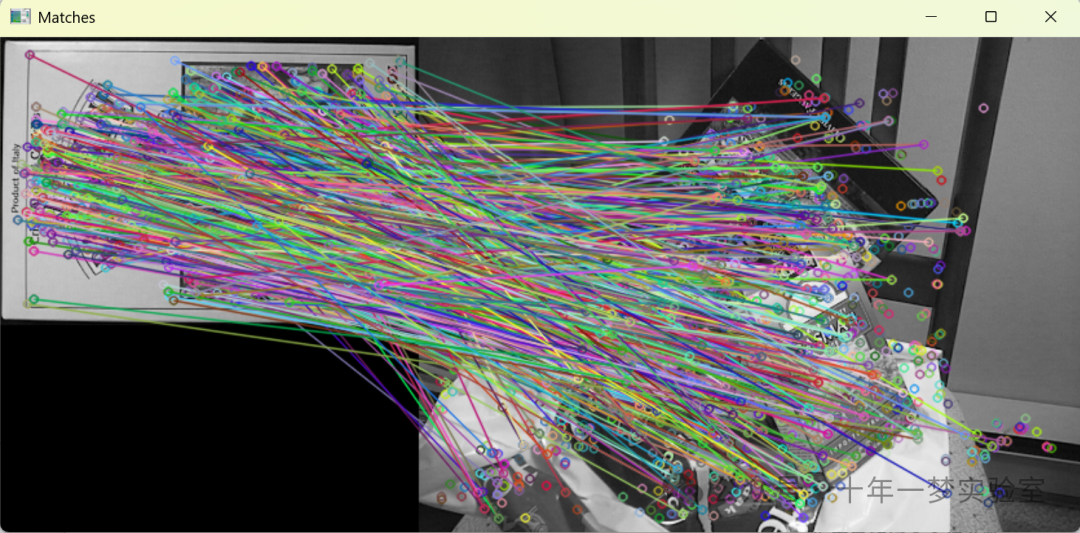
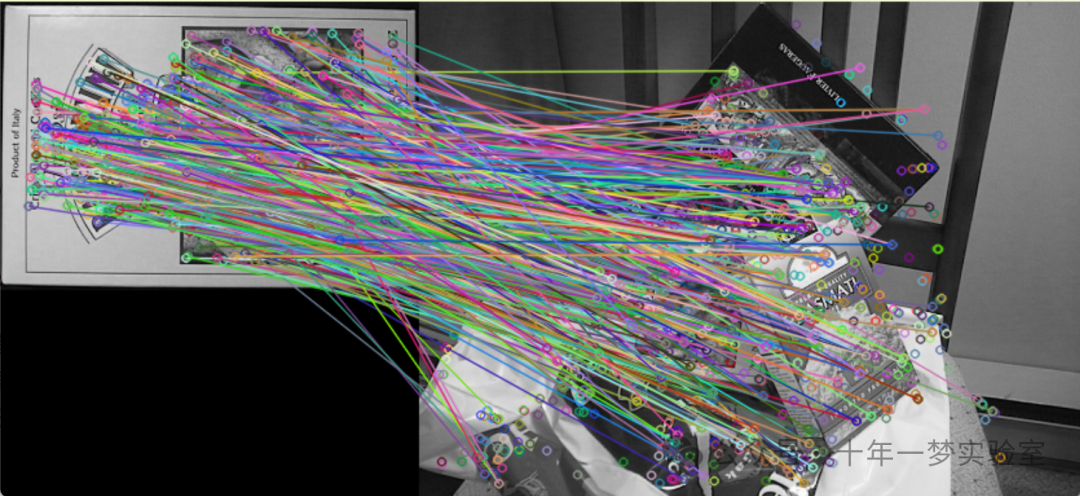
使用SURF算法检测两幅图关键点后暴力匹配
SURF特征检测
使用SURF(Speeded Up Robust Features)算法来检测两张图像之间的关键点,并使用FLANN(Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors)基于特征描述符向量进行匹配
图像特征点检测(SURF)、(FLANN)匹配和目标定位
1.feature_description—SURF_matching_Demo.cpp(Debug模式)使用SURF算法检测两幅图关键点后暴力匹配

box.png

box_in_scene.png
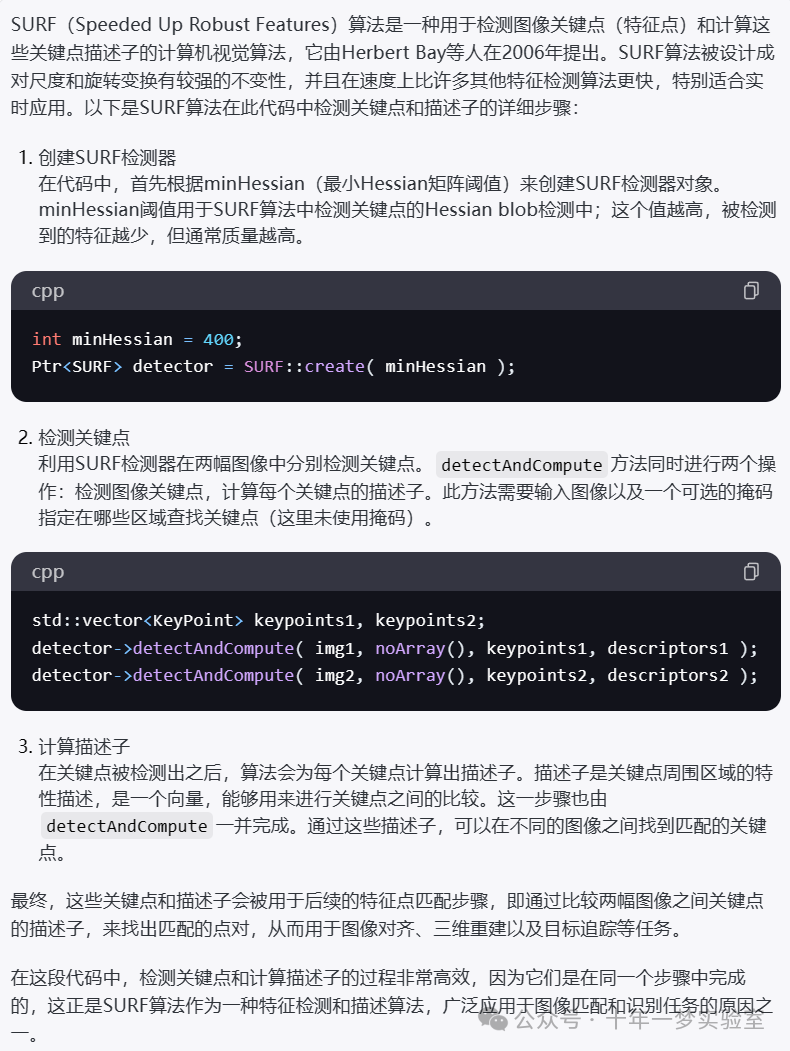
minHessian=400
minHessian=1000

minHessian=10000

#include <iostream> // 包含标准输入输出流库
#include "opencv2/core.hpp" // 包括OpenCV的核心功能头文件
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D // 如果定义了HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp" // 包括用户界面相关功能的头文件
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp" // 包括特征检测相关功能的头文件
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp" // 包括特殊特征检测的头文件(非free模块)using namespace cv; // 使用cv命名空间
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d; // 使用cv的xfeatures2d命名空间
using std::cout; // 使用标准库中的cout
using std::endl; // 使用标准库中的endlconst char* keys = // 定义命令行参数"{ help h | | Print help message. }""{ input1 | box.png | Path to input image 1. }""{ input2 | box_in_scene.png | Path to input image 2. }";int main( int argc, char* argv[] ) // 主函数
{CommandLineParser parser( argc, argv, keys ); // 创建命令行解析器Mat img1 = imread( samples::findFile( parser.get<String>("input1") ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE ); // 读取第一张图片为灰度图Mat img2 = imread( samples::findFile( parser.get<String>("input2") ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE ); // 读取第二张图片为灰度图if ( img1.empty() || img2.empty() ) // 如果图片读取失败{cout << "Could not open or find the image!\n" << endl; // 打印错误信息parser.printMessage(); // 打印帮助信息return -1; // 返回错误代码}//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector, compute the descriptorsint minHessian = 400; // 设置SURF算法的Hessian阈值Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create( minHessian ); // 创建SURF特征检测器std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2; // 存放两张图片的关键点Mat descriptors1, descriptors2; // 存放两张图片的描述符detector->detectAndCompute( img1, noArray(), keypoints1, descriptors1 ); // 检测并计算img1的关键点和描述符detector->detectAndCompute( img2, noArray(), keypoints2, descriptors2 ); // 检测并计算img2的关键点和描述符//-- Step 2: Matching descriptor vectors with a brute force matcher// Since SURF is a floating-point descriptor NORM_L2 is usedPtr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::BRUTEFORCE); // 创建暴力匹配器std::vector< DMatch > matches; // 存放匹配结果matcher->match( descriptors1, descriptors2, matches ); // 执行匹配//-- Draw matchesMat img_matches; // 存放匹配之后的图片drawMatches( img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2, matches, img_matches ); // 绘制匹配结果//-- Show detected matchesimshow("Matches", img_matches ); // 在窗口中显示匹配结果waitKey(); // 等待用户按键return 0; // 程序成功结束
}
#else
int main() // 如果没定义HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
{std::cout << "This tutorial code needs the xfeatures2d contrib module to be run." << std::endl; // 提示需要xfeatures2d模块return 0; // 程序结束
}
#endif这段代码是使用OpenCV库进行图像特征点检测和匹配的示例。它通过SURF算法来检测两幅图片中的特征点,并使用暴力匹配器来找出这些特征点之间的匹配关系。最终将匹配的结果用图形化的方式展示出来。这对于很多计算机视觉任务,比如物体识别、图像拼接等是非常实用的。如果环境中没有安装OpenCV的xfeatures2d模块,则给出提示信息。
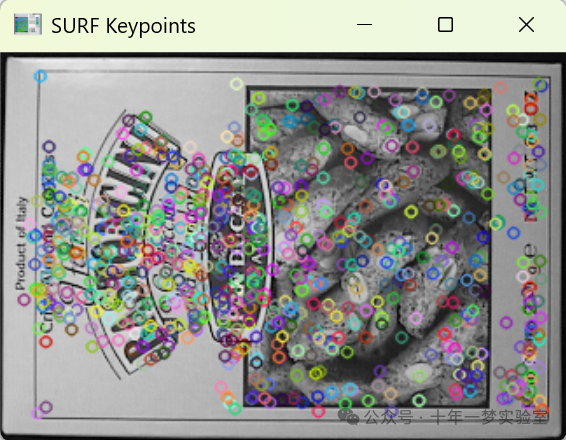
2.feature_detection—SURF_detection_Demo.cpp SURF特征检测

#include <iostream> // 包含输入输出流的头文件
#include "opencv2/core.hpp" // 包含OpenCV核心功能的头文件
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp" // 包含OpenCV GUI功能的头文件
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp" // 包含OpenCV特征检测相关功能的头文件
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp" // 包含OpenCV extra features2d模块的头文件,例如SURFusing namespace cv; // 使用cv命名空间
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d; // 使用cv::xfeatures2d命名空间,因为SURF是其中的一部分
using std::cout; // 使用标准命名空间下的cout
using std::endl; // 使用标准命名空间下的endlint main( int argc, char* argv[] )
{CommandLineParser parser( argc, argv, "{@input | box.png | input image}" ); // 命令行参数解析器Mat src = imread( samples::findFile( parser.get<String>( "@input" ) ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE ); // 读取图像文件转换为灰度图if ( src.empty() ){cout << "Could not open or find the image!