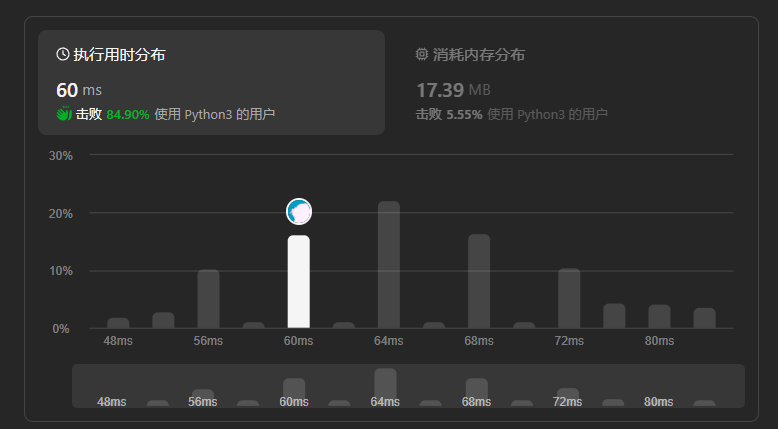
二叉树
二叉树的理论基础
二叉树是结点的度数之和不超过2的树,二叉树总共有五种基本形态
二叉树的种类主要有:
- 满二叉树
- 完全二叉树
二叉树的存储方式
- 顺序存储
- 链式存储
二叉树的遍历方式
- 先序遍历(深度优先搜索)
- 中序遍历(深度优先搜索)
- 后序遍历(深度优先搜索)
- 层次遍历(广度优先搜索)
对于二叉树结点的定义:
class TreeNode:def __init__(self, val, left = None, right = None):self.val = valself.left = leftself.right = right
二叉树的递归遍历
先序遍历
class Solution:def preorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []return [root.val] + self.preorderTraversal(root.left) + self.preorderTraversal(root.right)
中序遍历
class Solution:def inorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []return self.inorderTraversal(root.left) + [root.val] + self.inorderTraversal(root.right)
后续遍历
class Solution:def postorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []return self.postorderTraversal(root.left) + self.postorderTraversal(root.right) + [root.val]
二叉树的非递归遍历
先序遍历
方法1:利用栈先进后出的性质,先把右孩子结点放入栈中,再将左孩子结点放入栈中,这样就可以先访问根节点, 在访问左孩子,最后访问右孩子了。
class Solution:def preorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []stack = [root]res = []while stack:node = stack.pop()# print(node)res.append(node.val)if node.right:stack.append(node.right)if node.left:stack.append(node.left)return res
方法2:按照中序遍历的算法,只需要将添加append操作放到前面去即可。但需要控制两个指针。
思路:沿着左子树一直往左下方走,左孩子不为空就一直进栈,同时将其值添加到res列表中。如果左孩子为空,则弹出栈顶元素,然后再访问该结点的右孩子,再重复上述的操作直到遍历结束。
class Solution:def preorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []stack = []res = []cur = rootwhile cur or stack:if cur:stack.append(cur)res.append(cur.val)cur = cur.leftelse:cur = stack.pop()cur = cur.rightreturn res
中序遍历
中序遍历参考先序遍历思路2,区别就是只需要append语句放到当cur指针为空的时候里面。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:def inorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []stack = []res = []cur = rootwhile cur or stack:if cur:stack.append(cur)cur = cur.leftelse:cur = stack.pop()res.append(cur.val)cur = cur.rightreturn res
后序遍历
思路:在进行先序遍历的时候,我们的思路是利用栈,首先访问根结点,然后将右子树添加到栈中,再将左子树添加到栈中,实现的效果是根左右的效果,而在进行后序遍历的时候,我们需要的的顺序是左右根,如果我们先序遍历算法中左右子树进栈的顺序修改之后,刚好可以得到我们后续遍历结果的逆序结果,最终的返回值设置为res[::-1]即为最终答案。
class Solution:def postorderTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []stack = [root]res = []while stack:node = stack.pop()# 根 右 左res.append(node.val)if node.left:stack.append(node.left)if node.right:stack.append(node.right)# 左 右 根return res[::-1]
层次遍历
层次遍历需要借助队列来实现,队列先进先出的特点可以很好的满足层次遍历按层遍历的需要。
代码模板(以力扣为标准)
class Solution:def levelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:if not root:return []queue = [root]res = []while queue:tmp = []for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.pop(0)tmp.append(node.val)if node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)res.append(tmp)return res
上面的代码还可以进行优化,Python中列表在进行pop(0)的时候,需要移动后面的元素,会导致时间复杂度变高,可以在用collections类中提供的双端队列deque来方便在队头队尾进行元素的插入和删除。
class Solution:def levelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:if not root:return []res = []queue = deque([root])while queue:tmp = []for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.popleft()tmp.append(node.val)if node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)res.append(tmp)return res
list:和添加操作类似,从list尾部移除(pop)元素是很快的,时间复杂度为O(1)。但从头部移除(pop(0))元素则时间复杂度为O(n)。deque:deque同样能够在两端移除元素,无论是popleft还是pop,时间复杂度都是O(1)。
这点在进行N叉树的层次遍历的时候可以体现的比较明显
429、N叉树的层次遍历
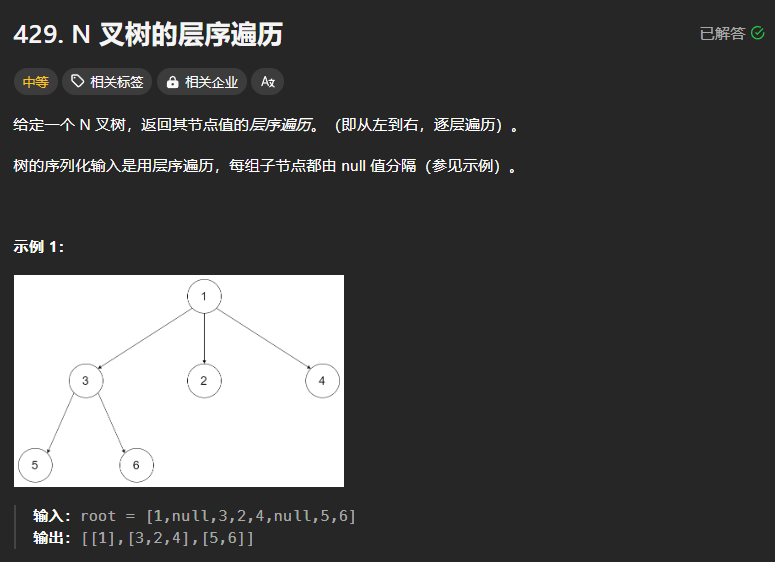
