:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性/字段,形成新的类型(指定属性/字段的数据类型)集合。
参数说明:
key:指定元素对象的某个属性作为map结果集合的key值。
value:指定元素对象的某个属性作为map结果集合的value值。
缺点:当元素中存在重复的key时,会有如下报错:Duplicate key XX。
11.2、【重点】Collectors.toMap(key, value, distinctStrategy)
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str, (length, str) -> str));作用:在11.1功能一致,多了一个第三参数,该参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免key重复报错问题。
参数说明:
distinctStrategy:去重逻辑,当遇到重复key时触发该逻辑。
11.3、【重点】Collectors.toMap(key, value, distinctStrategy, returnTypeSupplier)
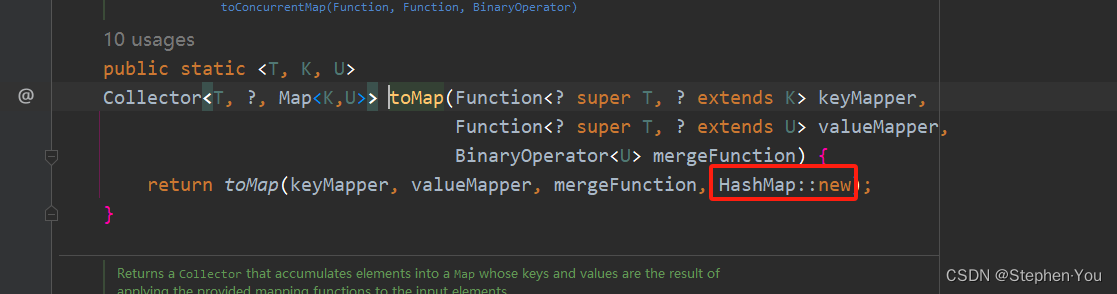
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str, (length, str) -> str, TreeMap::new));参数说明:
returnTypeSupplier:指定map结果集合的数据类型,通过查询源代码可知:当未指定该参数时,默认返回的是HashMap数据类型;如下:
测试代码:
1、StreamStringListTransformTest 测试类:
测试List<String>集合的Stream流式操作,实现数据类型转换的功能:
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;/*** Stream流的各种数据类型转换操作*/
public class StreamStringListTransformTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//List<String>集合原数据List<String> list = Arrays.asList("java", "python", "C#","php");//1、Collectors.toList()// List<String>克隆(代替流)List<String> listResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());listResult.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//2、Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)// List<String> 转为 ArrayList<String>ArrayList<String> arrayList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));arrayList.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//3、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)// List<String> 转为 LinkedList<String>List<String> linkedList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));linkedList.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//4、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new)// List<String> 转为 LinkedHashSet<String>LinkedHashSet<String> linkedHashSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));linkedHashSet.forEach(System.out::println);//LinkedHashSet是有序的System.out.println("--------------");//5、Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)// List<String> 转为 HashSet<String>HashSet<String> hashSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);//HashSet是无序的(按hash逻辑自动排序)System.out.println("--------------");//6、Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new)// List<String> 转为 TreeSet<String>TreeSet<String> treeSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));treeSet.forEach(System.out::println);//TreeSet是按自然顺序自动排序System.out.println("--------------");//7、Collectors.partitioningBy:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素分成key为true或false的两组集合,形成的map集合// List<String> 转为 Map<Boolean, List<String>>Map<Boolean, List<String>> partitioningByMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.length() > 2));System.out.println(partitioningByMap.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//8、Collectors.groupingBy:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素分成key为元素本身的集合,形成的map集合//List<String> 转为 Map<String, List<String>>Map<String, List<String>> groupingByMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s));System.out.println(groupingByMap.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//9、Collectors.collectingAndThen:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素形成的指定类型的结果集合后,再将结果集合做指定的结果集//List<String> 转为 Map<String, List<String>> 再转为 Set<String>Set<String> collectingAndThen = list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> s), Map::keySet));System.out.println(collectingAndThen.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//10、map:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性,形成新的指定集合//List<String> 转为 List<Integer>List<Integer> lengthList = list.stream().map(String::length).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(lengthList.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//11、Collectors.toMap:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性,组合成自定义类型的map结果集合//List<String> 转为 Map<Integer, String>//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>//注意:该函数有3个重载方法:// 11.1、2个参数(key,value):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key。// 第二个参数作为value。(缺点:当存在key重复的不同元素时,会有类似以下报错:Duplicate key 王五)// 11.2、3个参数(key,value,distinctStrategy):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key;// 第二个参数作为value;// 第三个参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免上面的key重复报错问题。// 11.2、3个参数(key,value,distinctStrategy,returnTypeSupplier):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key;// 第二个参数作为value;// 第三个参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免上面的key重复报错问题。// 第四个参数用于设置返回map的数据类型(如:TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap等),默认是返回HashMap。List<String> strList = Arrays.asList("java", "python", "C#","php", "java");//List<String> 转为 Map<Integer, String>
// Map<Integer, String> strList1 = strList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str));//报错:Duplicate key java
// System.out.println(strList1.toString());
// System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>
// Map<String, Integer> strList2 = strList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str, String::length));//报错:Duplicate key 4
// System.out.println(strList2.toString());
// System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>Map<String, Integer> strList3 = strList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str, String::length, (first, second) -> second));System.out.println(strList3.toString());System.out.println("--------------");Map<String, Integer> list1 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(str -> str, String::length));System.out.println(list1.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>Map<Integer, String> list2 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str));System.out.println(list2.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 Map<String, Integer>Map<Integer, String> list3 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str, (length, str) -> str));System.out.println(list3.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<String> 转为 TreeMap<String, Integer>TreeMap<Integer, String> list4 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(String::length, str -> str, (length, str) -> str, TreeMap::new));System.out.println(list4.toString());System.out.println("--------------");}
}2、Person实体类:
用于支持的测试:
public class Person {private String name;private Integer age;public Person() {}public Person(String name, Integer age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';}