\n" << endl;cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <Input image>" << endl;return -1;}//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector// 步骤1:使用SURF检测器检测关键点int minHessian = 400; // Hessian算子的阈值Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create( minHessian ); // 创建SURF检测器std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints; // 关键点的向量detector->detect( src, keypoints ); // 检测关键点//-- Draw keypoints// 绘制关键点Mat img_keypoints;drawKeypoints( src, keypoints, img_keypoints ); // 将检测到的关键点绘制到图上//-- Show detected (drawn) keypoints// 显示检测到(绘制的)关键点imshow("SURF Keypoints", img_keypoints ); // 创建一个窗口展示关键点waitKey(); // 等待任意键输入return 0;
}
#else
int main()
{std::cout << "This tutorial code needs the xfeatures2d contrib module to be run." << std::endl;return 0;
}
#endif这段代码的功能是使用SURF算法来检测图像中的关键点。首先,它使用命令行参数解析器读取图像,并将其转换为灰度图。如果无法读取图像,它会打印错误消息并退出程序。如果图像读取成功,它创建一个SURF检测器,并根据指定的Hessian阈值来检测图像中的关键点。然后,它将这些关键点绘制在源图像上,并使用imshow函数显示结果。如果没有安装OpenCV的xfeatures2d类的附加模块,它会在命令行输出一条信息,说明需要xfeatures2d模块才能运行此代码。
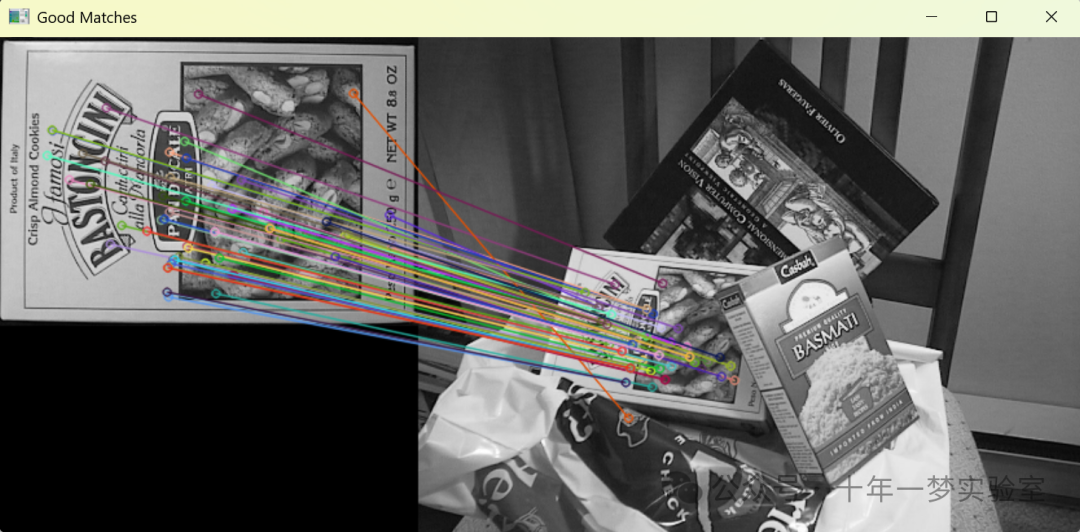
3. SURF_FLANN_matching_Demo.cpp 使用SURF(Speeded Up Robust Features)算法来检测两张图像之间的关键点,并使用FLANN(Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors)基于特征描述符向量进行匹配


#include <iostream> // 包含标准输入输出流库
#include "opencv2/core.hpp" // 包含OpenCV核心功能库#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D // 如果定义了HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D(检查xfeatures2d模块是否可用)
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp" // 包含OpenCV高级GUI库
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp" // 包含OpenCV特征点检测库
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp" // 包含OpenCV附加特征点检测库using namespace cv; // 使用cv命名空间
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d; // 使用cv::xfeatures2d命名空间
using std::cout; // 使用cout(标准输出)
using std::endl; // 使用endl(换行符)const char* keys = // 定义命令行参数"{ help h | | Print help message. }" // 帮助信息"{ input1 | box.png | Path to input image 1. }" // 输入图像1的路径"{ input2 | box_in_scene.png | Path to input image 2. }"; // 输入图像2的路径int main( int argc, char* argv[] ) // 主函数
{CommandLineParser parser( argc, argv, keys ); // 命令行解析器Mat img1 = imread( samples::findFile( parser.get<String>("input1") ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE ); // 读取输入图像1为灰度图Mat img2 = imread( samples::findFile( parser.get<String>("input2") ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE ); // 读取输入图像2为灰度图if ( img1.empty() || img2.empty() ) // 如果任一图像为空则打印错误信息{cout << "Could not open or find the image!