class Solution:def levelOrder(self, root: 'Node') -> List[List[int]]:if not root:return []# 使用双端队列存放queue = deque([root])res = []while queue:tmp = []for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.popleft()tmp.append(node.val)# N叉树 遍历孩子结点 ,孩子结点是一个可以迭代的对象for child in node.children:queue.append(child)res.append(tmp)return res
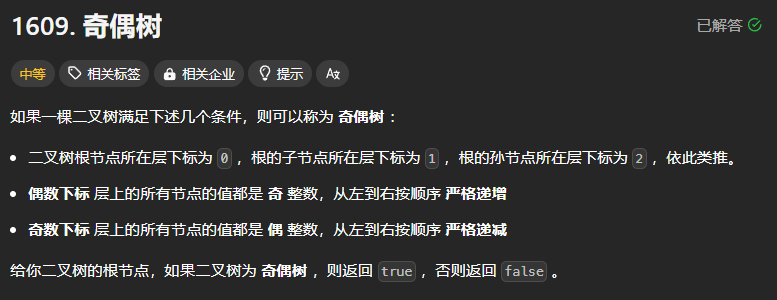
1609、奇偶数
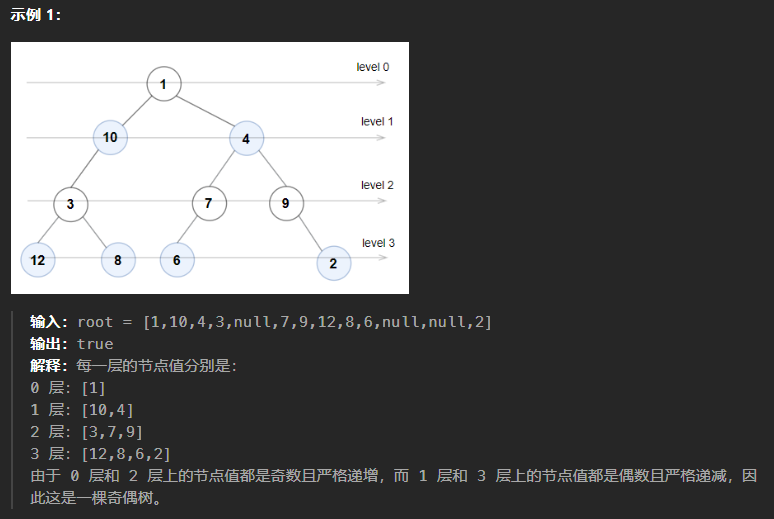
本题可以直接使用层次遍历,在遍历的过程中使用pre记录前一个结点,然后两个结点相减如果不满足题目的要求则返回false,在层次遍历的过程中用tag记录当前遍历的层数,如果层数和对应的数字奇偶不符,也返回False,直到程序运行结束返回True
class Solution:def isEvenOddTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:# 树中节点数至少为1 不用判断树为空的情况queue = deque([root])tag = 0 # 用于判断层数while queue:pre = float("-inf") if tag%2==0 else float("inf")for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.popleft()if tag%2==0:if node.val%2==0 or node.val-pre<=0:return Falseelse:if node.val%2==1 or node.val-pre>=0:return Falsepre = node.valif node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)tag+=1return True
本题中,使用list和使用deque的性能差别是非常明显的。
二叉树的层次遍历可以衍生出非常多的变种题目。
- 102.二叉树的层序遍历(opens new window)
- 107.二叉树的层次遍历II(opens new window)
- 本题和层次遍历的区别就是只需要返回res列表的逆序即可。
- 199.二叉树的右视图(opens new window)
- 637.二叉树的层平均值(opens new window)
- 429.N叉树的层序遍历(opens new window)
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值(opens new window)
- 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针(opens new window)
- 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II(opens new window)
- 104.二叉树的最大深度(opens new window)
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
199、二叉树的右视图
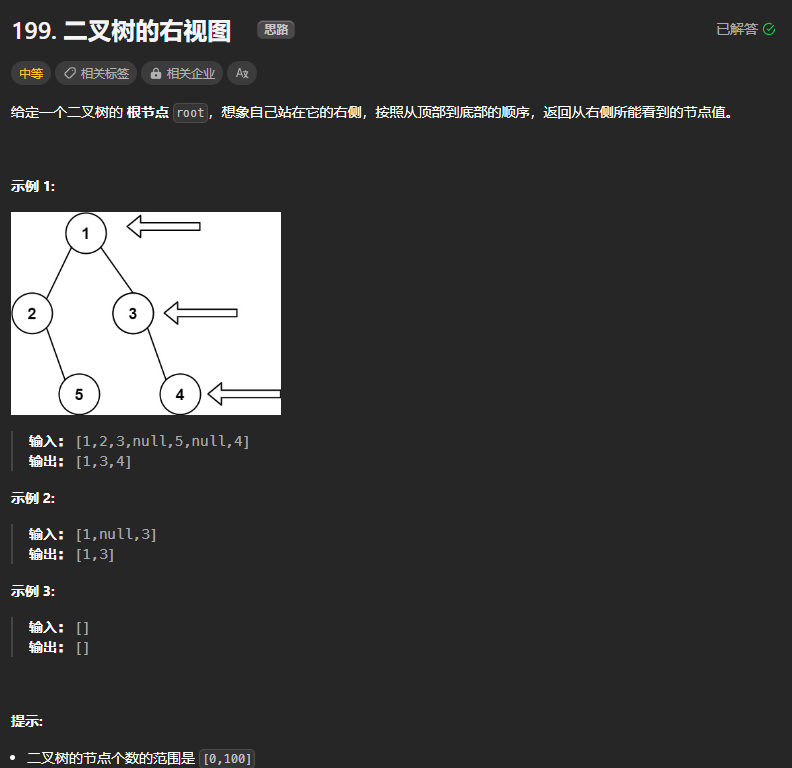
class Solution:def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []queue = [root]res = []while queue:tmp = 0for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.pop(0)# tmp.append(node.val)if node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)tmp = node.valres.append(tmp)return res
使用双端队列
class Solution:def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:if not root:return []queue = deque([root])res = []while queue:tmp = 0for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.popleft()if node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)tmp = node.valres.append(tmp)return res
111、二叉树的最小深度
本题的解题思路与二叉树的最大深度大同小异,唯一的区别就是在循环中进行判断当前节点的左右孩子结点是否为空,如果为空,则直接返回depth即可,如果不为空就一直进行循环,最后再返回depth,代码的主体框架与层次遍历是一致的。
# 层次遍历
class Solution:def minDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:if not root:return 0queue = [root]depth = 0while queue:depth+=1for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.pop(0)if node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)if not node.right and not node.left:return depthreturn depth
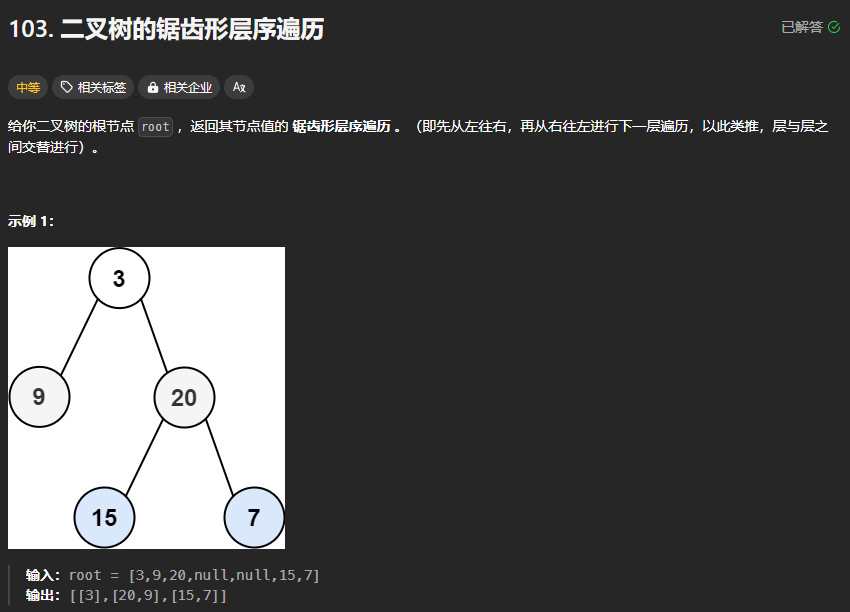
103、二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历

本题需要使用2个双端队列,一个用来存放树的结点,一个用来存放每一层的结点,用双端队列就是方便在队头和对尾进行插入。利用collections模块中的deque的方法:
appendleft():在队头进行插入append():在队尾进行插入pop():删除队尾的元素popleft():删除队头的元素
由于tmp是属于双端队列类型的,需要再最后往res数组中存放的时候,强制转换为list类型。
class Solution:def zigzagLevelOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:if not root:return []res = []queue = deque([root])flag = 0while queue:tmp = deque()for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.popleft()if flag % 2 == 0:tmp.append(node.val)else:tmp.appendleft(node.val)if node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)res.append(list(tmp))flag += 1return res
