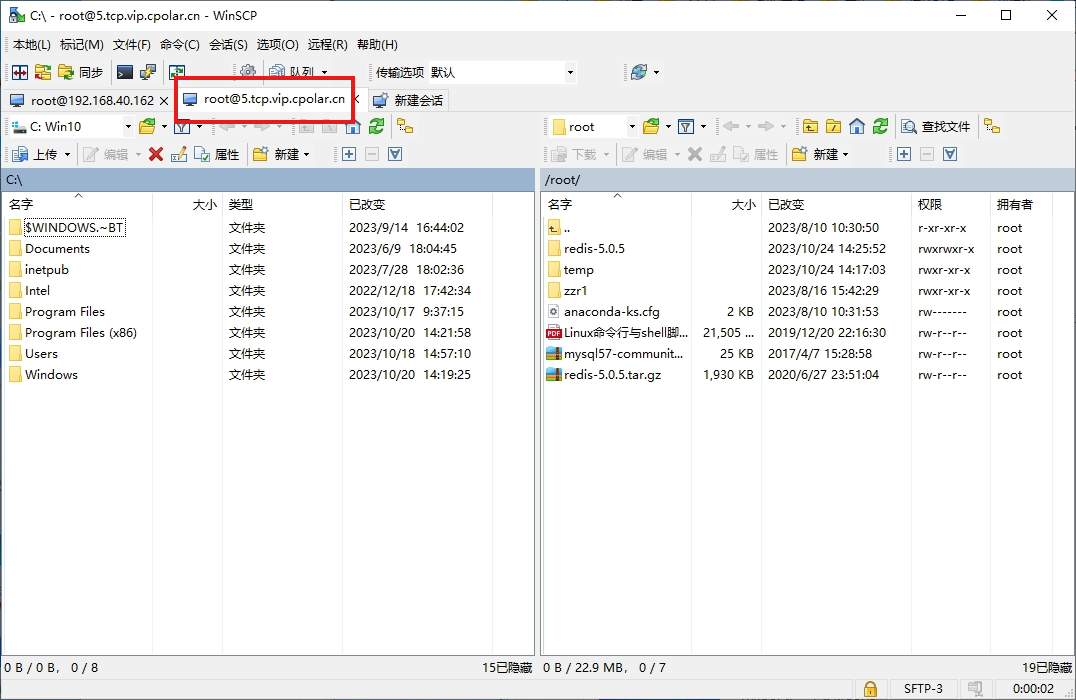
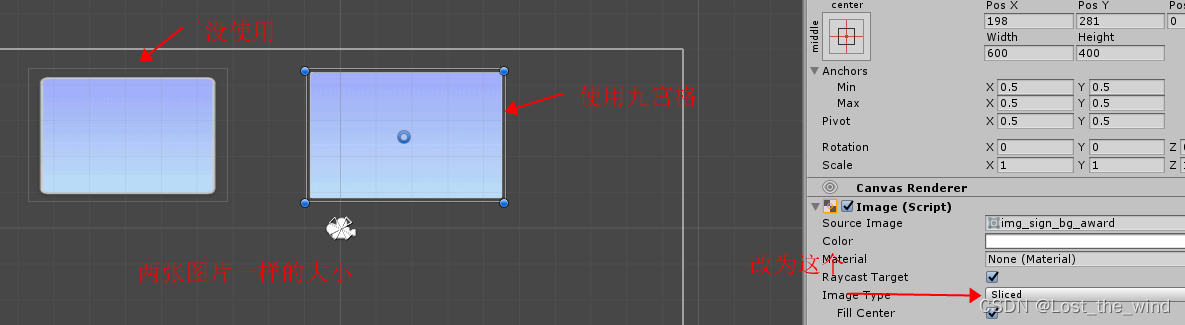
统一处理异常
SpringBoot设计,如果出现错误404或500,自动调用特定路径下的html页面(路径和名字都特定)。/templates/error/404.html、/templates/error/500.html。程序中有错误自动就调用该页面。
但是错误有异步请求错误,也想同时记录日志。则使用统一处理的方式,即全局配置。
@ControllerAdvice 是 Spring MVC 中的一个注解,用于定义全局控制器的通知(advice)。它允许您在整个应用程序范围内定义对控制器的异常处理、绑定属性以及其他全局控制器通知的方法。
具体来说,@ControllerAdvice 通常与 @ExceptionHandler、@InitBinder 和 @ModelAttribute 注解一起使用:
- @ExceptionHandler: 用于定义在控制器中抛出指定类型异常时的处理方法。
- @InitBinder: 用于定义在控制器中自定义数据绑定规则的方法。
- @ModelAttribute: 用于定义在所有请求处理方法之前执行的方法,通常用于在模型中添加公共属性。
通过将 @ControllerAdvice 注解添加到类上,您可以在该类中定义这些通知方法,并在整个应用程序中共享它们,以便统一处理异常、数据绑定和模型属性。这样可以提高代码的重用性和可维护性,并使全局控制器的配置更加简洁和清晰。
//手动重定向错误页面@RequestMapping(path = "/error", method = RequestMethod.GET)public String getErrorPage() {return "/error/500";}
// 是Controller全局配置类,不用对任何Controller再做配置,可以统一做Controller的全局配置。@ControllerAdvice用来修饰类。
// 异常处理方案@ExceptionHandler、绑定数据方案@ModelAttribute、绑定参数方案@DataBinder. 他们都用来修饰方法。
// 这里只演示,统一处理异常(@ExceptionHandler)
@ControllerAdvice(annotations = Controller.class) // 限定注解@Controller,否则组件扫描所有的bean
public class ExceptionAdvice {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ExceptionAdvice.class);@ExceptionHandler({Exception.class})// 处理哪些异常?Exception是所有异常的父类,所有异常都处理// 有异常controller会传过来Exceptionpublic void handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {// 记录日志logger.error("服务器发生异常:" + e.getMessage());//异常的概括for (StackTraceElement element : e.getStackTrace()) {//把异常所有栈的信息都记录下来logger.error(element.toString());}// 给浏览器响应// 要看是什么请求,想要服务器返回网页html/异步请求JSON(xml).从请求的消息头获取。String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with");if ("XMLHttpRequest".equals(xRequestedWith)) {// 异步请求response.setContentType("application/plain;charset=utf-8");PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();// 输出流writer.write(CommunityUtil.getJSONString(1,"服务器异常!"));// 输出JSON字符串}else{// 请求html,重定向到错误页面response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/error");}}
}统一记录日志
记录日志,不一定有异常。拦截器也是针对控制器的。没有对业务组件、数据访问层统一处理。