\n" << endl;parser.printMessage(); // 打印帮助信息return -1; // 返回-1表示错误}//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector, compute the descriptorsint minHessian = 400; // 定义Hessian阈值Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create( minHessian ); // 创建SURF检测器std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2; // 定义关键点向量Mat descriptors1, descriptors2; // 定义描述符矩阵detector->detectAndCompute( img1, noArray(), keypoints1, descriptors1 ); // 检测图像1的关键点和描述符detector->detectAndCompute( img2, noArray(), keypoints2, descriptors2 ); // 检测图像2的关键点和描述符//-- Step 2: Matching descriptor vectors with a FLANN based matcher// Since SURF is a floating-point descriptor NORM_L2 is usedPtr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::FLANNBASED); // 创建基于FLANN的描述符匹配器std::vector< std::vector<DMatch> > knn_matches; // 定义K邻近匹配向量matcher->knnMatch( descriptors1, descriptors2, knn_matches, 2 ); // 执行K邻近匹配//-- Filter matches using the Lowe's ratio testconst float ratio_thresh = 0.7f; // 定义Lowe's比率测试阈值std::vector<DMatch> good_matches; // 定义良好匹配向量for (size_t i = 0; i < knn_matches.size(); i++) // 遍历所有K邻近匹配{if (knn_matches[i][0].distance < ratio_thresh * knn_matches[i][1].distance) // 如果满足Lowe's比率测试则认为是良好匹配{good_matches.push_back(knn_matches[i][0]); // 添加到良好匹配向量中}}//-- Draw matchesMat img_matches; // 定义匹配结果图像drawMatches( img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2, good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1), std::vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS ); // 绘制良好匹配//-- Show detected matchesimshow("Good Matches", img_matches ); // 显示匹配结果图像waitKey(); // 等待按键事件return 0; // 返回0表示成功
}
#else // 如果没有定义HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D
int main() // 主函数
{std::cout << "This tutorial code needs the xfeatures2d contrib module to be run." << std::endl; // 打印错误信息return 0; // 返回0表示成功
}
#endif这段代码是一个使用OpenCV库进行图像处理的例子,特别是使用SURF(Speeded Up Robust Features)算法来检测两张图像之间的关键点,并使用FLANN(Fast Library for Approximate Nearest Neighbors)基于特征描述符向量进行匹配。首先,代码读取两张图像并将它们转换成灰度图。然后,SURF算法被用于检测关键点并计算描述符。接着,运用FLANN匹配器对这两组描述符进行匹配,并使用Lowe's比率测试过滤出良好的匹配点。最后,良好的匹配点被绘制并显示出来。如果没有安装OpenCV的xfeatures2d模块,代码将打印一条错误信息。