637、二叉树的层平均值

class Solution:def averageOfLevels(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[float]:res = []queue = deque([root])while queue:sum_ = 0count = 0for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.popleft()sum_ += node.valcount += 1if node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)res.append(sum_ / count)return res
二叉树的深度与高度
二叉树的深度与高度有一些区别,其中二叉树中的深度是指从根结点到该节点的路径长度。高度是指从叶子结点到当前结点的路径长度。
结点的深度是从根结点开始自顶向下逐层累加的。
结点的高度是从叶子结点开始自底向上逐层累加的。
在力扣中有几道题目是与二叉树的深度相关,一般而言如果是需要求深度的,都采用先序遍历的方法,因为先序遍历先遍历根结点,然后遍历孩子结点就可以得出其深度。满足其自顶向下的特点。一般而言可以采用递归方法。
深度:先序遍历 | 层次遍历
高度:后续遍历
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 559.n叉树的最大深度
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
根结点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度。
104、二叉树的最大深度
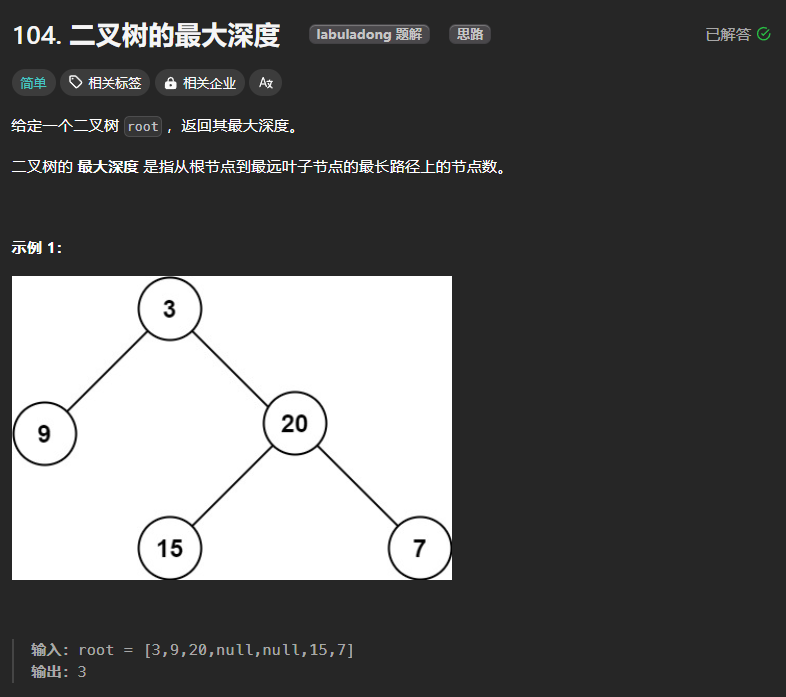
求最大深度,需要从根结点开始自定向下进行深度优先搜索DFS,因此采用先序遍历,采用递归的实现方式
class Solution:def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:# 先序遍历求最大深度 根左右 深度是从根节点到最后 高度是从叶子结点到当前节点的高度if not root:return 0left_height = self.maxDepth(root.left)right_height = self.maxDepth(root.right)height = 1 + max(left_height,right_height)return height
其中代码还可以精简为
class Solution:def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:if not root:return 0return 1+max(self.maxDepth(root.left),self.maxDepth(root.right))
559、n叉树的最大深度
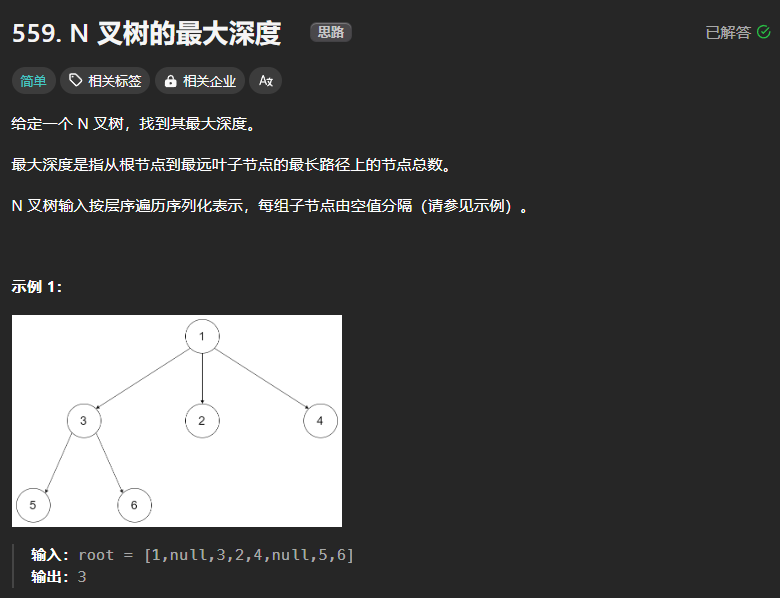
解题思路与二叉树的最大深度一致,唯一的区别就是通过for循环去遍历孩子结点
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):self.val = valself.children = children
"""class Solution:def maxDepth(self, root: 'Node') -> int:if not root:return 0max_depth = 0for ch in root.children:max_depth = max(max_depth,self.maxDepth(ch))return 1+max_depth
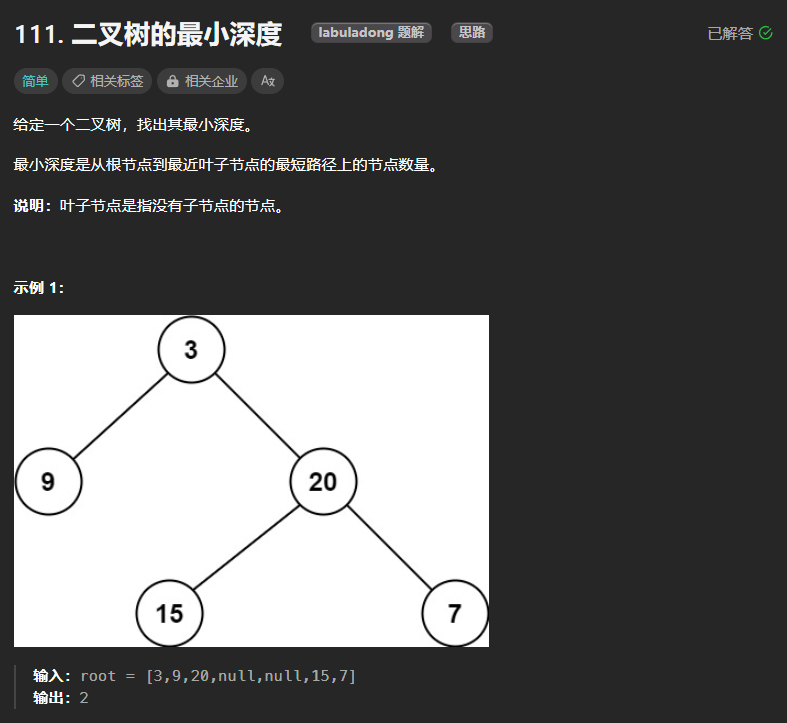
111、二叉树的最小深度
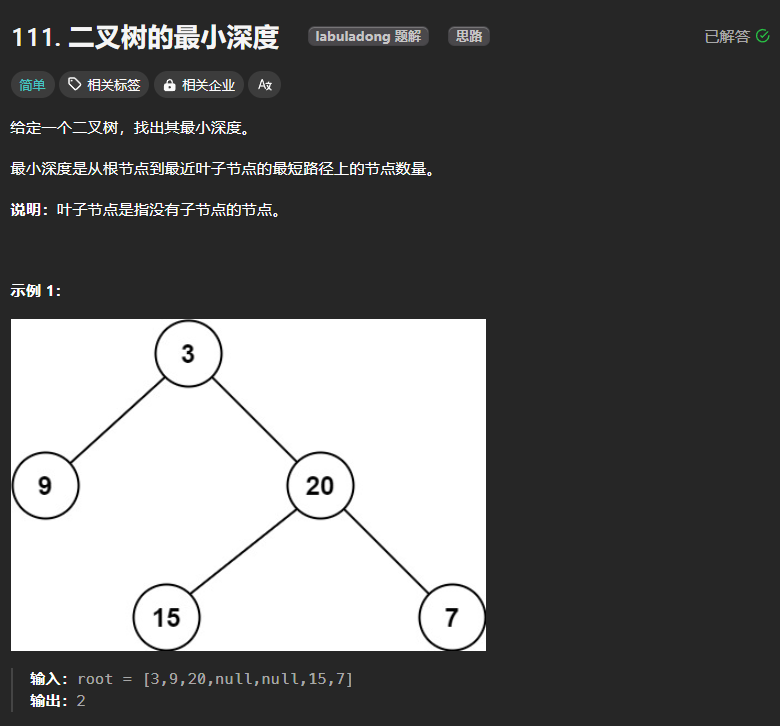
解题思路和求最大深度差不多,但是又有一个特殊情况,就是当二叉树为单分支的情况,即当出现某个节点的左孩子或者右孩子其中之一为空的时候,深度就要取最右孩子中的最大值了,否则就会结果为0+1。其余的情况就取最小值即可。
class Solution:def minDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:if not root:return 0left_depth = self.minDepth(root.left)right_depth = self.minDepth(root.right)if not root.left or not root.right:return 1+max(left_depth,right_depth)return 1+min(left_depth,right_depth)
特殊的二叉树
完全二叉树
补充:
110、平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树的定义是左右子树的高度之差不超过1的二叉树。
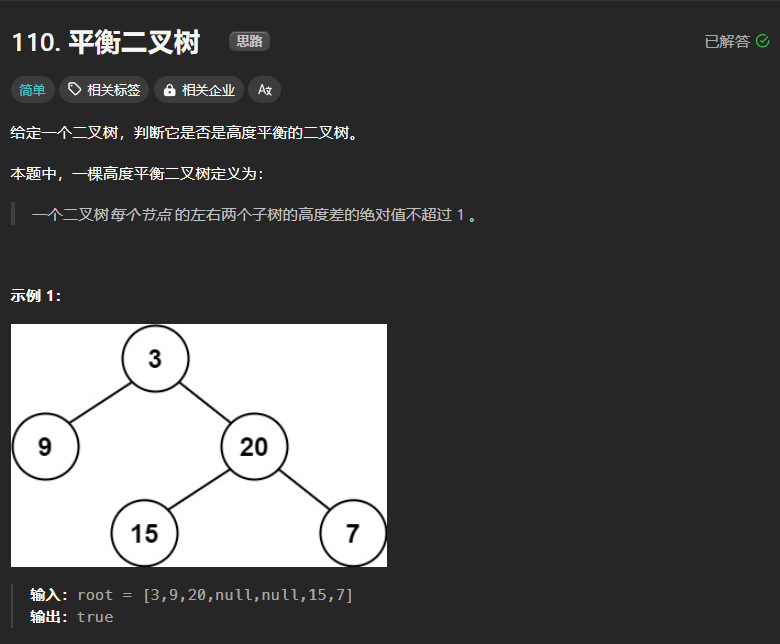
代码
定义一个获取结点高度的函数get_height(),如果当前结点为空,则返回0,然后分别获取该结点左孩子和右孩子的高度,如果左右孩子高度返回值是-1,则也返回-1,否则在判断左右子树高度之差是否大于1,如果大于1则也返回-1,如果左右子树高度之差小于1,则返回1+max(left_height, right_height)。主程序中,只需要判断对根节点进行判断get_height(root)是否为-1即可判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树。
class Solution:def isBalanced(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:def get_height(root):if not root:return 0left_height = get_height(root.left)if left_height==-1:return -1right_height = get_height(root.right)if right_height==-1:return -1if abs(left_height-right_height)>1:return -1else:return 1+max(left_height,right_height)return True if get_height(root)!=-1 else False
二叉排序树
练习题
116、翻转二叉树
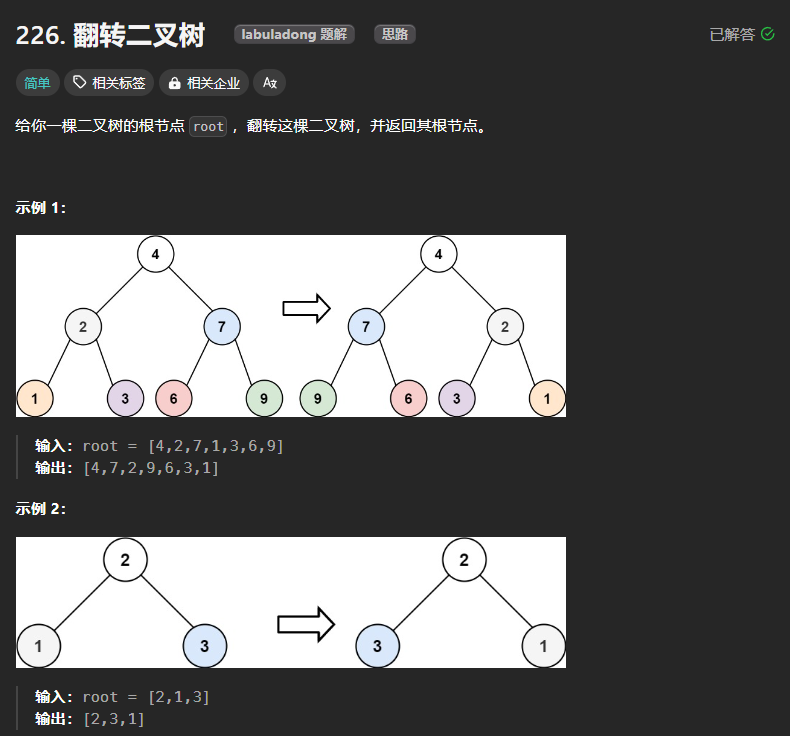
由示例可以看出,本题实际上需要实现的功能是沿着中间的一个轴翻转这颗二叉树,其本质实际只需要将二叉树每个结点的左右子树进行翻转即可。
翻转二叉树的核心思想就是:将二叉树中的每个节点的左右孩子进行交换即可。
需要注意的是,本题不能采用中序遍历的方法,可以采用先序遍历或者后序遍历
class Solution:def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:if not root:return rootself.invertTree(root.left)self.invertTree(root.right)root.left,root.right = root.right,root.leftreturn root