}3、StreamObjectListTransformTest 测试类:
测试List<Object>集合的Stream流式操作,实现数据类型转换的功能:
import xxx.Person;//注意:修改为引用的Person实体类的文件路径import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;/*** Stream流的各种数据类型转换操作*/
public class StreamObjectListTransformTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//List<Object>集合原数据List<Person> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Person("老六", 20));list.add(new Person("王五", 20));list.add(new Person("李四", 19));list.add(new Person("张三", 18));list.add(new Person("钱二", 17));list.add(new Person("赵一", 16));//1、Collectors.toList()// List<Object>克隆(代替流)List<Person> listResult = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());listResult.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//2、Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new)// List<Object> 转为 ArrayList<Object>ArrayList<Person> arrayList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));arrayList.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//3、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)// List<Object> 转为 LinkedList<Object>List<Person> linkedList = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new));linkedList.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("--------------");//4、Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new)// List<Object> 转为 LinkedHashSet<Object>LinkedHashSet<Person> linkedHashSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));linkedHashSet.forEach(System.out::println);//LinkedHashSet是有序的System.out.println("--------------");//5、Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)// List<Object> 转为 HashSet<Object>HashSet<Person> hashSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);//HashSet是无序的(按hash逻辑自动排序)System.out.println("--------------");// //6、Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new)
// // List<Object> 转为 TreeSet<Object>
// TreeSet<Person> treeSet = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));
// treeSet.forEach(System.out::println);
//TreeSet是按单一元素自然顺序自动排序,所以转换时会有类似以下报错:
// com.stephen.javademo.stream.bo.Person cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
// System.out.println("--------------");//7、Collectors.partitioningBy:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素分成key为true或false的两组集合,形成的map集合// List<Object> 转为 Map<Boolean, List<Object>>Map<Boolean, List<Person>> partitioningByMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(person -> person.getAge() >= 18));System.out.println(partitioningByMap.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//8、Collectors.groupingBy:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素分成key为元素本身的集合,形成的map集合//List<Object> 转为 Map<String, List<Object>>Map<String, List<Person>> groupingByMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getName));System.out.println(groupingByMap.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//9、Collectors.collectingAndThen:根据指定条件,将集合中所有元素形成的指定类型的结果集合后,再将结果集合做指定的结果集//List<Object> 转为 Map<String, List<Object>> 再转为 Set<String>Collection<List<Person>> collectingAndThen = list.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getName), Map::values));System.out.println(collectingAndThen.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//10、map:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性,形成新的指定集合//List<Object> 转为 List<String>List<String> nameList = list.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(nameList.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Object> 转为 List<Integer>List<Integer> ageList = list.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(ageList.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Object> 转为 Set<Integer>Set<Integer> ageSet = list.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(ageSet.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//11、Collectors.toMap:根据指定条件,提取集合中所有元素的指定属性,组合成自定义类型的map结果集合//List<Object> 转为 Map<Object, Object>//注意:该函数有3个重载方法:// 11.1、2个参数(key,value):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key。// 第二个参数作为value。(缺点:当存在key重复的不同元素时,会有类似以下报错:Duplicate key 王五)// 11.2、3个参数(key,value,distinctStrategy):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key;// 第二个参数作为value;// 第三个参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免上面的key重复报错问题。// 11.2、3个参数(key,value,distinctStrategy,returnTypeSupplier):// 第一个参数(元素对象的某个指定属性)作为key;// 第二个参数作为value;// 第三个参数用于配置当出现重复key时,对这些元素的value的操作处理逻辑,可以避免上面的key重复报错问题。// 第四个参数用于设置返回map的数据类型(如:TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap等),默认是返回HashMap。//List<Person> 转为 Map<Integer, String>
// Map<Integer, String> personMap1 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName));//报错:Duplicate key 王五
// System.out.println(personMap1.toString());
// System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<String, Integer>Map<String, Integer> personMap2 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, Person::getAge));System.out.println(personMap2.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<String, Person>Map<String, Person> personMap3 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getName, person -> person));System.out.println(personMap3.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<Integer, String>Map<Integer, String> personMap4 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName, (preValue, nextValue) -> nextValue));//(preValue, nextValue) -> nextValue):key重复时,取后者System.out.println(personMap4.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<Integer, String>Map<Integer, String> personMap5 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName, (preValue, nextValue) -> preValue));//(preValue, nextValue) -> preValue):key重复时,取前者System.out.println(personMap5.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 Map<Integer, String>Map<Integer, String> personMap6 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName, (preValue, nextValue) -> preValue+"、"+nextValue));//(preValue, nextValue) -> preValue+"、"+nextValue):key重复时,取两者拼接System.out.println(personMap6.toString());System.out.println("--------------");//List<Person> 转为 TreeMap<Integer, String>TreeMap<Integer, String> personMap7 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Person::getAge, Person::getName, (preValue, nextValue) -> preValue + "、" + nextValue, TreeMap::new));//(preValue, nextValue) -> preValue+"、"+nextValue):key重复时,取两者拼接System.out.println(personMap7.toString());System.out.println("--------------");}
}