drawMatches( img1, keypoints1, img2, keypoints2, good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1), std::vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
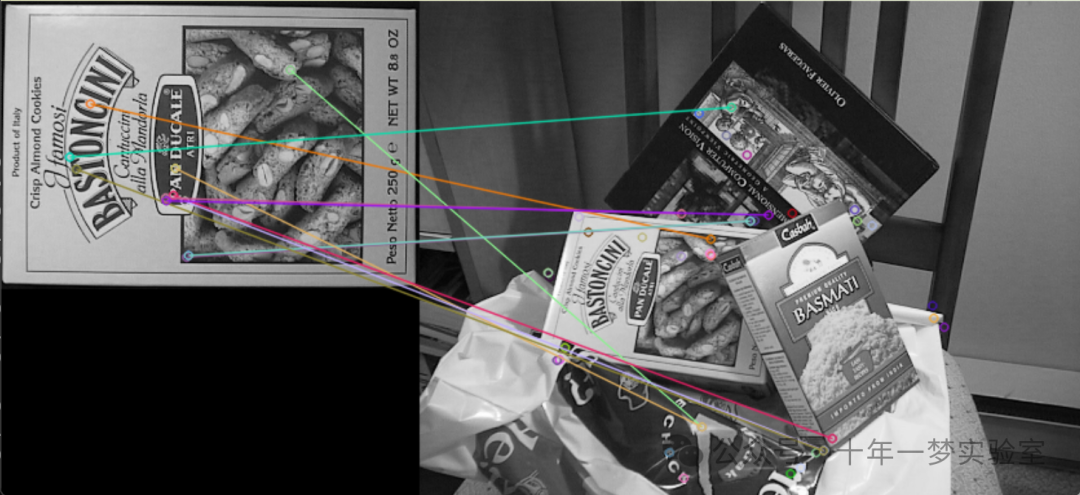
4.SURF_FLANN_matching_homography_Demo.cpp 图像特征点检测、匹配和目标定


// 引用必要的库
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core.hpp"
#ifdef HAVE_OPENCV_XFEATURES2D // 判断是否有xfeatures2d模块,如果有则进行下面的操作
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp"// 使用命名空间简化代码
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;// 定义程序参数
const char* keys ="{ help h | | 打印帮助信息}""{ input1 | box.png | 第一张输入图像路径}""{ input2 | box_in_scene.png | 第二张输入图像路径}";// 程序主函数
int main( int argc, char* argv[] )
{// 定义命令行解析器CommandLineParser parser( argc, argv, keys );// 读取图片Mat img_object = imread( samples::findFile( parser.get<String>("input1") ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );Mat img_scene = imread( samples::findFile( parser.get<String>("input2") ), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE );// 判断图片是否读取成功if ( img_object.empty() || img_scene.empty() ){cout << "无法打开或找到图片!\n" << endl;parser.printMessage(); //打印错误信息return -1;}//-- Step 1: 使用SURF检测器检测关键点并计算描述符int minHessian = 400; //设置SURF算法中的hessian阈值Ptr<SURF> detector = SURF::create( minHessian ); // 创建SURF检测器std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_object, keypoints_scene; // 定义储存关键点的向量Mat descriptors_object, descriptors_scene; //定义储存描述符的矩阵detector->detectAndCompute( img_object, noArray(), keypoints_object, descriptors_object ); // 在目标图片中检测关键点并计算描述符detector->detectAndCompute( img_scene, noArray(), keypoints_scene, descriptors_scene ); //在场景图片中检测关键点并计算描述符//-- Step 2: 通过FLANN匹配器对描述符向量进行匹配// 由于SURF是一个浮点数描述符,此处使用NORM_L2Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create(DescriptorMatcher::FLANNBASED);std::vector< std::vector<DMatch> > knn_matches; //定义knn匹配的结果向量matcher->knnMatch( descriptors_object, descriptors_scene, knn_matches, 2 ); //knn匹配//-- Step 3: 利用Lowe's比率测试过滤匹配点const float ratio_thresh = 0.75f;std::vector<DMatch> good_matches; //定义储存优质匹配点的向量for (size_t i = 0; i < knn_matches.size(); i++){if (knn_matches[i][0].distance < ratio_thresh * knn_matches[i][1].distance) //通过比率测试进行筛选{good_matches.push_back(knn_matches[i][0]);}}//-- Step 