中序遍历的时候可能会对一些节点重复的调换导致错误。
class Solution:def invertTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:# 采用后序遍历if not root:return rootleft = self.invertTree(root.left)right = self.invertTree(root.right)root.left,root.right = right,leftreturn root
101、对称二叉树
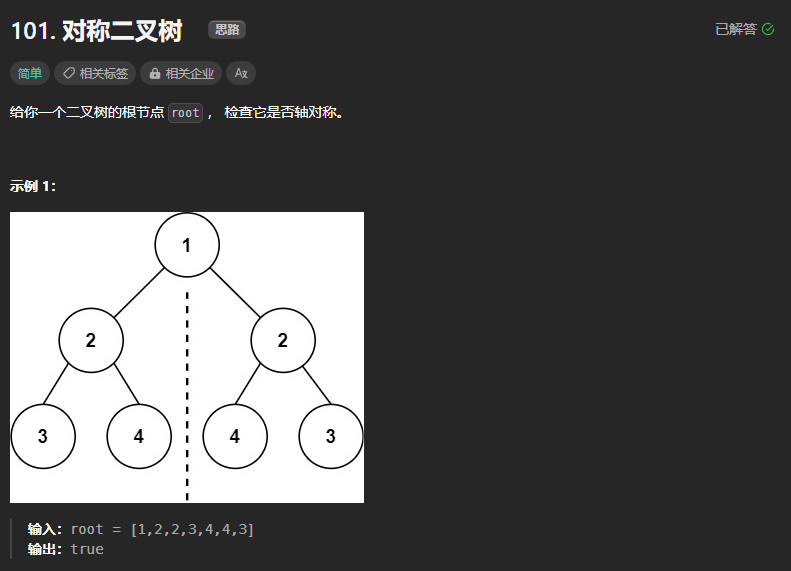
本题思路与翻转二叉树有点区别,翻转二叉树是直接对比左右孩子结点的值是否相等即可判断,而本题需要判断的是(例如在第三层中,判断根节点左孩子2的左孩子是否与根结点右孩子2的右孩子是否相等)对比的其实是外侧与外侧,内侧与内侧。
class Solution:def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:def compare(left,right):if left and not right: return Falseelif not left and right: return Falseelif not left and not right: return Trueelif left.val != right.val: return Falseout = compare(left.left,right.right)inner = compare(left.right,right.left)return out and innerif not root:return Truereturn compare(root.left,root.right)
100、相同的树
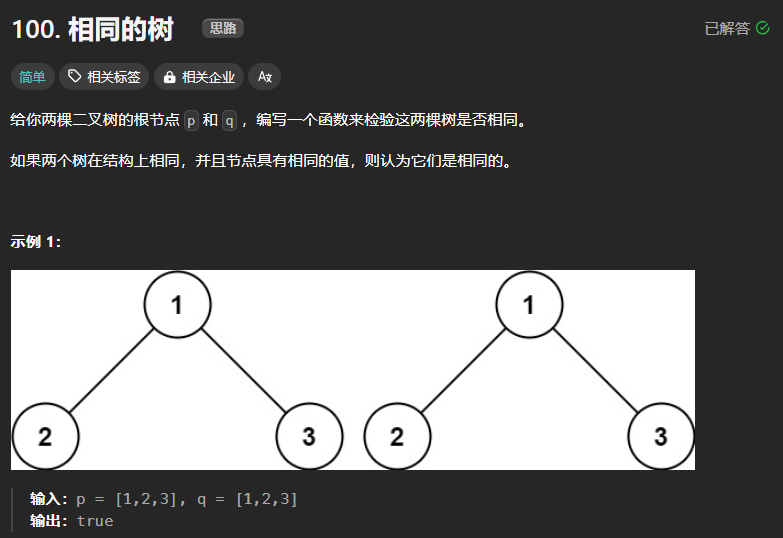
思路基本与对称二叉树一致,需要对两棵树的结点的值以及左右子树的值进行对比,如果不相同则返回,相等则继续递归,知道递归结束。
class Solution:def isSameTree(self, p: Optional[TreeNode], q: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:if not p and not q: return Trueelif not p or not q: return Falseelif p.val!=q.val: return Falsereturn self.isSameTree(p.left,q.left) and self.isSameTree(p.right,q.right)
572、另一棵树的子树
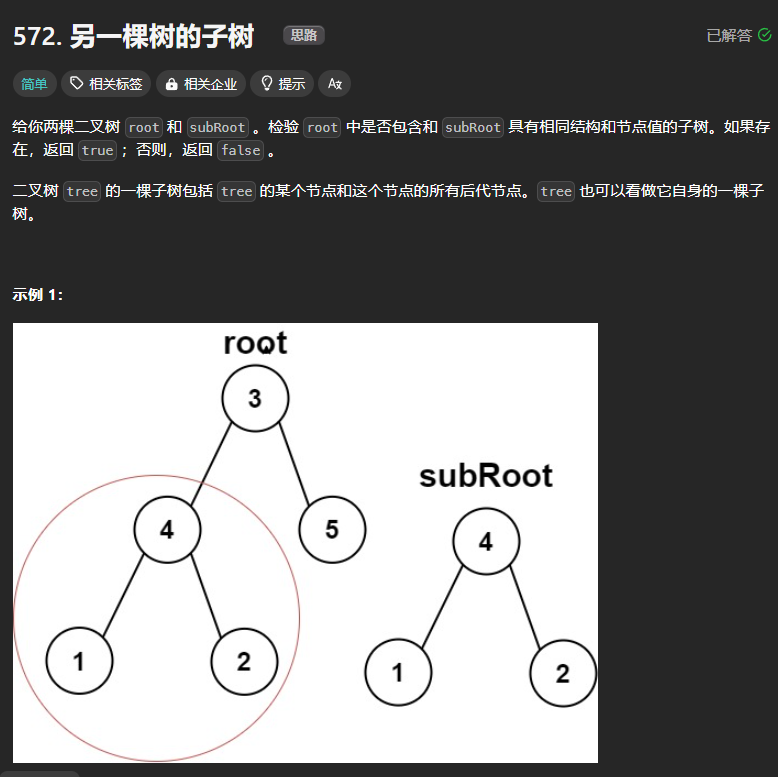
解题思路与相同的树一致,只需要遍历root这棵树的每个结点,然后再与subRoot进行判断是否是相同的树即可。
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:def isSubtree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], subRoot: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:def isSame(s,t):if not s and not t:return Trueelif not s or not t:return Falseelif s.val!=t.val:return Falsereturn isSame(s.left,t.left) and isSame(s.right,t.right)# 遍历root的所有结点与subRoot进行比较if not root:return Falsestack = [root]while stack:node = stack.pop()if isSame(node,subRoot):return Trueif node.left:stack.append(node.left)if node.right:stack.append(node.right)return False
222、完全二叉树的节点数量

解题思路1:可以直接按照普通二叉树的遍历进行记录总共多少个结点(前中后序遍历+层次遍历都可以解决这个问题),时间复杂度为 O(n)
(此方法没有利用完全二叉树的性质)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:if not root:return 0return 1 + self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right)
使用层次遍历
class Solution:def countNodes(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:if not root:return 0num = 0queue = [root]while queue:for _ in range(len(queue)):num+=1node = queue.pop(0)if node.left:queue.append(node.left)if node.right:queue.append(node.right)return num
解题思路2:利用完全二叉树的性质,如果是满二叉树结点的数量可以用2的深度-1次方 再 -1 来进行计算。时间复杂度为O(logn * logn)
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:if not root:return 0left = root.leftright = root.rightleftdepth = 0rightdepth = 0while left:leftdepth+=1left=left.leftwhile right:rightdepth+=1right=right.rightif leftdepth==rightdepth:return (2<<leftdepth)-1leftnum = self.countNodes(root.left)rightnum = self.countNodes(root.right)return leftnum+rightnum+1
257、二叉树的所有路径
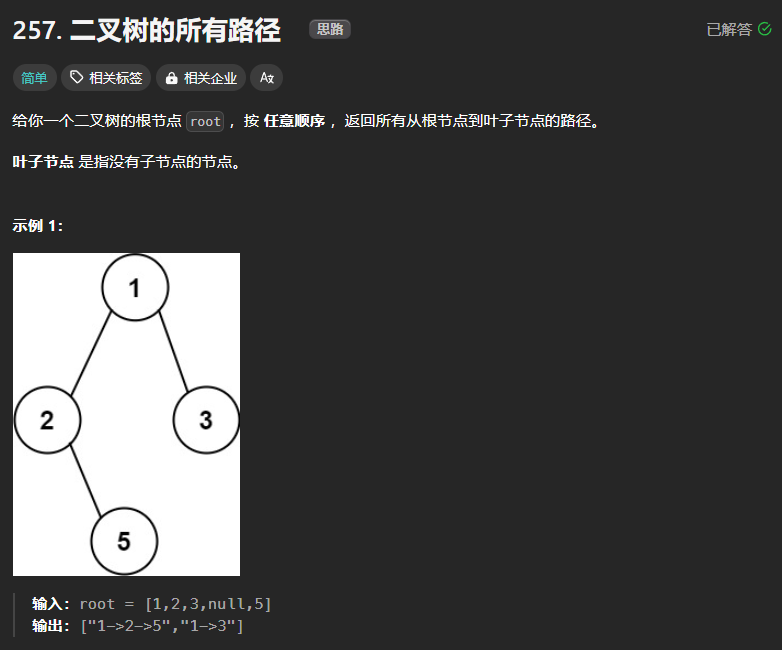
本题使用DFS与BFS均可解决。
使用DFS的时候需要注意在递归的过程中如果当前结点为空则不进行处理,不为空时才进行处理。
class Solution:def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:# 使用DFS解决def find_path(node,path):# node结点不为空if node:path+=str(node.val)# 叶子结点if not node.left and not node.right:paths.append(path)else:path+="->"find_path(node.left,path)find_path(node.right,path)paths = []find_path(root,"")return paths
使用BFS解决