想对业务层统一记录日志,而统一记录日志是系统功能,不要和业务功能混在一起实现。否则在想对记录日志的位置进行改变时,将会非常麻烦,因为业务bean有很多个,需要修改的时候得一个个改。
由此引入了AOP的方式,即面向切面编程,切面是一个一个组件。业务Bean是一个一个target。我们要先声明切点的位置,再通知要做什么事。只需要对切面组件编程即可,不需要再进到业务Bean中去改,提升了编程效率。
Aspect切面:
- 注解@Component @Aspect
- 声明切点的位置@Pointcut(切点的位置:返回值 包.类.方法.参数) pointcut()
- 通知具体逻辑,5个注解@Before @After AfterReturning @AfterThrowing @Around
Target: 是业务Bean
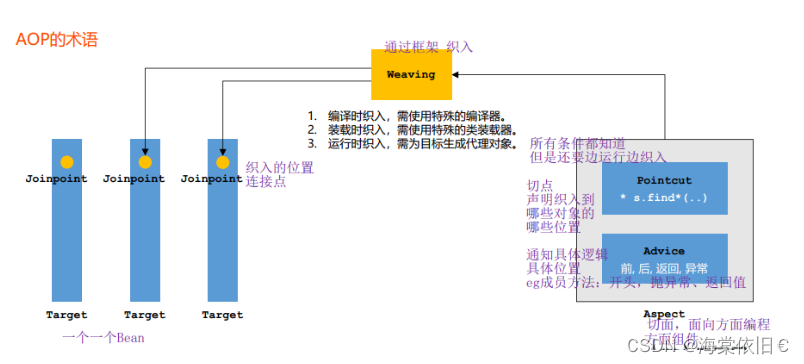
AOP实现有两种:
AspectJ 和 Spring AOP。一般用后者即可。它是运行时织入,通过代理的方式,只在方法处有连接点。Spring AOP(面向切面编程)通常通过代理的方式来实现,主要有以下几个原因: - 无侵入性: 通过代理方式实现 AOP 可以避免对现有代码的侵入性。即使目标类没有实现任何接口,也可以通过 Spring AOP实现切面功能。
- 动态性: 代理方式允许在运行时动态地应用切面。这意味着可以在运行时决定是否应用切面,以及如何应用切面,而无需在编译时硬编码切面逻辑。
- 单一职责原则: 通过代理方式实现 AOP可以使目标类专注于自身的业务逻辑,而将横切关注点(如日志记录、事务管理等)从目标类中解耦出来,符合单一职责原则。
- 多个切面组合:代理方式允许将多个切面组合应用于目标类,而无需修改目标类的代码。这种灵活性使得可以根据需求组合不同的切面,实现更加复杂的功能。
- 易于管理: 通过代理方式实现的切面可以集中管理,例如在配置文件中声明切面和通知的关系,而无需在每个目标类中显式地声明切面逻辑。
统一记录日志示例
@Component
@Aspect
public class ServiceLogAspect {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ServiceLogAspect.class);@Pointcut("execution(* com.nowcoder.community.service.*.*(..))")public void pointcut() {}@Before("pointcut()")public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {// 参数:连接点// 用户[1.2.3.4],在[xxx],访问了[com.nowcoder.community.service.xxx()].ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();String ip = request.getRemoteHost();String now = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date());String target = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() + "." +joinPoint.getSignature().getName();// 得到该连接点的类名和方法名logger.info(String.format("用户[%s],在[%s],访问了[%s].", ip, now, target));}@After("pointcut()")public void after() {System.out.println("after");}@AfterReturning("pointcut()")public void afterRetuning() {System.out.println("afterRetuning");}@AfterThrowing("pointcut()")public void afterThrowing() {System.out.println("afterThrowing");}@Around("pointcut()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {// 参数:连接点System.out.println("around before");Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();// 连接点调用目标组件的方法,返回目标组件的返回值System.out.println("around after");return obj;}
}