4: 绘制优质匹配点Mat img_matches;drawMatches( img_object, keypoints_object, img_scene, keypoints_scene, good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1), std::vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );//-- Step 5: 找到场景图片中的目标位置std::vector<Point2f> obj;std::vector<Point2f> scene;for( size_t i = 0; i < good_matches.size(); i++ ){//-- 从优质匹配点中获取关键点obj.push_back( keypoints_object[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );scene.push_back( keypoints_scene[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );}Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, RANSAC ); //计算单应性矩阵//-- Step 6: 获取目标图片的角点(the object to be "detected")std::vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);obj_corners[0] = Point2f(0, 0);obj_corners[1] = Point2f( (float)img_object.cols, 0 );obj_corners[2] = Point2f( (float)img_object.cols, (float)img_object.rows );obj_corners[3] = Point2f( 0, (float)img_object.rows );std::vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);perspectiveTransform( obj_corners, scene_corners, H); //对目标点进行透视投影变换//-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )line( img_matches, scene_corners[0] + Point2f((float)img_object.cols, 0),scene_corners[1] + Point2f((float)img_object.cols, 0), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4 );line( img_matches, scene_corners[1] + Point2f((float)img_object.cols, 0),scene_corners[2] + Point2f((float)img_object.cols, 0), Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );line( img_matches, scene_corners[2] + Point2f((float)img_object.cols, 0),scene_corners[3] + Point2f((float)img_object.cols, 0), Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );line( img_matches, scene_corners[3] + Point2f((float)img_object.cols, 0),scene_corners[0] + Point2f((float)img_object.cols, 0), Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );//-- Step 7: 展示检测到的匹配imshow("Good Matches & Object detection", img_matches );waitKey(); //等待用户按键return 0;
}
#else
int main()
{std::cout << "这个教程代码需要xfeatures2d contrib模块才能运行." << std::endl;return 0;
}
#endif以上代码实现了一个物体识别程序,它能从一张场景图像中找到另一张目标图像的位置。首先,通过SURF检测器找到两张图片的关键点和描述符。接着,通过FLANN匹配器找到匹配的点,并通过Lowe's比率测试进行筛选,得到优质的匹配点。最后,根据这些匹配点找到目标图片在场景图片中的位置,并在匹配图上绘制出目标的角点。