class Solution:def binaryTreePaths(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[str]:# 使用BFS 层次遍历paths = []if not root:return pathsqueue = [root]path_lst = [str(root.val)]while queue:node = queue.pop(0)path = path_lst.pop(0)if not node.left and not node.right:paths.append(path)else:if node.left:queue.append(node.left)path_lst.append(path+"->"+str(node.left.val))if node.right:queue.append(node.right)path_lst.append(path+"->"+str(node.right.val))return paths
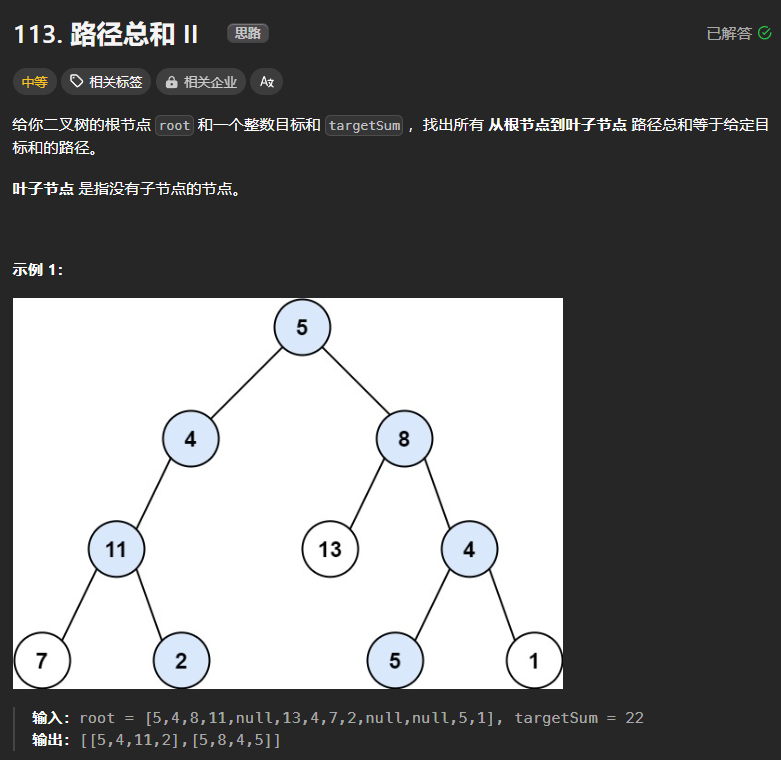
113、路径总和II
class Solution:def pathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:def find_path(node,path):if node:# path+=[node.val]path=path+[node.val]if not node.left and not node.right:if sum(path)==targetSum:paths.append(path)else:find_path(node.left,path)find_path(node.right,path)paths = []find_path(root,[])return paths
这里需要注意一个问题,就是path+=[node.val]和path=path+[node.val]这两句代码的写法有点不同,+=是在原来的path上进行修改,而直接赋值是可以形成一个新的列表,在递归的过程中就出现一个新的列表。这是由于python中列表是可变类型的,如果列表也是和字符串一样属于不可变类型的话,就可以直接使用+=操作了。
988、从叶结点开始的最小字符串
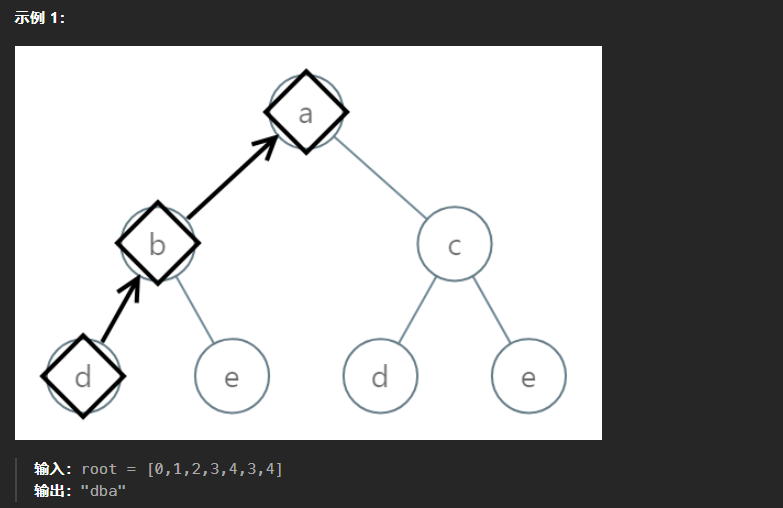
本题思路与二叉树的所有路径思路一致,只需要在其中添加一个用来进行比较的变量即可,注意这里所说的变量不可以是字符串,因为字符串是不可修改的。这里也需要注意是从叶子结点开始的,所以最终求得的路径path需要进行逆序处理[::-1]
class Solution:def smallestFromLeaf(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> str:# print(myhash)def find_path(node,path):if node:path+=str(myhash[node.val])# print(node.val,path)if not node.left and not node.right:minleaf[0] = min(minleaf[0],path[::-1])else:find_path(node.left,path)find_path(node.right,path)myhash = {i: chr(ord('a') + i) for i in range(26)}minleaf = ["z"*8500]find_path(root,"")return minleaf[0]
404、左叶子之和
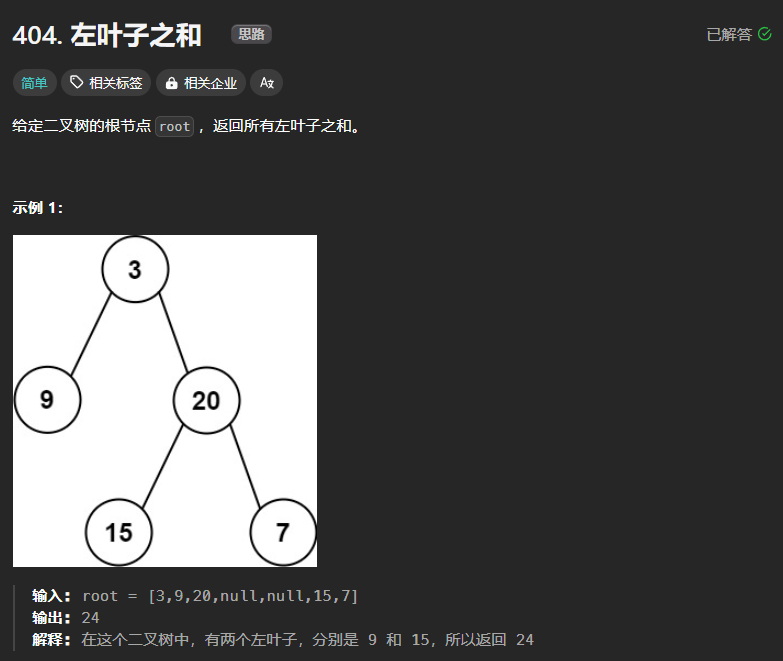
思路:
本题采用DFS的方式去解决。需要注意到底什么是左叶子,左叶子是指该节点不为空,同时其左右孩子为空,通过递归的方式去寻找这样的结点,然后对其求和。
class Solution:def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:# 递归程序如果碰到结点为空则返回0if not root:return 0# 如果该节点没有左右孩子 也返回if not root.left and not root.right:return 0# 遍历左子树left_num = self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left)# 如果有左孩子并且孩子为叶子结点则进行统计if root.left and not root.left.left and not root.left.right:left_num = root.left.valright_num = self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right)return left_num + right_num
236、二叉树的最近公共祖先

从下往上对结点进行处理,采用后序遍历的方法,先左再右再中
情况1: p和q都为某个节点的孩子结点
情况2:p是q的父节点或者q是p的父节点
class Solution:def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':if not root:return rootif root==q or root==p:return rootleft = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q)right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q)if left and right:return rootelif not left and right:return rightelif not right and left:return leftelif not left and not right:return left
106、从中序和后序遍历序列构造二叉树
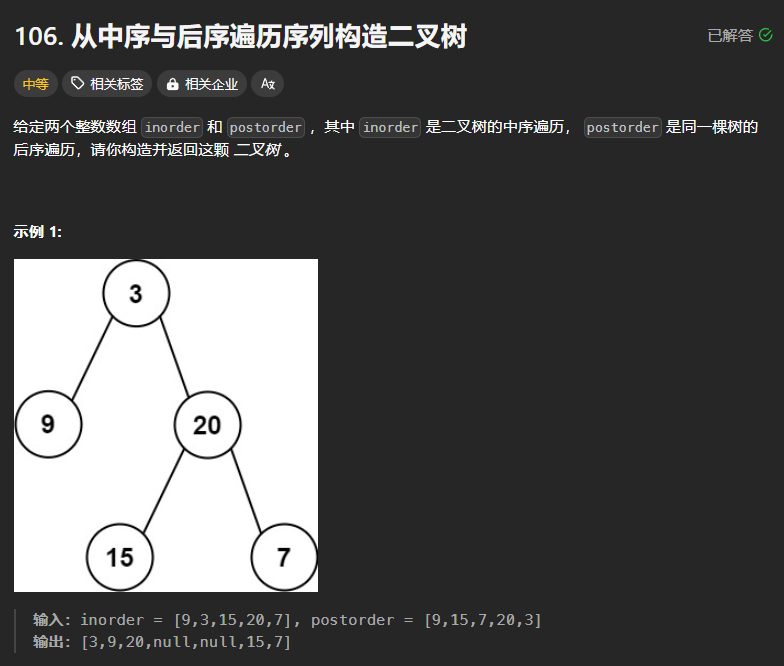
思路:
首先在后序遍历序列中找到根结点,然后创建一个根节点
找到切割的位置
-
对先序序列进行切割,分为左子树和右子树
-
对后序序列进行切割,分为左子树和右子树
-
构造根节点的左子树,使用递归的方法,传递进去的参数是先序数组的左边和中序数组的左边
-
构造根节点的右子树,使用递归的方法,传递进去的参数是先序数组的右边和中序数组的右边
class Solution:def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:if not postorder:return None# 找到根结点root_val = postorder[-1]root = TreeNode(root_val)# 找到切割位置qiege = inorder.index(root_val)inorder_left = inorder[:qiege]inorder_right = inorder[qiege+1:]postorder_left = postorder[:len(inorder_left)]postorder_right = postorder[len(inorder_left):len(postorder)-1]root.left = self.buildTree(inorder_left,postorder_left)root.right = self.buildTree(inorder_right,postorder_right)return root
105、从先序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树
需要注意的是:在寻找先序遍历进行迭代的时候,由于根节点是一定位于第一位的,所以寻找左和右的时候切割点是从位置1开始(包含位置1)往后找len(inorder_left)这个大小,然后剩余的部分【preorder[1+len(inorder_left)]】作为preorder_right
class Solution:def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:# 通过数组来构造二叉树if not preorder:return Noneroot_val = preorder[0]root = TreeNode(root_val)qiege = inorder.index(root_val) # 中序切割点# print(qiege,inorder)/inorder_left = inorder[:qiege] # 中序inorder_right = inorder[qiege+1:]preorder_left = preorder[1:1+len(inorder_left)]preorder_right = preorder[1+len(inorder_left):]root.left = self.buildTree(preorder_left,inorder_left)root.right = self.buildTree(preorder_right,inorder_right)return root
654、最大二叉树
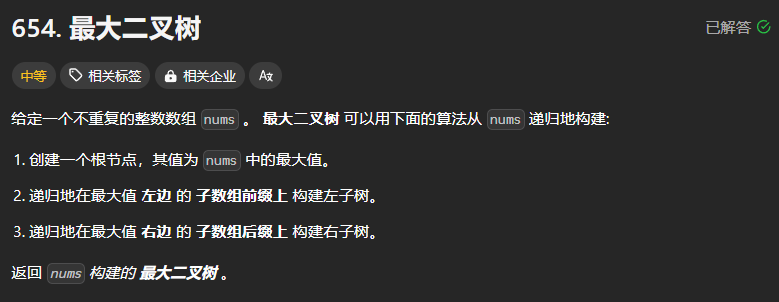
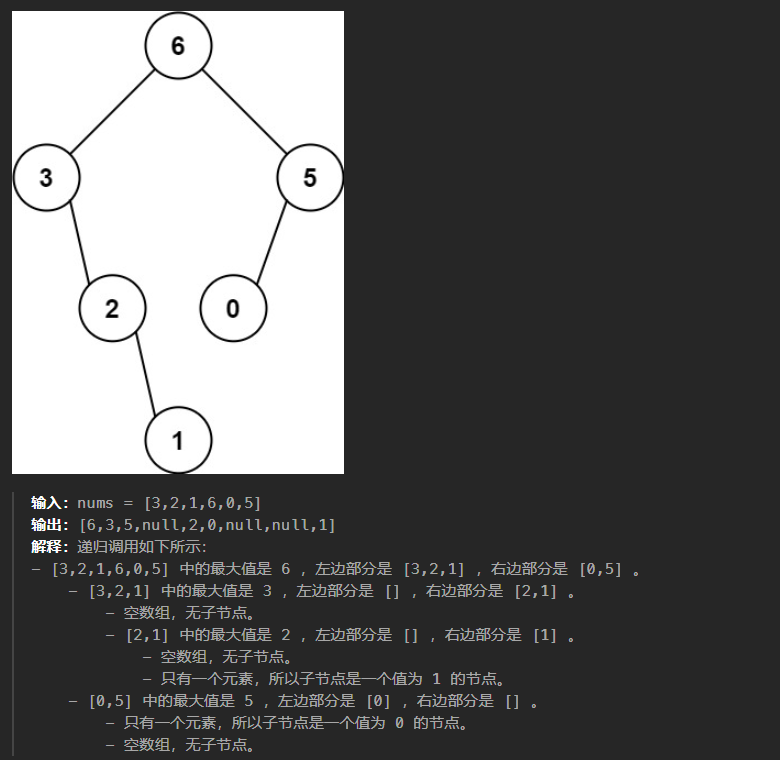
思路:使用递归的方式
递归三部曲
返回值为TreeNode类型
参数为nums数组
题目中的范围nums的长度是大于等于1的,因此不需要考虑nums为空的情况
-
找到数组中最大值的下标,最大值用来构造根节点,下标用来对数组进行切割
maxValue = float("-inf") maxIndex = 0 for i,value in enumerate(nums):if maxValue<value:maxValue = valuemaxIndex = i -
最大值左区间 构造左子树
if maxIndex > 0:new_list = nums[:maxIndex]node.left = self. -
最大值右区间 构造右子树
首先根据最大值对该数组进行切割,切割完毕后,根据数组的左边与右边分别进行递归,这类似于106从中序和后序遍历序列构造二叉树。最终返回构造好的二叉树root。
class Solution:def constructMaximumBinaryTree(self, nums: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:if not nums:return Noneif len(nums)==1:return TreeNode(nums[0])root_val = max(nums)root = TreeNode(root_val)qiege = nums.index(root_val)nums_left = nums[:qiege]nums_right = nums[qiege+1:]root.left = self.constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums_left)root.right = self.constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums_right)return root
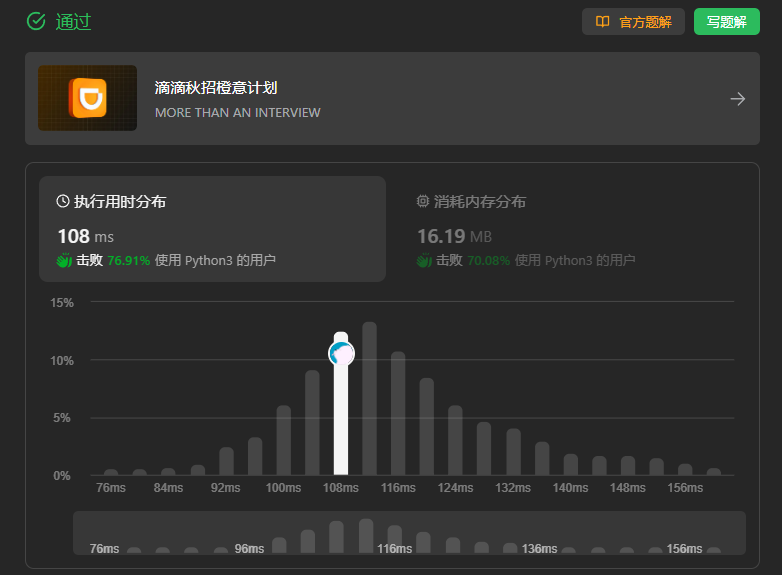
998、最大二叉树II

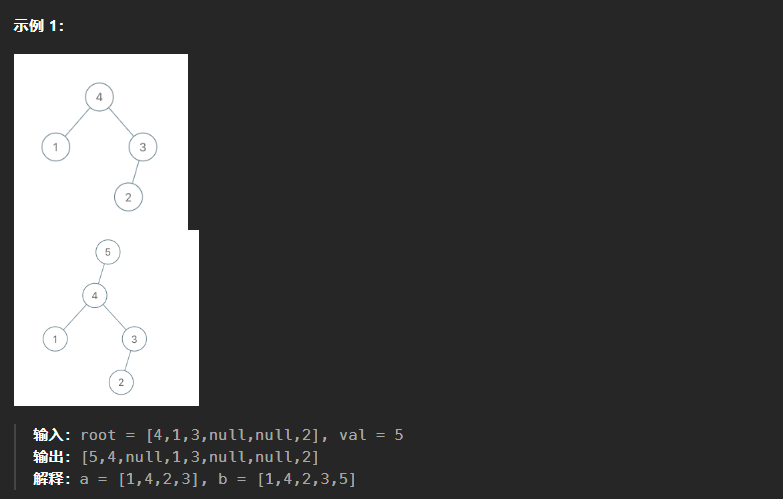

本题和上一题相比,难点就在于可能需要对这颗二叉树进行重新构造,但是在构造的过程中也有省事的地方,就是只需要往右插入。如果val值大于原树的根节点值,则直接将原树放在val结点的左子树即可。如果小于最大值,向右子树进行遍历,同时记录当前结点的父节点,方便val结点的插入。
class Solution:def insertIntoMaxTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:node = TreeNode(val)prev = Nonecur = root# 遍历root 往右子树遍历while cur and cur.val>val:# 记录当前结点的父节点prev = curcur = cur.right# 如果val大于原树的最大值if not prev:node.left = curreturn node# 遍历到了右子树合适的位置 换结点else:# prev.right = nodenode.left = curreturn root
98、验证二叉搜索树(二叉排序树BST)

本题思路很简单,利用二叉排序树的性质即可:二叉排序树中序遍历的结果是递增的。
方法:
- 采用非递归遍历算法 设置最小值 在中序递归的过程中进行比较
- 采用迭代法,设置最小值,如果出现不满足性质的节点直接返回False
# 递归遍历算法
class Solution:# 添加一个最小值 每次进行比较的时候更新最小值def __init__(self):self.min_= float("-inf")def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:if not root:return True# 左left = self.isValidBST(root.left)# 根if self.min_ < root.val:self.min_ = root.valelse:return False# 右right = self.isValidBST(root.right)return left and right
# 非递归遍历算法
class Solution:def isValidBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:# 中序遍历 判断值是否小于等于if not root:return Truestack = []p = rootmin_ = float("-inf")while p or stack:if p:stack.append(p)p = p.leftelse:p = stack.pop()# print(min_,p.val)if min_ < p.val:min_ = p.valelse:return Falsep = p.rightreturn True
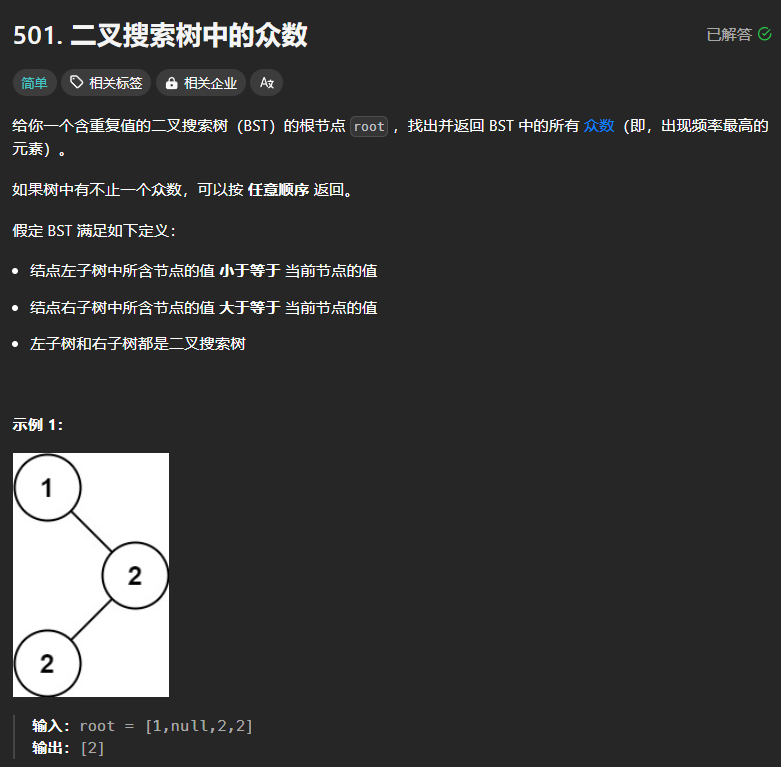
501、二叉搜索树中的众数
思路:
对二叉树进行中序遍历,遍历的过程中统计字符出现的最大次数。其中在递归的过程中需要将max_freq指定为全局变量。
class Solution:def findMode(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:max_freq = 0myhash = {}def dfs(root):nonlocal max_freqif not root:return dfs(root.left)myhash[root.val] = myhash.get(root.val,0)+1max_freq = max(max_freq, myhash[root.val])dfs(root.right)dfs(root)return [k for k,v in myhash.items() if v==max_freq]
结果
- 使用迭代法的中序遍历同时不使用字典来统计出现的频率
class Solution:def findMode(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:# 使用迭代法的中序遍历stack = []p = rootpre = Nonefreq = 0max_freq = 0res = []while stack or p:if p:stack.append(p)p = p.leftelse:p = stack.pop()if pre is None:freq = 1elif pre.val == p.val:freq+=1else:freq = 1# 如果频率和最大频率相等 则往结果数组中添加if freq==max_freq:res.append(p.val)if freq > max_freq:res = [p.val]max_freq = freqpre = pp = p.rightreturn res
这个方法的核心是用freq和max_freq进行比较,同时使用pre指针指向前一个结点,这样就方便在中旬遍历的过程中记录已经出现的结点值了。有如下几种情况:
- 针对
pre- 如果
pre为None,则更新freq=1 - 如果
pre不为None且pre的值与p的值相等,则将freq+1 - 如果
pre不为None且pre的值与``p不相等,仍然将freq`=1
- 如果
- 针对
freq和max_freq- 如果
freq==max_freq,则往返回值的列表中添加该元素(p.val 即结果的众数) - 如果
freq>max_freq,则对res列表进行更新,同时更新max_freq - 如果
freq<max_freq,可以不进行任何处理
- 如果
701、二叉搜索树中的插入
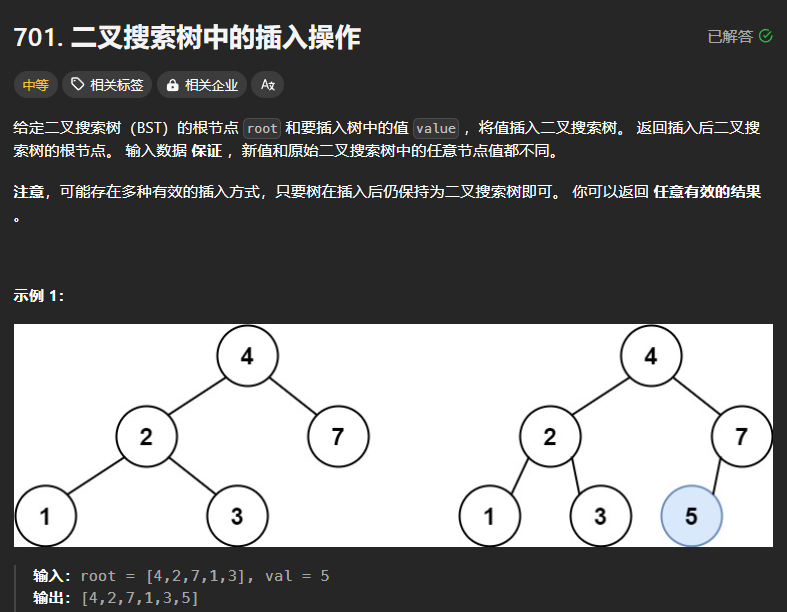
遍历二叉树直到该值应该出现的地方为止,利用二叉搜索树的性质,如果根节点的值小于value,则再右子树进行递归,否则在左子树进行递归。
class Solution:def insertIntoBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], val: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:# 根if not root:return TreeNode(val)if root.val>val:root.left = self.insertIntoBST(root.left,val)if root.val < val:root.right = self.insertIntoBST(root.right,val)return root
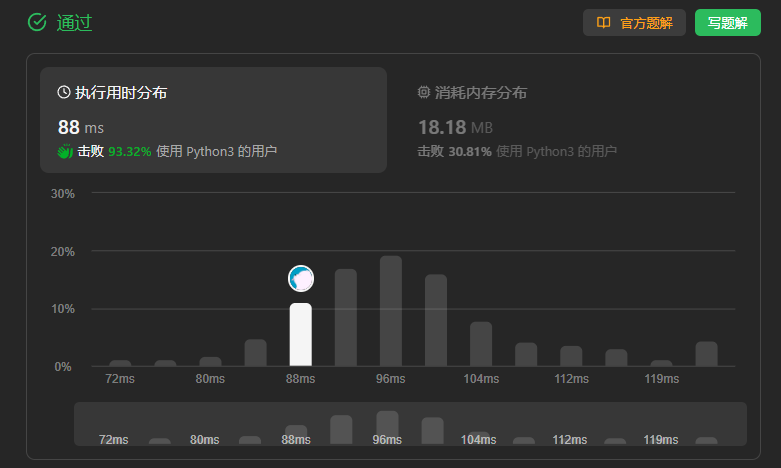
450、二叉搜索树中的删除
题目中要求的返回值是二叉搜索树中可能被更新的根结点的引用
class Solution:def deleteNode(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], key: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:if not root:return rootif root.val==key:if not root.right and not root.left:return Noneelif not root.left:return root.rightelif not root.right:return root.leftelse:cur = root.rightwhile cur.left is not None:cur = cur.leftcur.left = root.leftreturn root.rightelif root.val > key:root.left = self.deleteNode(root.left,key)else:root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right,key)return root
108、将有序数组转化为二叉搜索树

思路:本题思路类似于从106、中序和后序遍历构序列构造二叉树和654、最大二叉树的解题思路,需要找到中间的切割点,然后通过递归的方式分别构造左右子树,需要注意的就是对于递归的结束条件的处理如下:
if not nums:return None
if len(nums)==1:return TreeNode(nums[0])
一共两种情况,因为再往下就涉及到数组的切割问题。
- 如果数组为空,则直接返回None
- 如果数组的长度为1,则直接返回以数组中唯一元素构造出二叉树结点即可
class Solution:def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:# 本题思路就是通过数组来构造一颗二叉树,需要保持树的平衡,方法将就是从中间进行构造if not nums:return Noneif len(nums)==1:return TreeNode(nums[0])qiege = len(nums)//2# print(qiege)root = TreeNode(nums[qiege])nums_left = nums[:qiege]nums_right = nums[qiege+1:]root.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums_left)root.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums_right)return root
123、有序链表转换为二叉搜索树
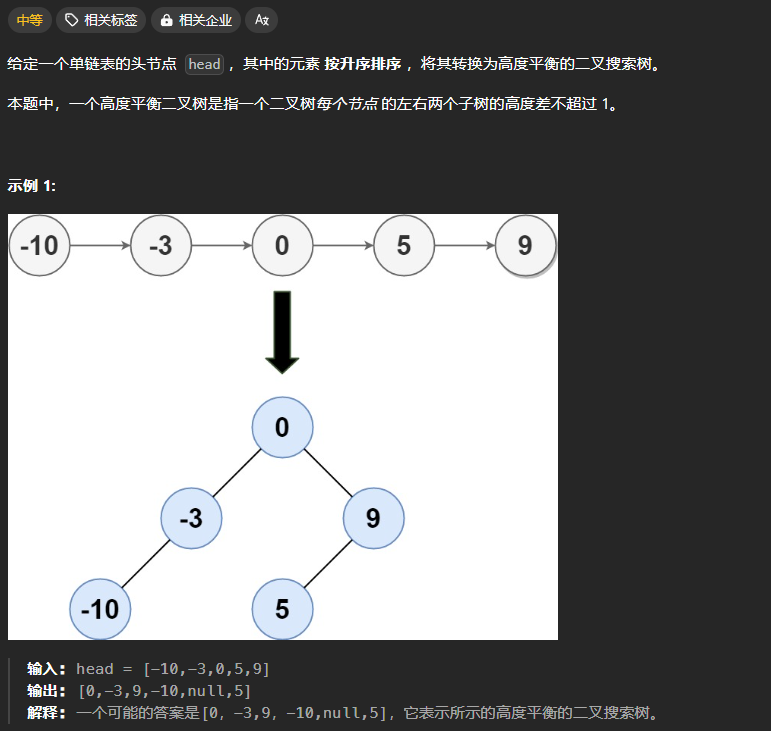
本题中的要求是转换为高度平衡的二叉搜索树,即要求是一颗平衡二叉树,所以需要从数组的中间进行构建,核心思路参考108题。
class Solution:def sortedListToBST(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:# 如何构建二叉搜索树?def construct(nums):if not nums:return Noneif len(nums)==1:return TreeNode(nums[0])qiege = len(nums)//2root = TreeNode(nums[qiege])nums_left = nums[:qiege]nums_right = nums[qiege+1:]root.left = construct(nums_left)root.right = construct(nums_right)return rootp = headnums = []while p:nums.append(p.val)p=p.nextnums.sort()return construct(nums)
538、把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
针对二叉搜索树的题目,一定要好好利用其中序遍历得到的是一个递增的序列这一性质!!!
思路:根据题目的要求,本题中的树是二叉搜索树,在中序遍历的过程中是递增的,但是要求实现的是将node节点的的值修改为大于等于该节点值的所有节点值的和。因此我们可以采用逆序中序遍历的方法,逆序中序遍历中的结点值与当前结点的结点值相加起来,得到该结点现在的值。
需要注意的是,使用Python的时候,局部变量的问题,也就是我们pre指向前一个结点值,我们需要用nonlocal pre来申明pre不是局部变量,这样在递归的过程中才能够访问到外层嵌套函数中定义的pre值。
class Solution:def bstToGst(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:# 使用右中左的遍历顺序进行遍历 往前叠加值def dfs(root):nonlocal preif not root:return dfs(root.right)root.val += prepre = root.valdfs(root.left)pre = 0dfs(root)return root
1038、从二叉搜索树到更大的和树
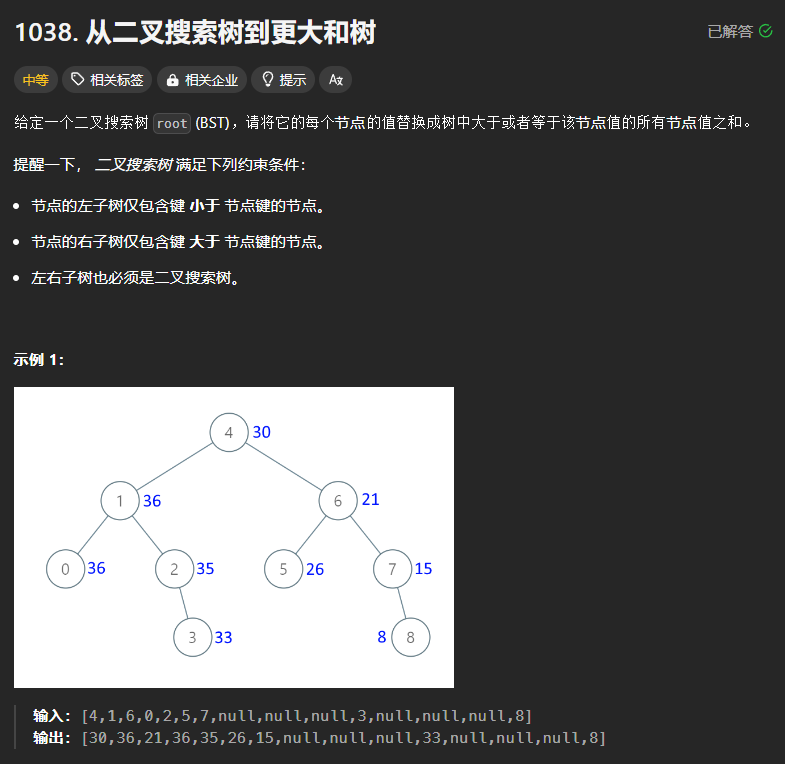
本题与上一题思路一样,不再重复赘述。
530、二叉树的最小绝对值差
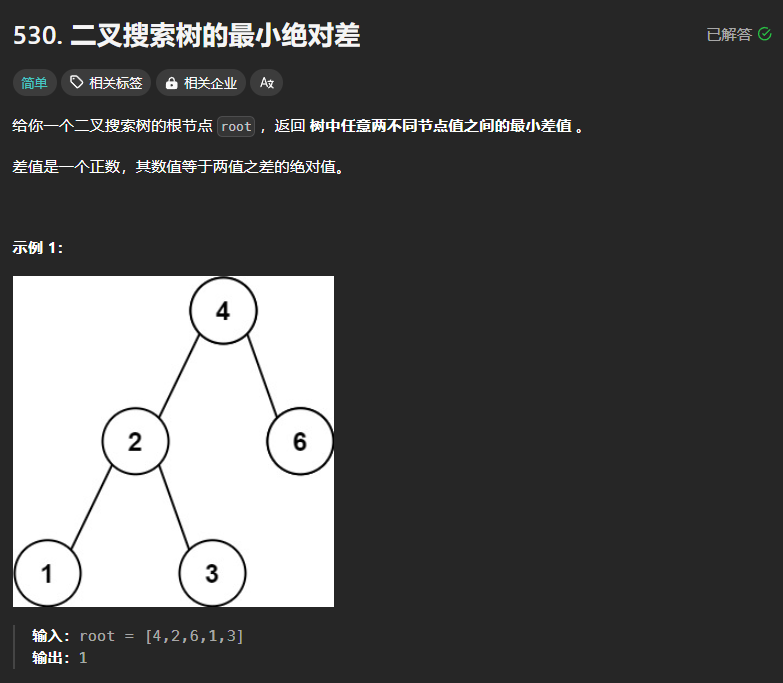
思路:本题的树是二叉搜索树,根据其性质可以进行中序遍历,然后在得到的遍历序列中求最小绝对差
方法1 递归方法
class Solution:def getMinimumDifference(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:def dfs(root):if not root:return []return dfs(root.left) + [root.val] + dfs(root.right)nums = dfs(root)res = float("inf")for i in range(len(nums)-1):res = min(abs(nums[i]-nums[i+1]),res)return res
方法2 迭代方法
在迭代法中,需要用pre记录前一个节点的指针,其初始值可以设置为任意值
class Solution:def getMinimumDifference(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:# 使用中序遍历 然后求差值stack = []p = rootpre = float("inf")res = float("inf")while p or stack:if p:stack.append(p)p = p.leftelse:p = stack.pop()res = min(abs(pre-p.val),res)pre = p.valp = p.rightreturn res
99、恢复二叉搜索树
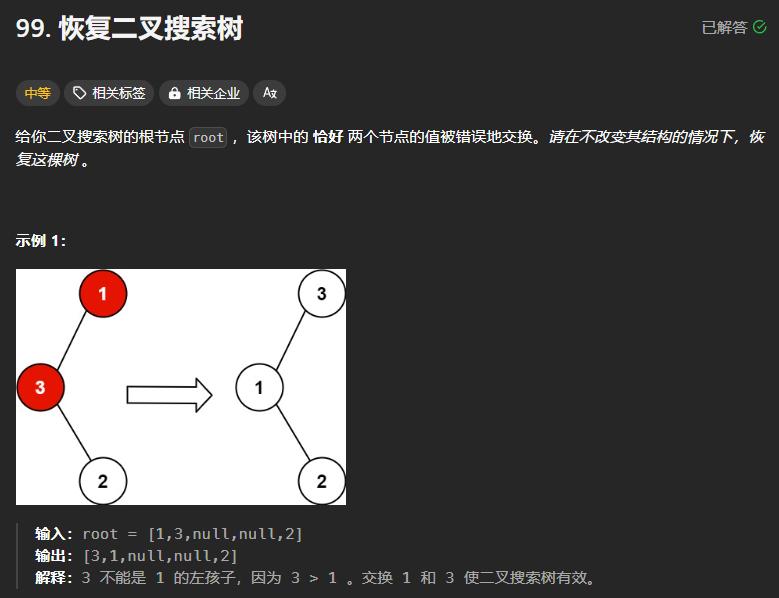
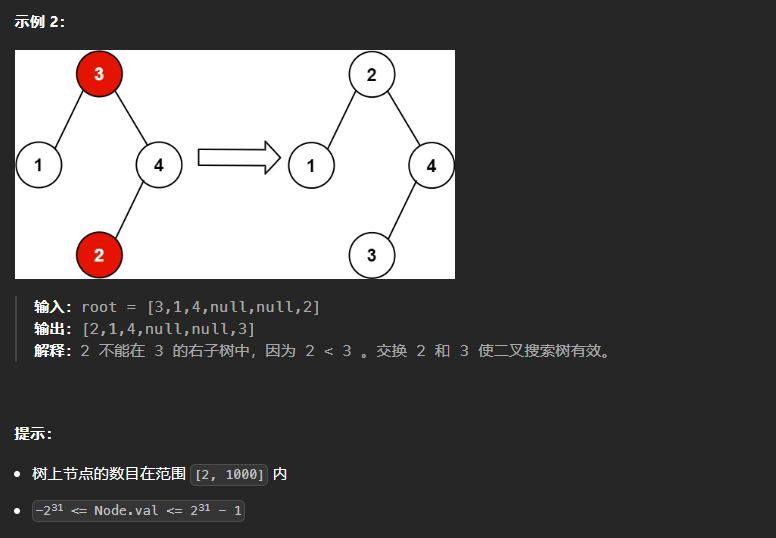
本题的思路是:寻找出两个顺序颠倒的两个位置,在树遍历结束之后交换两个的值
bigger和smaller分别记录最大和最小值,其中bigger在进行初始化的时候需要进行赋值
bigger = TreeNode(float("-inf"))
class Solution:def recoverTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> None:"""Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead."""# 中序遍历 交换节点stack = []p = rootpre = Nonesmaller = Nonebigger = TreeNode(float("-inf"))while p or stack:if p:stack.append(p)p = p.leftelse:p = stack.pop()# print(p.val,end=" ")if pre and pre.val>p.val:if bigger.val < pre.val:bigger = presmaller = ppre = pp = p.rightsmaller.val,bigger.val = bigger.val,smaller.val